Anatomy and Physiology II - Section 3, Lesson 12
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Q: What is the role of the enteric nervous system in digestion?
A: It controls local, short reflexes in the GI tract, independent of the CNS.
Q: What do sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves regulate in digestion?
A: Long reflexes that pass through the central nervous system.
Q: What cells are responsible for hormonal regulation of the GI tract?
A: Enteroendocrine cells in the mucosa from stomach to colon.
Q: What stimulates G cells to release gastrin?
A: Peptides, amino acids, and stomach distension.
Q: What does gastrin do?
A: Stimulates HCl secretion, stomach motility, and relaxes the pyloric sphincter.
Q: What stimulates S cells to release secretin?
A: Acidic pH in the small intestine.
Q: What does secretin do?
A: Stimulates bicarbonate (pancreas), bile production (liver), and inhibits gastric motility and secretion.
Q: What stimulates CCK cells to release cholecystokinin (CCK)?
A: Presence of lipids and polypeptides in the small intestine.
Q: What does CCK do?
A: Stimulates pancreatic juice and bile release, and relaxes the hepatopancreatic sphincter.
Q: What stimulates K cells to release gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP)?
A: Presence of lipids and glucose in the small intestine.
Q: What does GIP do?
A: Inhibits gastric secretion/motility and stimulates insulin release.
Q: What is somatostatin’s main action?
A: Inhibits secretion of GI hormones, especially gastrin and histamine.
Q: What secretes histamine in the stomach?
A: Enterochromaffin cells (histaminocytes).
Q: What does histamine do in digestion?
A: Stimulates HCl secretion from parietal cells.
Q: What secretes serotonin in the GI tract?
A: Enterochromaffin cells of the gastric mucosa.
Q: What is serotonin’s action in digestion?
A: Induces contraction of stomach muscles.
Q: Where is salivation coordinated?
A: Salivary nuclei in the pons and medulla oblongata.
Q: What triggers salivation before food enters the mouth?
A: Thought, sight, or smell of food.
Q: What nerves relay taste signals to the salivary nuclei?
A: Facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves.
Q: How does chewing enhance salivation?
A: Pressoreceptors activated by jaw muscles send signals to salivary nuclei.
Q: Which nerves carry signals from the salivary nuclei to the glands?
A: Facial and glossopharyngeal nerves.
Which hormone stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach?
Gastrin
Somatostatin
CCK
Secretin
Which hormone stimulates the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach?
Gastrin
Somatostatin
CCK
Secretin
correct
Which hormone stimulates stomach contractions?
Serotonin
Secretin
Gastrin
Somatostatin
Serotonin
What is the function of the small intestine?
Releasing digestive enzymes proteases trypsin, chymotrypsin, and elastase to aid in protein digestion
Releasing digestive hormones, including secretin and CCK, which stimulate digestive processes to break down the proteins
Cutting proteins into smaller polypeptides and their constituent amino acids
Breaking down protein-rich food with the help of pepsin and hydrochloric acid
Releasing digestive hormones, including secretin and CCK, which stimulate digestive processes to break down the proteins
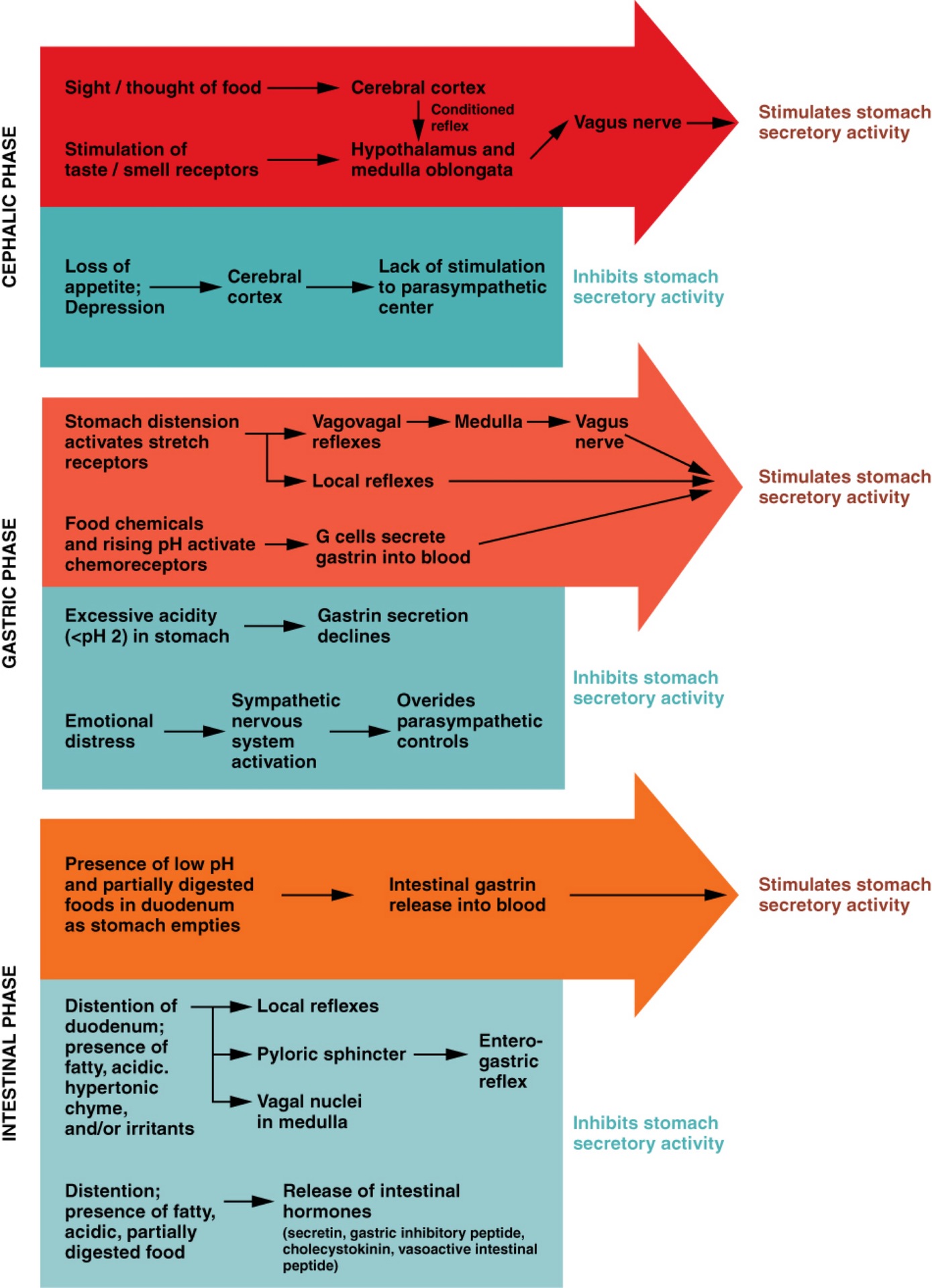
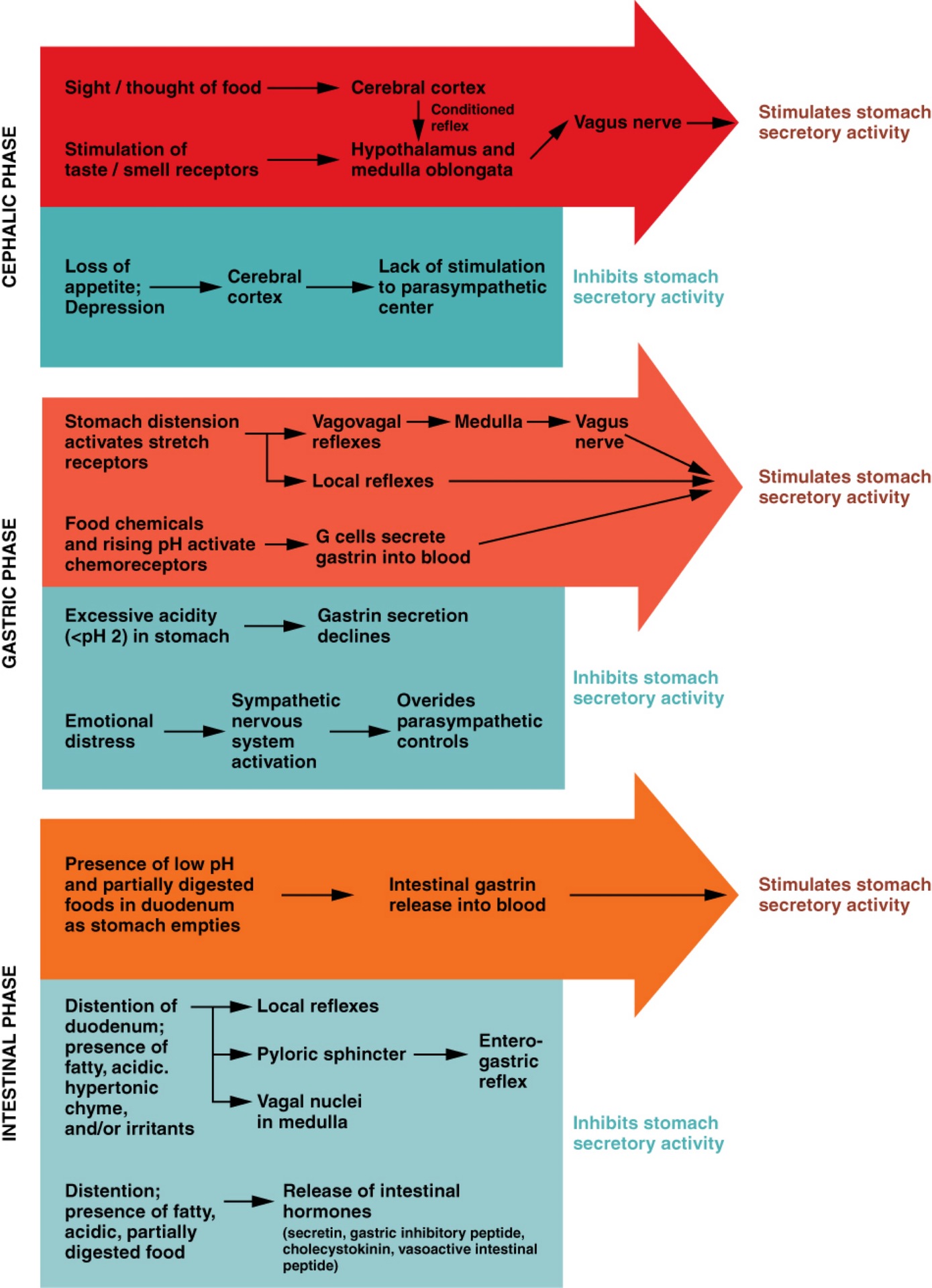
Q: What are the three phases of gastric secretion?
A: Cephalic, gastric, and intestinal phases.

Q: What triggers the cephalic phase of gastric secretion?
A: Sight, smell, taste, or thought of food; involves a conditioned reflex.
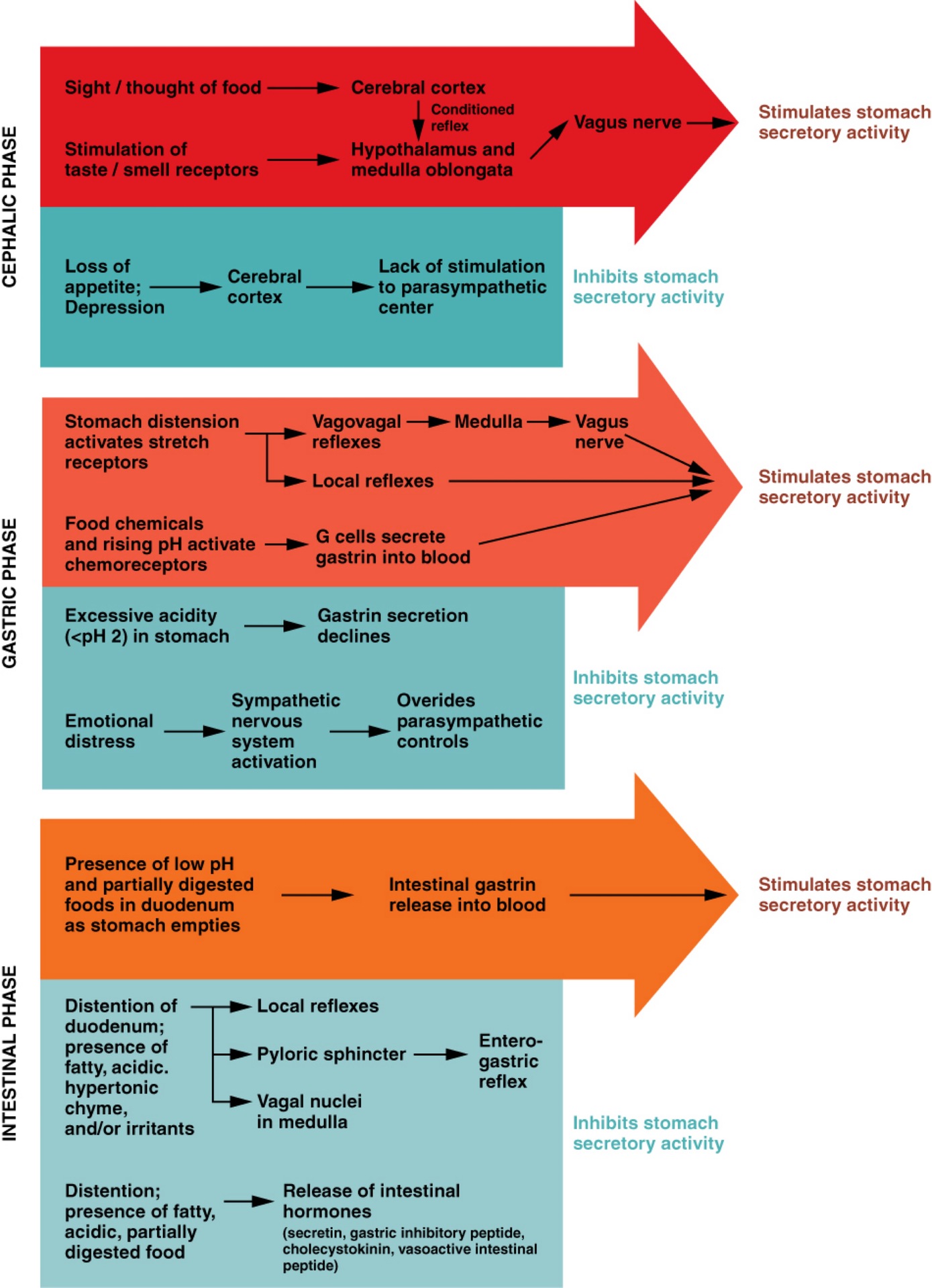
Q: What happens during the cephalic phase?
A: Brain signals increase gastric juice secretion in anticipation of food.
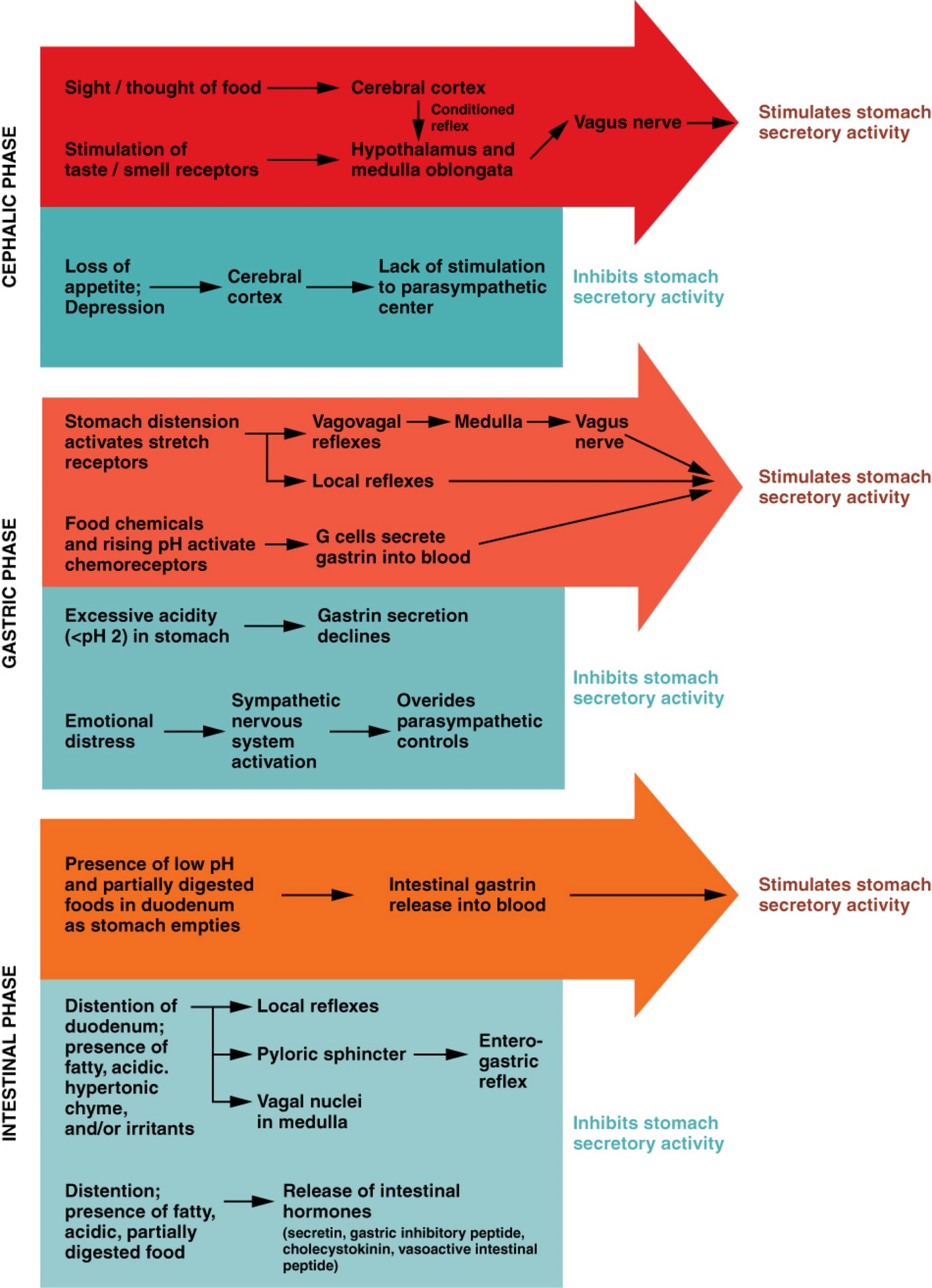
Q: What can inhibit the cephalic phase?
A: Depression and loss of appetite.
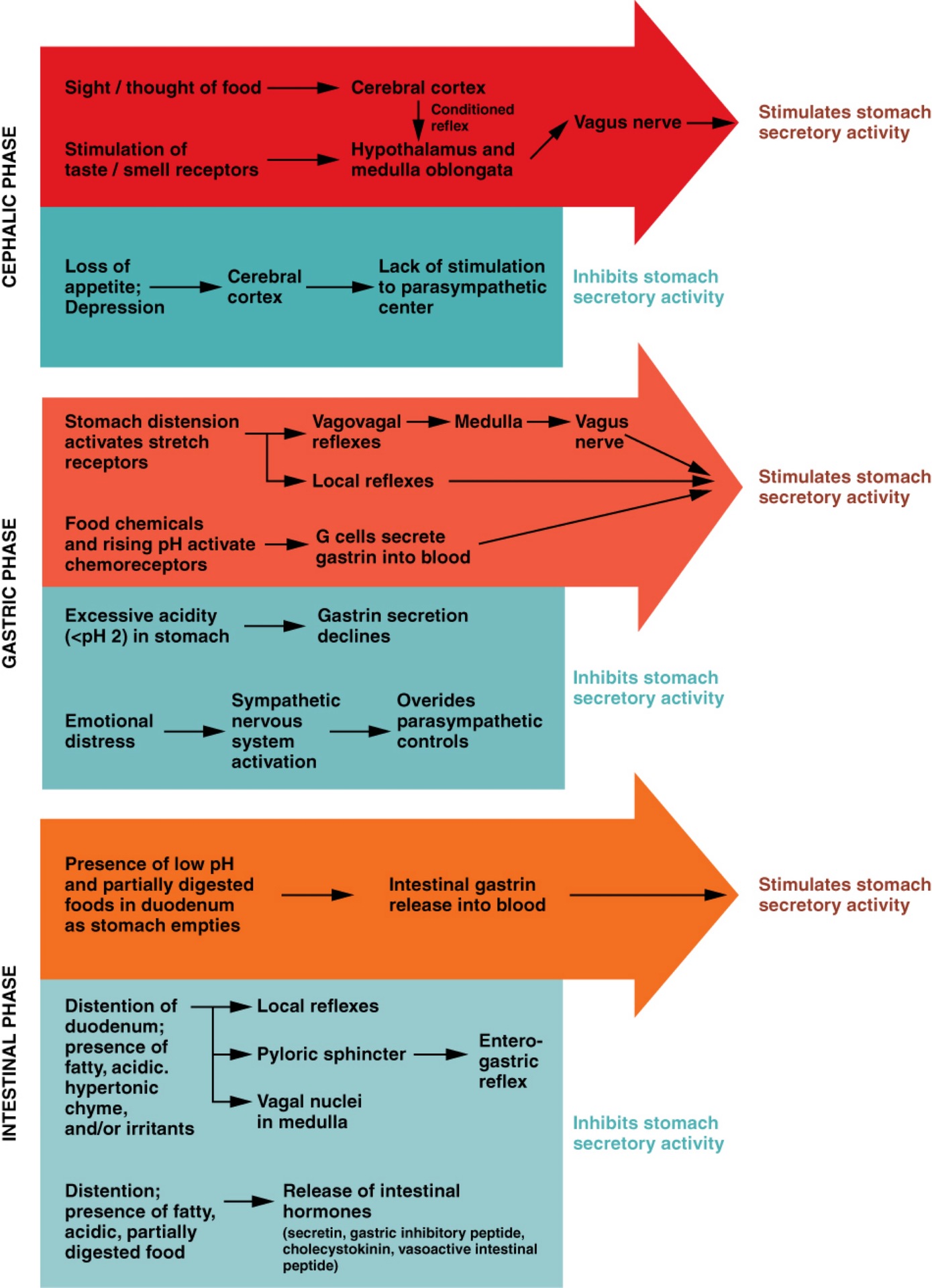
Q: What triggers the gastric phase of secretion?
A: Food entry into the stomach causes distension and protein presence.
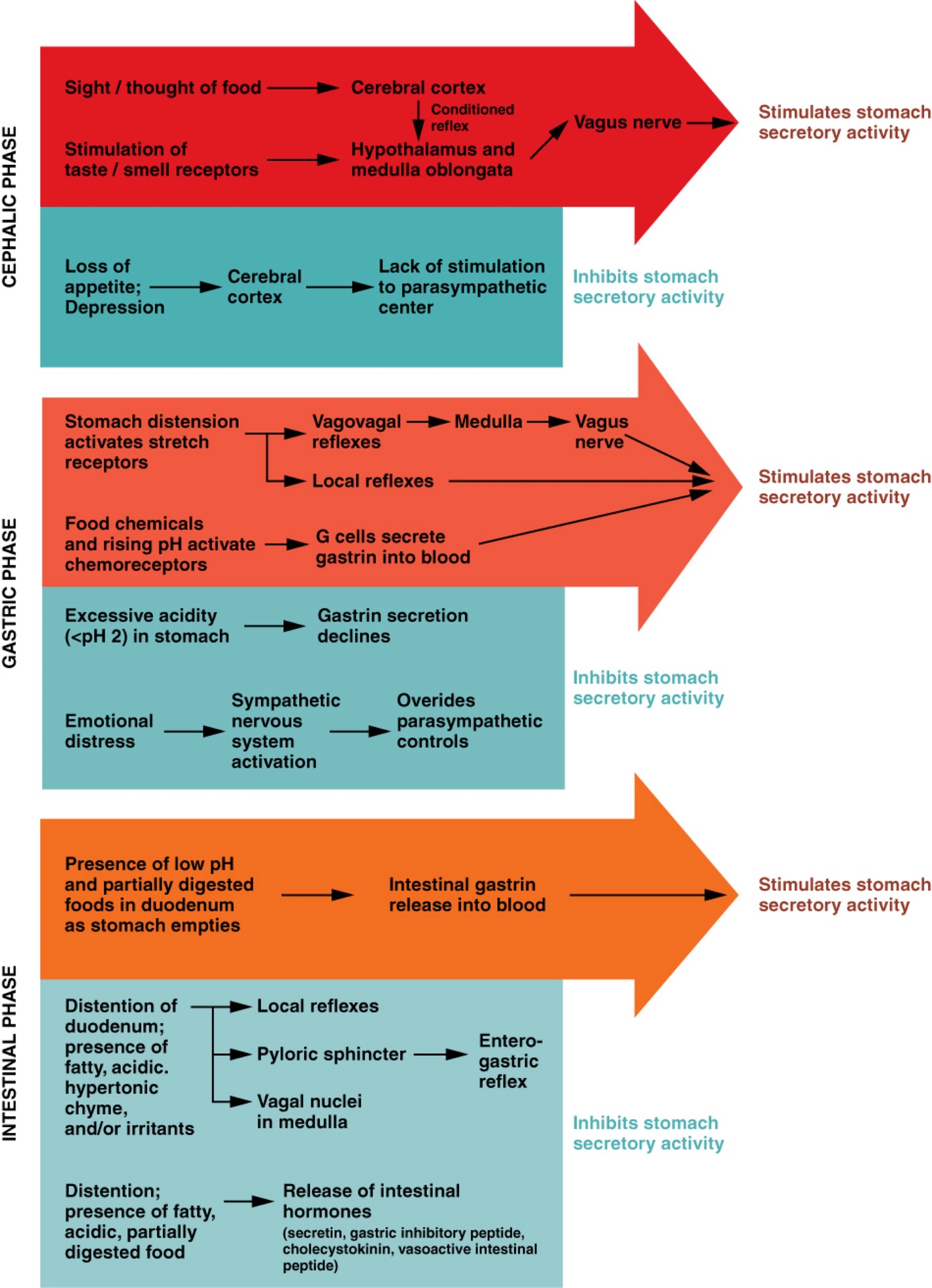
Q: What hormone is released during the gastric phase and what does it do?
A: Gastrin; increases HCl production and stimulates gastric motility.
Q: What prevents excessive acid in the stomach?
A: Low pH inhibits HCl secretion and increases mucus production.
Q: What happens in the early intestinal phase?
A: Intestinal gastrin briefly stimulates gastric secretion.
Q: What happens in the later intestinal phase?
A: Enterogastric reflex inhibits gastric secretion and tightens pyloric sphincter.
Q: What controls gastric emptying?
A: Neural and hormonal mechanisms regulate timing and rate.
Q: What slows gastric emptying?
A: Fatty chyme, duodenal stretch, and hormone release (CCK and secretin).
Q: What triggers the enterogastric reflex?
A: Duodenal distension and chyme composition.
Q: What do CCK and secretin do?
A: CCK promotes bile release; secretin promotes pancreatic juice and inhibits gastric glands.
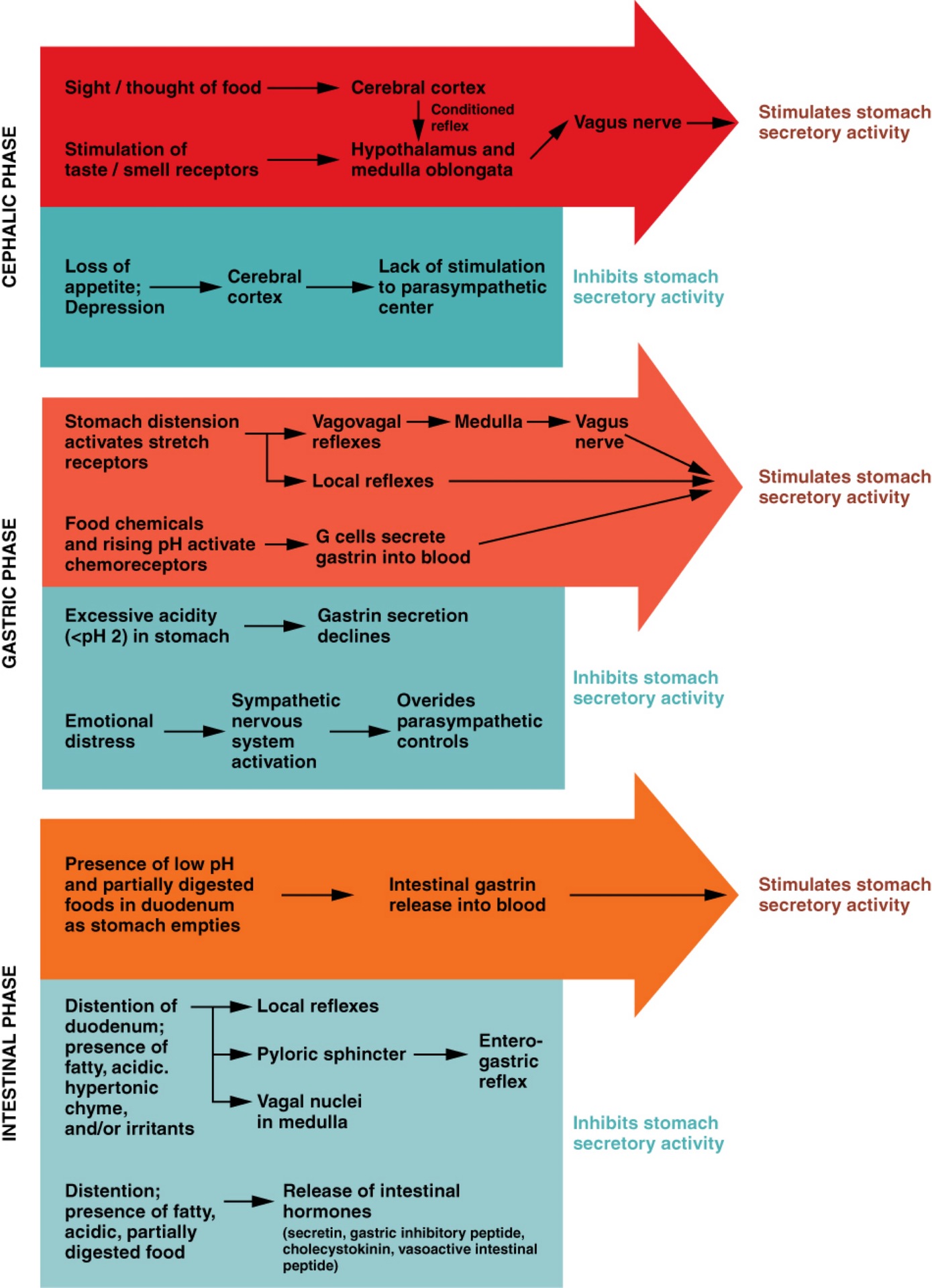
Q: What is the result of the enterogastric reflex?
A: Reduced gastric secretion and motility; tightened pyloric sphincter.
Stomach secretory activity can be inhibited by emotional distress/depression during which phases(s) of digestion?
Cephalic
Gastric
Intestinal
Cephalic and gastric
Cephalic and gastric
Q: What is the cephalic phase of gastric secretion?
A: The initial (reflex) phase that occurs before food enters the stomach.
Q: What is the gastric phase of gastric secretion?
A: The phase that begins when food enters the stomach.
Q: What is the intestinal phase of gastric secretion?
A: The phase that begins when chyme enters the intestine.
Q: What is cholecystokinin (CCK) and what does it do?
A: A hormone that enhances secretin’s effects and causes bile to flow into the duodenum.
Which two nerves send efferent signals from the salivary nuclei?
Choose 2 answers.
Facial nerve
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Vagus nerve
Hypoglossal nerve
Facial nerve
Glossopharyngeal nerve
Which activity corresponds to the gastric phase of digestion?
When chyme in the duodenum stimulates more gastrin to be released, leading to stomach emptying
When food enters the stomach, which causes it to become distended and the stretch receptors to stimulate gastric secretions and motility
When food is smelled, which stimulates HCl and gastric juices to be secreted.
When food enters the mouth, which stimulates HCl and gastric juices to be secreted
When food enters the stomach, which causes it to become distended and the stretch receptors to stimulate gastric secretions and motility
Which stimulus would inhibit secretory activity in the stomach?
Excessive acidity in the stomach
Stomach distention
Low pH in the duodenum
Smell of food
Excessive acidity in the stomach
Which cell type secretes glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP)?
CCK cells
K cells
S cells
G cells
K cells
Where are the salivary nuclei found?
Choose 2 answers.
Pons
Cerebral cortex
Medulla oblongata
Hypothalamus
Pons
Medulla oblongata