ESCI 274 Lecture 3: Greenhouse Gasses
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:35 PM on 2/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
Greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere over time (CO2, CH4, N2O, F-gasses)
1. CO2 dissolves into rainwater-> slightly acidic water (carbonic acid- H2CO3)
2. Acidic water weathers (dissolves) major earth surface rocks (silicate rocks)
3. Carbon gets washed into oceans -> combines with calcium -> deposited on ocean floor (calcium carbonate CaCO3)
4. Becomes rock that becomes part of the tectonic driven rock cycle, eventually released through volcanic activity related to plate tectonics back into the atmosphere
2
New cards
Sources of greenhouse gas emissions (natural vs anthropogenic; global vs more localized areas; who emits more)
* **Natural sources**: volcanic eruptions, forest fires, dust, etc.
* **Anthropogenic sources**: fossil fuel emissions (soot), land burning, for clearing, etc.
* **Global**: global agreement could make a difference
* **More localized areas**: transportation sector produces the most greenhouse gases
* **Who emits more**: global
* **Anthropogenic sources**: fossil fuel emissions (soot), land burning, for clearing, etc.
* **Global**: global agreement could make a difference
* **More localized areas**: transportation sector produces the most greenhouse gases
* **Who emits more**: global
3
New cards
Natural Greenhouse effect
Solar radiation goes into the atmosphere from the sun, more reradiated heat goes back into space, less reemitted heat goes into the earth, less greenhouse gasses
4
New cards
Human enhanced Greenhouse effect
Solar radiation goes into the atmosphere from the sun, less re radiated heat escapes into space, more re-emitted heat goes into the earth
5
New cards
CO2 variations over time and space
* The kneeling curve is a graph that represents the concentration of carbon dioxide in earth atmosphere since 1958
* It has increased from Co2 concentration (ppm) 315 to ppm 420 2023
* It has increased from Co2 concentration (ppm) 315 to ppm 420 2023
6
New cards
CO2 impact on oceans
1. Human activities rise level of carbon in the atmosphere
2. Carbon reacts with seawater creating carbonic acid
3. Carbonic acid decreases pH
* The ocean holds 50x more carbon than the atmosphere
* Ocean is currently supersaturated-> ocean acidifies causes undersaturation
7
New cards
Early Anthropogenic Hypothesis; what is it, and what is the proof?
* **Hypothesis**: Human activities during the end of the last major ice age (late holocene) caused increases in methane (CH4) and carbon (CO2).
\
* **Proof**: holocene trends were opposite in direction for the three previous inter glaciations reached by Vostok Drilling
\
* **Proof**: holocene trends were opposite in direction for the three previous inter glaciations reached by Vostok Drilling
8
New cards
Impact of greenhouse gasses on the climate system (GWP, atmospheric lifetime)
* **GWP** = global warming potential
\
* **Atmospheric LIfetime**- of a species measures the time required to restore equilibrium in the atmosphere following a sudden increase or decrease in concentration of the species in question in the atmosphere
\
* For the short-lived gases, the GWPs decline with time as they disappear faster than the CO2 standard. Conversely, the GWPs for very long-lived gases, like SF6, increase with time as they remain in the atmosphere longer than CO2
\
* **Atmospheric LIfetime**- of a species measures the time required to restore equilibrium in the atmosphere following a sudden increase or decrease in concentration of the species in question in the atmosphere
\
* For the short-lived gases, the GWPs decline with time as they disappear faster than the CO2 standard. Conversely, the GWPs for very long-lived gases, like SF6, increase with time as they remain in the atmosphere longer than CO2
9
New cards
Earths radiation budget
* Overall balance between incoming energy for the sun and the outgoing thermal (longwave) and reflected (shortwave) energy from the earth
* can only be measured from space
* Our planet absorbs nearly 70% of the solar radiation it receives from the sun and reflects the other 30% back into space. About 30% is reflected off the top of the atmosphere, clouds, and surfaces of icecaps, ocean, and land. Absorbed radiation is then reemitted as heat. Greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere absorb some of this radiation and reemit it again, sending some downward to warm the atmosphere and the surface through greenhouse effect.
* can only be measured from space
* Our planet absorbs nearly 70% of the solar radiation it receives from the sun and reflects the other 30% back into space. About 30% is reflected off the top of the atmosphere, clouds, and surfaces of icecaps, ocean, and land. Absorbed radiation is then reemitted as heat. Greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere absorb some of this radiation and reemit it again, sending some downward to warm the atmosphere and the surface through greenhouse effect.
10
New cards
Shortwave radiation
From sun
11
New cards
Longwave radiation
from earth surfaces (albedo)
12
New cards
Albedo
* The proportion of light that is reflected by a surface
* Dark =absorption
* Light= reflectance
* Surface without snow or ice absorbs more heat (70% absorbed, 10% reflects off water, 20% reflects off the land)
* Surface with snow and ice reflects more heat (85-90% reflected, 10-15% absorbed)
* Dark =absorption
* Light= reflectance
* Surface without snow or ice absorbs more heat (70% absorbed, 10% reflects off water, 20% reflects off the land)
* Surface with snow and ice reflects more heat (85-90% reflected, 10-15% absorbed)
13
New cards
Ozone good vs. bad
* **Ozone**: formed through a complex series of reactions from NO2, NO, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and ultraviolet sunlight
* **Good**: ozone in the stratosphere (90% of ozone is in stratosphere),
* **Bad**: ozone in the troposphere (10% of ozone is in the troposphere)
* Ground level (tropospheric) ozone is a GHG and major component of smog
* **Good**: ozone in the stratosphere (90% of ozone is in stratosphere),
* **Bad**: ozone in the troposphere (10% of ozone is in the troposphere)
* Ground level (tropospheric) ozone is a GHG and major component of smog
14
New cards
Ozone human impact
Increase in tropospheric ozone, decrease in stratospheric ozone
15
New cards
Tropospheric O3
Positive radiating force
16
New cards
Stratospheric O3
Negative radiating force
17
New cards
Tropospheric O3 Impacts on health
Direct (respiratory issues), indirect (greenhouse gasses, may be toxic to plants)
18
New cards
Stratospheric O3 impacts on health
Direct (UV radiation, skin cancer, etc), indirect (greenhouse gases)
19
New cards
Ozone and health
* The upper respiratory tract is not effective at moving ozone, most inhaled ozone reaches the lower respiratory tract, ozone and chemical constituents of airway lining fluid-> very reactive chemical intermediates
* This is reversible if exposure is short term.
* Ozone and its products damage airway epithelial cells resulting in inflammation (over a period of days to weeks inflammation subsides and cells are restored)
* Ozone is associated with increased mortality, absolute effect of ozone mortality is higher in adults, the ozone mortality relationship is most prominent during the warm season
* This is reversible if exposure is short term.
* Ozone and its products damage airway epithelial cells resulting in inflammation (over a period of days to weeks inflammation subsides and cells are restored)
* Ozone is associated with increased mortality, absolute effect of ozone mortality is higher in adults, the ozone mortality relationship is most prominent during the warm season
20
New cards
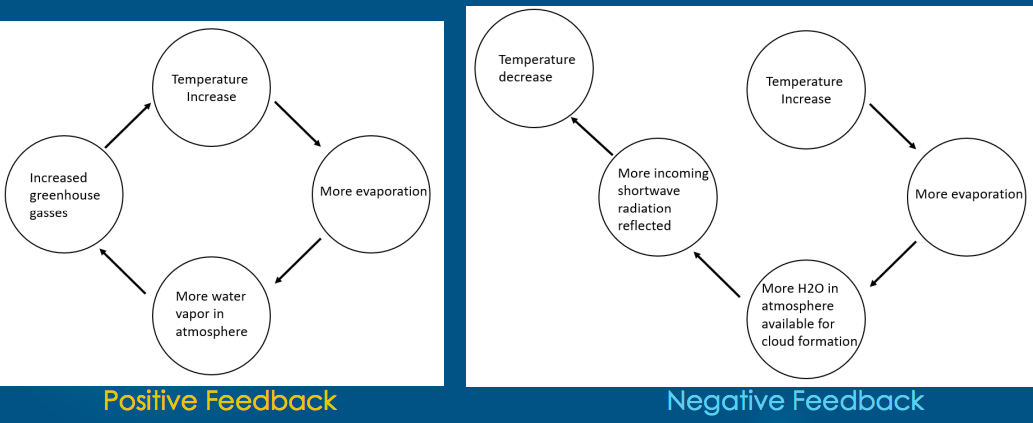
Positive Feedback Loops
Enhance/amplify changes. Tend to move the system away from its equilibrium to a more unstable state
21
New cards
Negative Feedback Loops
Buffer changes. Tends to hold a system close to its equilibrium state making it more stable
22
New cards
The carbonic cycle diagram
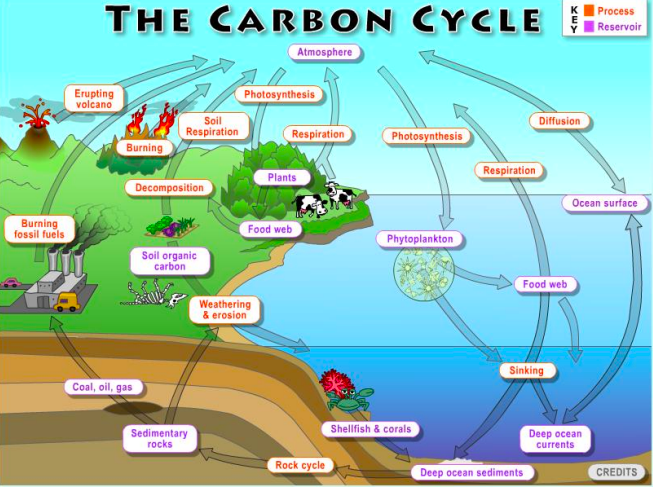
23
New cards
Short-term carbon cycle (biological process) diagram
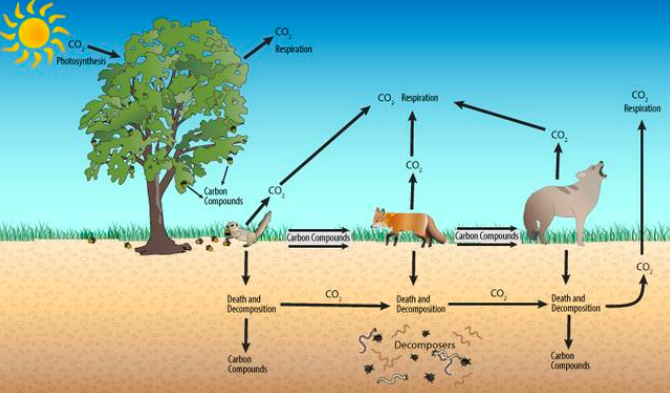
24
New cards
Fast Carbon cycle diagram
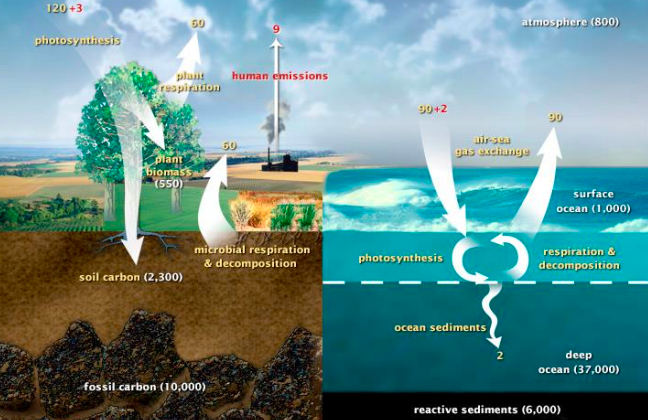
25
New cards
CO2 ocean impacts diagram

26
New cards
Aerosols diagram
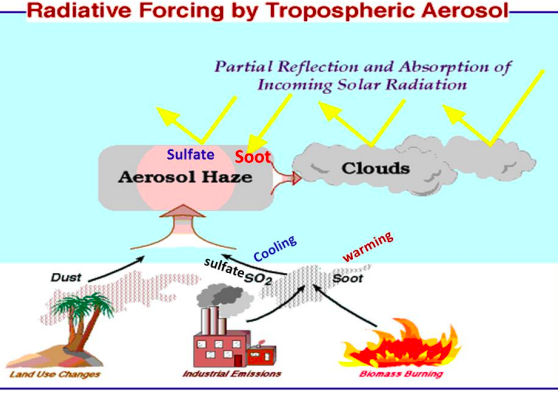
27
New cards
Ozone diagram
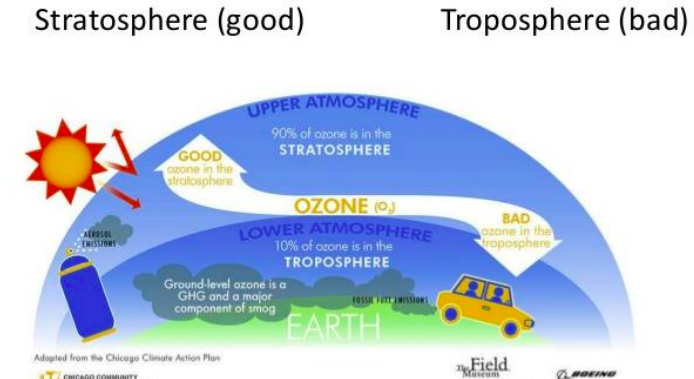
28
New cards
Climate feedbacks: water vapor diagram