APUSH Test 1 - Review till War of 1812
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
What kind of diverse Native American groups populated North America?
Hunter gatherers in the north (woodlands)
When did Columbus “claim the Americas?
1492
Who did Columbus “claim” the americas for?
Spain (King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella)
What was Columbus looking for?
A shortcut to India
What other European empires settled? Where did they settle? What did they do?
Dutch - New York ; Fur Trade
Spanish - Mexico and Florida ; Gold
French - Canada (Quebec) , Mississippi River ; fur trade
British - East (most instance undertaking)
Who did tensions arise between? What were the issues?
Indians and Europeans
Over land, violence, (also known as the 7 years war)
What/Where was initial colonization located?
Chesapeake (Virginia and Maryland)
Why did people colonize in these places?
For profit by crash crops (tobacco)
What populations were used to grow these cash crops?
Slave plantations
Where did the practice of using slave plantations in order to earn profit from cash crops spread to?
The Carolinas (rice, indigo, sugar)
What other group was used besides slaves?
Indentured servants - people who willingly sold themselves into slavery for a temporary time in order to get land in America out of it
What was Bacon’s Rebellion?
Indentured slaves uprising because they weren’t getting what they were promised after their 7 years were over
What was the effect of Bacon’s Rebellion?
Owners returned to using slaves
Who settled in New England? Why?
Puritan separatists
Because they wanted religious freedom and a clear break from the Church of England
How did the Puritans in force law?
Through moral behavior (would have been persecuted in England)
What were the Middle Colonies classified as?
Bread basket colonies
What were the Southern Colonies classified as?
Cash crop colonies
What were the New England colonies classified as?
Manufacturing ships and rum colonies
True or False: The colonies started out very divided.
True
What was the First Great Awakening?
A religious revival
What was Jonathan Edwards’s central message?
“God is mad at you, fix yourself, he is the only one keeping you from hell”
What was happening along the Ohio River?
Fur trading
How did the French and Indian War affect American identity?
Gave a sense of unity amongst colonists (they united in defense)
What is mercantilism? (in the context of the revolutionary war)
Colonists forced to buy and sell from British ONLY
Why did the British make this policy?
Britain wanted to make back their debt from the loss they had in defending the colonists during war times
What was the Proclamation of 1763? How did colonists react?
British banned them from settling in new territory ; they were upset
When did the fight for independence/ revolution start?
1775
Who was the good commander against the British?
George Washington
What other country supported America against the British?
France. They were great help for the colonists and they had their own agenda against the British.
What were the two different groups of Americans? What was the effect of the conflicting ideas?
Patriots : conflict with crown/Britain
Loyalists : loyal to crown/Britain
There was also a group who wanted to stay neutral.
They ended up fighting each other in a “mini civil war”
What was the Treaty of Paris? When was it signed? Who signed it?
Recognized US independence ; claim to British land west of Mississippi River
1783
Britain
Where was Washington inaugurated?
New York (our old capital alongside Philadelphia)
When was the United States “born”? Virginia? New York?
United States : 1776
Virginia : 1607
New York : 1664
Even though they severed ties with England like they wanted, what problem was still apparent?
The colonies couldn’t band together as there was no common enemy to defend themselves against. “The enemy of my enemy is my friend.,.
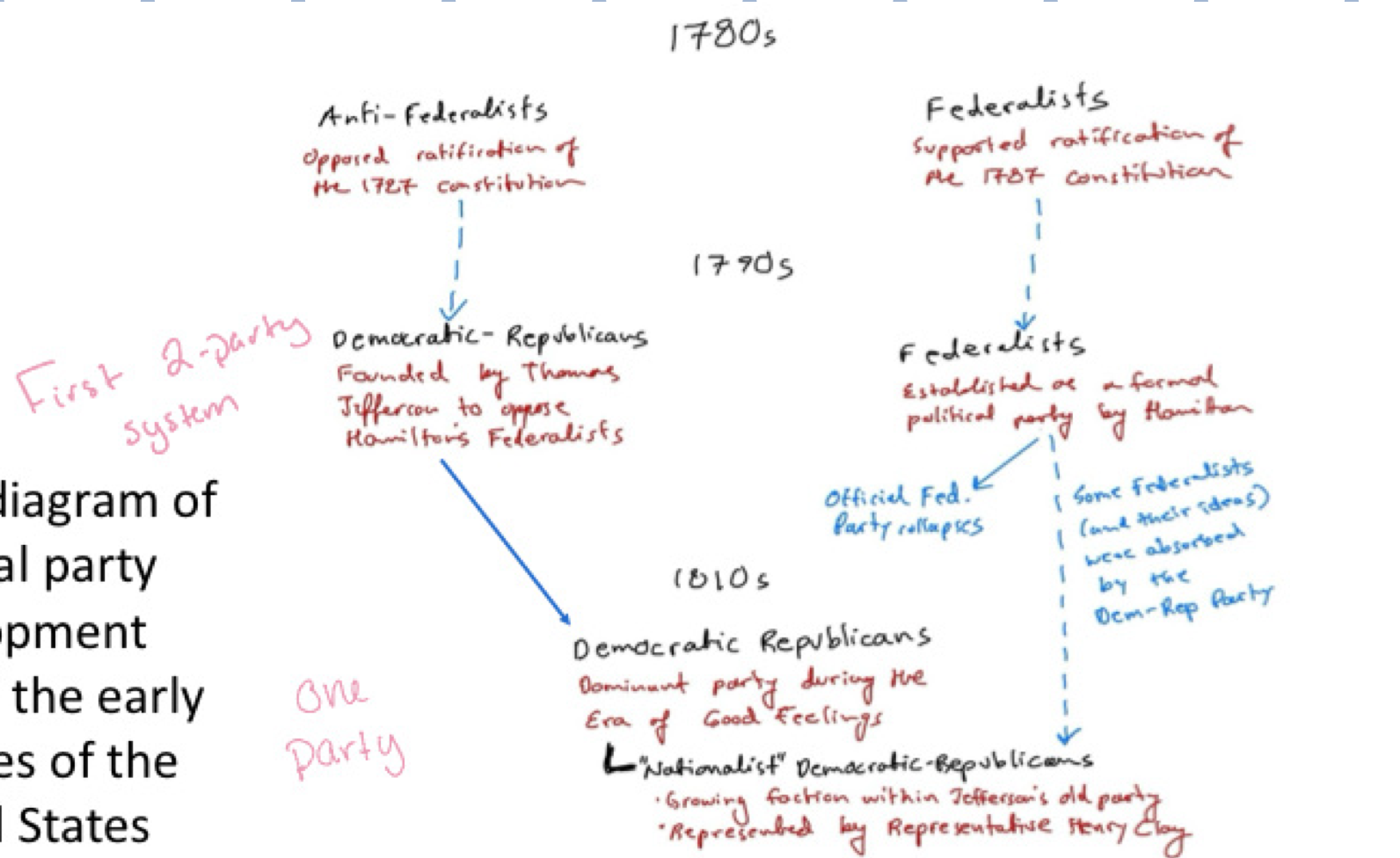
Articles of Confederation (1781-1789)***
Weak federal government, only a congress (federalists didn’t like)
When was the Constitution “born”?
1789
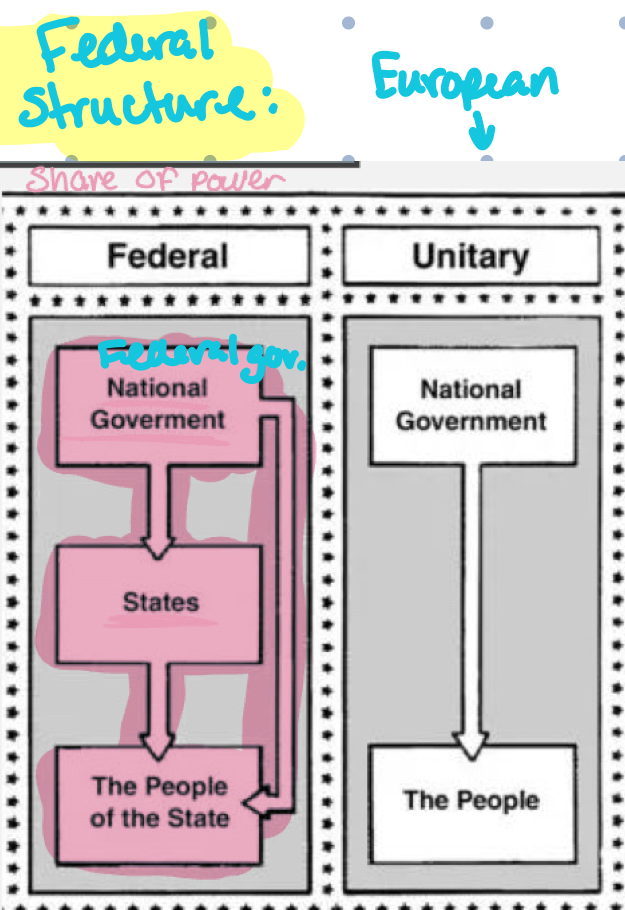
What did a strong federal government entail?***
Offices : President, Congress, and Judiciary
Country unified under the same rules and military
Still reserved power for state government (limited federal gov)
Who opposed a strong federal government?***
Anti-federalists
Why were the Democratic Republicans weary?
Thought that this type of government would favor wealthy elites
Thought “one-size fit all” rules would be applied to every state
Who gets to say state or federal interprets constitution rules?
Democratic-Republicans : states (nullify - Virginia and Kentucky resolutions)
Federal : US Supreme Court (winner of Marbury vs Madison)
What did the colonies having poor roads lead to?
Poor communication and internal travel which adds to no sense of national identity
What did the low levels of literacy among colonists lead to?
Harder to spread ideas, which led to the need for indigenous literature (american authors)
The US was largely ______.
agricultural
What plantations were largely populated in the south?
Large cash crop plantations
Subsistence farming
northerners farmed just enough to get by
Break down the regional specialization. Which two are opposites?
North : manufacturing - wage labor
South : slave labor
West : farming families
The two opposites are North and West
What is a Yeoman farmer? Who supported this?
you are your own boss (full liberty)
Jefferson and the Democratic-Republicans
Jefferson though everyone should farm for themselves/their own families and be their own boss
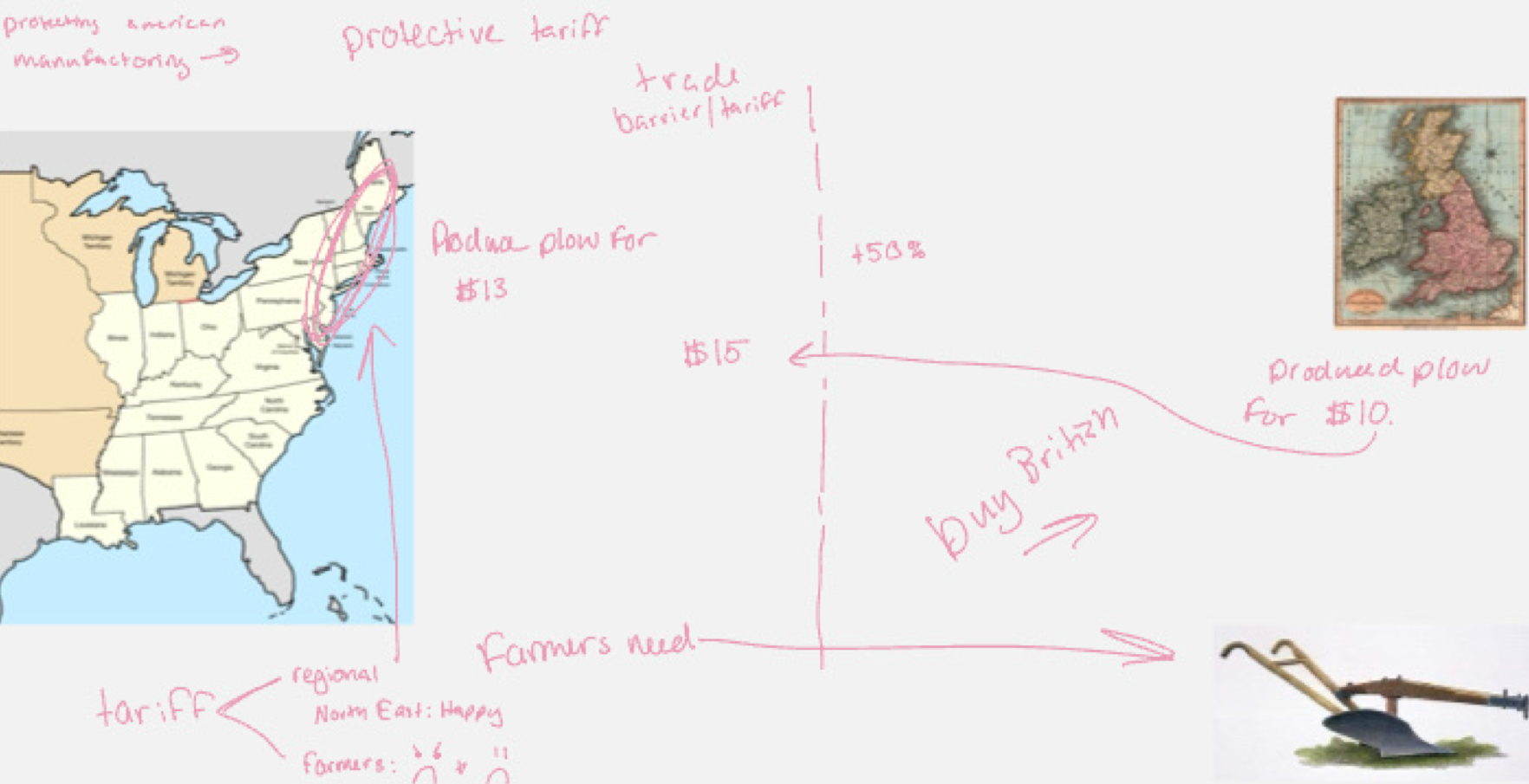
Hamilton’s National Bank
favored industry with protective tariffs (raising outside good prices for the more expensive US prices for better economy)
Yeomen farmers suffered with higher prices
Know federal government vs european chart:
Know tariff map and what it means:
Was slavery practiced everywhere? If so, how were they paired?
Yes.
Spanish and Native Americans (they all died)
Americans and Africans
Slaves were…
1) caught
2) traded
3) transferred (Middle Passage along Atlantic)
When was the Haitian Revolution? Where was it located?
1791-1804 ; West Indies owned by French
What occurred during the Haitian Revolution?
slaves rose up and killed plantation owners
owners in US got scared —> led to being more controlling/harsher rules
What rules were put in place for Americans following the Haitian Revolution?
Americans banned from participating in slave trade (to end importation of more slaves)
Trade becomes more domestic, newly encouraging slave marriage
How did slaves affect politics?
Slaves increase states’ political rivalries
3/5ths compromise - 3/5 slaves count for the population number for weights of the votes
True or False : Slave owning was gradually outlawed in the Northern states (late 18th century)
True
True or False : abolitionist movement means they see blacks and whites as equals
False
What intensified slavery issues?
West Expansion (would it be allowed in the west?)
Regional states interest ___ National interest
>
Power blocs between states:
North : industrial with economically and financially powerful cities
South : agricultural, export based slave economies, expand slavery
West : agricultural, subsistence farming, divided on slavery
Which war was the War of 1812?
2nd war between US and Britain
What was the cause of the War of 1812?
Reaction to British and offensive reasons
What were the reactions?
British interference with US ships (impounding cargo)
Impressment*** - taking American sailors and imprisoning them on their ships
British supporting Indian tribes (giving them guns to work against colonists)
What were the offensives?
Americans went to capture British Canada
Want to prove national strength
Why was it a divisive war for the Americans?
Federalists were “pro-British” and anti-war (didn’t want to disrupt trade with Britain in New England bc their economy relied on it)
How long did the War of 1812 last?
2 ½ yrs (1812-1815)
American ____ poorly led and organized (didn’t go well at first)
army ; failed invasion of Canada (1812)
American ____ defends against Britain (Great Lakes)
navy
What did Britain do during the War?
Sent a lot of redcoats
captured/burned DC (symbolic)
What did colonists do in defense?
stopped them from getting Baltimore (important port city)
heroic defense of Fort McHenry (Sept 1814)
Who was Francis Scott Key?
a victim of imprisonment and was there, he was inspired to write a poem —> our national anthem
What was the British attempt to capture New Orleans?
wanted to cutoff Mississippi river to starve out colonists, fail
defeated by Andrew Jackson (Jan 1815)
fought by soldiers, regular men, and some free blacks
Who opposed the war from the beginning?
Federalists
What is embargo? What effect did it have on the economy?
ban on trade with a country
economy suffered
How did New England symbolize tension from disagreement with government?
Some NE colonies resisted embargo (started smuggling in Brtiish Canada)
discussed nullifying (rejecting) embargo
talk of secession (cut off ties with US) and forming their own peace with Britain
What convention was organized? What was discussed?
Hartford Convention (CT)
discussed issues having to do with embargo and trading
What killed the Federalist party?
after making peace with Britain, Federalists were seen as traitors
kills federalist party —> Demo-Rep domination
What was the Era of Good feelings?
a time of political “peace” in the US as there was only one significant political party
What was the only significant party in the US during the Era of Good Feelings?
Democratic-Republican party
Since the old federalists were absorbed into the Demo-Rep party, what factions arose?
Older wing : states rights and Jefferson ideas
New ”nationalist” wing : national unity and economic growth (Federalist)
Understand chart that explains the breakdown of the Federalist and Democratic-Republican Parties:
Who was Henry Clay? What ideas did he bring with him?
first Western politician (Kentucky)
new nationalist party ideas
What did Henry Clay want?
wanted a unified American system, not per state
What was Henry Clay’s 3 Part Plan?
1) protective tariff
2) national banking system
3) federal funding for roads on canals