Chapter 5: a focus on autism spectrum
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Revisiting adaptive functioning…why now with ID and ASD?
work on conceptual, social and life/practical skills is a core part of programming both ID and ASD
looking at skills applicable across neurodevelopmental challenges
thinking of down syndrome moderate ID and ASD/ID
conceptual skills
challenges in receptive language (difficulties understanding others)
challenges in expressive language (difficulty expressing thought)
understanding the values of money and their function
self-directions (motivations, self-regualtory activities)
social skills
interpersonal skills
self-esteem
responsibility
following rules
practical skills
eating, dressing, toileting
taking medication
daily functional living skills fall in this domain
case study
Kali is having challenges in the social, conceptual, and practical domains. she has a difficult time knowing social rules, learning how to interact with others in social interactions, understanding the function of money and finally making her bed.
which domains do each other these skills fall under?
social rules
being able to understand social skills and rules
function of money
conceptualization
interacting with others
social
must be able to understand children and their needs
making their bed
functional
sorting laundry, making bed
assessment of basic learning abilities
imitation
considered one thing and the person is to follow you
matching objects
auditory discrimination
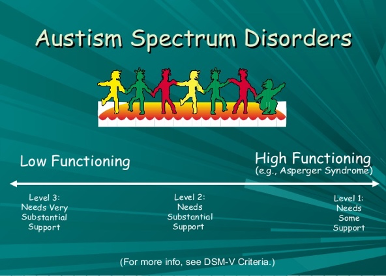
the ASD spectrum
concerns happen when multiple challenges occur
severe: restricted behaviours,lack of awareness, no initiation of conversation
moderate: support for children, not as extensive as severe
high functioning: previously known as asperger’s syndrome
brief history
1940s- Leo Kanner (early infantile autism) enlarged head circumference
50s- Bruno Bettelheim (psychoanalysis, refrigerator mothers)
today…a neurodevelopmental disorder (exploring the genome)
today..speaking of cause of ASD
very complex neurodevelopmental disorder with a biological basis
considered a neurological disorder that is influenced by both environmental and genetic factors
it spans the genome
introduction to core deficits and the spectrum
core challenges of ASD
social communicative issues
restrictive repetitive behaviorus
symptoms become increasingly noticeable around the age of 2-3 years of age
rating of autism through levels 1-3
1 in 36 children have ASD
increased prevalence-better tools with good psychometric properties
ASD more information
autism is 4 to 5 times more likely in boys than girls
it is estimated two thirds of individuals with ASD have a ID
Temple Gradin
woman with autism
frustrated that she could not talk
importance of early intervention for children with ASD
words gradually came to her
was kicked out of school for being different
thinks in pictures
area1: social and communication challenges
looking across the spectrum there is a general difficulty in relating to others
difficulty with social and emotional reciprocity
can be limited shared enjoyment, joint attention and emotional expression
harder for people with autism to put themselves in others shoes
if you leave the child over time does the child look back and show enjoyment over parents showing parents things
seeing a cluster of symptoms
assessed through observation and interview
symptoms usually become apparent in toddler years
joint attention
when you are talking and someone makes reference of something
ex. taking about coffee and what you got you would automatically look at the cup you are talking about, shifting attention to the cip and then back to the individual. may not see this as much in kids with autism
rett syndrome
rare genetic syndrome that develops within the first 18 months of life
more prevalent in girls
characterized by such symptoms as nearly constant repetitive hand movements, loss of acquired spoken language, gait abnormalities and partial or complete loss of acquired purposeful hand skills
ABA: behaviour intervention-Lovaas study
project BEST-CASE: a model for developing an intensive early childhood intervention program for children with autism spectrum disorder. provent practice
incidental training
transfer and teaching in the natural environment
applied behaviour analysis
the use of learning principles to address interfering behaviours and improve well-being is a key feature of ABA
positive reinforcement, shaping and chaining are all features of ABA
ex. brushing your teeth, comes with multiple steps and children with autism need extra help and guidance with these skills
want to wokr with the children when they are young to develop these skills in order for easier way of keeping these skills throughout the child’s life
alternative communication
often part of ABA program
importance of collaboration
SLP would prescribe the best measure to help the child, what device, vocal signals that work best for the child will be described here
if the things that are prescribed for the individual are not what the child likes this will not reinforce these beahviour you are trying to teach so you need to ensure that child is responsive to the treatment
case: chris
followed form age 4-7
has few vocals given his age
intensive work on his speech
,worked with a device with stickers and velcro
child would use this to say what he wanted
child must keep eye contact in order to get what they want
uses joint attention
took a while to get to next stage
got to a point at age 6 where he was not vocalizing but making sentences with an ipad
from this he was able to imitate what was being said and learned how to speak
now is fluently speaking
RRBs
lower order
self injury, echolalia
higher order
OCD-like, preoccupations
continued talk of building on strengths and giving children and youth a voice
incident training
discrete-trial training video
Case 2: Don
using CBT/behaviour therapy
age 8
use of learning principles
high functioning (asperger’s syndrome)
anxiety around loud sounds
anticipatory
breaking things down into small pieces/small changes in the environment
relaxation training
fear of losing
social communication
conversation skills
self-monitoring language (using ABA and CBT)
autism spectrum disorder
a neurodevelopmental disorder involving impairments in the domains of social communication and the performance of restricted repetitive behaviours
echolalia
repetitions of the same sounds over and over
tourettes disorder
characterized by a combination of chronic motor and vocal tics and can include uncontrollable movements of the head and ittering of vocalizations that sound odd to others
According to the cognitive perspective, which of the following contribute to intermittent explosive disorder?
harsh punishment as children
correct
faulty cognitions
correct
negative beliefs
pyromania
People with this disorder deliberately set fires, feel tension and arousal before the act, are fascinated with fires, and derive pleasure when witnessing fires.
The treatment for pyromania that shows the most promise is based on the cognitive behavioural model
conduct disorder
An impulse-control disorder that involves repeated violations of the rights of others and society’s norms and laws.
anton, a 5 yr old boy with autism spectrum disorder is con sodered a musical prodigy. while showing little interests in social interaction and displaying a severe impairment in speech, he can play incredibly difficult piano pieces at a pro level from memory. anton is displaying
autistic savant syndrome
what is true of Rett syndrome
the child begins to show neurological and cognitive impairments after 4 years of age
it has some of the same symptoms as autism spectrum disorder
girls with ADHD tend to what their symptoms
internalize
the following medications are used to treat tourette’s disorder
SSRIs
atypical antipsychotic agents