Meiosis I
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
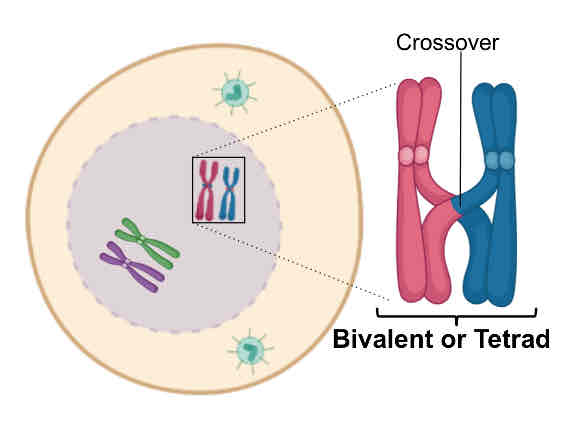
Chromosomes condense Nuclear envelope disappears
Two centrosomes start forming the spindle
Each chromosome composed of 2 sister chromatids
Homologous chromosomes crossover, exchanging DNA
Prophase I
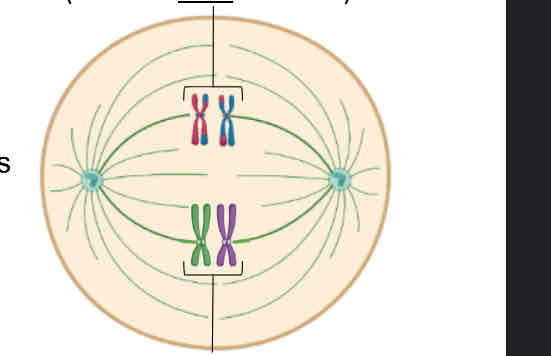
Homologs still stuck together
Pair of homologs
Microtubules from opposite poles attach to each homolog
Homologs are aligned at the metaphase plate side-by-side
Orientation of each pair of homologs on the spindle is random
Metaphase I
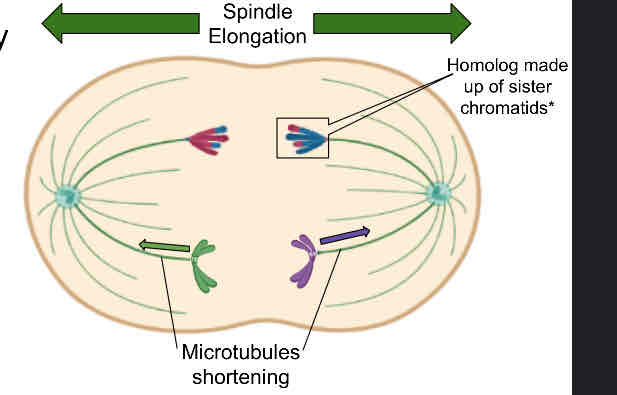
HOMOLOGS are separated by 2 forces
Spindle elongation
Shortening of the microtubules attached to chromosomes
Sister chromatids remain attached to each other at their centromeres
Anaphase I
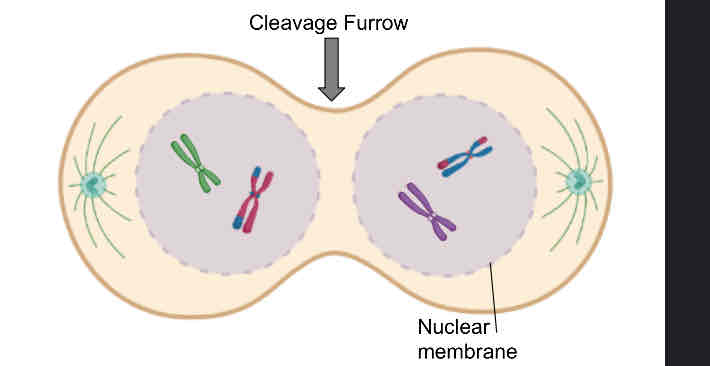
Nuclear envelope re-forms around each daughter nucleus
Sister chromatids are no longer identical because of crossing over (prophase I)
Cytokinesis occurs after telophase I
Meiosis II occurs after an interval of variable length
Telophase I