Physics Exam 5
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Xrays are electromagnetic waves carrying much __ energies than visible light
Higher
Formula for kinetic energy of a moving object
KE = ½ mv2
Energy is __ proportional to mass, but changes by the square of the velocity
Directly
Energy is __ proportional to speed
Exponentially
Which has a bigger impact on energy? Mass or velocity
Velocity
What are the 2 possibilities for a projectile electron to interact with atoms in the anode
Interact with an orbital electron
Interact with the nucleus
Where are xrays actually produced
Anode at the actual focal spot
“Braking” radiation is called
Bremsstrahlung
Positive attraction from the nucleus pulls the electron toward it as the electron passes, which does what
Slows and deflects it
What type of radiation is an interaction with the nucleus
Bremsstrahlung
Energy lost from deceleration is emitted as
Xray
What type of radiation accounts for the vast majority of the xrays in the beam
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung radiation is responsible for the __ nature of the xray beam
Heterogenous or poly-energetic nature
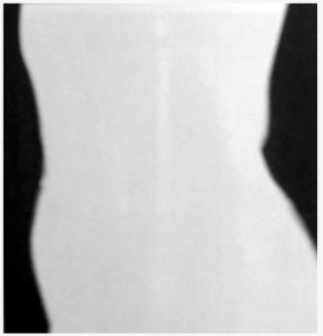
A silhouette image such as this would result from what beam
Mono-energetic
The closer a projectile electron passes to the nucleus, the more it will be decelerated, so the __ energy it will lose
More
The amount of energy lost goes into
Xray produced
The closer the electron passes to the nucleus, the __ the energy of the xray produced
Higher
Which is more likely? A projectile electron will pass closer to the nucleus or a projectile electron will pass further from the nucleus
It will pass further from the nucleus
Are more xrays produced at lower or higher energies
Lower
The higher the kV, the (more or less) xrays produced
Less
What type of beam will provide adequate subject contrast
Poly-energetic
What interactions happen in the anode
Bremsstrahlung and characteristic
What interactions happen within matter (the patient)
Photoelectric, Compton, scatter
Xray are ___ waves with energies much __ than light and most other forms of electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic, higher
In order to generate such energetic waves, electrons emitted from the xray tube filament must acquire extreme amounts of __ energy by the time they strike the anode
Kinetic
What is the formula for the total kinetic energy that a moving object will be carrying
KE=1/2 mv2
The energy changes __ to the mass
Proportionately
Energy increases by the __ of the velocity
Square
With the large voltages supplied by the step-up transformer of an xray machine, the electrons reach speeds of up to __ the speed of light
50-80%
Mass of a single electron
9.1 × 10-31 kg
Einsteins theory of relativity states that as a particle approaches the speed of light, it (gains or loses) mass
Gains
What are the 2 possibilities of the electron
It may interact with an orbital electron or it may interact with the atom’s nucleus
An electron passes near the atomic nucleus and the positive attraction will cause it to brake or slow down. What is this called?
Bremsstrahlung
During brem, the deceleration in the speed of the electron represents a loss of __ energy and that energy which is loss is emitted as an xray __
Kinetic, photon
What does Bremsstrahlung mean in German
Braking radiation
Which type of radiation accounts for the vast majority of the overall xray beam
Brems
The closer an electron passes to the nucleus, the __ will be the deceleration of the electron
Greater
The attractive force of the nucleus also causes the electron to __ in its path of travel toward the nucleus
Bend
The greater the deceleration of the electron, the (more or less) it deviates from its original direction and the more __ energy is lost
More, kinetic
The closer the electron passes by the nucleus, the __ the energy of the emitted xray
Higher
Brems occurring at various distances from the nucleus, provides a wide range of xray energies and is responsible for the __ or __ nature of the xray beam
Heterogenous or poly-energetic
Heterogeneity contributes to what within the patient’s body
Differential absorption
Differential absorption provides __ in the remnant beam and makes the radiographic image possible
Subject contrast
If all of the xrays were of the same energy, the info reaching the IR would result in a
Silhouette image
Computers can modify the image in many ways, but they cannot
Create information that was not present in the first place
The full range of information from different tissues in the body must be represented within the __ beam that reaches the detectors
Remnant
The distance at which a projectile electron will pass by the atomic nucleus is a function of
Statistical probability
At a greater distance from the nucleus, a larger __ is contained within the sphere of that radius surrounding the nucleus
Volume
The volume of a sphere will increase by the __ of the radius distance
Cube
As we get further from the nucleus, the volume of space (Increases or decreases) exponentially
Increases
Is it more likely that an electron will pass close to or further away from the nucleus
Further away
With brems, many more xrays will be produced at (higher or lower) energies
Lower
The higher the energy, the (more or fewer) brem xrays are produced up to the set kVp
Fewer
The anode itself acts as a
Filter
Filters absorb xrays with the __ energies
Lowest
Why are more xrays produced at low energies
Filtration
Why are fewer xrays produced at high energies
The statistical distribution of brem xrays produced
The electron interacts with one of the atoms orbital electrons. When it passes near an orbital electron, its repulsive charge can eject the orbital electron out of its orbit, leaving a vacancy in that atom. What type of radiation is this?
Characteristic
After the orbital electron is ejected out of its orbit, the atom, left with a positive charge will eventually pull in another electron from a __ orbit to return to a neutral state
Higher
What is the atoms state with the least energy called
Ground state
When an electron falls from an outer orbit down into an inner orbit, there is a loss of __ energy
Potential
After a loss of potential energy, it is emitted as a
Characteristic X-ray
What type of radiation makes up only a small portion of the overall beam
Characteristic
Why are characteristic xrays still important in producing a radiographic image if they only take up a small portion of the beam
They possess higher energies that can penetrate through the patient to the IR
Characteristic x-rays depend entirely on what
The difference in energy levels between different orbital shells in the atoms
During characteristic radiation, xrays will be emitted at __ energies, rather than a range
Discrete
How many characteristic xrays can be produced from each shell
3-4
How to predict the energies from characteristic xrays
Subtract the binding energies for the higher shell from that of the vacant shell
If the vacancy is in the L shell of a tungsten atom, and electron falls into the M shell, what is the energy of the emitted xrays
12-3= 9 Volts
K shell binding energy
69
L shell binding energy
12
M shell binding energy
3
N shell binding energy
1
O shell binding energy
.01
What term refers to the movement of several electrons as they fall in sequence from higher energy levels to fill vacancies in lower energy shells
Characteristic cascade
What is initiated when a projectile electron knocks out an inner shell electron of a tungsten or rhenium atom
Characteristic cascade
In tungsten atoms, characteristic xrays will be produced in the __ shell
Innermost or K
Characteristic xrays produced in the K shell produce how many kilovolts of enrgy
57,66,68,69
A vacancy in the L shell will produce xrays of __ kV
9,11, and 12
A vacancy in the M shell will produce xrays of __ kV
2 and 3
Shells further than the M shell will produce electromagnetic waves, but these will be of such low energy, less than 1 kV, that they would be classified as __ rather than xrays
Ultraviolet light
Inherent filtration will remove virtually all of the __ kV x-rays
2-3
The characteristic x-rays having __ kV largely escape the xray tube and are considered part of the useful xray beam
57,66,68,69 kV
The bell curve represents __ radiation
Heterogenous (brem)
The spikes represent __ radiation
Homogenous (characteristic)
A total filtered xray beam is generally __ and has an average energy of __ of the set kVp
Heterogenous, 1/3
Only about __% of the energy deposited by projectile electrons into the anode in converted into xrays, the other 99.5% is lost as heat, infrared radiation, and light
0.5%
A process called __ momentarily raises orbital electrons to a higher energy level
Excitation
In __, the repulsive negative charge of passing projectile electrons can slightly raise the energy of orbital electrons without knocking them out of their atoms
Excitation
Excited electrons immediately fall back into their normal energy level by emitting their excess energy in the form of __
Infrared radiation and light
After excited electrons fall back into their normal energy, __ radiation is absorbed by the anodes other molecules, causing increased molecular vibration
Infrared
Increased molecular vibration is __
Heating
What is responsible for most of the heat generated in xray tube anodes
Infrared radiation
Standard diagnostic xray tubes use an alloy of __ and __ for the target material, embedded in the circular focal track area of the anode disc
Tungsten and rhenium
The higher the atomic number of the target material, the more __ it is and the (More or less) xrays are produced
Efficient, more
Atoms with higher atomic numbers improve the __ of the xray beam
Quality
Gold atomic number
79
Tungsten atomic number
74
Rhenium atomic number
75
Some specialty xray tubes use __ to achieve an increase in xray production and quality
Gold