[1] Algorithms and Flowcharts
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Problem solving phase
Implementation phase
A typical programming task can be divided into two phases
Problem solving phase
produce an ordered sequence of steps that describe solution of problem
Algorithm
sequence of steps that describe solution of problem
Implementation phase
implement the program in some programming language
First produce a general algorithm (one can use pseudocode)
Refine the algorithm successively to get step by step detailed algorithm that is very close to a computer language
Steps in Problem Solving
Pseudocode
an artificial and informal language that helps programmers develop algorithms
Pseudocode
very similar to everyday English
Flowchart
a schematic representation of a sequence of operations, as in a manufacturing process or computer program (dictionary)
Flowchart
a graphical representation of the sequence of operations in an information system or program (technical)
Information System Flowchart
Program Flowchart
Two Types of Flowchart
Information System Flowchart
shows how data flows from source documents through the computer to final distribution to users
Program Flowchart
shows the sequence of instructions in a single program or subroutine
True
True or False?
Different symbols are used to draw each type of flowchart.
Flowchart
shows logic of an algorithm
Flowchart
emphasizes individual steps and their interconnections
Flowchart
its example is control flow from one action to the next
Oval or Terminal Symbol
denotes the beginning or end of the program

Parallelogram or Input-output Symbol
denotes an input operation

Rectangle or Process Symbol
denotes a process to be carried out e.g. addition, subtraction, division, etc.
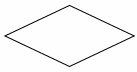
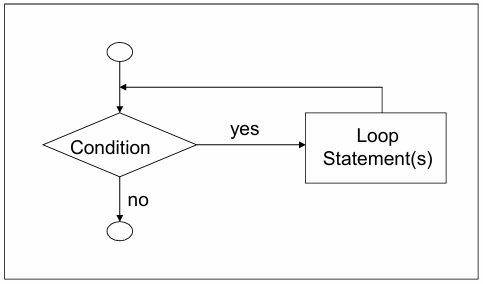
Diamond or Selection Symbol
denotes a decision (or branch) to be made
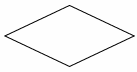
Diamond or Selection Symbol
in using this symbol, the program should continue along one of two routes (e.g. if/then/else)
Flowchart
a graph used to depict or show a step by step solution using symbols which represent a task
Symbols
consist or geometrical shapes that are connected by flow lines
Flowchart
it is an alternative to pseudocoding
pseudocode; flowchart
a _________ description is verbal, a _________ is graphical in nature

Terminal Symbol
indicates the beginning and end points of an algorithm

Process Symbol
shows an instruction other than input, output, or selection

Input-output Symbol
shows an input or an output operation
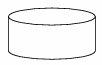
Disk storage I/O Symbol
indicates input from or output to disk storage
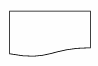
Printer Output Symbol
shows hardcopy printer output
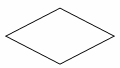
Selection symbol
shows a selection process for two-way selection
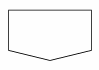
Off-page connector
provides continuation of a logical path on another page

On-page connector
provides continuation of logical path at another point in the same page
Flow lines
indicate the logical sequence of execution steps in the algorithm
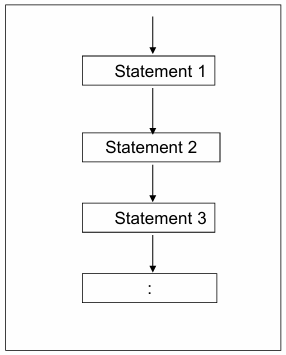
Sequence Control Structure
What do you call this flowchart structure?
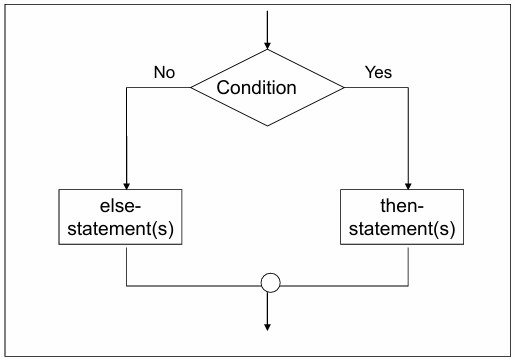
Selection Control Structure
What do you call this flowchart structure?
Repetition Control Structure
What do you call this flowchart structure?