Conservation of Biodiversity Exam 1
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ASU BIO 322
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
True or False? Extinction is a natural process, so the current extinction rate is nothing to be concerned about
False (although it is a natural process, humans accelerate and intensify it to be much more rapid than normal, which means that if this rate continues, it will qualify as the 6th mass extinction event)
What animals are at highest risk for extinction?
Large animals that need lots of space, resources, and have a long reproductive cycle (large mammals), sensitive animals that are highly affected by temp, water, and pollution levels, and rare animals that either have small ranges or high levels or specialization
What is carrying capacity, and what affects it?
number of individuals an environment can support, affected by how many resources each individual consumes and how many people consume it
What is overpopulation?
when the number of individuals in an area exceeds the carrying capacity of the area
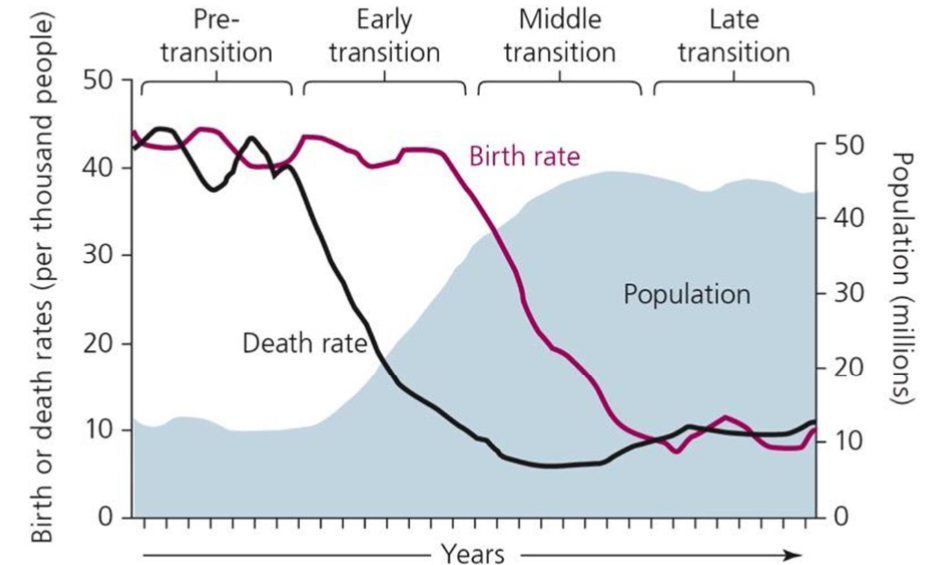
What does this graph show?
The demographic transition where the population increases due to reduced death rates during industrialization
What is ecological footprint?
the land needed for an individuals resources and waste, related to emissions, food, electricity, etc.
True or False? We are over the Earth’s carrying capacity
True (we have been over the capacity for decades, but have been able to support the population off of nonrenewable resources)
What is the IPAT model?
(I=PxAxT) that measures human (I)mpact based on (P)opulation, (A)ffluence (average resouce use, ecological footprint, etc) and (T)echnology. It shows that increased population and resource use increases impact, and that technology can increase or decrease impact.
What is the primary cause of species loss?
land change for agriculture
What is direct vs indirect habitat loss?
direct is land cover change (like deforestation) while indirect is degradation (water pollution)
True or False? The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is a reliable and unbiased source of climate information
False (the EPA has strict rules that influence/bias what gets funded and published, and they can alter policies to push an agenda. For example, in 2018 they were deleting documents with the phrase “climate change”, which is information erasure)
What is genetic diversity and why is it important?
diversity of genes within a species, important for evolution and resilience of the species
What is functional diversity and why is it important?
what functions a species performs, important for relating back to humans and ecosystem services (example, bees pollinating)
What is taxonomic/species diversity and why is it important?
the number and variety of distinct species in a particular area, important for environmental resilience because it supports many ecosystem services
What is the biological species concept?
reproductive isolation
What is the morphological species concept?
physiological traits
What is the phylogenetic species concept?
common ancestry
What is species richness?
total number of different species in community (same number of species, but not necessarily evenly distributed)
What is species evenness?
the relative abundance of each species (how equal is the species populations, % make up)
What is the shannon-wiener index?
measures species richness and evenness and combines into a single score, where 1 is a high level of biodiversity and 0 being a low level
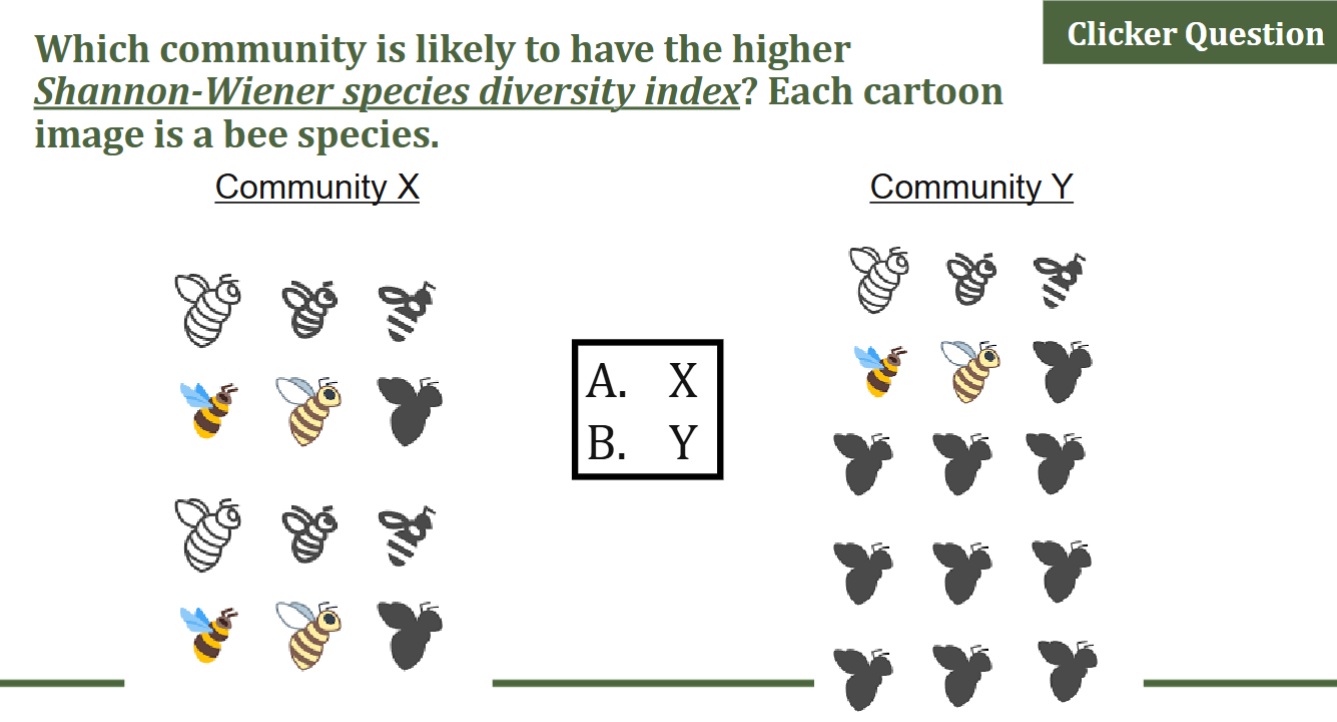
Which community is likely to have the higher Shannon-Wiener species diversity index? Each cartoon
image is a bee species.
A) community x
True or False? About 85% of species are unknown to science, with a majority of that being invertebrates
True
What does latitudinal diversity mean?
describing how there are more species near the equator
What are endemic organisms?
organisms that are only found in one area and no where else
What is a gene drive?
process of inheritance by which a gene is guaranteed to pass from one generation to the next, and ultimately throughout a population
What is post normal science?
facts are uncertain, values are in dispute, stakes are high, and decisions are urgent (like with malaria)
What is anthropocentrism?
human based approach to conservation, species consideration for instrumental value (serves as a means to achieve a desired goal)
What is ecocentrism?
moral consideration of ecosystems in conservation, species consideration for its intrinsic value (worth for its own sake)
What is a normative statement?
express desire or judgement about the desirability of a situation (world as it “should be”)
What is ecological economics?
putting value on environmental resources (monetary, intrinsic, instrumental, aesthetic, etc)
What are provisioning services?
products (food, shelter, fuel, meds, etc), this service is the easiest to quantify and usually included in the GDP
What are cultural services?
non material services (recreation, aesthesis, spiritual, intellectual, etc), very hard to quantify because it not only relates to single experiences and mental health benefits, but also to person identity (how do you quantify having “Arizonan” as part of your identity?)
What are regulating services?
services that control or regulate climate, pests, pathogens, soil/water quality, etc to be more desirable to humans (microbial water purification, mangrove tree wave break, etc)
What are supporting services?
services that are needed for the function of other ecosystem services (plant productivity—→supports food chain, pollinators—→ food production and plant reproduction, plant transpiration—→water cycling, etc)
What is natural capital and natural interest?
Natural capital is the wealth of resources on Earth. Then the natural interest is the potential increase/decrease value based on the rate of use.
(So if discussing tuna, there is a number of fish and that value is the natural capital. If we fish the tuna a small amount, the natural capital of fish will reproduce (natural interest) increasing population of tuna. But if we overfish, the rate of reproduction cannot keep up and the population will diminish despite the generational accruing interest
What is a triple bottom line?
an assessment of the costs of goods/services past just economic cost, including social and environmental costs (like fast fashion filling up landfills), includes both internal and external costs
What is true cost?
the sum of internal and external costs of a good/service. Internal costs ARE taken into account when pricing because it considers raw materials, manufacturing, labor, and taxes. External costs DO NOT get taken into account when pricing, because it considers costs like deforestation, soil degradation, and water use.
What is the stated preference/contingent valuation method?
stated willingness to pay for something
What is the revealed preference valuation method?
examined willingness to pay for something (watch actions, either through travel costs, willingness to pay premiums, or price per unit area of a natural product)
What is the replacement costs valuation method?
how much it would cost to replace a service with a human-made alternative
What is the difference between ecological economics and environmental economics?
Ecological economics is a field that brings together ecology, economics, anthropology, history, and more in a way that embeds humans in ecological systems, incorporates external costs.
Environmental economics is a subdiscipline of economics that applies standard economics to environmental assets, focusing largely on humans and ignoring external costs.

What does this figure show?
It shows that in conservation, generally as the number of people involved increases, the direct impact a single person decreases. But on a national level, there is a bubble in impact level. This is because community members and individuals can make large differences on a national level by advocating for policy changes.
What were the key parts of the Endangered Species Act when it was made in 1973?
It created the “Federal List of Endangered and Threatened Wildlife and Plants” which protected species declining in population. To label a species as endangered, it required for a designated critical habitat for recovery, and to be a named, defined species. Additionally, it protected endangered species from take on federal, state, or private land.
What is take?
killing, harassing, collecting, harm, or endangerment
What does the phrase “shoot, shovel, and shut up” mean and how does it relate to the ESA?
The Endangered Species Act protects animals even on private land, which restricts what people can do if the animal is around. So a concern is that the ESA encourages people to shoot endangered species, and hide the evidence so that they don’t have restrictions on their property.
What are the new changes to the ESA?
A “God Squad” was created which can grant exemptions to the ESA. Getting a species listed has more requirements, which has made it so less than 5% of proposed species get listed. Experimental reintroduction species have less protection. Phrasing to the ESA guidelines have changed to allow more loopholes, including the following:
“Do not” was changed to “not likely to” in context to projects jeopardizing listed species
Definition of habitat changed to only count areas of current occupancy instead of all previous essential land
Phrase “foreseeable future” changed to specific timelines, which allow for degradation up until that time instead of an immediate halt of jeopardizing action
Why is international conservation (aka conservation past national boundaries) important?
Because species can have ranges outside of national boarders, and need protection in both places to be effective (ex: monarch butterfly migration in US and Mexico). International conservation efforts can effect the habitats of species. And international trade determines demand for animals/body parts (ex: Elephant ivory)
What is CITES?
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (of Wild Fauna and Flora): an international treaty that regulates the global trade of endangered species and body parts, including ivory, pelts, caviar, exotic pets, etc.
What is CBD, and has it been successful?
Convention on Biological Diversity: and international treaty that promotes sustainable use of ecosystems and biodiversity, attempts to go further that CITES by supporting conservation of all, not just endangered species.
Its has had limited success due to lack of enforcement. There are no punishments for not meeting goals and no punishments for backing out
What is the IUCN?
The international list that defines threatened species. Good for bringing attention to species at risk, but only describes 7% of defined species
What is the single species conservation approach, and what are its advantages/disadvantages?
It focuses on a single species to protect biodiversity and ecosystems. Its main downside it how narrow in focus it is, but can be very useful if the species of focus has a large beneficial impact to other at risk species. Additionally, it can be easier to get support for, since people can get behind protecting “cool/cute” animals (like tigers or elephants, over a random frog)
What is a systems approach to conservation, and what are advantages/disadvantages?
It focuses on the ecosystem as a whole, usually targeting protected areas or policy making. It’s main advantage is that it has the potential to be more influential and overarching than a single species approach, but it can be more difficult to protect and get funding for
Define all these species terms: Keystone, foundation, indicator, flagship, umbrella
Keystone: central to the function of an ecosystem, without them there will be a cascading loss of biodiversity (sea otters prevent urchin overpopulation, helping kelp and all species reliant on kelp)
Foundation: physically important for the structure of the ecosystem (trees, coral, kelp)
Indicator: Indicative of health of an ecosystem (canary in the coal mine situation)
Flagship: symbol of an ecosystem, often used to get public attention and support for broader environmental protection (polar bear)
Umbrella: species that if saved, would help save many other species in the region. Relates to a conservation strategy where the picked protected species often has large migratory ranges or large habitat needs, making an overlap in their habitat protection and the habitat ranges of other species (Panda habitat protection has a 96% overlap with other species endemic to China)
What are 3 ways to achieve conservation on private land?
1) purchase and protect lands (land trusts make it so the conservation group owns and sets rules to the land, but allows others to use the land)
2) conservation easements (these are legally binding agreements between the landowner and the government where the landowner retains the land with limits on development and other rights in exchange for potential tax benefits or payment)
3) Impose mandatory laws and regulations to restrict activities (like the ESA)
True or False? There are 5 levels of protection and level V is full protection, while level I is limited protection
False (There are 6 levels of protection! And the level of protection is reversed, with Category I being the most protected, and encompassing things like strict nature reserves. Category VI is protected areas with sustainable use of natural resources)
True or False? Protected areas are not examples of fortress conservation
True (protected areas aren’t trying to reach “pristine nature” by fortressing off all human activities, they aim to conserve for future generations through sustainable use)
What does the term leakage mean in conservation?
When policy/conservation changes reduce the amount of unsustainable practices in one region by displacing it to another region