Rates, equilibrium and pH
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Define rate of reaction?
The change in quantity of reactant or product per unit time
State the units of concentration?
mol dm-3
What is meant by the order of a reaction?
the power to which the concentration of a reactant is raised in the rate equation
State the reaction orders?
Zero order
First order
Second order
What is a Zero order reaction with respect to A?
Rate is independent of [A]
Rate = [A]0
What effect does changing [A] have on rate in a zero order reaction?
no effect
What is a first order reaction with respect to [A]?
rate is directly proportional to [A]
Rate = [A]1
If [A] doubles in a first order reaction, what happens to the rate?
the rate doubles
If [A] triples in a first order reaction, what happens to the rate?
The rate triples
What is a second order reaction with respect to [A]?
Rate =[A]2
If [A] doubles in a second order reaction, what happens to the rate?
the rate increase by 2 squared therefore rate = 4
If [A] triples in a second order reaction, what happens to the rate?
The rate increases by 3 squared therefore rate = 9
What is the general rate equation for reactants A and B?
Rate= k[A]m[B]n
What does k represent in the rate equation?
The rate constant
What does the overall order of a reaction mean?
the sum of all individual orders: m+n
State the 2 ways which the rate of reaction can be continuously measured?
monitoring by gas collection
Monitoring by mass loss
What does a colorimeter measure?
the amount of light absorbed by a solution
What concentration graph does a zero order reaction produce?
A straight line with a downward curve
What concentration graph does a first order reaction produce?
a downward curve with a decreasing gradient
Define half life in terms of a first order reaction?
the time taken for half of a reactant to be used up
What concentration graph does a second order reaction produce?
A downward curve
Draw the rate- concentration graphs for zero order, first order and second order?
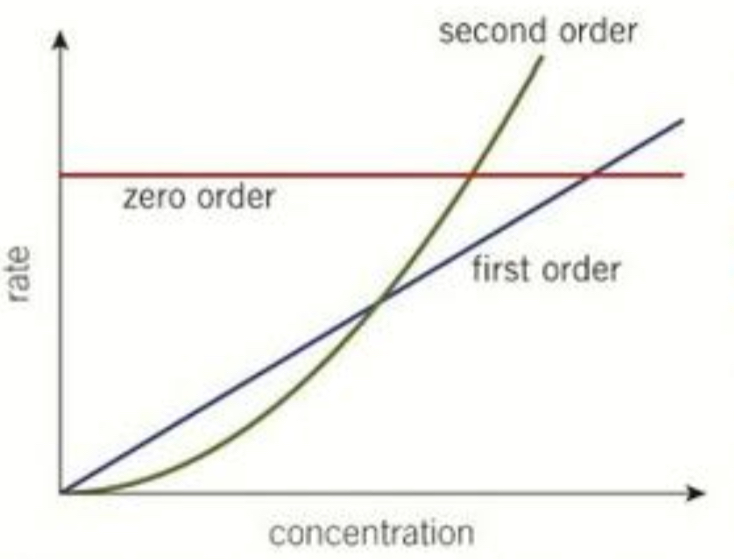
Define the initial rate?
the rate at the start of the reaction where t=0
What type of reaction is a more convenient method to obtain the initial rate of a reaction?
a clock reaction
What does a common clock reaction rely on?
The formation of iodine
How do iodine clocks work?
the time taken from the start of the reaction and the appearance of the iodine colour can be measured
Define stoichiometry?
the relative amounts of the species in the reaction
What gives you the stoichimetry of a chemical reaction?
the balancing numbers
Define the reaction mechanism?
the series of steps which make up an overall reaction
Define the rate determining step?
the slowest step in a multi step reaction
What happens to the value of k as temperature increases?
k also increases
State the 2 factors which contribute to the increased rate and rate constant when temperature increases?
shifts Boltzmann distribution to the right which increases the proportion of particles that exceed activation nervy
Particles move faster and collide more frequently
What is the Arrhenius equation an exponential relationship between?
the rate constant(k) and temperature (T)
What does the exponential factor represent?
the proportion of molecules that exceed Ea and have sufficient energy for a reaction to take place