Male reproductive system
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Function of testosterone
o Growth of muscle and bone, increase in heigh
o Enlargement of larynx
o Deepening of voice
o Growth of hair: Face, axillae, chest, abdomen and pubis
o Enlargement of penis, scrotum and prostate gland
o Maturation of seminiferous tubules
o Increase production of sebum → Spots
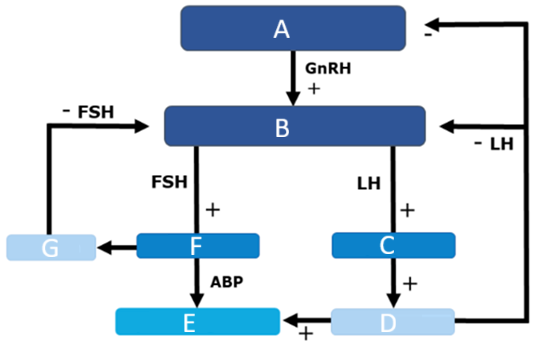
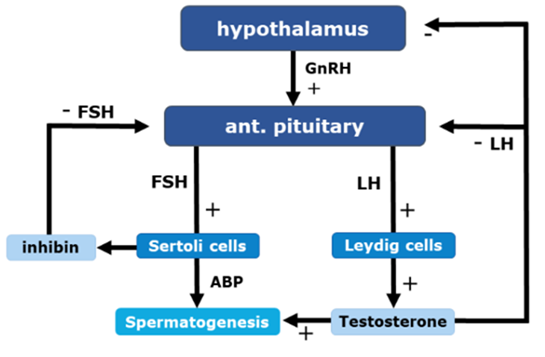
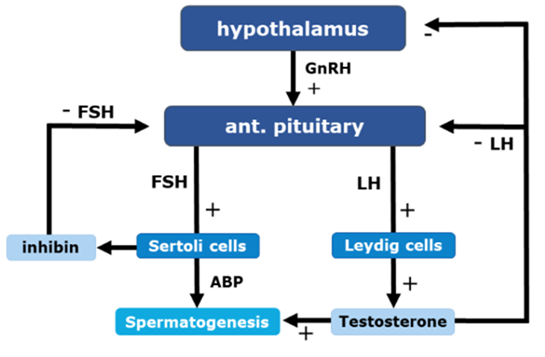
3 constrictions of the male urethra
o the internal urethral sphincter
o external urethral sphincter
o external urethral orifice
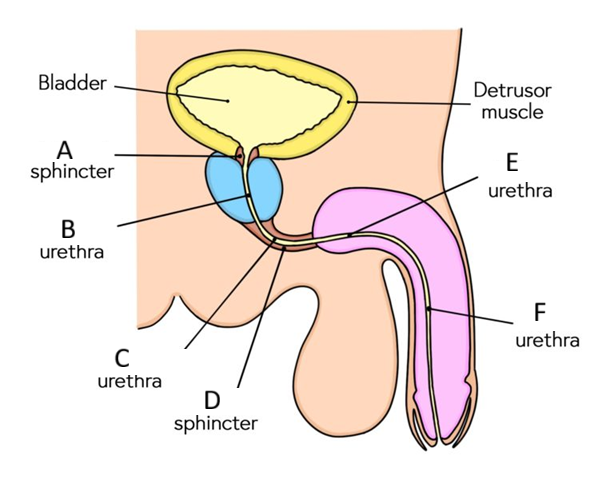
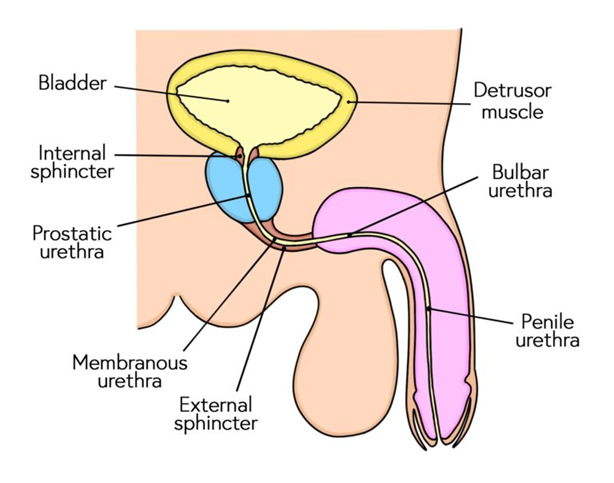
Arterial supply to the different urethras
Prostatic: inferior vesical artery
membranous: bulbourethral artery (branch of the internal pudendal artery)
Penile: internal pudendal artery
Nerve supply to male urethra
prostatic plexus
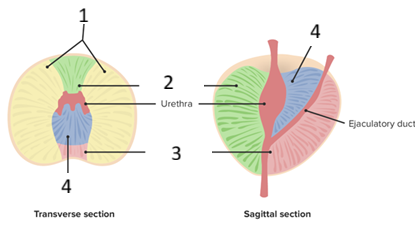
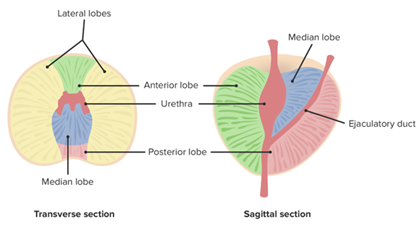
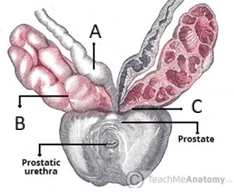
Name the lobes of the prostate
anterior lobe
posterior lobe
L lateral lobe
R lateral lobe
median lobe
Name the zones of the prostate
central zone (25%)
transitional (10%)
peripheral (65%)
Which zone of the prostate typically undergoes benign hypoplasia (BHP)
transitional zone
Function of the prostate
To secretes proteolytic enzymes into the semen → break down clotting factors in the ejaculate → allows semen to remain fluid to move throughout the female reproductive tract
What secretes the proteolytic enzymes and how do they enter into the semen?
The prostate
The proteolytic enzymes leave via the prostatic ducts that open into the prostatic portion of the urethra with openings at each side of the seminal colliculus (or verumontanum), secreting the enzymes into the semen immediately before ejaculation
Arterial and venous supply to the prostate
Arterial supply
o the prostatic arteries (mainly derived from the internal iliac arteries)
Venous drainage :
o the prostatic venous plexus, draining into the internal iliac veins
Nerve supply to the prostate
receives sympathetic, parasympathetic and sensory innervation from the inferior hypogastric plexus
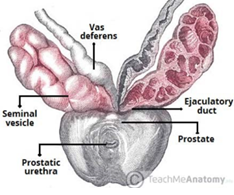
Location of seminal vesicles
located between the bladder fundus and the rectum (separated from the rectum by the rectovesicle pouch and the rectoprostatic fascia)
Structure of the seminal vesicles (including type of epithelium lining)
has a honeycombed, lobulated structure with a mucosa lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium → grow taller with increased levels of testosterone
What structures form the ejaculatory duct?
the duct of seminal vesicles combines with the vas deferens
Function of the parts of the fluid secreted by seminal vesicles
** Release fluid in the late ejaculate fractions containing:
o Alkaline fluid – neutralises the acidity of the male urethra and vagina to help survival of spermatozoa.
o Fructose – provides an energy source for spermatozoa
o Prostaglandins – have a role in suppressing the female immune response to foreign semen
o Clotting factors – designed to keep semen in the female reproductive tract post-ejaculation
What is semen made up of?
mostly water, seminal vesicle secretions, testicular spermatozoa, prostatic secretions, and mucus from the bulbourethral gland.
Blood supply to seminal vesicles
inferior vesicle, internal pudendal and middle rectal arteries
**all stem from the internal iliac artery
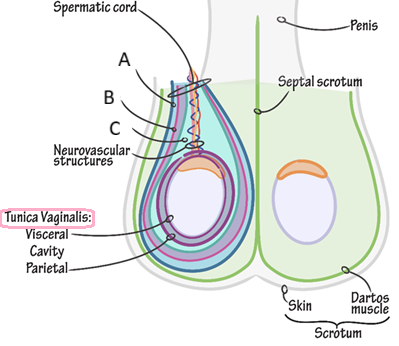
Describe the location of the spermatic cord
** begins in the inferior abdomen and ends in the scrotum
It passes through the inguinal canal, entering the scrotum via the superficial inguinal ring, ending at the posterior border of the testes
What does the spermatic cord contain
o Blood vessels:
→ arteries eg. Testicular artery
o Nerves:
→ Genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve:
→ Autonomic nerves
o Other structures:
→ Vas deferens
→ Processus vaginalis
→ Lymph vessels
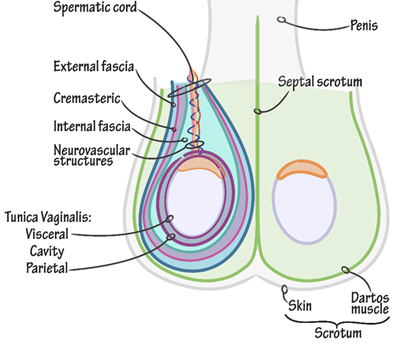
What epithelium lines the epididymis?
columnar epithelium
What are the different sections of the epididymis
o Head: most proximal part, formed by the efferent tubules of the testes
o Body
o Tail: most distal part that marks the origin of the vas deferens
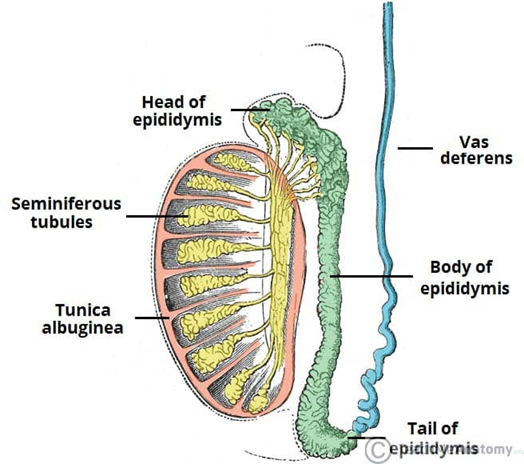
Function of the vas deferens
transports sperm to the prostatic portion of the urethra for ejaculation
How are sperm produced and where do they go to be stored?
Spermatozoa are produced in the seminiferous tubules (in the testes). The developing sperm travels through the tubules, collecting in the rete testes
The efferent tubules transport the sperm from the rete testes to the epididymis for storage and maturation
Function of the tunica vaginalis
a closed sac of parietal peritoneal origin that contains a small amount of viscous fluid that lubricate the surfaces of the testes and allowing for friction-free movement
Arterial supply to the testes
the paired testicular arteries (arise directly from the abdominal aorta)
also supplied by branches of the cremasteric artery (from the inferior epigastric artery) and the artery of the vas deferens (from the inferior vesical artery)Fep
Venous drainage of the testes
paired testicular veins formed from the pampiniform plexus in the scrotum
the left testicular vein drains into the left renal vein the right testicular vein drains directly into the inferior vena cava.
Innervation of the testes
testicular plexus
What type of tissue is the scrotum made of?
pouch of pigmented skin consisting of fibrous tissue, Connective tissue, and Smooth muscle
What does 1 compartment of the scrotum contain?
1 testis, 1 epididymis and testicular end of a spermatic cord
Function of the dartos muscle
acts to help regulate the temperature of the scrotum, by wrinkling the skin it decreases surface area, reducing heat loss
Blood supply to the scrotum
o the anterior scrotal arteries (from the external pudendal artery)
o the posterior scrotal arteries (from the internal pudendal artery)
The scrotal veins follow the major arteries, draining into the external pudendal veins
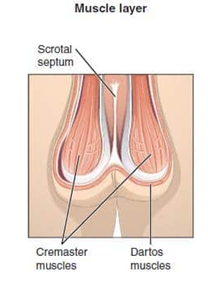
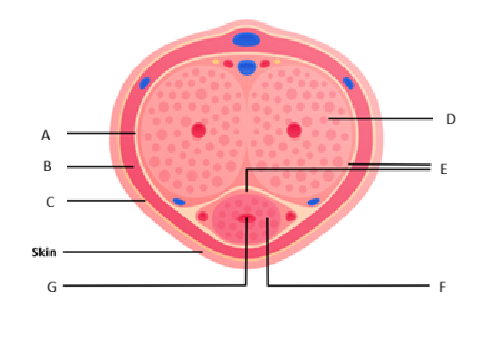
Lymphatic drainage of scrotum
superficial inguinal nodes
Nerve supply to scrotum
o Anterior and anterolateral aspect: Anterior scrotal nerves derived from the genital branch of genitofemoral nerve and ilioinguinal nerve
o Posterior aspect: Posterior scrotal nerves derived from the perineal branches of the pudendal nerve and posterior femoral cutaneous nerve
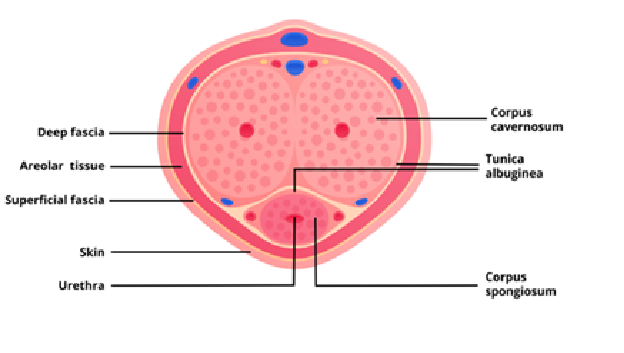
Name the muscles of the penis and their function
Bulbospongiosus (x2): contracts to empty the spongy urethra of any residual semen and urine. The anterior fibres also aid in maintaining erection by increasing the pressure in the bulb of the penis.
Ischiocavernosus (x2) – surrounds the left and right crura of the penis. It contracts to force blood from the cavernous spaces in the crura into the corpora cavernosa → helps maintain erection
Name the ligaments of the penis
Suspensory ligament connects the erectile bodies of the penis to the pubic symphysis.
Fundiform ligament runs down from the linea alba, surrounding the penis and attaching to the pubic symphysis
Arterial supply to the penis
o Dorsal arteries of the penis
o Deep arteries of the penis
o Bulbourethral artery
** all branches of the internal pudendal artery which arises from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery
Venous drainage of the penis
o The cavernous spaces are drained by the deep dorsal vein of the penis → empty into the prostatic venous plexus
o The superficial dorsal veins drain the superficial structures of the penis, such as the skin and cutaneous tissues
Nerve supply to the penis
o supplied by S2-S4 spinal cord segments and spinal ganglia.
o Sensory and sympathetic innervation to the skin and glans penis is supplied by the dorsal nerve of the penis (branch of the pudendal nerve)
o Parasympathetic innervation is carried by cavernous nerves from the peri-prostatic nerve plexus → responsible for the vascular changes which cause erection
What is the body of the penis composed of?
of three cylinders of erectile tissue: 2 corpora cavernosa, and the corpus spongiosum

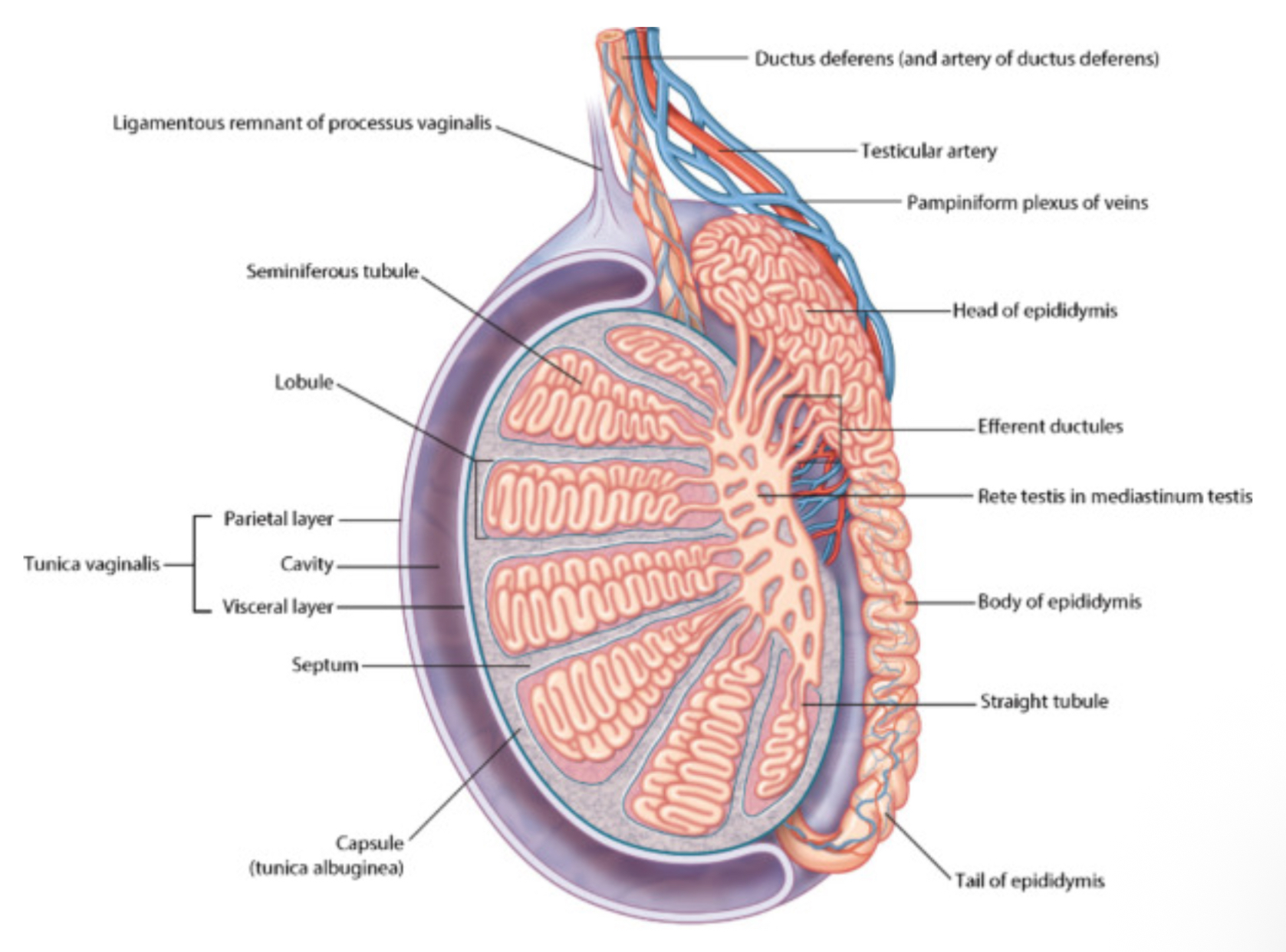
At what temperature do sperm need to be at and what maintains them at this temp?
2-4 degrees below body temp
Dartos muscle:by wrinkling the skin it decreases surface area
Pampiniform venous plexus → acts as countercurrent heat exchanger
How is the cremaster reflex started and which spinal roots does it test?
Downward stroke on the medial left thigh → testicular should contract
Gentiofemoral nerve (originated from L1 and L2)