Somatic Nervous System
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
List the types of neurons
Relay
Motor
Sensory
Give the breakdown of spinal nerves
31 pairs (8 cervical nerves (7 vertebrae), 12 thoracic vertebra and nerves, 5 lumbar nerves and vertebra, 5 sacral nerves and vertebra)
Where does the spinal cord end on an adult (IMPORTANT)
spinal cord ends between L1 and L2 vertebra (for children its L3)
What is the role of Glial cells in the PNS
major scaffolding components of nervous tissue
→Satellite cells support cell body of neuron (glial of PNS)
What are schwann cells
support axons (wrap around it, saltatory conduction means signal can jump between junctions (aka nodes of ranvier))
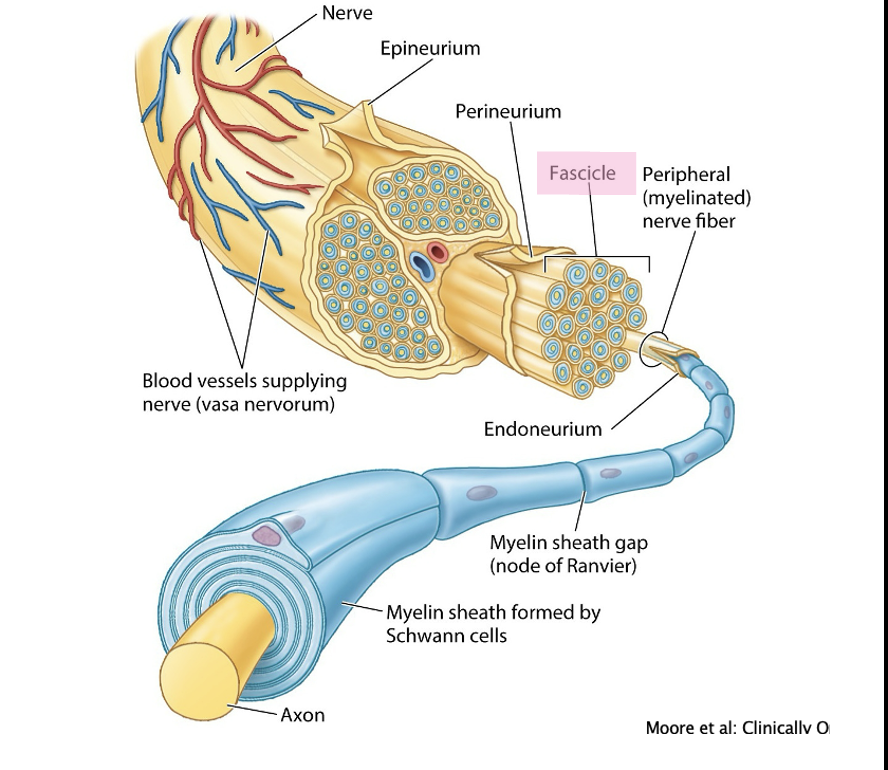
What is a fascicle
a bundle of multiple axons (each with its own endoneurium).
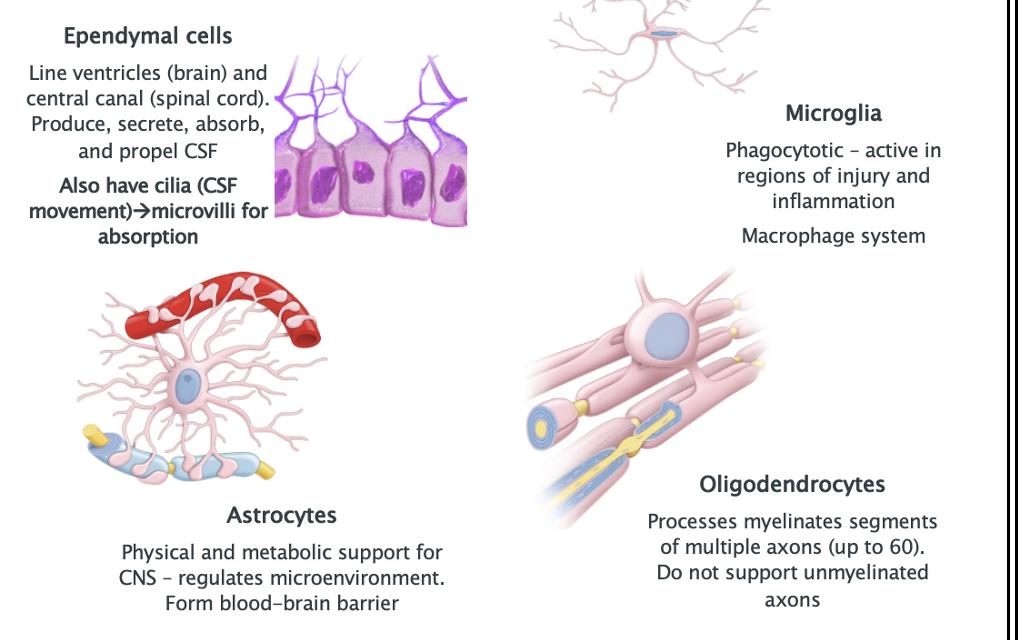
List the Glial cells of the CNS and their role
Ependymal cells
Astrocytes
Oildogendrocytes
Microglia
What are the 2 types of nerve damage
Damage to PNS:
→Crushed nerve can result in regeneration of axon due to intact connection to cell body
Severed nerve usually requires surgical intervention
Damage to CNS – any growth by injured axons blocked by astrocyte proliferation and thus do not usually recover
Give the dermatome map
T4= nipple
T10= umbilical
L1= ‘hands in pockets’
L4= knee
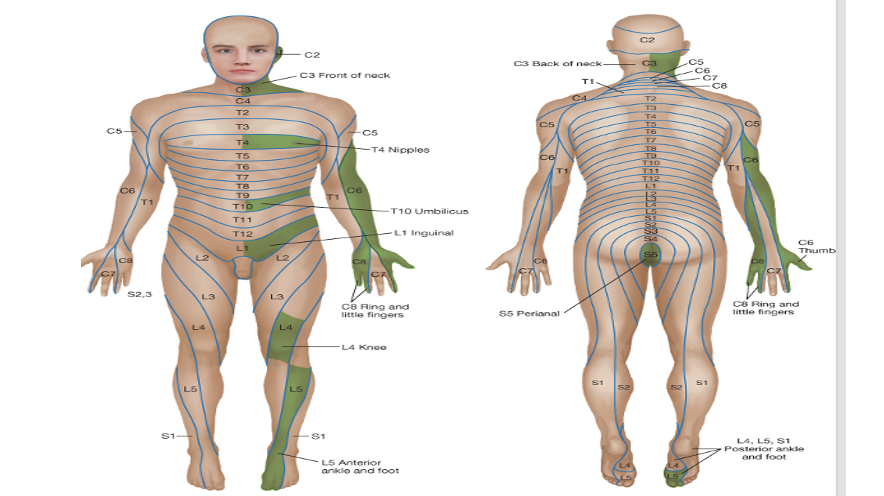
What is a dermatome
unilateral area of skin innervated by sensory fibres of one spinal nerve
Overlap by adjacent spinal nerves
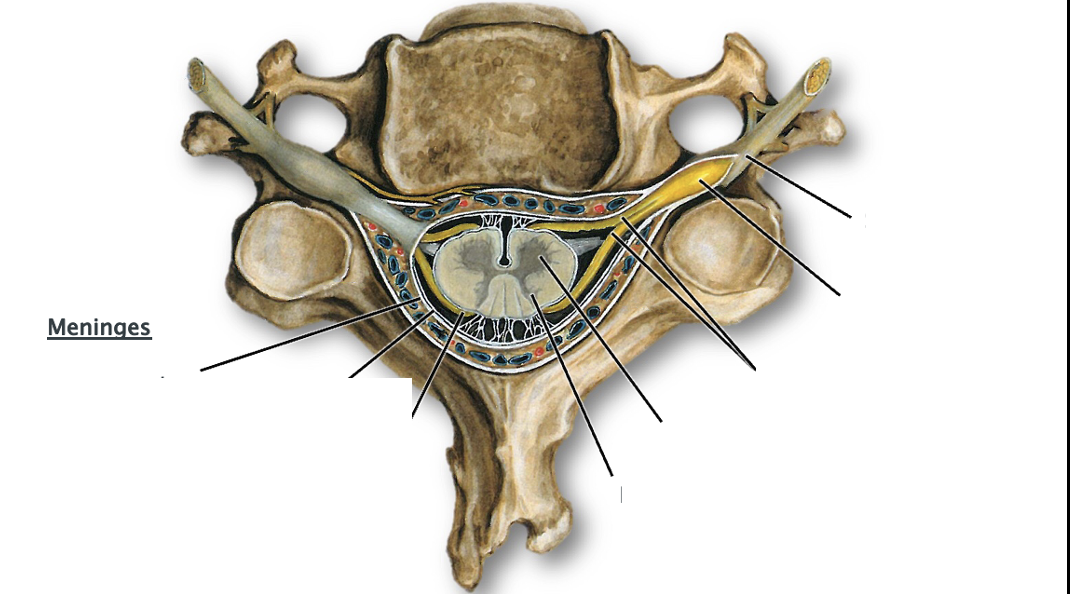
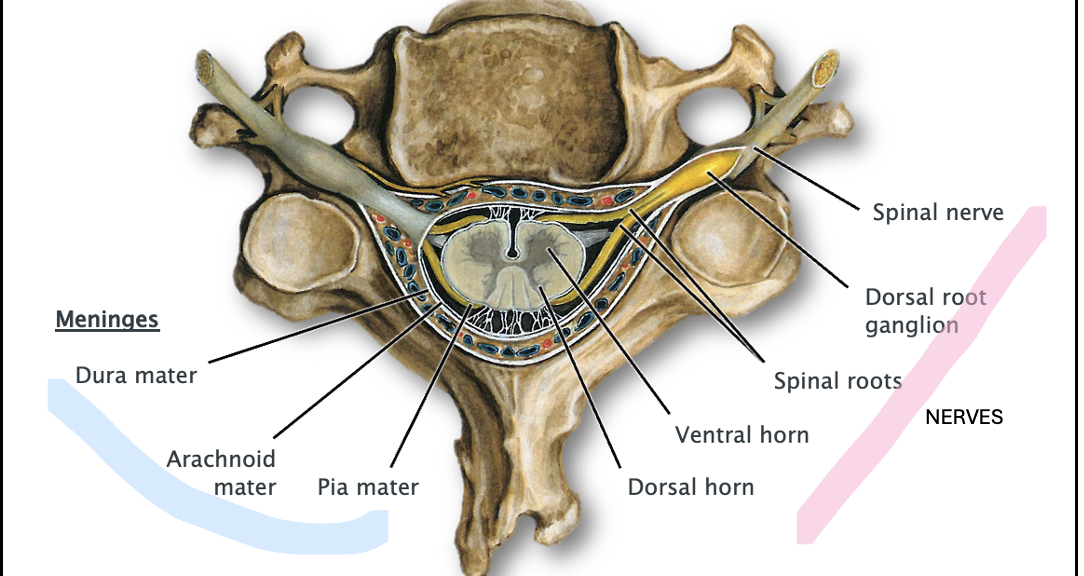
List the areas of the spinal cord and meninges on this cervical vertebra
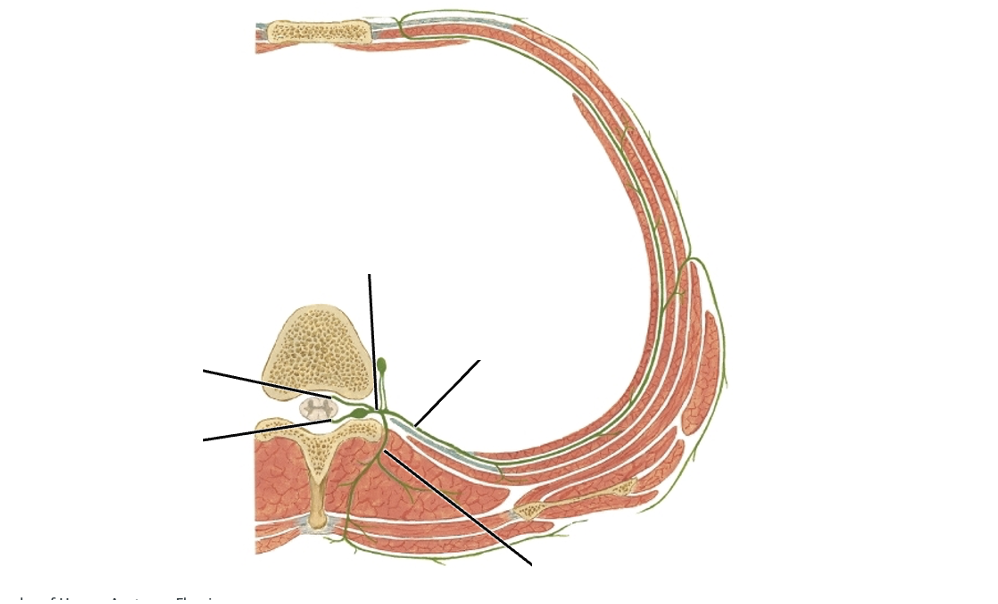
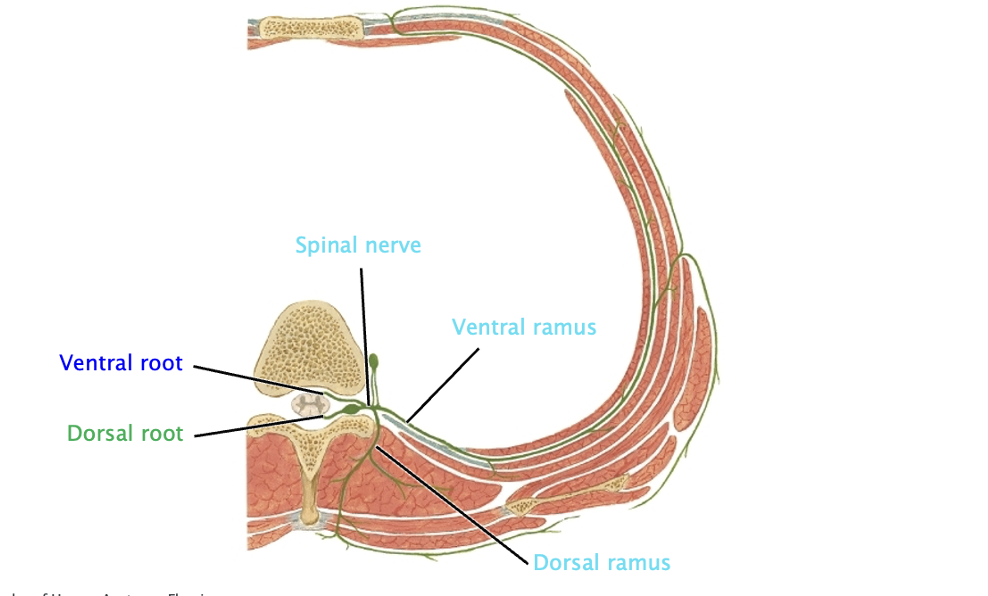
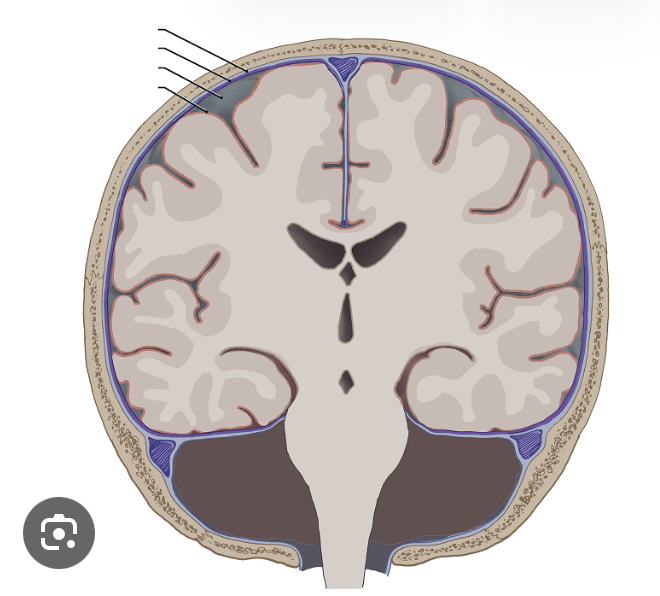
Lable this typical thoracic spinal section
-Dorsal root: sensory input
-Ventral root: motor input
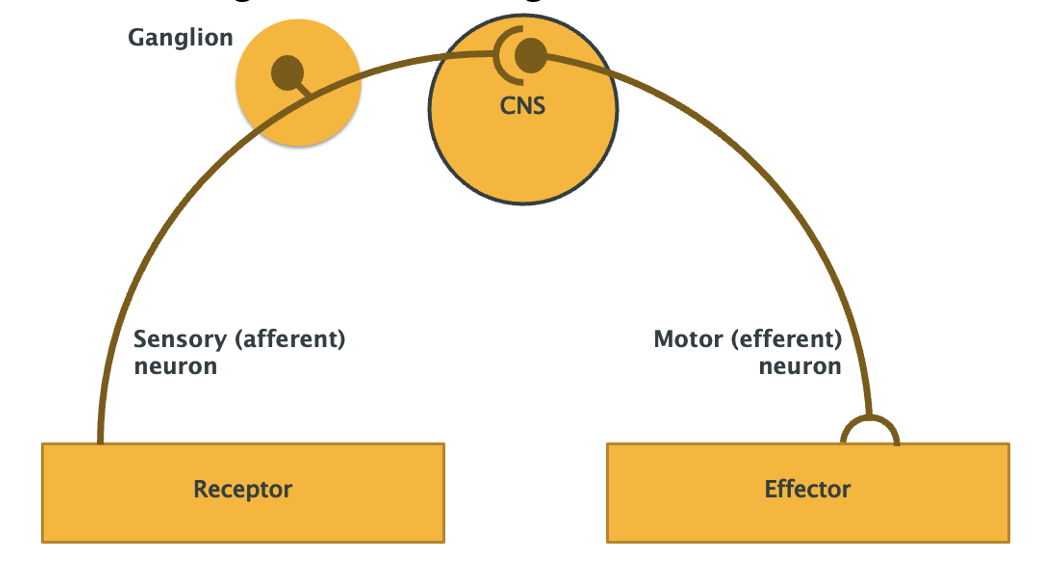
Draw a basic reflex arc
-Smallest functional unit of NS
-route followed by nerve impulses from receptor to effector
-Reflex testing is a valuable diagnostic aid
What info do cranial and spinal nerves carry
Cranial: infro to and from brain
Spinal: to and from spinal cord
Where is motor info transmitted
From CNS to vol skeletal muscles
Via somatic nervous system
and to autonomic nervous system
What are the 2 directions of neurons
Afferent: sensroy info towards CNS
Efferent: motor info away from CNS
What is a nerve plexus
network of nerve fibres, formed by several individual nerve branches
from different regions of the CNS fusing together. Plexuses allow multiple nerve fibres (for
example spinal nerves arising from several spinal cord segmental levels)
What is the spinal cord divided into
outer region called white matter and a central, ‘H’ shaped region, the grey matter with a central canal
What is the denticulate ligament
pia mater forms a delicate membrane laterally between the spinal cord and the dura mater
What is the importance of teh subarachnoid space
contains CSF
Lable these sections

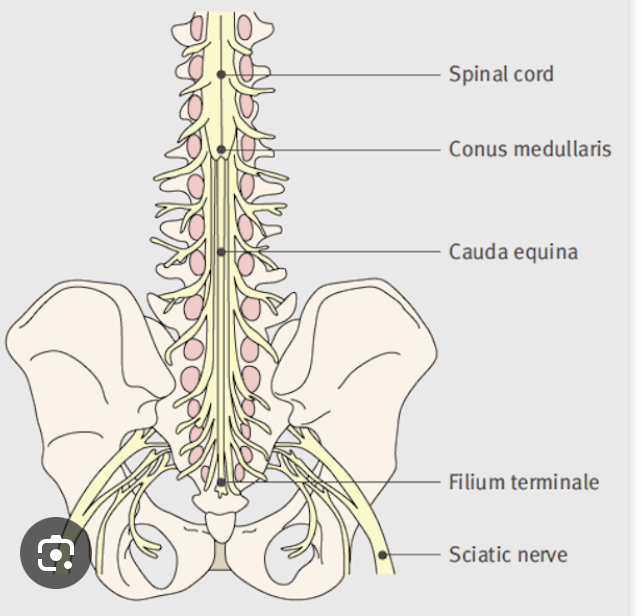
What is the tapered end of the spinal cord called
Conus medullaris
Give the location and importance of the epidural space
Between bones of the bertebral canal and dura mater
Clinically used for injection of anathetics
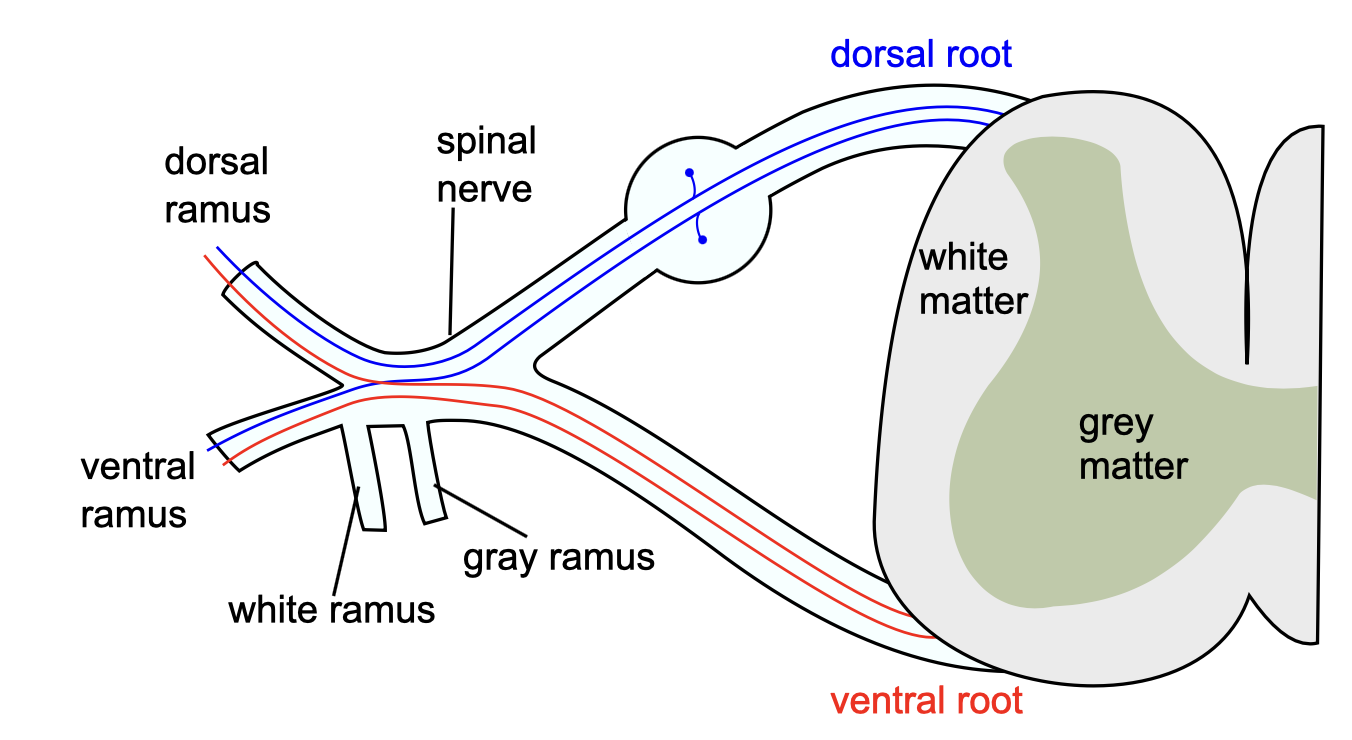
Locate the nerve fibers assoicated with the ventral and dorsal horns
What is the impact of damage to L1
likely to affect the lower lumbar and sacral spinal cord segments resulting in very serious consequences
How many cranial nerves are there and name them
List the spinal nerves
31 pairs of symmetrically arranged spinal nerves, namely,
→8 cervical, 12 thoracic,5 lumbar, 5 sacral and 1 coccygeal.
=Each spinal nerve contains axons and dendrites which transmit information respectively from or to the spinal cord. They are distributed mainly to the trunk and limbs.
What symptoms may arise if spinal nerves are damaged
Tingling of lower legs and arms
Pain
Numbness
What is the epineurium
group of fascicles are bound together and surrounded by dense irregular connective tissue
What surrounds fasicles
surrounded by a sheath of specialised cells that form two to seven layers termed the perineurium
Within each fascicle the nerve fibers, BV are embedded and surrounded by loose CT (endometrium)
What is the cauda equina
bundle of spinal nerves at lower end
a fibrous remnant of pai mater is present (filum terminale)
What cell bodies are located within the dorsal root ganglion
Pseudounipolar sensory neurons
→transmit sensory info e.g. pain
What cell bodies are located within the VENTRAL root ganglion
Motor neurons
→carry motor impulses away from CNS to muscles
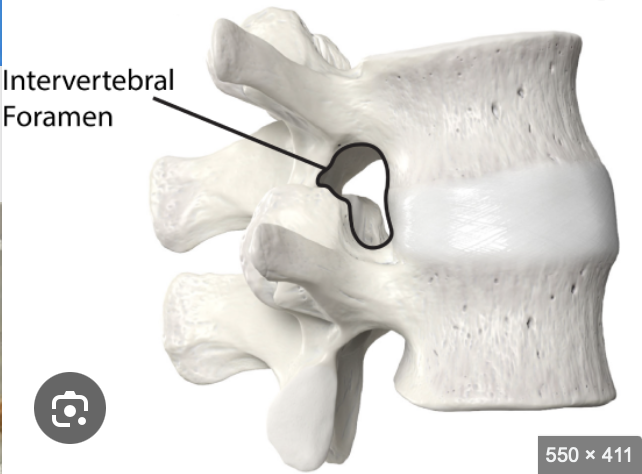
Where do the majority of spinal nerves emerge from
intevertebral foraman
thoracic, lumbar and sacral from below theur numberical vertebrae (cervical are above)
A patient presents with trauma to the back. They have tenderness over the 7th and 8th thoracic spinous processes. The clinician is concerned that the spinal cord may have been damaged. In your group, discuss which segments of the spinal cord may have been affected by the injury.
T7–T8 vertebral injury affects T9–T10 spinal cord segments (cord lies higher than vertebrae).
These segments correspond roughly to the umbilical (T10) dermatome.
Possible effects: motor and sensory loss below the umbilicus.
What area is a lumbar puncture carried out at
L3-4
avoids damage to spinal cord as only cauda equina nerve roots and CSF
Dua and arachoid at risk of puncture
Describe the order of tissues in which the needle goes through to get CSF sample
Skin
Subcutaneous tissue (fat and fascia)
Supraspinous ligament
Interspinous ligament
Ligamentum flavum
Epidural space
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater → enters subarachnoid space (CSF)
Define dermatome
area of skin supplied by single spinal nerve
Define myotome
a region of skeletal muscle innervated by a single nerve
What types of nerve plexus are there
Somatic plexuses (supply skin, vol skeletal muscles and joints from ventral rami)
Autonomic plexus (blood vessels and viscera in thorax, ab and plevis)
What is the cervical plexus
ventral rami of cervial spinal nerves C1-4
supply skin and muscles of head and neck and shoulder region
What is the brachial plexus
ventral rami of C5-8 and T1
supplies skin, muscles of upper limb (via axially, musculocutaneous, radial, ulnar, median)
What is the lumbar plexus
ventral rami of L1-4
supply muscles and skin of anterior and medial aspect of thigh via femoral and obturator nerves
What is the sacral plexus
ventral rami of L4-5 and S1-4
posterior aspect of thigh, leg and foot via sciatic nerve
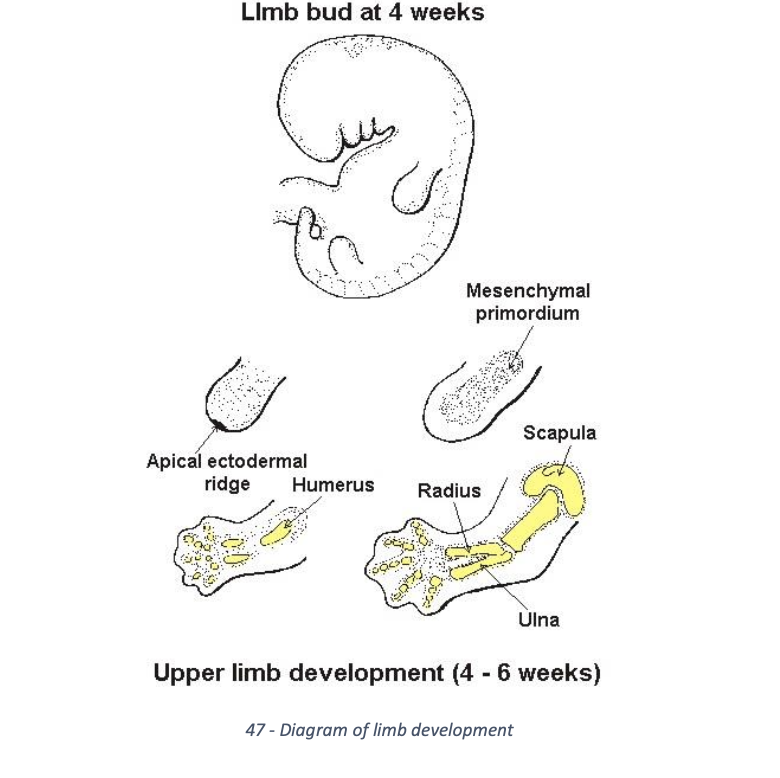
Explain limb development at week 4
upper and lower limb appear at week 4
ectoderm at tip of bud intro by mesoderm to form apical extodermal ridge
this structure directs growth of limb and prolifeartion of mesenchyme
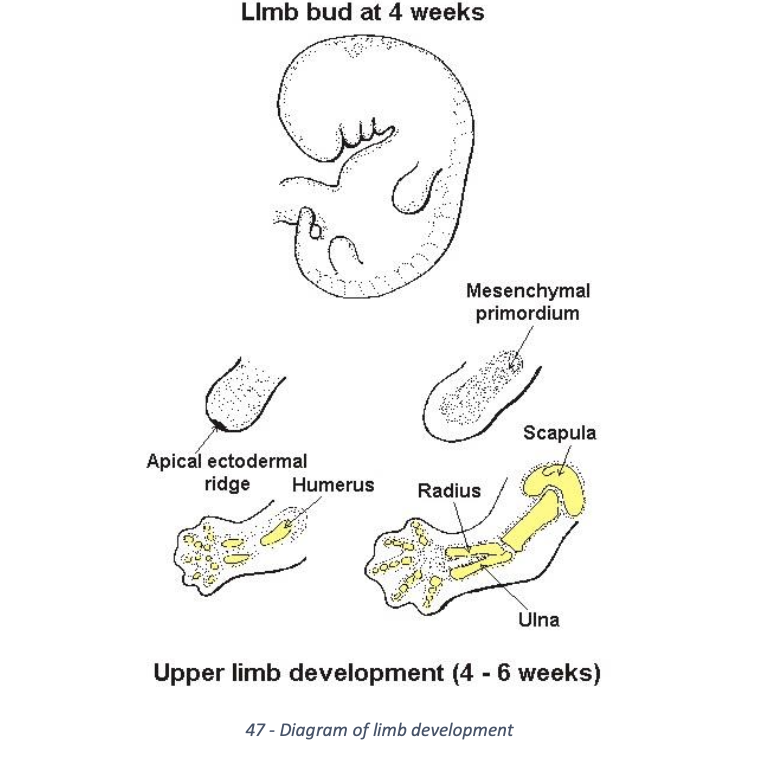
Explain limb development at week 6
limb buds form handplates and footplates
digits formed by cell death allowing seperation
Describe the developmental rotation of limbs and dermatomes
occurs within weeks 6-8
upper limbs rotates laterally
lower limb rotate medially