623 3.1 Balance and Falls in Elderly
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
falls
Leading cause of injury-related deaths among people age 65 and older
death
Over 3,000 falls per month lead to _________ in adults 65 and older
hip fracture, TBI
highest resulting injuries from falls in those 65 and older
1/4
__/___ adults aged 65 and older falls each year, and half do not tell their doctor
$50 billion
cost of treating injuries from falls per year
fractures
PRIMARY consequence of falls
67
Balance confidence below ___& leads to an increase in falls
32
% of people who end up in the hospital or require assistance w/ activities after falls
sensory impairments, pathologies, cognitive deficits, medications, environment
5 main factors that contribute to falls
4+
number of prescription drugs that increased the risk for falls compared to fewer
dirty/cluttered home, external factors that lead to slipping/tripping/bumping, faulty footwear
Environmental examples that lead to falls
Sensory Environment
The conditions which exist or are perceived to exist in the real world around us that impact balance
ID cause
ID modifiable RFs
Control Environmental Hazards
Education
4 steps to fall prevention
Install handrails, improve lighting, repair steps and flooring, install grab bars, remove clutter, use non-slip mats and treads
Education for fall prevention examples
results from the combined function of multiple sensory, motor, and neural systems
What does it mean for balance to be integrated?
vestibular, visual, proprioceptive
3 sensory systems needed for optimal balance
cerebellum, cerebral cortex, brainstem
three main integration sites of sensory input for balance
all the systems involved in balance constantly communicate and influence each other in real time
What does it mean for balance to be interactive
Gaze stability
ability to maintain gaze or visual focus on an external target during movement
Postural Stability
The ability to maintain the body's center of gravity (COG) over the base of support (BOS) in a given sensory environment
Center of mass
An imaginary point in space that is at the center of the total body mass; unique point where body forces sums to zero (all particles of body are equally distributed)
F (depends on mass distribution, not orientation)
T/F. COM depends on vertical orientation
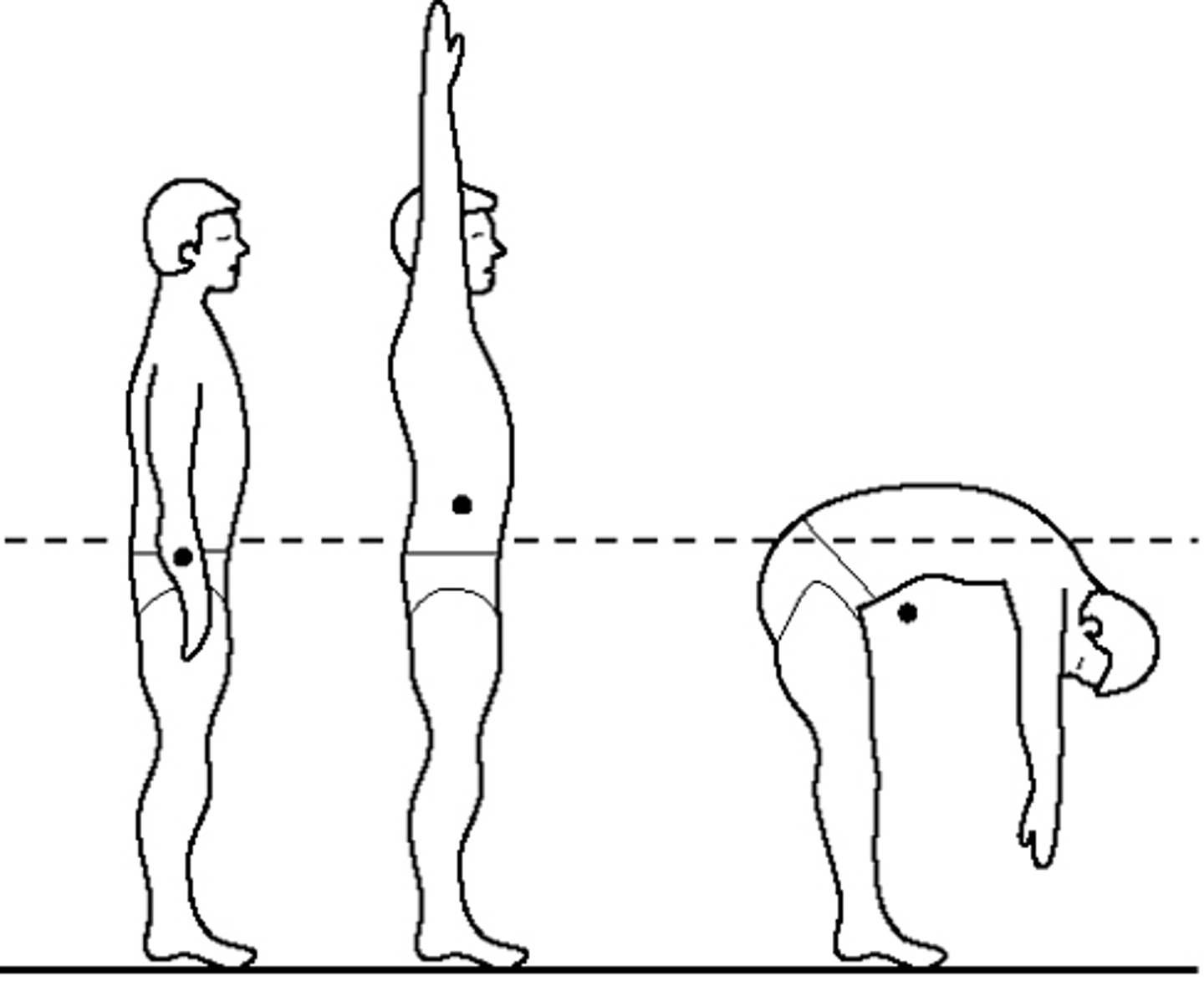
COM
The point where if a force is applied, it moves in the direction of the force without rotating
Center of Gravity (COG)
The vertical projection of the COM onto the ground; point of origin about which all particles of body are equally distributed
vertical
COG refers only to __________ direction in which gravity acts
Center of pressure
A vertical line projecting downward from the actual center of gravity into the force plate; a representation (indirect measure) of center of gravity
Center of Pressure (COP)
vertical ground reaction force vector; weighted average of all the pressures over the surface of the area in contact witht he ground
between the two feet
If both feet are in contact with the ground, where would the net center of pressure lie?
BOS
The area of the object that is in contact with the support surface (anteroposterior length of the foot and mediolateral width of stance)
COG
When _____ leaves the BOS, people are at highest risk of falling
limits of stability
The furthest distance in any direction a person can lean away from midline (upright vertical) without altering the BOS, reaching or falling
12.5º total, (8º forward, 4.5º backward)
Normal limits of stability AP
16º total (8º R and L)
Normal limits of stability ML
core
strength in what area can help improve limits of stability?
COM over BOS
how to maintain postural stability
motions of COM and COP
how to minimize postural stability
COM & COP back to optimal location
how to restor postural stability
Quiet Standing
Present during quiet standing to maintain balance
Net center of pressure
How is quiet standing measured?
Static Balance
Ability to maintain an upright posture and keep the COG within the limits of BOS
Dynamic Balance
Ability to maintain stability during weight shifting and changes in BOS
dynamic balance
balance in which falls usually occur, and where we would need the most therapy
BOS
Theoretical limits of stability (LOS) during stance are traditionally considered to be dependent on what measure?
static standing (insufficient in dynamic situations)
LOS is valid during what type of balance?
position, velocity
Stability limits depend on what two dynamic factors?
maintains steady balance w/o handheld support
Normal Static Balance
Accepts max challenge and can shift weight easily w/in full range
Normal Dynamic Balance
Able to maintain balance w/o handheld support w/ limited postural sway
Good Static Balance
Accepts mod challenge, balances while picking objects off the floor
Good Dynamic Balance
Maintains balance w/ handheld support, may need occasional min assist
Fair Static Balance
Accepts min challenge, balances while turning head/trunk
Fair Dynamic Balance
Requires Handheld support and mod/max assist to balance
Poor Static Balance
Unable to accept challenge or move w/o LOB
Poor Dynamic Balance
T
T/F: Balance must be maintained to achieve GAIT
keep body COM w/in BOS
Gait Standing GOAL in terms of balance
Body moves over ground w/ one step - balance drastically altered
Gait Initiation changes to balance
COG moves forward as we voluntarily initiate forward falling (accelerated COG ahead of BOS)
Gait Acceleration changes to balance
Move body outside BOS and prevent falling
Gait Goal
COP moves posterior and toward the swing limb (accelerates COG forward)
What happens in the release phase of gait initiation?
rapid activation of stance limb
What happens in the unloading phase of gait initiation?
forward under stance foot
after unloading the stance limb, where does the COP move?
mirror images
How are COP and COM trajectories different in gait termination from gait initiation
w/in BOS
During termination of gait, the COG must move where?
forward along medial border of each support foot
How does COG move relative to the support foot during gait?
accelerated away from support foot toward future position of swing foot
How does COG move relative to the support foot during single limb support of gait?
VOR, motor impulses for postural adjustments and eye movements
Motor output of balance is determined by:
visual, vestibular, somatosensory (proprioception)
sensory systems in dynamic equilibrium for balance
F (always try to improve the area they are deficient in before strengthening leftover areas)
If an individual is deficient in their sensory system, we should try to improve the other two systems first. T/F
ankle muscles, legs/thighs, trunk muscles
Motor systems of dynamic equilibrium
ankle, hip, step
Motor strategies relied on in order from first to last
relay info about head position, linear/rotational/accelerating movements of the head, gaze stability, balance/posture stability, overall orientation in space
Vestibular system function on motor ouput
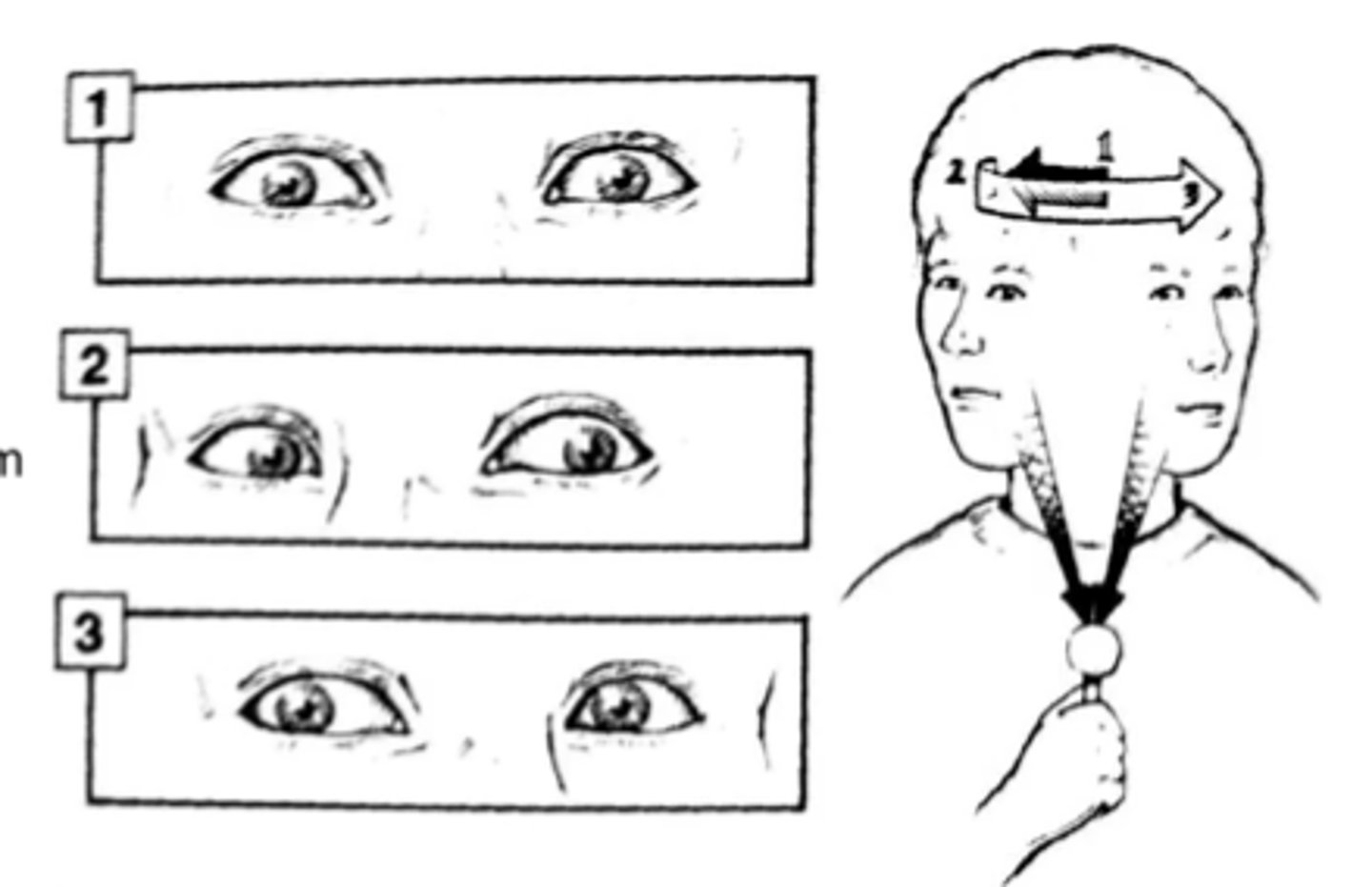
Fudka Step Test
a balance assessment that helps detect potential problems with the vestibular system. During the test, a person marches in place with eyes closed and arms outstretched
rotation >30º
positive fudka test
must assess balance and vestibular dysfunction for ppl w/ high fall risk
decrease fall risk
decrease injury risk
improve functional mobility
improve QoL
role of healthcare interdisciplinary team in balance