The Cardiovascular System: The Heart and Blood Vessels/Circulation
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A and P2- Exam 2: Chapters 19, 20, and 21
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
The heart beats how many bpm
75
The space in which the heart is located in the thoracic cavity
mediastinum
The atrium of the heart
receives blood from the body and pumps it into the ventricles
The ventricles of the heart
receives blood from the atria and pumps to lungs and the rest of the body
All _____ carries blood away from the heart.
arteries
All _____ carries blood to the heart.
veins
The circuit that moves blood to and from lungs for gas exchange
the pulmonary circuit
The circuit that moves blood to and from the rest of the body
the systemic circuit
The pericardium is
serous membrane surrounding the heart and vessels
The upper chambers of the heart are called
atria
The lower chambers of the heart are called
ventricles
The arteries where gas exchange occurs- CO2 exits, O2 enters
pulmonary capillaries
The right ventricle pumps _______ blood into the pulmonary trunk
deoxygenated
Both the superior and inferior vena cava end up in the
right atrium
The artery that distributes blood to the rest of the body is called
the aorta
The ear-like supplemental blood sac is called
the auricle
The fat-filled grooves that house coronary vessels is called
sulcus
The heart wall layers are
endocardium, myocardium, and epicardium
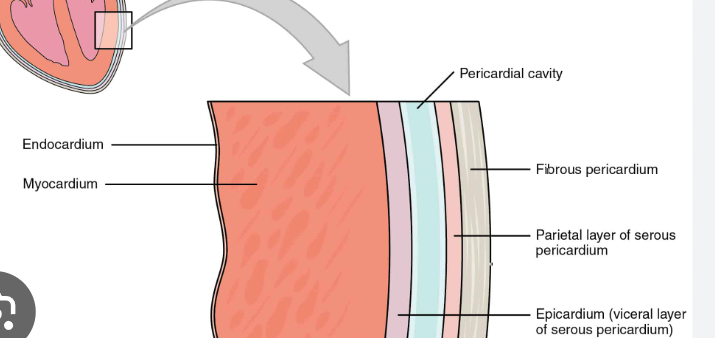
A layer of the heart that holds the heart in place, protects it from damage and infection, and anchors it within the chest cavity.
pericardium
The pericardium has two layers
the fibrous pericardium and the serous pericardium
The serous pericardium has two layers
the parietal and visceral layer (or pericardial cavity)
The ventricle that is thicker
left ventricle
The division between the two atria is called
interatrial septum; fully closes after birth
The division between the two ventricles is called
interventricular septum
division between the atria and ventricles; contains 4 valves to allow blood flow
the atrioventricular septum
The coronary sinus is
the largest vein in the heart
the innermost layer of the vessel walls where large arteries contain internal elastic membrane for stretch
tunic intima
thick middle layer of the vessel wall that allows for vasoconstriction/vasodilation
tunica media
outer layer of the vessel wall made up of elastic connective tissue which hold the vessel in place
tunica externa
internal elastic membrane
provides support and enables stretching of the vessels
arteries closest to the heart are called
elastic arteries
arteries farthest from the heart are called
muscular arteries
small arteries, located just before capillaries is called
arterioles
The three kinds of capillaries include
continuous, fenestrated, and sinusoid
Capillaries that are fully put together and are the most common
continuous capillaries
Capillaries that are characterized by tiny pores and allows larger molecules to pass through
fenestrated capillaries
Capillaries that have many gaps allowing almost all things to pass through
sinusoid capillaries
Sphincters are
muscle that controls blood flow in to capillaries based on O2 and nutrient need
Capillary beds is where
the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste occurs
Part of the vein that collects deoxygenated blood from capillary beds and transport it into larger veins
venules
pressure is low in veins, so they hold more of the blood than arteries
Venous as reservoirs
The venous system contains two pumps
the skeletal muscle and respiratory pump
The parts of the heart that control electrical impulses, enforcing contraction
SA node, AV node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers
Auscultation is
the action of listening to the heart; s1-4 sounds
The amount of blood that is pumped out of the heart (from vent.) in one minute is called
cardiac output
Beats per minute
Heart rate
Volume of blood pumped by each ventricle is called
stroke volume
Equation for cardiac output is
CO = SV x HR
The amount of blood that enters the ventricle is known as
preload
The resistance that the heart's ventricles must overcome to pump blood out during a contraction is known as
afterload
How hard the myocardium has to contract to eject blood out of the ventricles
contractility
A resting HR can change based off of
parasympathetic which slows it down or sympathetic which speeds it up
arteries/veins are thicker than arteries/veins because of the higher pressure they have to withstand from the heart
arteries are thicker than veins
tiny blood vessels within the walls of larger blood vessels that supply them with oxygen and nutrients
vasa vasorum
small nerve fibers that supply nerves to blood vessel walls to control blood flow through vasoconstriction/vasodilation
nervi vasorum
excess tissue fluid is called
edema
the average pressure in a person's arteries over a single cardiac cycle
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP), calculated by diastolic + (systolic-diastolic)/3
a measure of a vessel's ability to expand in response to a change in blood volume is called
compliance
system of veins and other vessels that return deoxygenated blood from the body's tissues and organs back to the heart and lungs is called the
venous system
mass movement of fluids into and out of capillary beds is known as
bulk flow
fluid movement from capillary bed to tissue is known as
filtration
movement of fluid from tissue to capillary bed
reabsorption
the “push” pressure of fluid inside the capillary, promoting filtration
hydrostatic pressure (HP)
the “pull” pressure caused by proteins inside of the blood, promoting reabsorption
osmotic pressure (OP)
decides whether fluid leaves or reenters the capillary, depending on whether it is positive or negative is called the
Net filtration pressure (NFP)
a special blood pathway that carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver before it goes back to the heart, nutrients are processed, stored, or released as needed and toxin are filtered out here
hepatic portal system