Path 10: Free Radicals
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what are free radicals
unstable chemical species with a single unpaired electron in an outer orbital, making it highly reactiive
what do free radicals do?
attack other molecules by stealing an electron (oxidation) or donating an electron (reduction)
endogenous free radicals
from cellular oxidative processes
exogenous free radicals
sunlight, gamma irradiation, pollution, cigarette smoke, drugs, alcohol, heavy metal
reactive oxygen species
-can be radicals or not
-
O2 accepts 4 electrons
-to become H2O
what is the most reactive oxygen species?
Hydroxyl radical (OH)
Haber-Weiss reaction
O2- + H2O2 -----> more reactive OH radical
polyunsaturated fatty acids are most prone to what?
lipid peroxidation
-bc they have unsaturateed double bonds that react with free radical
lipid peroxidation
the destruction of polyunsaturated lipids, leading to membrane damage and increased permeability
oxidative damage of proteins
-affects tertiary, quaternary structure as well as enzymatic function
-can change function, stability, localization; can lead to increased proteasomal degradation
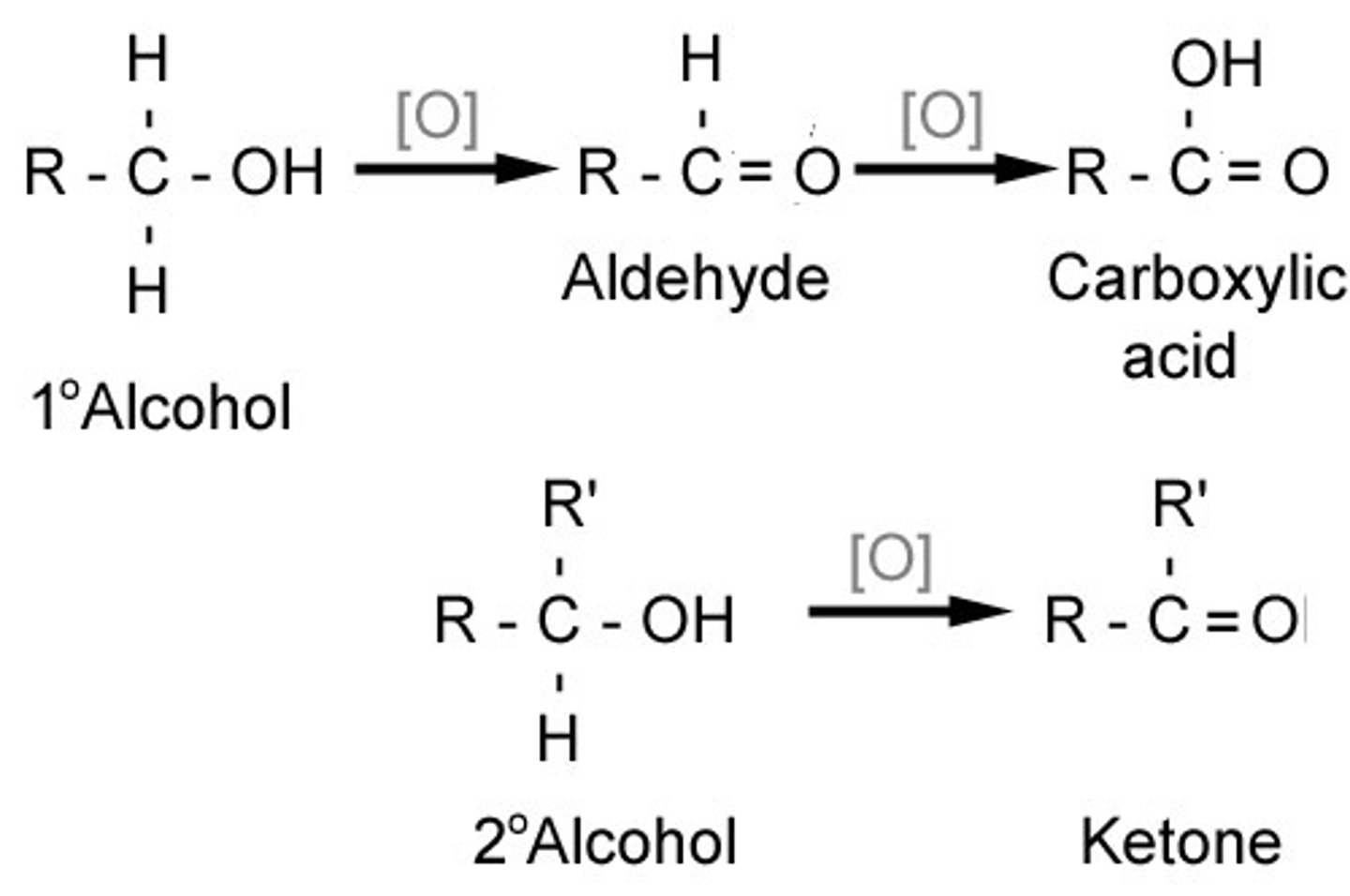
Oxidation of Aldehydes and Ketones
-When aldehydes are further oxidized, they form carboxylic acids (any oxidizing agent stronger than PCC)
-ketones cannot be oxidized further
oxidative damage of DNA
OH free radical can attack DNA, causing strand breaks and mutation, leading to carcinogenesis
formation of 8-oxyguanine
-example of oxidative damage to DNA
-can cause mismatching in base-repair and replication, can cause G--> transversion
beneficial use of free radicals
-neutrophils and macrophages use free radicals to kill bacteria
-however, this can cause extra damage to the infected tissue
-signaling associated with angiogenesis
how do neutrophils/macrophages kill bacteria?
-they use free radicals!
-increased O2 uptake generates O2- by NADPH oxidase into phagosome......
Angiogenesis
formation of new blood vessels
how is free radical production balanced?
antioxidant defense system; imbalance leads to oxidative stress
Antioxidant defense system
includes superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and physiological compounds that are anti-oxidants
mild oxidative stress leads to
cellular adaptation, excess stress leads to damage to biomolecules
what biomoelcues work to detoxify ROS?
enzymes and anti-oxidants
Vitamin E
can give a hydrogen atom to neutralize a radical
-is fat soluble, thus can protect membranes from lipid peroxidation
-can be regenerated by vitamin C
disorders with pro-oxidative shift
cancer, Diabeetus M, acetaminophen poisoning, retinopathy of prematurity, iron and copper overload, carbon tetrachloride
leading cause of blindness in babies
retinoptathy
-treatment of RDS in newborns destroys retinal cells, leading to blindness
disorders with inflammatory oxidative conditions
atherosclerosis, neurodegenerative disease, rheumatoid arthritis, HIV, ischemia, sleep apnea