Clinical Pearls for Urology
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
What is vesicoureteral reflux?
retrograde passage of urine from the bladder into the upper urinary tract
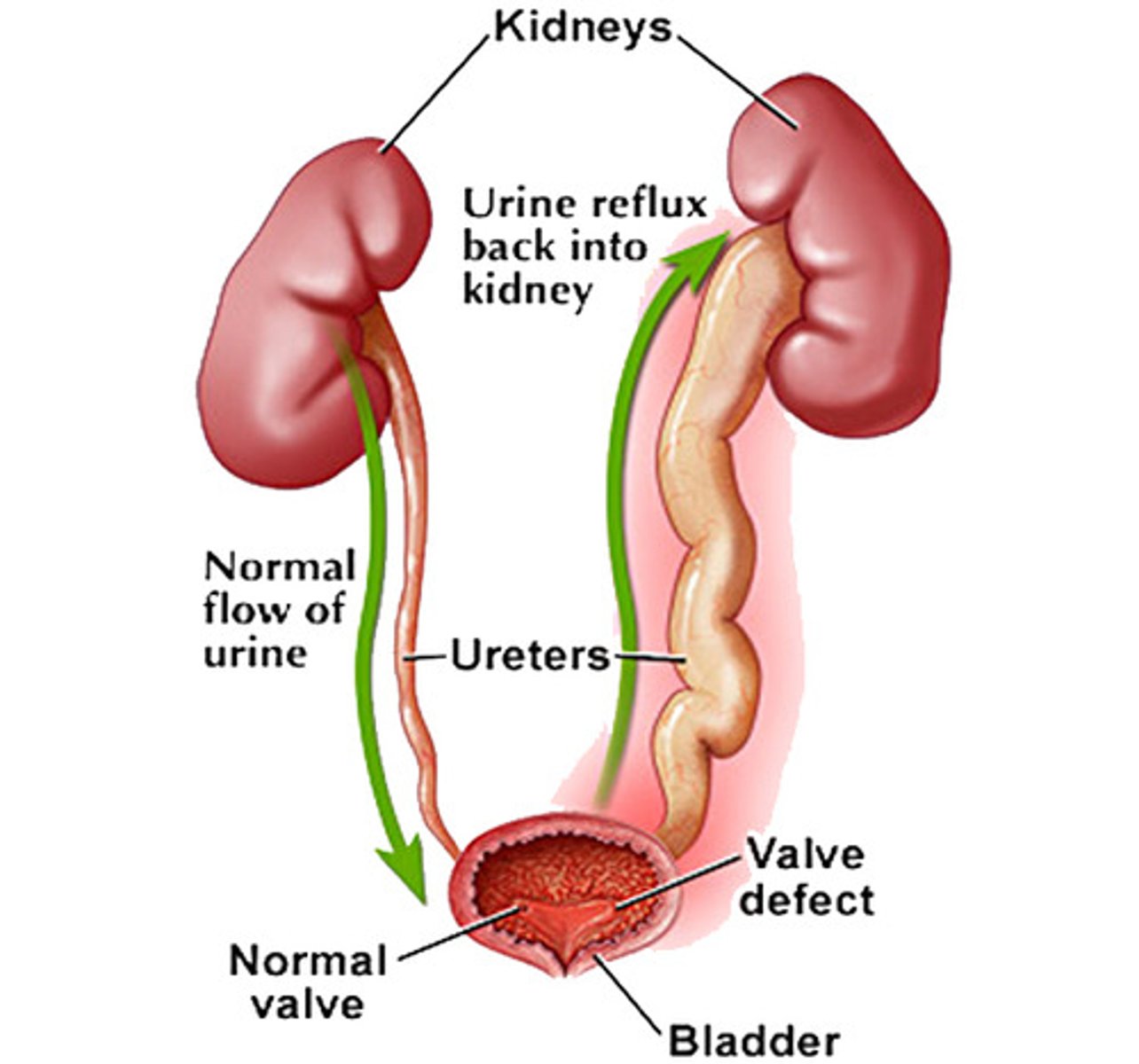
Who is most likely to have vesiculoureteral reflux?
caucasian >> AA
female > males
When are people diagnosed with vesiculoureteral reflux?
-prenatal on ultrasonography (hydronephrosis)
-postnatal after having a febrile UTI
If someone is <2 months and has vesiculoureteral reflux what med do you give?
Cephalexin, Ampicillin or Amoxicillin
If someone is >2 months and has vesiculoureteral reflux what med do you give?
Bactrim (TMP-SMZ)
urethral prolapse presentation
-painless bleeding
-can become painful or cause urinary symptoms
-beefy red donut shaped protrusion
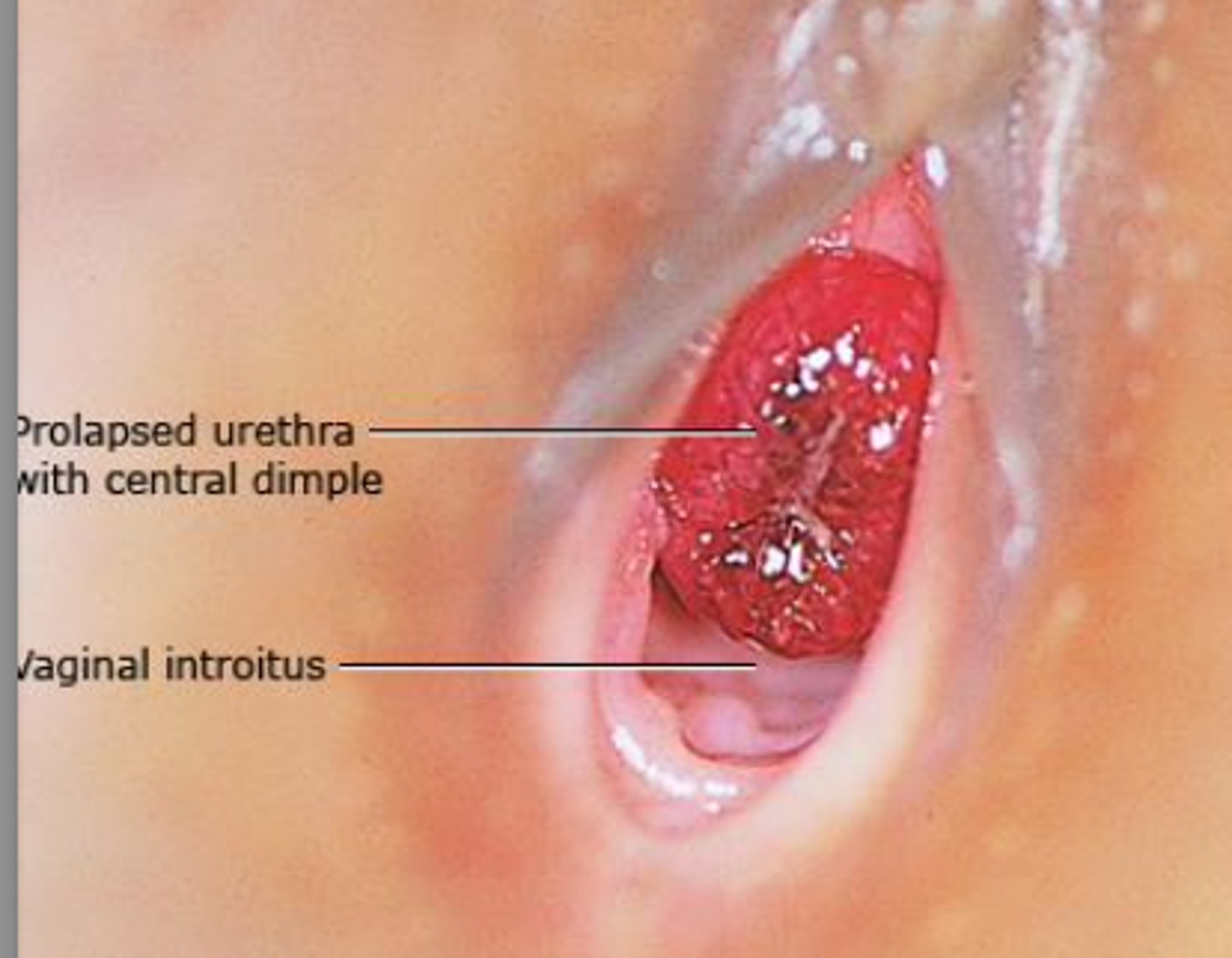
Conservative treatment for urethral prolapse
-observation
-topical estrogen
-anti-inflammatory creams
-sitz baths
If a reduction is done on a urethral prolapse, what needs to be done after?
cystoscopy to rule out ureterocele
What is Epispadias?
Dorsal location of the urethra (rare)
What is often associated with epispadias?
bladder exstrophy
What is the most common cause of urethral stricture in developed countries?
iatrogenic
What is the most common cause of urethral stricture in developing countries?
trauma
Presentation of urethral stricture
Obstructive voiding symptoms
◦Decreased force of stream
◦Incomplete bladder emptying
◦Terminal dribbling
◦Intermittency of stream
Urinary retention
Urinary tract infections
What diagnostic test is most useful for diagnosing an anterior urethral stricture?
Retrograde Urethrogram (RUG)
What diagnostic test is most useful for diagnosing a posterior urethral stricture?
Voiding Cystourethrogram (VCUG)
What is the most common initial treatment for urethral stricture?
urethral dilation and endoscopic urethrotomy
-note: high rate of recurrence
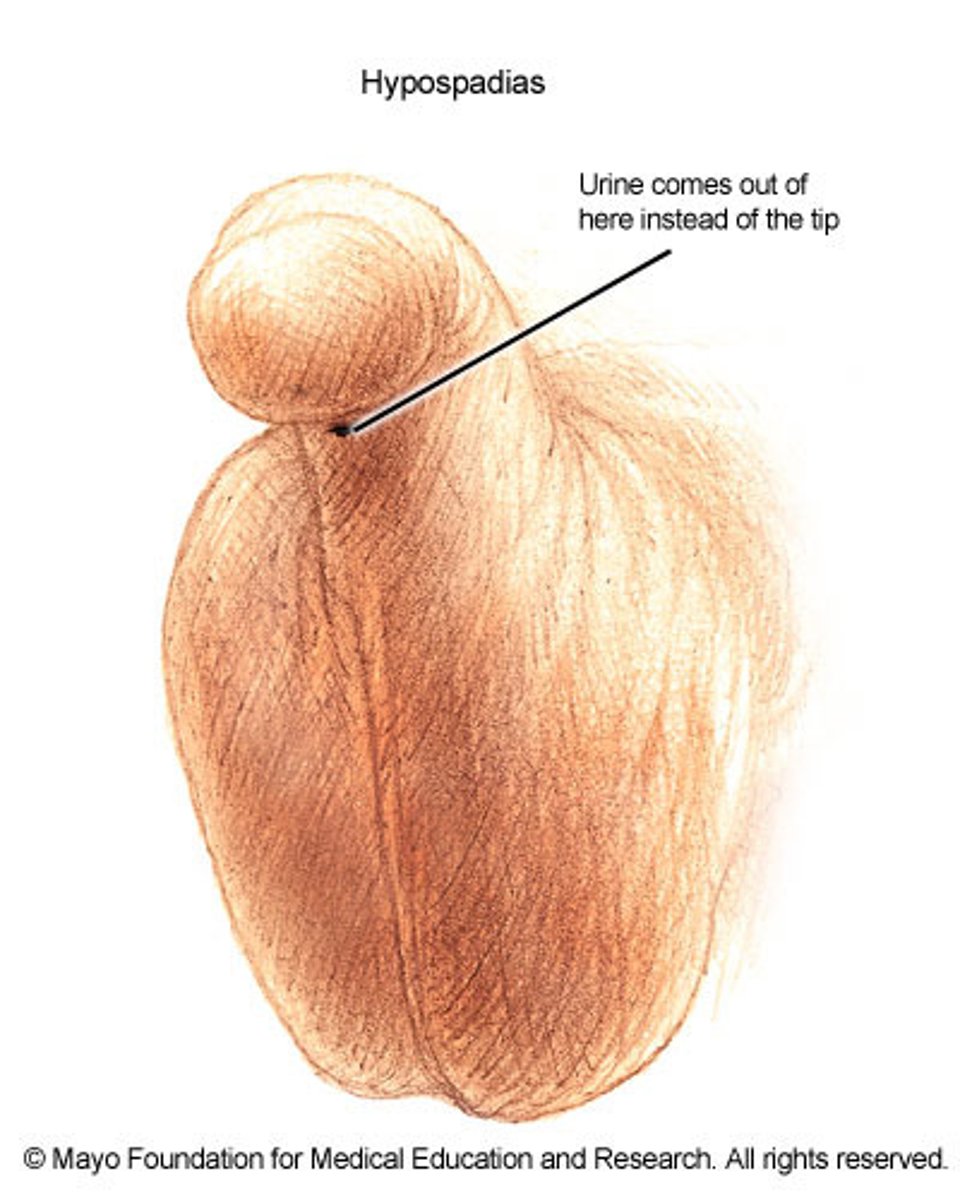
What is hypospadias?
congenital anomaly resulting in abnormal ventral placement of the urethral opening
What is an environmental cause for hypospadias?
prenatal exposure to estrogenic compounds --> leads to disruption of androgenic stimulation
Describe forme fruste in hypospadias
2 urethral openings at penis tip
Describe a standard case of hypospadias
ventral or dorsal placement of urethral opening
What is Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis?
chronic urinary obstruction with chronic infection leading to suppurative destruction of renal tissue
What types of cells are characteristic of Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis?
foamy lipid-laden histiocytes (xanthoma cells)
Common cause of Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
E. coli
presentation of Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
-usually unilateral mass
-fever
-chills
-flank pain/mass
-bacteriuria
-Hx of urolithiasis
What would you see on urinalysis of Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
WBCs and protein
treatment for Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
partial or total nephrectomy
What does a renal abscess result from?
severe infection that leads to liquefaction of renal tissue which is then sequestered, forming an abscess
common cause of renal abscess (pathogen)
E. coli
presentation of renal abscess
-fever
-chills
-flank mass/pain
-abdominal pain
-dysuria
What is the characteristic finding of a renal abscess on imaging?
"ring" sign that forms from the inflammatory wall around fluid collection causing a rim around mass
treatment for renal abscess
Ampicillin or vancomycin + amino glycoside
-can do surgical drainage
What is Pyonephrosis?
bacterial infection of a hydronephrotic, obstructed kidney
-leads to suppurative destruction of the renal parenchyma and potential loss of renal function
-puss in the kidney that is hydronephrotic
Presentation of pyonephrosis
-VERY ILL
-fever
-chills
-flank pain
-Hx or calculi or surgery is common
-lower urinary tract symptoms often absent
-sepsis can happen QUICKLY
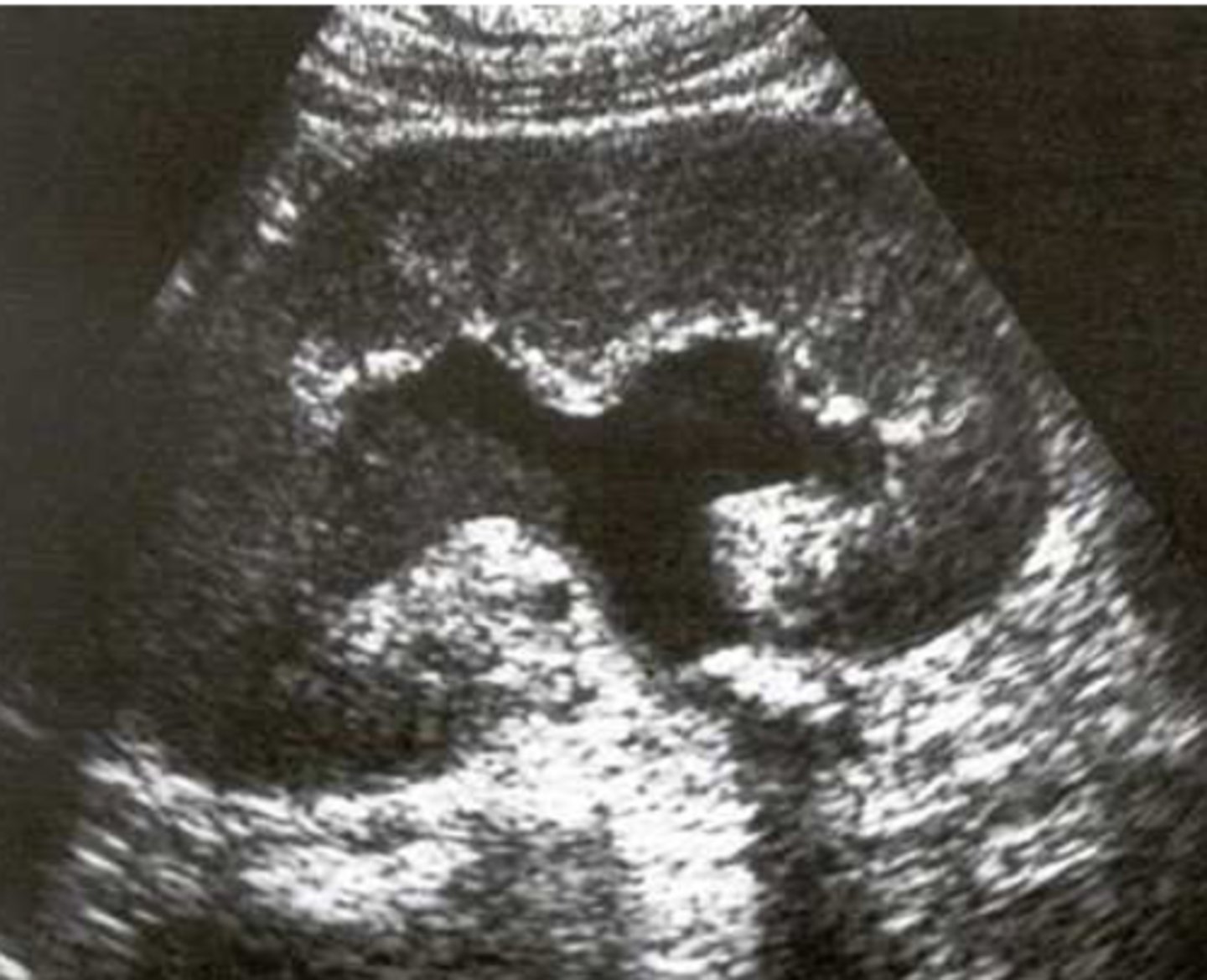
What would you see on a renal US if someone has pyonephrosis?
dilated pyelocalyceal system with fluid debris levels
-calculi possible
what is acute pyelonephritis?
infectious inflammatory disease involving the kidney parenchyma and renal pelvis
risk factors for acute pyelonephritis
-women
-sexual intercourse "Honeymoon cystitis"
-menopause: decreased bladder tone
-pregnancy
most common cause of acute pyelonephritis
E. coli
common cause of acute pyelonephritis in sexually active women
staph saprophyticus
presentation of acute pyelonephritis
-fever
-tachycardia
-back/flank pain
- positive CVA tenderness
-nausea/vomiting
What is the definitive diagnosis for acute pyelonephritis?
urine culture
inpatient treatment for acute pyelonephritis
-IV ampicillin
-IV ceftriaxone
-IV ciprofloxacin
outpatient treatment for acute pyelonephritis
-Ciprofloxacin
-Levofloxacin
-Bactrim
How does someone get chronic pyelonephritis?
repeated or inadequate treatment for renal infections, which leads to scarring, atrophy of kidney, and renal insufficiency
Presentation of chronic pyelonephritis
-most asymptomatic and found on imaging incidentally
-Hx of frequent UTIs or pyelonephritis
-chronic flank pain
-renal failure
-HTN, anemia
How is the diagnosis made for chronic pyelonephritis?
radiologic or pathologic exam
Goal for treatment of chronic pyelonephritis?
prevent further damage
What is emphysematous pyelonephritis?
necrotizing infection characterized by the presence of gas within the renal parenchyma or perinephric tissue
Patients with what underlying condition usually present with emphysematous pyelonephritis?
diabetes melitus
Common pathogen in emphysematous pyelonephritis
E. coli
Presentation of emphysematous pyelonephritis
-fever
-chills
-flank pain
-abdominal pain
-n/v
How is the diagnosis made for emphysematous pyelonephritis?
imaging --> see gas in renal parenchyma
Treatment for emphysematous pyelonephritis
-control blood sugar
-relieve obstruction
-kidney removal
How is Recurrent cystitis defined?
2 or more culture positive UTIs in 6 months or 3 or more culture positive UTIs in 1 year
RF for recurrent cystitis
-sexual intercourse
-use of spermicides
-incomplete bladder emptying
-maternal FHx of UTI
-post-menopausal
Treatment for recurrent cystitis
lifestyle modifications
-avoid use of spermicides
-urinate after intercourse
-wipe front to back
-increase water intake
Supplements
-D-mannose
-cranberry
Methanamine hippurate
What is interstitial cystitis?
chronic bladder pain w/o a known etiology and with negative urine cultures
presentation of interstitial cystitis
-pain (exacerbated by filling of bladder)
-pressure
-discomfort or spasms of bladder
-urinary frequency/urgency
What is the goal of treatment in interstitial cystitis?
relieve symptoms
What meds can be given to those with interstitial cystitis?
Amitriptyline and NSAIDs
What is the diagnostic tool of choice for asymptomatic bacteriuria?
clean-catch voided urine
What is acute cystitis/UTI?
confined to the bladder/lower urinary tract
What is the common pathogen that causes acute cystitis/UTI?
E. coli
symptoms of acute cystitis/UTI
-dysuria
-urinary frequency/urgency
-suprapubic pain/pressure
-occasionally hematuria
How do you treat acute cystitis/UTI?
-Nitrofurantoin
-Bactrim
-Fosfomycin
-Fluoroquinolones
What is Complicated cystitis/UTI?
infection that is no longer just in the bladder
Presentation of Complicated cystitis/UTI?
active UTI with:
-fever
-flank pain
-CVA tenderness
-pelvic or perineal pain in men
-n/v
Important things needed to diagnose Complicated cystitis/UTI
-good H&P
-urinalysis and urine culture
What is the DOC for Complicated cystitis/UTI?
fluoroquinolones
Primary HSV presentation
-can be severe
-multiple painful genital vesicles/ulcers
-dysuria and sometimes urinary retention
-fever
-tender inguinal LAD
-headache
non primary HSV presentation
-fever, lesions and less systemic symptoms
What is the preferred diagnostic tests for HSV in active lesions?
-viral culture
-PCR
What meds treat HSV and how soon should you start them?
-Meds: Acyclovir, Valcyclovir, and Famciclovir
-start within 72 hours of lesion presentation
What types of HPV cause genital warts?
types 6 and 11
What types of HPV cause penile cancers?
types 16 and 18
What is the most common presentation of HPV?
genital warts
diagnosis for HPV
mostly clinical
-can get biopsy if unsure
Patient applied treatment for HPV
-Imiquimod 5% cream
-Podophyllotoxin 0.5% solution or gel
-Sinecatechins 15% ointment
Clinician applied treatment for HPV
-cryotherapy
-trichloroacetic acid
-surgical removal
What is the causative agent for syphilis?
Treponema pallidum
What is the epidemiology for syphilis?
-men in western US
-MSM
-AA
-ages 20-34 y/o
presentation of early syphilis
-painless chancres
-regional lymphadenopathy
-heals spontaneously w/in 3-6 weeks
presentation of secondary syphilis
-rash (diffuse, symmetric macular or papular rash with lesions that are copper, red, or reddish-brown)
-systemic signs (fever, HA, malaise, sore throat)
-adenopathy
-neuro (HA, meningitis)
-MSK (osteitis and synovitis)
Presentation of late syphilis
-up to 20 years after infection
-cardiovascular
-gummatous (granulomatous, modular lesions occurring on skin and bones)
What test is more specific for syphilis diagnosis?
Treponemal test
What test is highly specific for neurosyphilis?
CSF-VDRL
How do you treat syphilis?
Penicillin G
What is the most common cause of urethritis in men?
Chlamydia
What is the causative agent for chlamydia?
Chlamydia trachomatis
RF for chlamydia
-young age (<25)
-race (highest in AA)
-incarcerated populations
-military recruits
-new or multiple sexual partners
-Hx of previous chlamydial infections
-unprotected sexual intercourse
presentation of chlamydia
-most are completely asymptomatic
-urethritis is MC clinical manifestation in males and cervicitis is MC in females
-could have epididymitis
-could have proctitis
Progression of cervicitis due to what has a high rate of infertility?
due to chlamydia
What is the classic triad for reactive arthritis?
Conjunctivitis/uveitis
Urethritis
Arthritis
"Chlamydia Upsets All"
What is the test of choice to diagnose chlamydia?
Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT)
Treatment for Chlamydia?
doxycycline or azithromycin
What is the causative agent for Gonorrhea?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Presentation of gonorrhea
-urethritis (MC)
-epididymitis
-extragenital infection
-conjunctivitis (if spread to eyes)
-sore throat
What is the classic triad for disseminated infection of gonorrhea?
Tenosynovitis
Polyarthralgias
Dermatitis
"Ten Polyamorous Dermatologists got gonorrhea"
How do you diagnose Gonorrhea?
NAAT is test of choice
If you get a microscopy of gonorrhea, what will you see?
-polymorphonuclear leukocytes with intracellular gram negative diplococci
Treatment for Gonorrhea
Ceftriazone + Doxycycline (to treat for chlamydia)