AP Psych: Unit 1
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AP Psychology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Peripheral Nervous System
-Outside the spine and brain
-Neurons
Central Nervous System
-Brain and spine (center of body)
Somatic
nervous system responsible for voluntary movements and sensory information processing.
Autonomic
-Automatic
-Involuntary movements
Sympathetic
Fight or flight response
Parasympathetic
Parasympathetic → Parachute
Calms your body’s response after fight or flight response
Sensory Neuron
-Sensation
-Receive raw material from the body’s sense organs, like free nerve endings in epidermis
-Different for each sense
-Respond to non-chemical stimulation
-Sensory neurons send afferent signals
-Afferent signals arrive at the brain
Motor Neuron
-Reflex
-Connected to all our muscles → causes them to contract
-Neurons in the arm muscle respond to voluntary and involuntary signals
-Motor neurons receive efferent signals
-Efferent signals exit the brain
Glia
-More than 10x glia than neurons
-Support neurons
-Communicates with other cells, but not with electricity
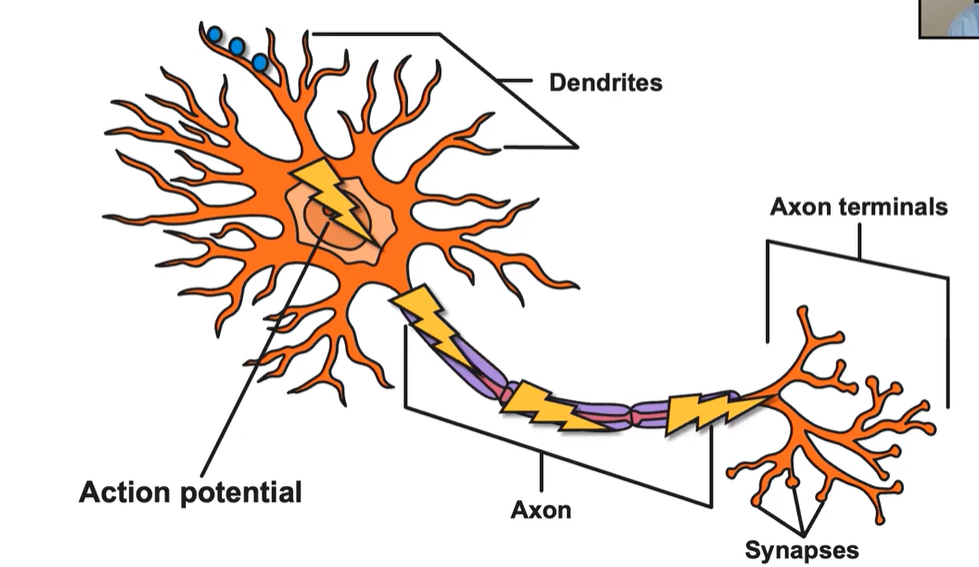
Neurons
-Building blocks of the nervous system
-Jobs:
Receive messages
Carry messages
Send messages
Soma
Neuron’s body
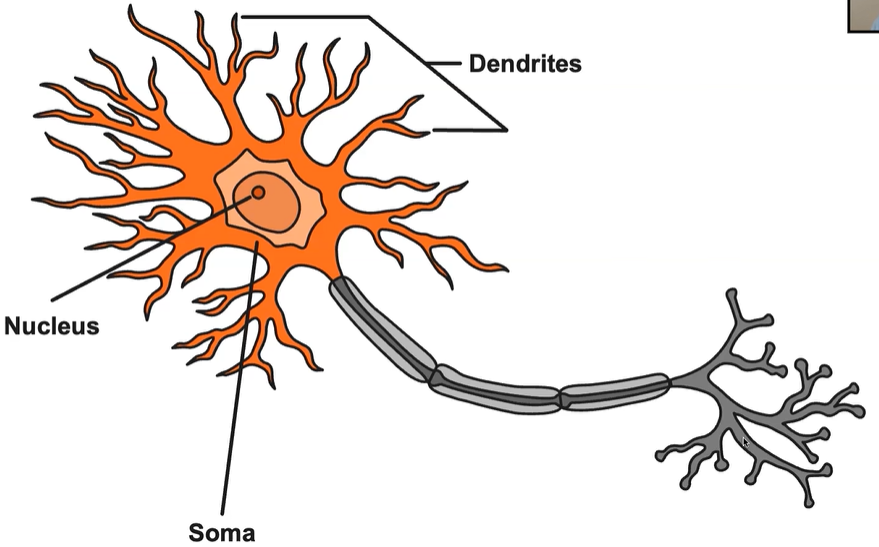
Dendrites
Receive messages from other neurons and convey them to the soma.
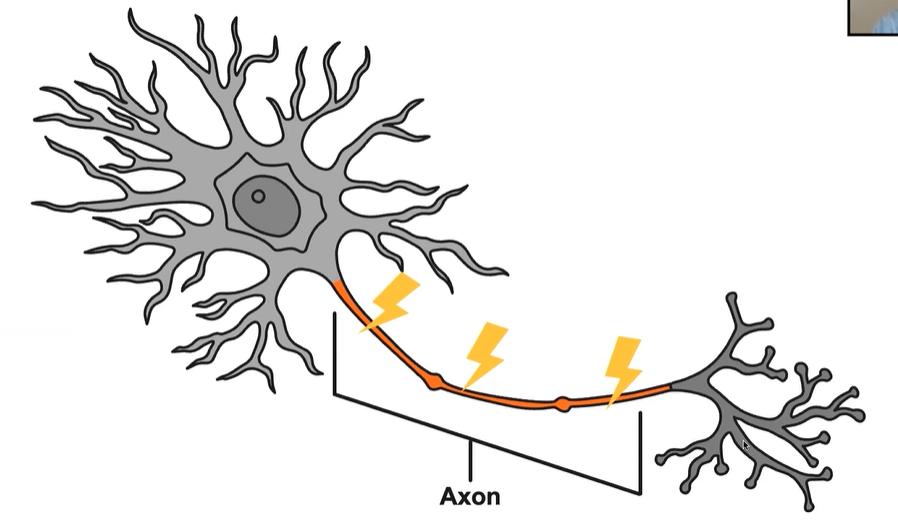
Axon
Carry neural messages or electrical impulses down the length of the axon.
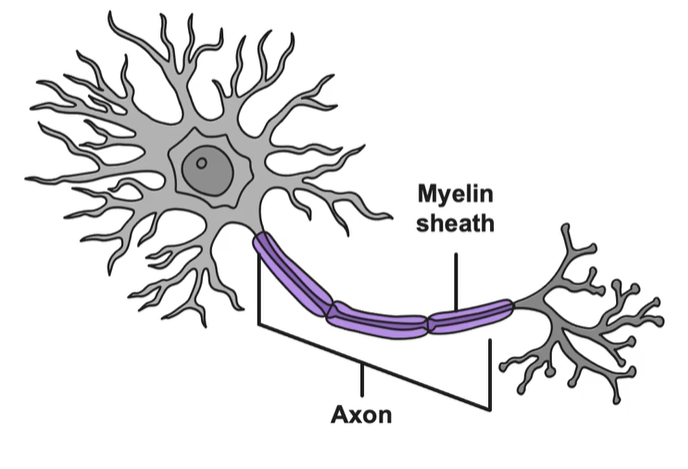
Myelin Sheath
A fatty substance encasing most neurons of the brain.
-Protects and insulates the axon, speeding up transmission of nerve impulses
-Disorders caused from deterioration of myelin sheath: Multiple Sclerosis
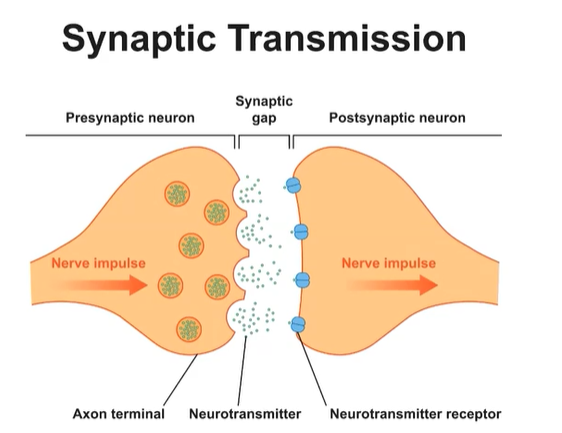
Axon Terminal
Contains terminal buttons
-Communicate with other neurons

Synapse/ Synaptic Gap
-After each terminal button
-Neurotransmitters cross this gap and lock into the dendrite of the postsynaptic neuron.
DSATs
Acronym for the order of neural firing:
Dendrites
Soma
Axon
Terminal Button
synapse (synapses are small = little s)
Neurons fire when…
shift in energy → creating action potential
Neuron
-terminal button → action potential = neurotransmitters released into the synapse.
-Neurotransmitters lock into the dendrites of the next neuron
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
Makes the neuron more likely to fire again
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Makes the neuron less likely to fire again
Resting Potential
-negative 70 millivolts
-Polarized (Po = Positive Outside)
All or None Law
Once neuron reaches threshold, it will fire with the same intensity every time.
Action Potential
Electric impulse that travels down the axon.
Depolarization
-Change in electricity creates a positive charge inside the neuron (+30 millivolts)
-During action potential
Refractory period
brief period where neuron can’t fire again.
Reuptake
-The sending neurons recollects neurotransmitters (up- take).
-The neurotransmitters can be reused in successive neural firings
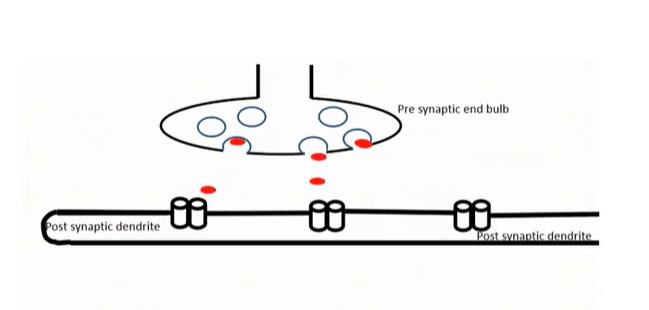
Firing Threshold
Step 1 (Firing Threshold)
Threshold is reached → neuron fires → action potential travels down the axon to the terminal
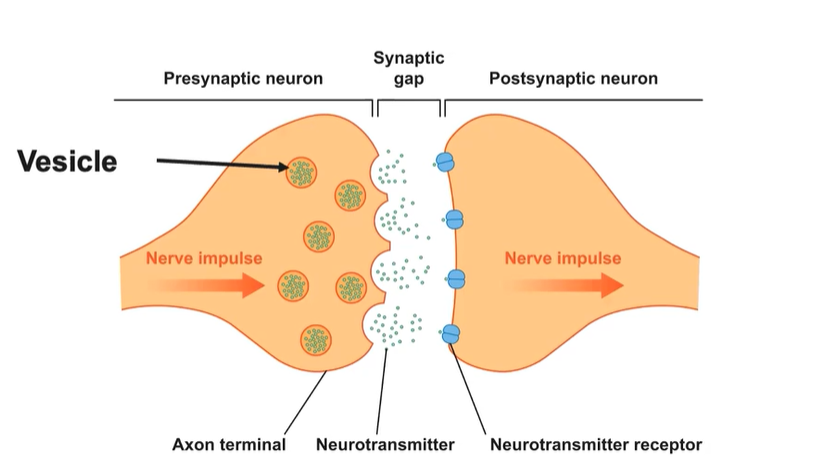
Step 2 (Firing Threshold)
Terminal buttons → electrical impulses cause the synaptic vesicles to open → neurotransmitters travel across the synapse.
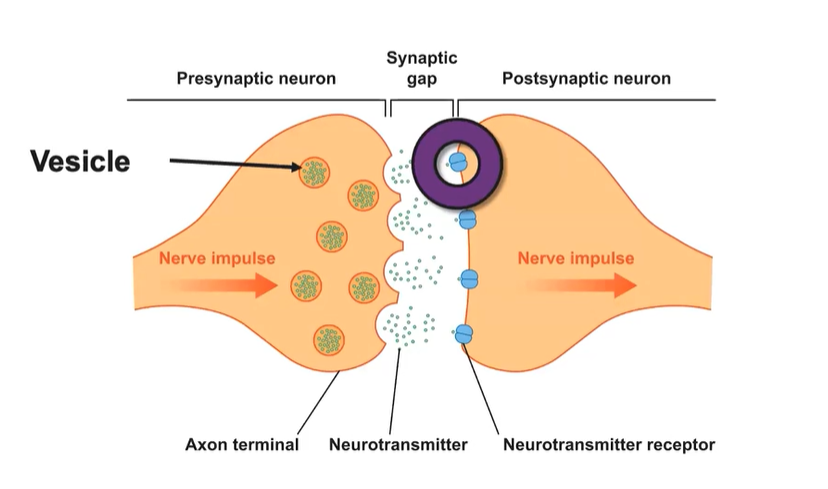
Step 3 (Firing Threshold)
Neurotransmitters lock into the dendritic receptors/ postsynaptic receptor site (like lock and key) → reuptake
Glutamate
-Most abundant excitatory neurotransmitters
-Enhances learning and memory by strengthening synaptic connections.
-Mnemonic: Glued to your mate = excitement
GABA
-Most abundant inhibitory neurotransmitter.
-Brakes of CNS
-Associated with anxiety disorders
-Mnemonic: Get A Brake Adjustment
Acetylcholine (ACh)
-Found in CNS and PNS
-Movement, learning, and memory
-Diminished ACh → Alzheimer’s
-Mnemonic: To ACE psych test, you need ACh; to hit an ACE in tennis, your body needs ACh
Dopamine
-Linked to the anticipation of pleasure or reward
-Movement, attention, and learning
-Lack of dopamine → Parkinson’s
-Excess → schizophrenia
-Mnemonics:
Dopamine, pleasure, Parkinson’s
DopaMINE- mine, mine, mine (pursuit of pleasure)
Endorphins
-Natural painkiller; reward
-Stimulated by intense exercise → euphoric feelings
-Mnemonic: End pain
Epinephrine aka Adrenaline
-Both a neurotransmitter and a hormone
-Boosts energy
-Fight or flight
Norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
-Alertness, arousal
-Heightened sensitivity of what’s around you
-Sleep cycle
-Low levels associated with depression
Serotonin
-Mood, appetite, dreams, sleep
-Low level associated with depression
-Mnemonic: roton = rotten → avoid rotten foods, moods, and nights of sleep
Agonists
-Enhance/ stimulates neurotransmitters
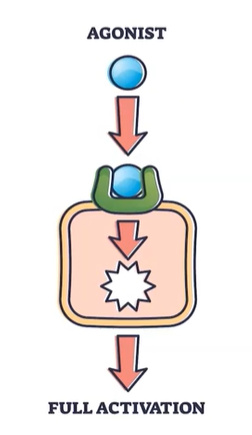
Direct agonists
-Mimic the neurotransmitter and binds with the receptor of the next neuron
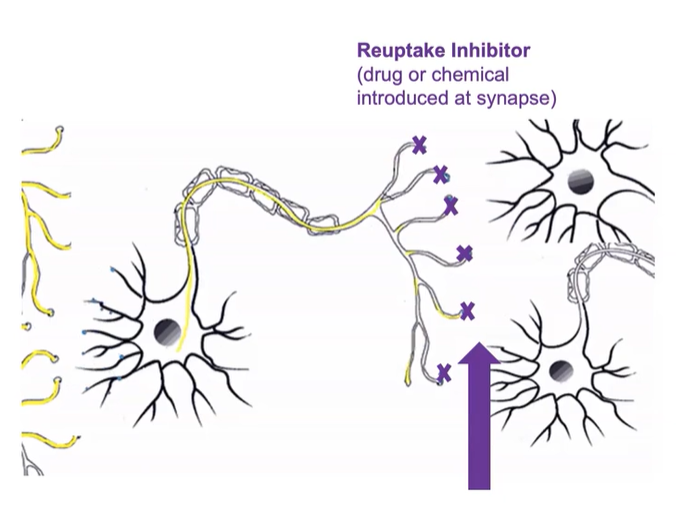
Indirect agonist (Reuptake inhibitor)
-Blocks the reuptake of a neurotransmitter
-Enhances communication between neurons
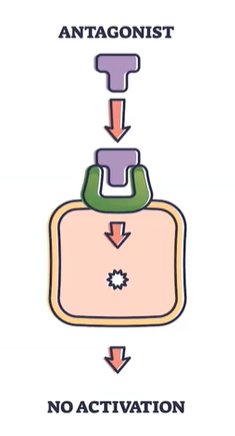
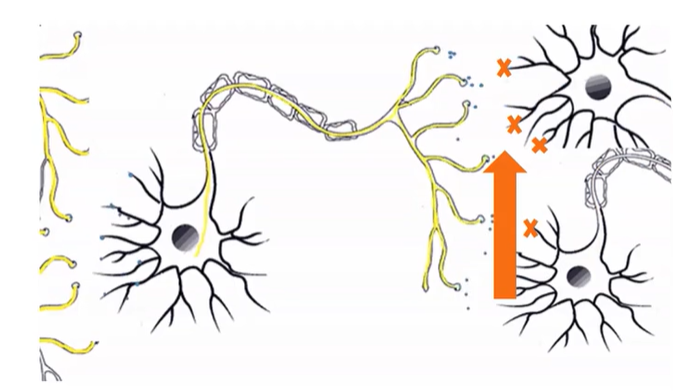
Antagonist
-Inhibit neurotransmitters
-Often binds to receptors but doesn’t stimulate it (slows the neurotransmitter)
-Blocks neurotransmitters from being released by a terminal or from binding to the receptor site
Drugs…
-Activate dopamine-producing neurons in the brain’s reward system
-Increase in dopamine → greater reward → desire more drug intake
-Creates tolerance, physical dependence → withdrawal symptoms
Influence of Drugs on Synaptic Transmission
-Impact AT the synapse
Blood-brain Barrier
-Allows some chemicals to pass from the blood into the brain but prevents other chemical structures from entering.
Depressants
-Slow or inhibit CNS functions
-Creates drowsiness, sedation, or sleep
-Relieve anxiety and lower inhibition
-Combining them can be deadly
Alcohol
-GABA inhibitor