AP Bio : Unit 2
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
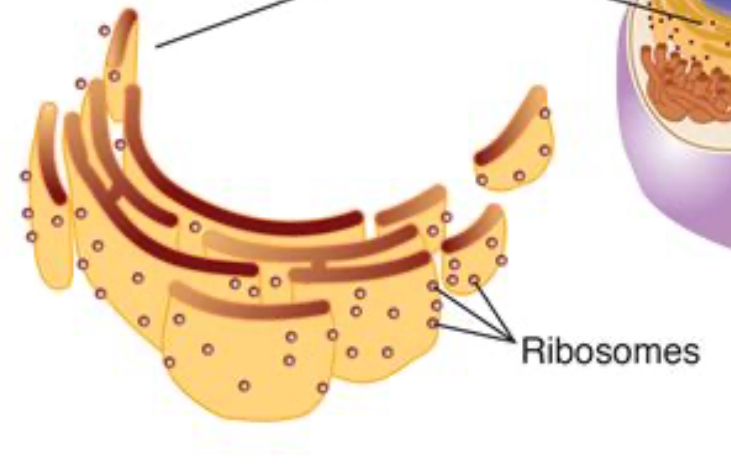
Ribosomes
do protein synthesis
Ribosomes picture
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Smooth or rough, in the cytoplasm
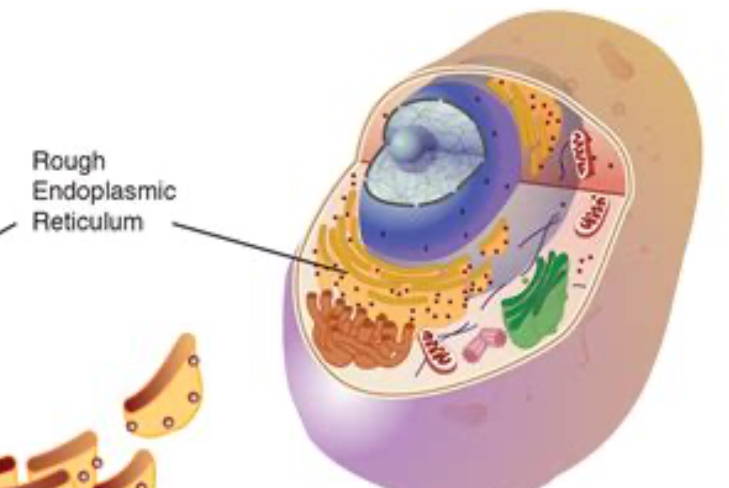
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
has ribosomes, helps w/ protein synthesis
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) picture
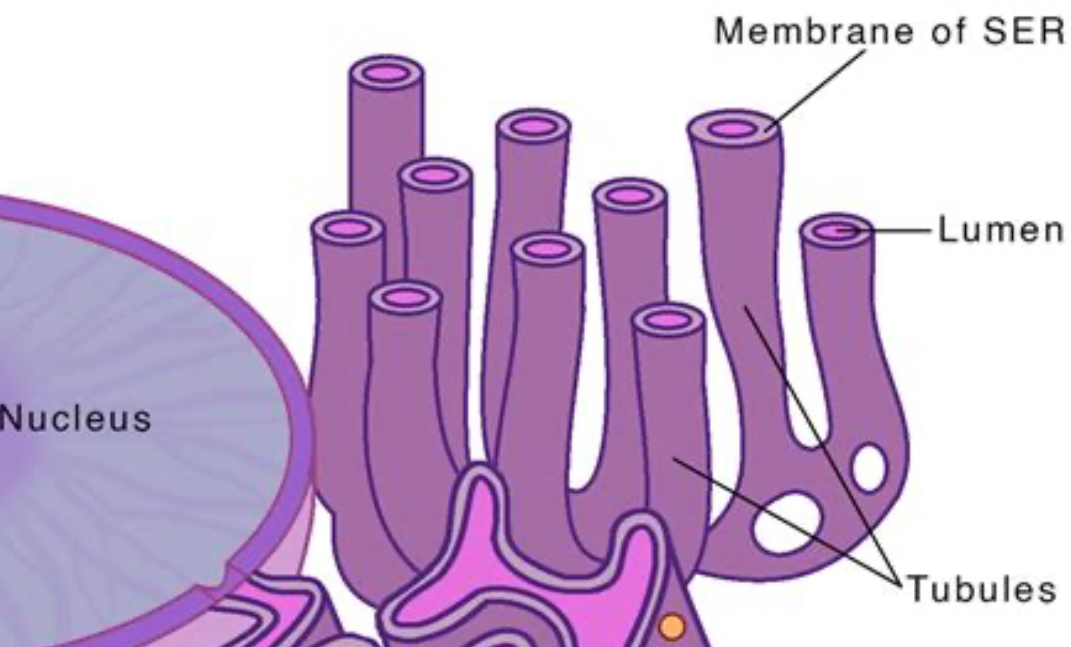
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
helps lipid synthesis, detoxophyies
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) picture
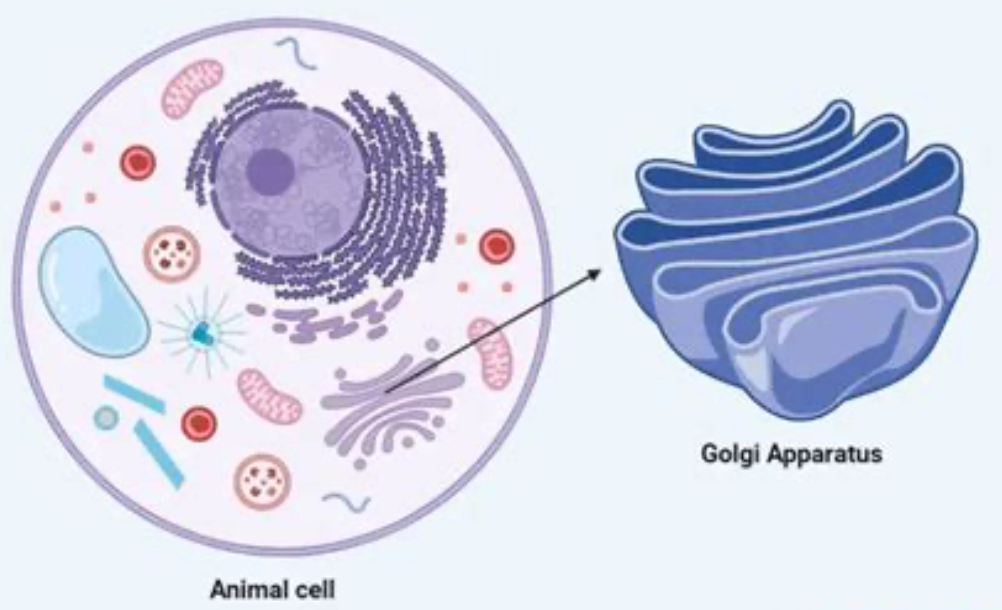
golgi complex
refines, folds, modifies protein packs protein for transport
golgi complex picture
vesicle
envelopes protein out of ribosome→transports to golgi complex→transports out of cell
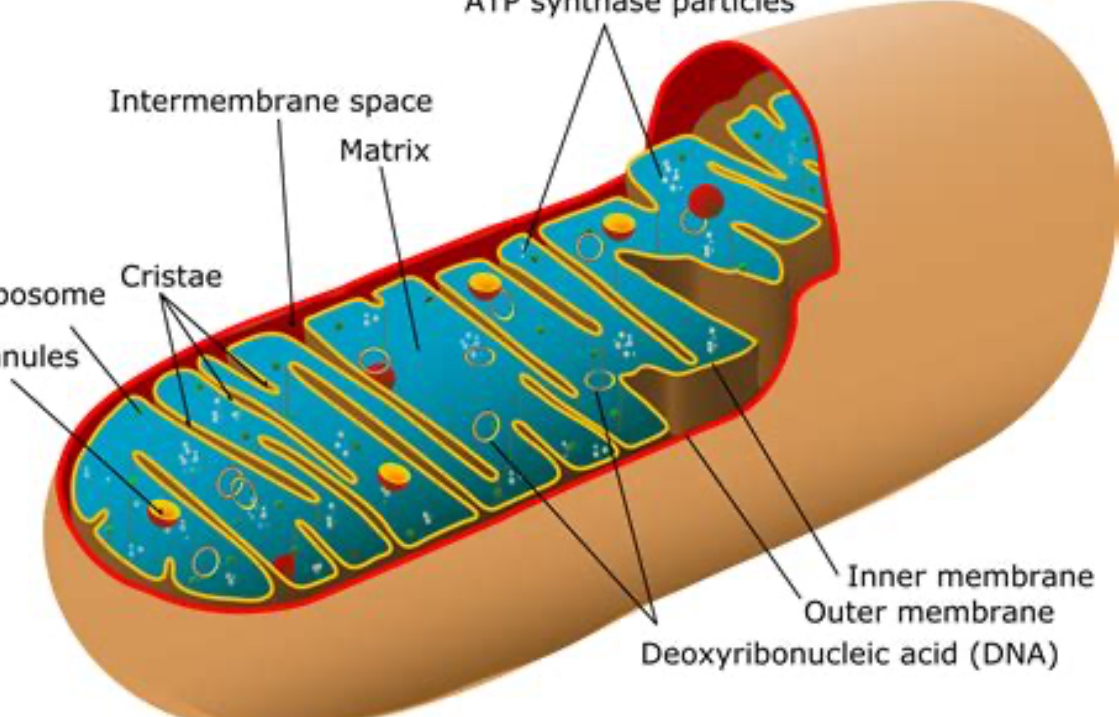
mitocondria
makes ATP, does aerobic resperation
mitocondria picture
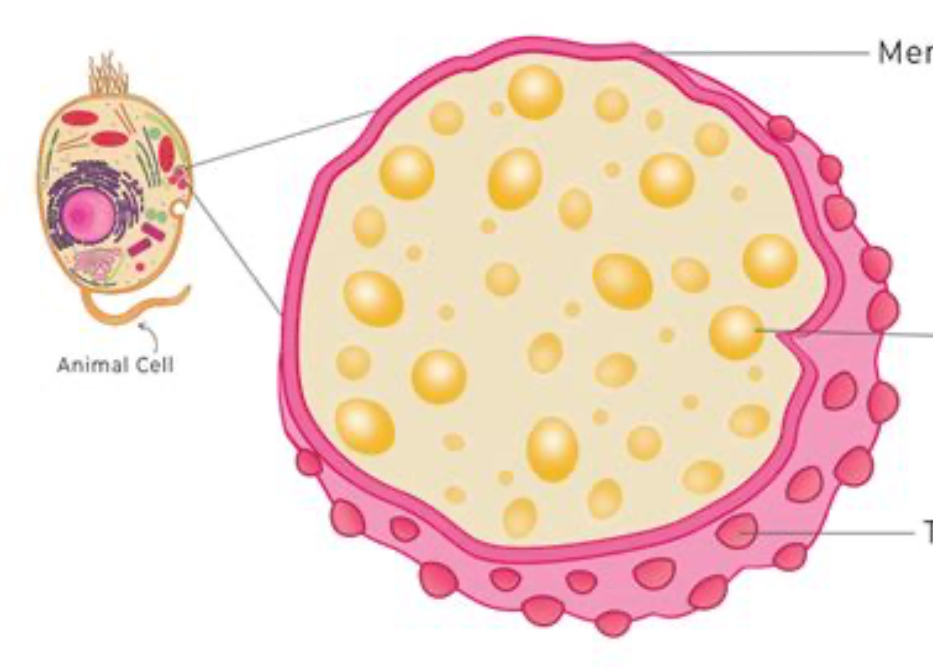
lysosome
digestion and waste removal enzymes
lysosome picture
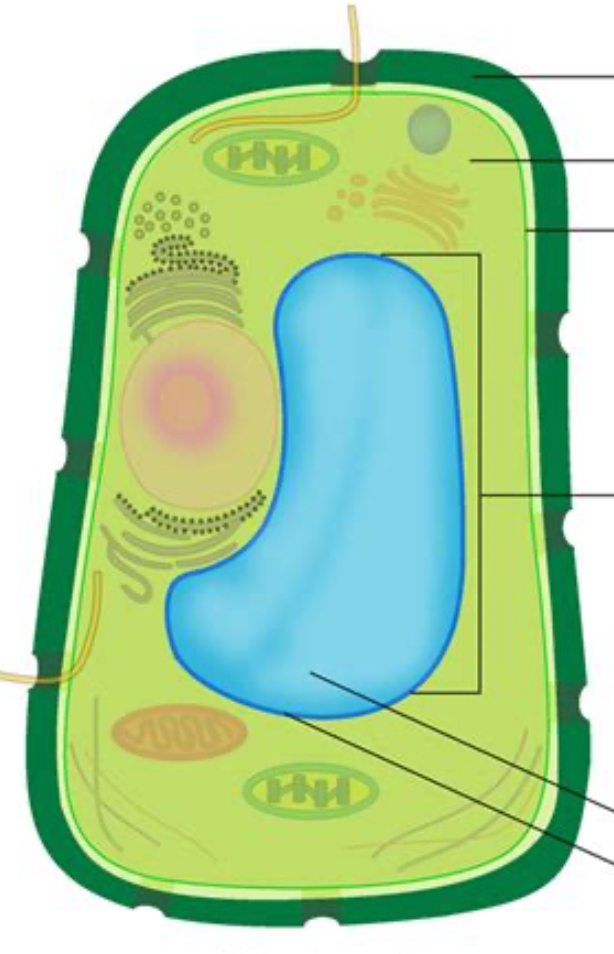
vacuole
storage, only in plants
vacuole picture
chloroplast
does photosynthesis, only in plants
chloroplast picture
nucleolus
makes ribosomes
nucleolus picture
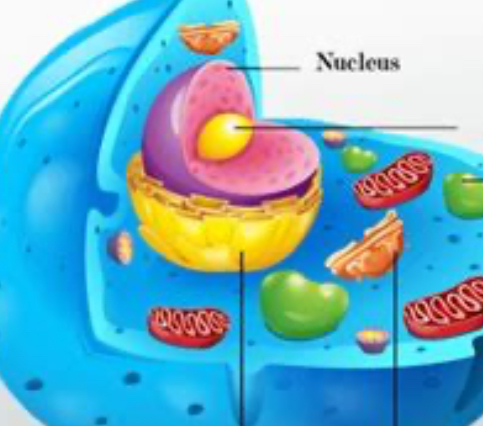
all cells have…
cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, chromosomes
plasma/cell membrane
lipid bilayer, structure of cells, maintains cellular homeostasis
small SA:V ratio
high metabolism, eat a lot, loose heat fast
large SA:V ratio
low metabolism, retain lots of heat
when SA:V gets large…
cells split to be small again
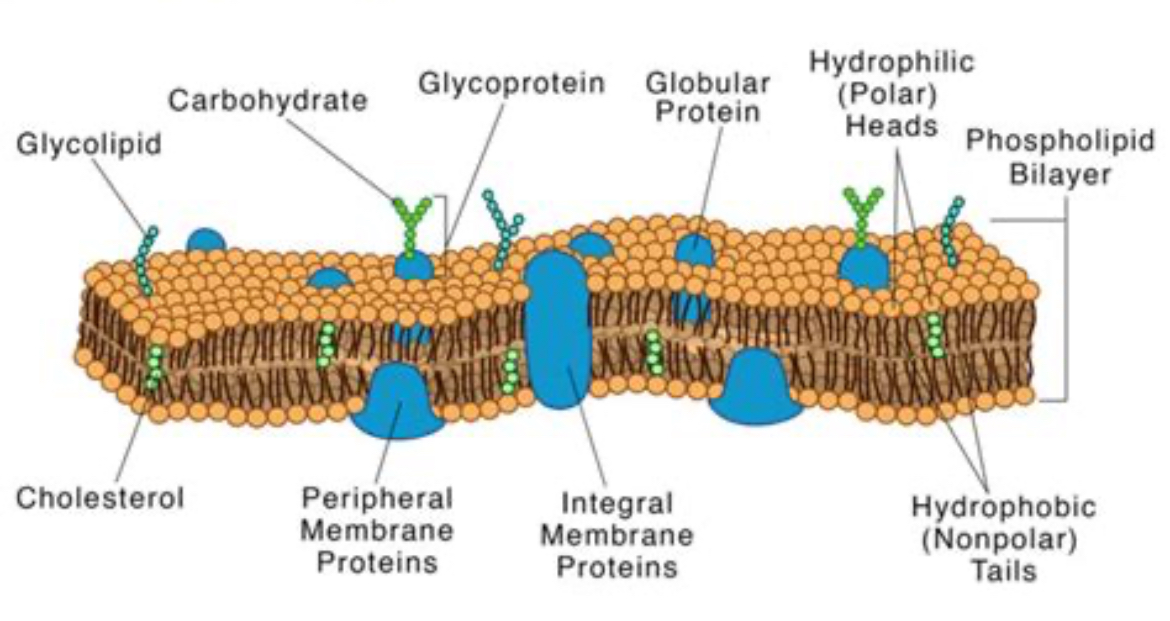
fluid mosaic model structure
phospholipids, protein, cholertral, glycoproteins, glycolipids
fluid mosaic model picture
phospholipid structure
phosphate heads face out, fatty acid tails face in
phospholipid picture
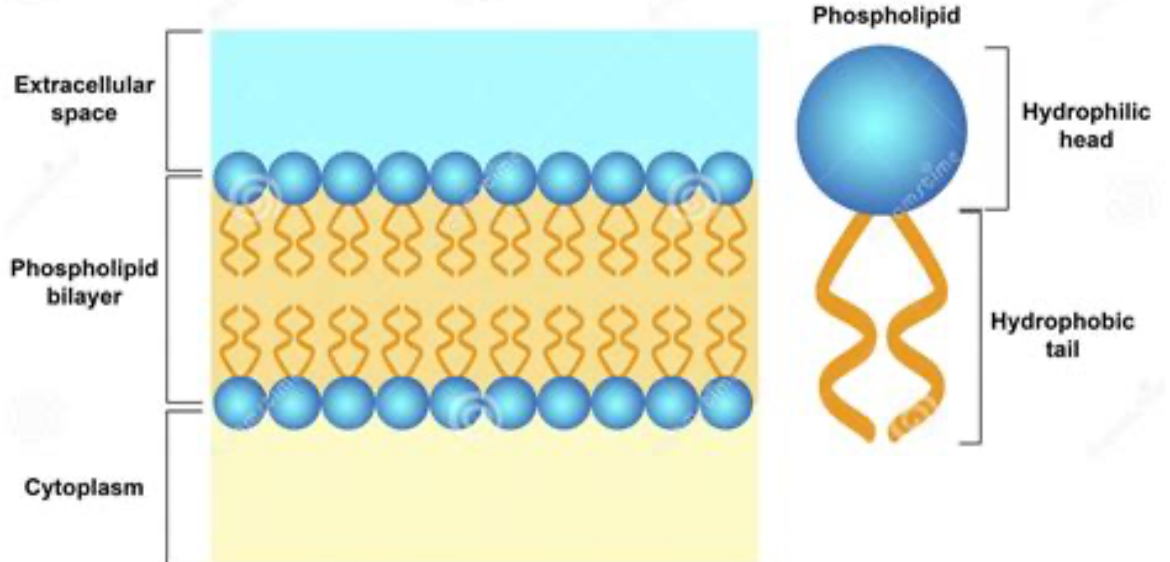
selectively permeability
phospholipid membrane regulates movement of things in and out of cells
embedded proteins
transport, cell recognition, signal transportation
cholesteral
in between phospholipids in the bilayer, regulates membrane rigidity
glycoprotein
cell recognition & communication in cell membrane, fused to heads
glycolipd
cell recognition & communication in cell membrane, fused to tails
membrane transport : small np
small non polar molecules allowed through
membrane transport : large charged
need proteins to move them through membrane via protein channel
prokaryotic cells
‘primitive’ cell, no membrane bound organelles
eukaryotic cells
compartmentalized prokaryotic cells, membrane bound organelles
prokaryotic to eukaryotic cells by…
endosymbiosis doing compartmentalization of the prokaryotic cell
aqueous
water like
intracellular metabolic processes
synthesis and breakdown processes in the cell
plant cell walls made from
made of cellulose
fungi cell walls made from
chitin and carb+protein
bacteria cell walls made from
peptoglycan and carb+protein
endocytosis/exocytosis
molecules entering or exiting the cell via vesicles, requires ATP
active transport
requires ATP, substance movement against the concentration grain
passive transport
diffusion (small np) or facilitated diffusion (uses protein channels) with the concentration grain
hypertonic
lower concentration of water inside cell
hypotonic
higher concentration of water inside cell, plants prefer this(makes them rigid)
tonic
water inside and outside cell is =
water potential
=pressure potential+solute potential, concentration of water in a solution
pressure potential
pressure put on a solution based on how its stored
solute potential
measure of how solute impacts water in a solution
ץ=-iCRT i is….
i=1 if sucrose in solution i=2 if NaCl in solution
glucose is transported in and out of cells by…
glutes (facilitated diffusion)