HBIO4 cell transport
what is a cell membrane made up of
phospholipids
what is the head group of a phospholipid made of
glycerol and a phosphate group
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
what is a cell membrane made up of
phospholipids
what is the head group of a phospholipid made of
glycerol and a phosphate group
what is glycerol
an alcohol
what is the tail group of a phosphate group made of
a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid
what is the bond in phosphate heads
polar
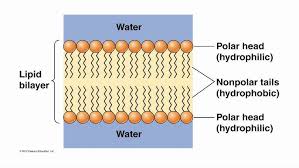
which group of a phospholipid is hydrophilic
head
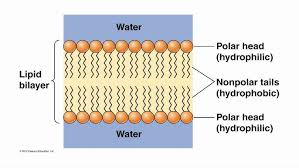
which group of a phospholipid is hydrophobic
tails
what are the 5 proteins in the cell membrane
receptor, channel, gated channel, transport, glycoprotein
what steroid is in the cell membrane of animal cells
cholesterol
what is the purpose of having cholesterol in the cell membrane
maintains fluidity
what MM is cholesterol
lipid
what does maintaining fluidity do in the cell
holds structure in non homestatic temperatures
which protein in the cell membrane is transmembrane
receptor
what is a word that describes the fact that receptor protein has hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
amphipathic
what secondary PRO conformation makes up the hydrophobic region of a receptor protein
alpha helices
what are the three sub parts of endocytosis
phagocytosis, pinocytosis, receptor-mediated endocytosis
what are the 6 major types of cell transport
diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, active transport, exocytosis, endocytosis
what 3 types of cell transport are passive
diffusion, osmosis, facilitation diffusion
what 3 types of cell tranport are active
active transport, exocytosis, endocytosis
define diffusion
movement of molecules from high conecentration to low concentration
what do most systems result in from diffusion
dynamic equilibrium
what is the opposite of dynamic equalilbriam
static equalilbrium
define osmosis
movement of water from high concentration to low concentration through SPM
solute
being dissolved
solvent
does the dissolving
what does active transport go against
the concentration gradient
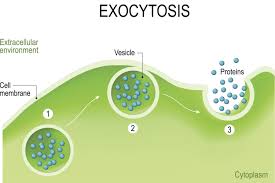
exocytosis
large amount of molecules leaving the cell
why can a vesicle fuse with the cell membrane
they are both make of phospholipids
what is a result of exocytosis
vesicle fuses with cell membrane
define phagocytosis
the process used for the cell to eat solid food
endocytosis
large amounts of material enter the cell
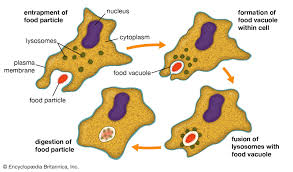
what is a pseudopodium
an extendable part of the cytoplasm that engulfs food
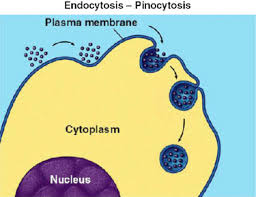
define pinocytosis
the process used for the cell to absorb liquid material
how does pinocytosis work
the cell collapses onto liquid
what are the 3 results of osmosis
hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic
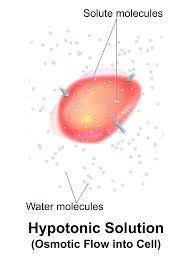
what is the result of a hypertonic solution on an animal cell
becomes shriveled
what is the word for a hypotonic solution in a plant cell
turgid
what is the homeostatic state of a plant cell
turgid
what is the homeostatic solution for an animal cell
isotonic
what is it called when a plant cell is in a isotonic solution
flaccid
what is it called when an animal cell is in a hypertonic solution
shriveled
what is it called when an plant cell is in a hypertonic solution
plasmolyze
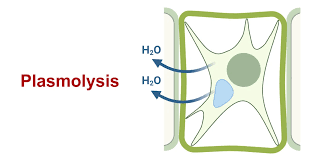
what happens to a plamolyzed plant cell
cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall
why are plant cells able to sustain a hypotonic/turgid state
because of cell wall
what quality is specific to a receptor PRO
an area like an active site
how does the active site know which molecule to bind to
specific charges
what types of things bind to receptor proteins
hormones (insulen)
what specific qualities do channel proteins do channel proteins posses
makes a pathway through cell membrane for certain sized molecules
what type of molecules do channel proteins help transport
polar
what do gated channel proteins have that channel proteins don’t
gates on end of protein
what specific qualities do glycoproteins posses
CHO chains attached to outside that act as a flag
what purpose do glycoproteins serve
they act as an antigen
what two things cannot pass through the cell membrane
ions and polar molecules
why cant ions and polar molecules pass through SPM
tails being hydrophobic
does passive transport use energy
no
what is osmotic pressure
minimum pressure that can be applied to stop the flow of solvent through SPM
how do you demonstrate osmosis
add sugar
EXTRA RANDOM FACTS: what protein is red blood cells made up of
hemoglobin
what is an effect of receptor mediated endocytosis
cell forms a vesicle
what material is received in receptor mediated endocytosis
drugs