Operations and Supply Chain Strategy: Key Concepts and Risk Management
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the primary focus of operations and supply chain strategy?
Setting broad policies and plans for using a firm's resources, integrated with corporate strategy.
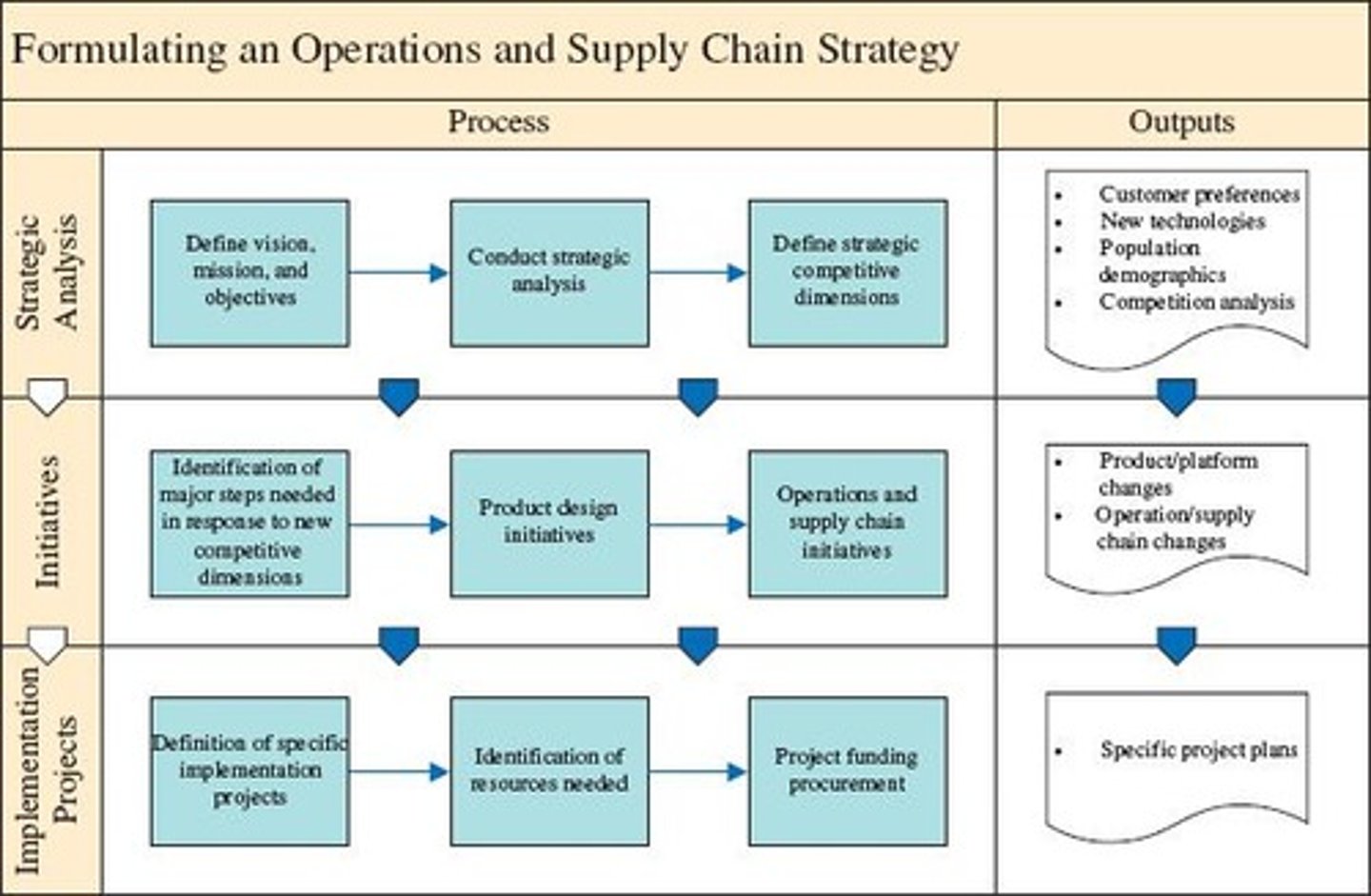
What does operational effectiveness relate to?
The core business processes needed to run the business, spanning all functions from customer orders to shipping products.
How is operational effectiveness reflected in a business?
It is reflected directly in the costs associated with doing business.
What are the competitive dimensions that influence customer decisions?
Cost or Price, Quality, Delivery Speed, Delivery Reliability, Coping with Changes in Demand, Flexibility and New-Product Introduction Speed, and Other Product-Specific Criteria.
What is the goal of being a low-cost producer in operations strategy?
To compete in the market where customers cannot distinguish between products or services from different firms.
What are the two characteristics that define quality in products or services?
Design quality and process quality.
What does design quality refer to?
The set of features that a product or service contains.
Why is process quality critical in operations?
It relates directly to the reliability of the product or service, aiming to produce defect-free outcomes.
How does delivery speed impact competitive advantage?
A firm's ability to deliver products or services quickly can provide a significant advantage over competitors.
What is delivery reliability in the context of operations strategy?
The ability to supply the product or service on or before the promised delivery date.
Why is coping with changes in demand important for a company?
It affects the company's ability to compete, especially when demand fluctuates.
What does flexibility refer to in operations strategy?
The ability of a company to offer a wide variety of products and to adapt processes for new product development.
What is the significance of technical liaison and support in operations?
It involves providing technical assistance for product development, especially during early design and manufacturing stages.
What does meeting a launch date entail in operations strategy?
Coordinating with other firms on complex projects, where manufacturing may occur simultaneously with ongoing development work.
What is the impact of economies of scale on a company with increasing demand?
Costs are continuously reduced, making investments in new technologies more justifiable.
What is the importance of delivery reliability for service firms like Federal Express?
It is the cornerstone of their strategy, ensuring products or services are delivered as promised.
How does flexibility influence new product introduction speed?
It refers to the time required for a company to develop and convert processes to offer new products.
What is the relationship between operational effectiveness and business costs?
Operational effectiveness directly influences the costs associated with running a business.
What role does quality play in customer attraction?
Different customers are attracted by varying attributes of quality, influencing their purchasing decisions.
How can a company gain a competitive edge through delivery speed?
By offering faster service than competitors, such as onsite repairs within hours versus days.
What is the strategic significance of being able to change production volume?
It allows a company to respond effectively to market demand fluctuations.
What does 'support it' refer to in product-specific criteria?
Providing necessary technical assistance and ensuring coordination for product development and launch.
What is the benefit of coordinating work between firms on a project?
It reduces the total time required to complete the project.
What is the significance of supplier after-sale support?
It involves the availability of replacement parts and modifications to existing products, with speed of response being crucial.
How does environmental impact relate to competitive dimensions?
It involves criteria such as carbon dioxide emissions and the use of nonrenewable resources, impacting sustainability.
What are some examples of other dimensions affecting product competitiveness?
Factors such as colors available, size, weight, fabrication site location, customization, and product mix options.
What are trade-offs in operations management?
They occur when activities are incompatible, requiring management to focus resources on critical performance parameters.
How does focusing on speed of delivery affect product flexibility?
If a company prioritizes speed of delivery, it cannot offer a wide range of products flexibly.
What is straddling in the context of competitive strategy?
It refers to a firm trying to match competitor offerings by adding features or services, which can create trade-off issues.
What are order winners?
Specific marketing-oriented dimensions that differentiate a product from competitors, such as cost, quality, and reliability.
What are order qualifiers?
Dimensions used to screen a product or service as a candidate for purchase, like screen size and cost in a notebook computer.
What are activity-system maps?
Diagrams that illustrate how a company's strategy is executed through supporting activities.
What is supply chain risk?
The likelihood of a disruption impacting a company's ability to continuously supply products or services.
What are supply chain coordination risks?
Risks associated with daily management of the supply chain, typically managed with safety stock and lead time.
What are disruption risks in supply chain management?
Risks caused by natural or manmade disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, terrorism, or pandemics.
What happens when a company tries to straddle multiple market segments?
It may lose market share in both segments due to necessary trade-offs in product design.
What factors can be considered as order-winning criteria?
Cost, product quality, reliability, and other competitive dimensions.
How do companies typically manage supply chain coordination risks?
By using strategies like safety stock, safety lead time, and overtime.
What is the impact of supply chain disruptions?
They disrupt the normal flow of goods and materials, exposing firms to operational and financial risks.
What is an example of an order qualifier for a notebook computer?
Screen size, weight, operating system version, and cost.
What is the role of management in addressing trade-offs?
Management must decide which performance parameters are critical and allocate resources accordingly.
Why is speed of response important in after-sale support?
It ensures customer satisfaction and maintains competitive advantage in the market.
What are some dimensions related to environmental impact?
Carbon dioxide emissions and the use of nonrenewable resources.
What is the relationship between trade-offs and operational performance?
More of one performance characteristic often necessitates less of another, requiring strategic focus.
What are the three steps in the Risk Management Framework?
1. Identify sources of potential disruptions. 2. Assess the potential impact of the risk. 3. Develop plans to mitigate the risk.
What is the focus of the first step in the Risk Management Framework?
Analyzing the firm's supply chain to identify potential disruptions, especially highly unlikely events that could significantly disrupt operations.
What factors should be considered when assessing the potential impact of a risk?
Financial impact, environmental impact, ongoing business viability, brand image/reputation, and potential human lives.
What are the four types of risk management strategies?
1. Avoidance: Avoid risks with high probability of financial loss. 2. Accept: Accept risks when mitigation costs exceed toleration costs. 3. Transfer: Share or transfer risks with low probability but high financial impact. 4. Limit: Take action to address and manage exposure to risks.
What is an example of a risk management strategy for natural disasters?
Contingency planning, including alternate sites and insurance.
How can country risks be mitigated?
Through currency hedging and locally producing/sourcing.
What strategy can be employed to handle supplier failures?
Utilizing multiple suppliers.
What is a strategy for mitigating network provider failures?
Supporting redundant digital networks.
What approach can be taken to manage regulatory risk?
Conducting upfront and ongoing research, obtaining good legal advice, and ensuring compliance.
How can commodity price risks be addressed?
By multisourcing and commodity hedging.
What strategies can be used to mitigate logistics failures?
Maintaining safety stock, detailed tracking, and alternate suppliers.
What is a method to handle inventory risks?
Pooling inventory and maintaining safety stock.
How can major quality failures be prevented?
By carefully selecting and monitoring suppliers.
What strategy can be used to prevent loss of customers?
Implementing service/product innovation.
What measures can be taken against theft and vandalism?
Insurance, security precautions, knowledge of likely risks, and patent protection.
What is productivity?
A common measure of how well a country, industry, or business unit is using its resources.
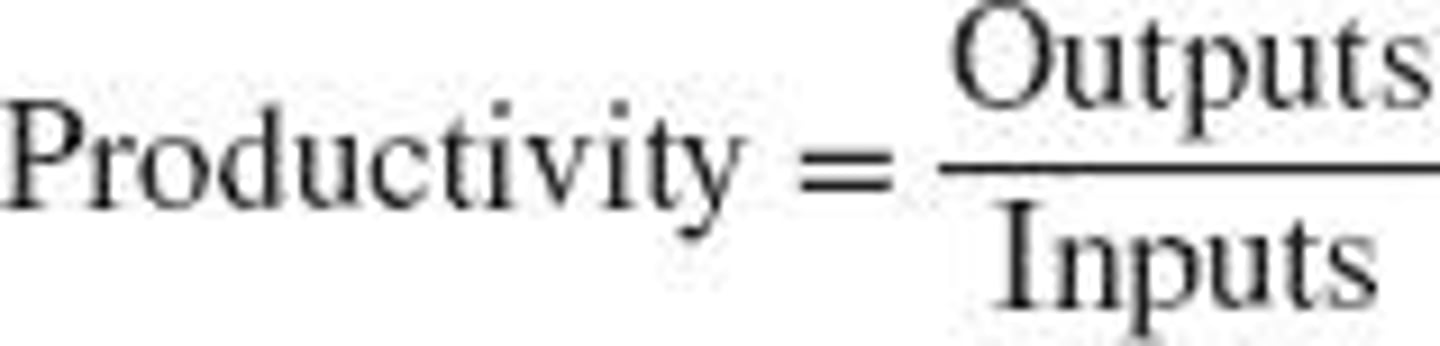
How can productivity be compared?
By comparing a company to similar operations within its industry or measuring productivity over time within the same operation.
What is partial productivity?
The ratio of some output to a single input.
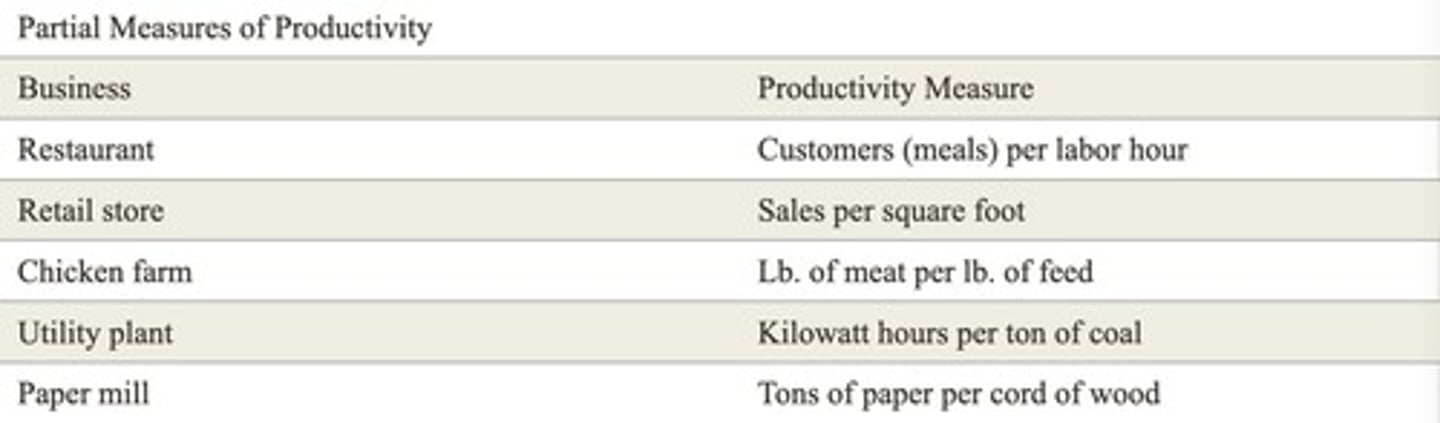
What is multifactor productivity?
The ratio of some output to a group of inputs, but not all inputs.
What is the total factor measure of productivity?
The ratio of all outputs to all inputs, describing the productivity of an entire organization or nation.