Chapter 15 - Regulation
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Genetics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Gene regulation/ genetic control
determines when, where, and how much a gene is expressed
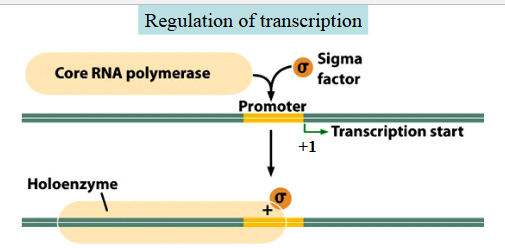
Regulation of transcription
Every gene = RNA coding region
Regulatory regions are not transcribed
transcription factors are DNA-binding proteins that recognize specific sequences within the regulatory region(s) near a gene and either activate or repress it
In bacteria the sigma factor helps core RNA polymerase bind to the promoter and start transcription at +1 forming the holoenzyme
Operon
Common in prokaryotes, rare in eukaryotes
A cluster of structural genes with similar functions under the control of a regulatory system that responds based on changes in environmental conditions
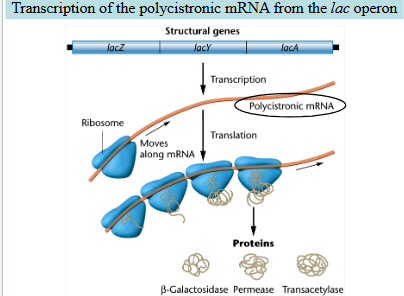
Transcription of the polycistronic mRNA (a single mRNA that contains genetic information from multiple genes) from the lac operon
The lac operon has three structural genes: lacZ, lacY, lacA.
Transcription produces a single polycistronic mRNA.
Ribosomes move along this mRNA to code for three lac operon proteins: β-galactosidase, Permease, and Transacetylase.
The lac operon (specific operon)
The genes of the lac operon are only expressed when glucose is absent and lactose is present
The gene will only be expressed if the cell needs to use lactose for energy BUT glucose is the cells main source of energy
B- galactosidase is made when glucose is absent but lactose is present
Products of the structural genes of the lac operon (products made when the lac operon is on)
lacZ gene product: B- galactosidase
an enzyme that breaks down lactose (a disaccharide) into galactose and glucose
can isomerize lactose into allolactose
lacY gene product: permease
membrane transporter for lactose
facilitates lactose entering the bacterial cell
lacA gene product: transacetylase
NOT involved in lactose metabolism
involved in the removal of by- products of lactose digestion form the cell