PSYCH Midterm Study Guide
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
Psychology
scientific study of behavior (what we do) and mental processes (inner thoughts and feelings).
Nature versus Nurture
Contribution of genes and experience in the development of behaviors or traits.
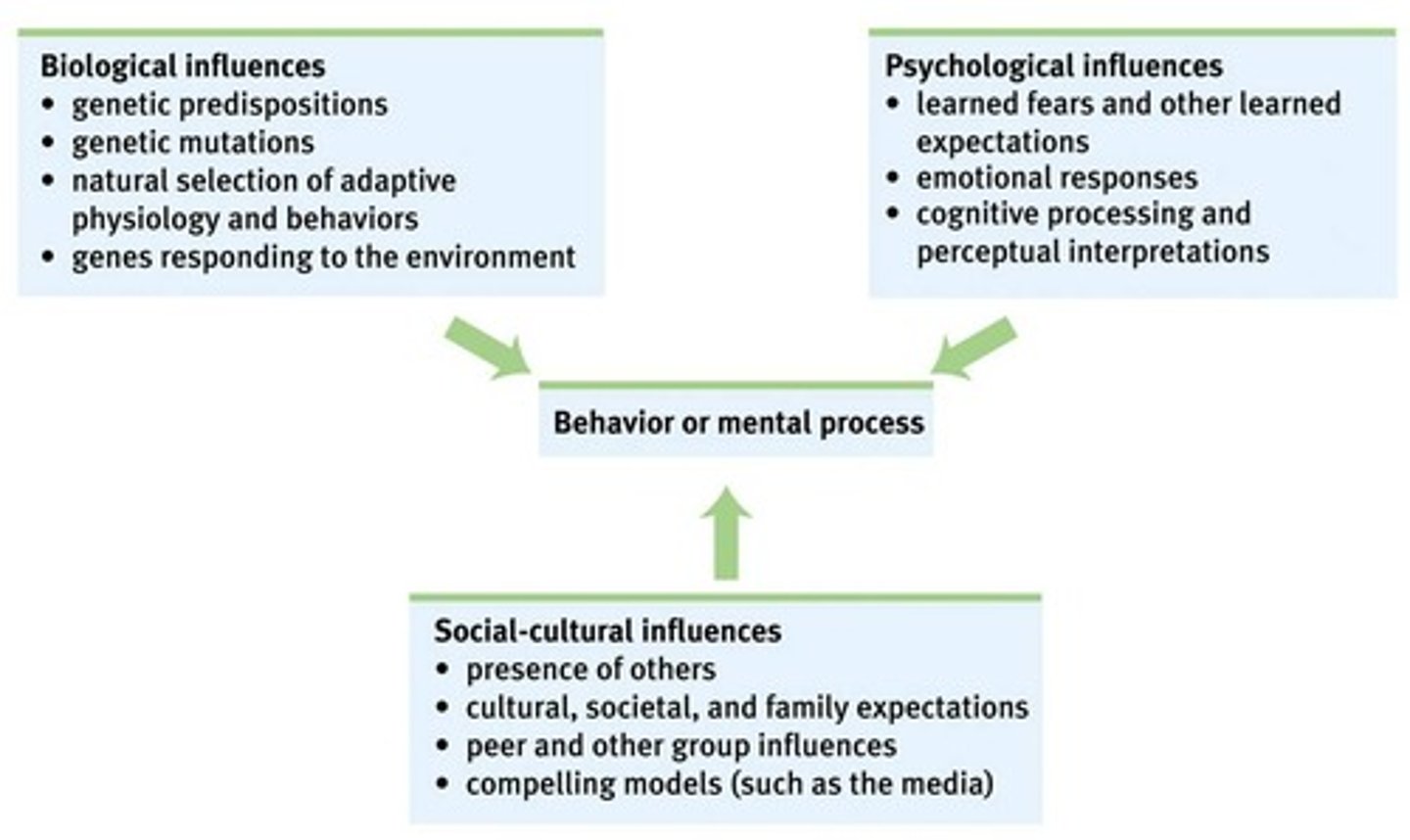
Biopsychosocial approach
integrate different levels of analysis.
Hindsight Bias
the 'I-knew-it-all-along' phenomenon. After learning the outcome of an event, many people believe they could have predicted that very outcome.
Overconfidence
Sometimes we think we know more than we actually know.
Anagram Unscrambling
People said it would take about 10 seconds, yet on average they took about 3 minutes (Goranson, 1978).
Order in Random Events
Given random data, we look for order and meaningful patterns, leading us to overestimate our intuition.
Scientific Attitude
composed of curiosity (passion for exploration), skepticism (doubting and questioning) and humility (ability to accept responsibility when wrong).
Critical Thinking
does not accept arguments and conclusions blindly. It examines assumptions, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence and assesses conclusions.
Theory
an explanation that integrates principles and organizes and predicts behavior or events.
Hypothesis
a testable prediction, often prompted by a theory, to enable us to accept, reject or revise the theory.
Research Observations
would require us to administer tests of self-esteem and depression.
Correlation
When one trait or behavior accompanies another, we say the two correlate. r = +0.37.
Correlation Coefficient
a statistical measure of the relationship between two variables.
Scatterplot
a graph comprised of points that are generated by values of two variables. The slope of the points depicts the direction, while the amount of scatter depicts the strength of the relationship.
Perfect positive correlation
(+1.00).
Perfect negative correlation
(-1.00).
No relationship
(0.00).
Correlation and Causation
Correlation does not mean causation!
Nervous System
acts as a continuous communication system, but is broken down into two parts for study: The central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
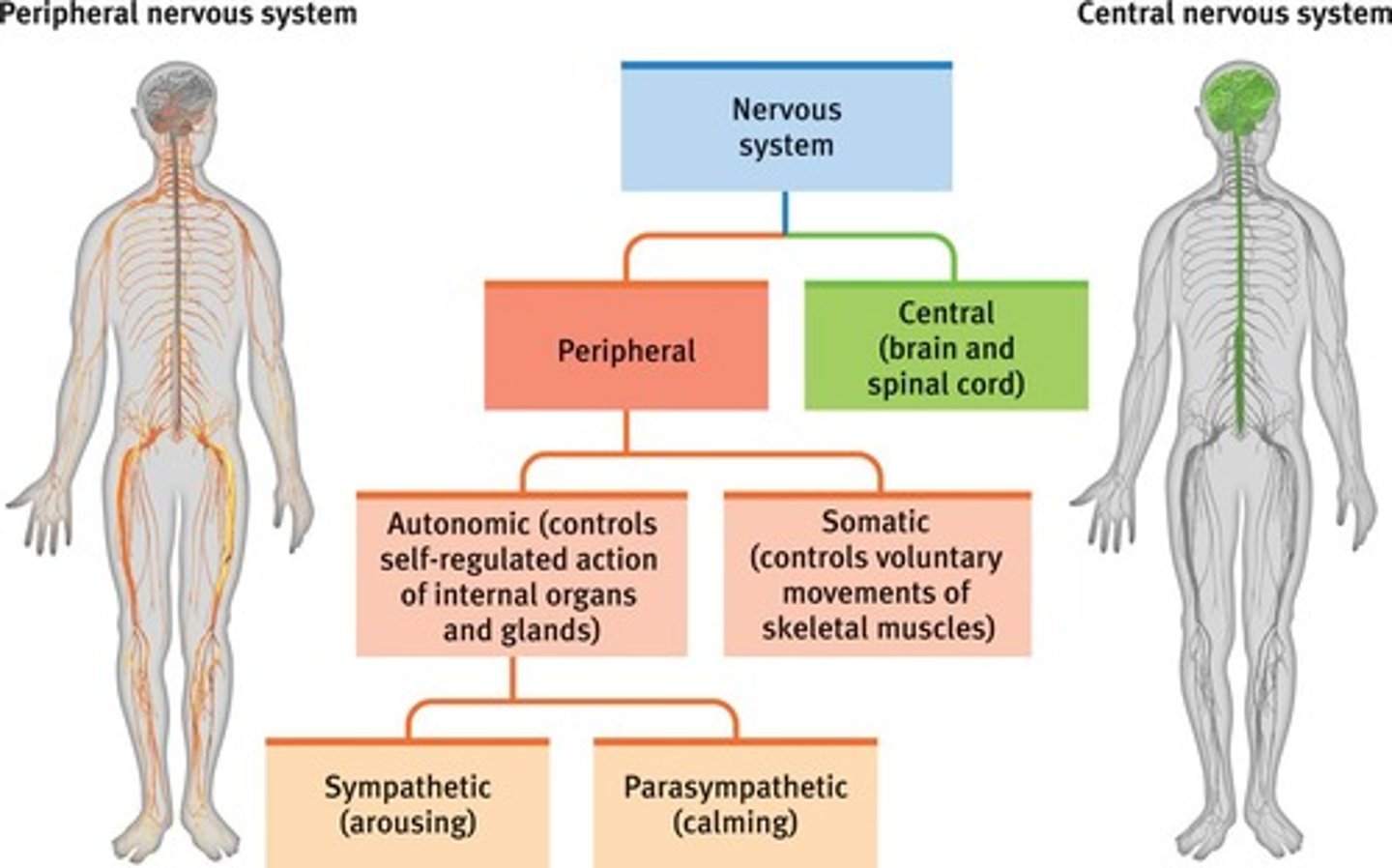
Central Nervous System
consists of the spinal cord and brain.
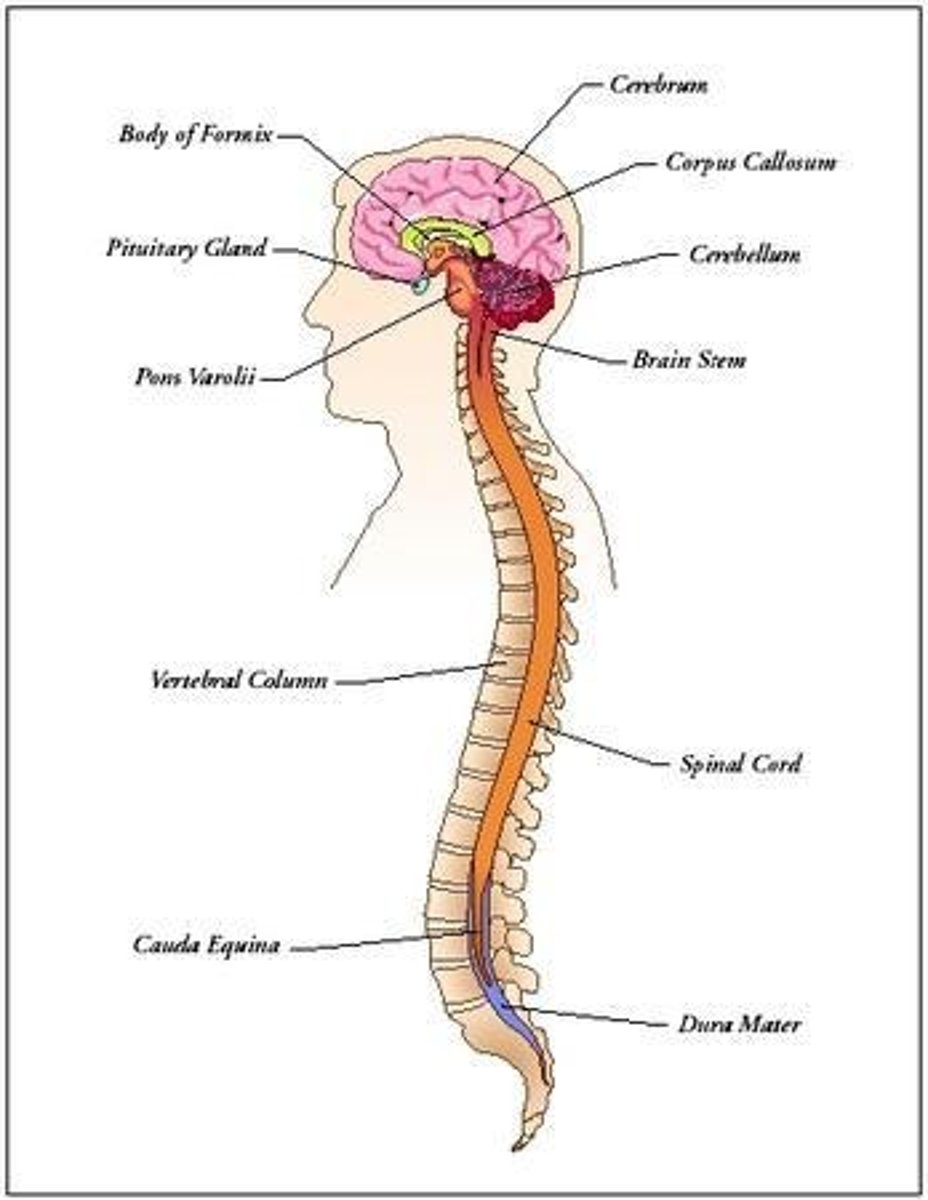
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The CNS consists of the spinal cord and brain, receiving and sending sensory input and coordinating motor output.
Cerebral Cortex
A thin, highly convoluted outer layer of gray matter covering both hemispheres that are divided into lobes.
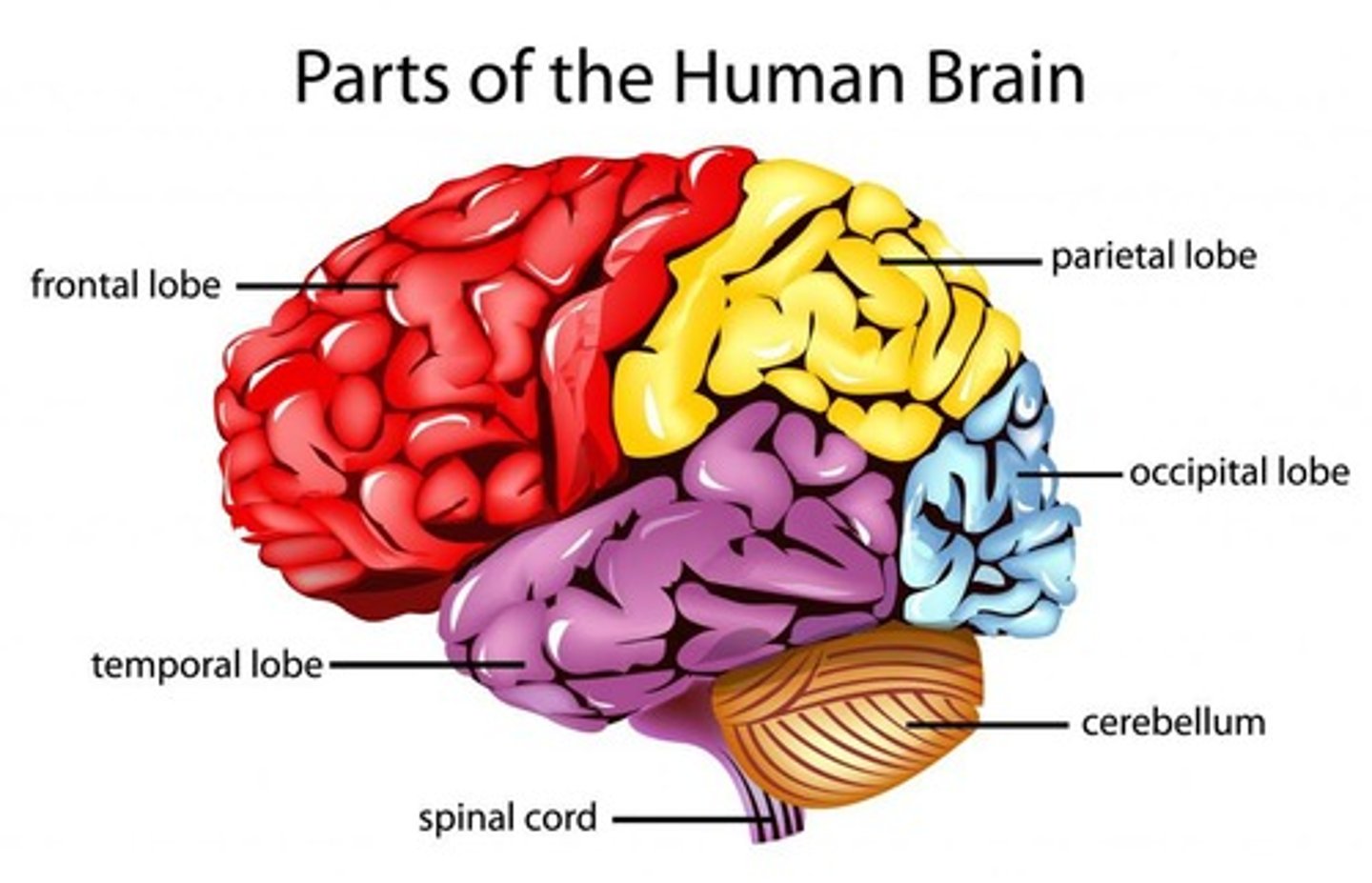
Cerebrum (Forebrain)
The two hemispheres are connected by the corpus callosum allowing info to be shared between the hemispheres.
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for walking, speech, intellect, judgment, and personality.
Temporal Lobe
Involved in hearing, smell, memory, and interpretation.
Parietal Lobe
Interprets sensory info from receptors and spatial understanding.
Occipital Lobe
Responsible for vision.
Motor Cortex
The area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements.
Sensory Cortex
Receives information from the skin surface and sense organs.
Broca's Area
Part of the left frontal lobe where the speech center is located.
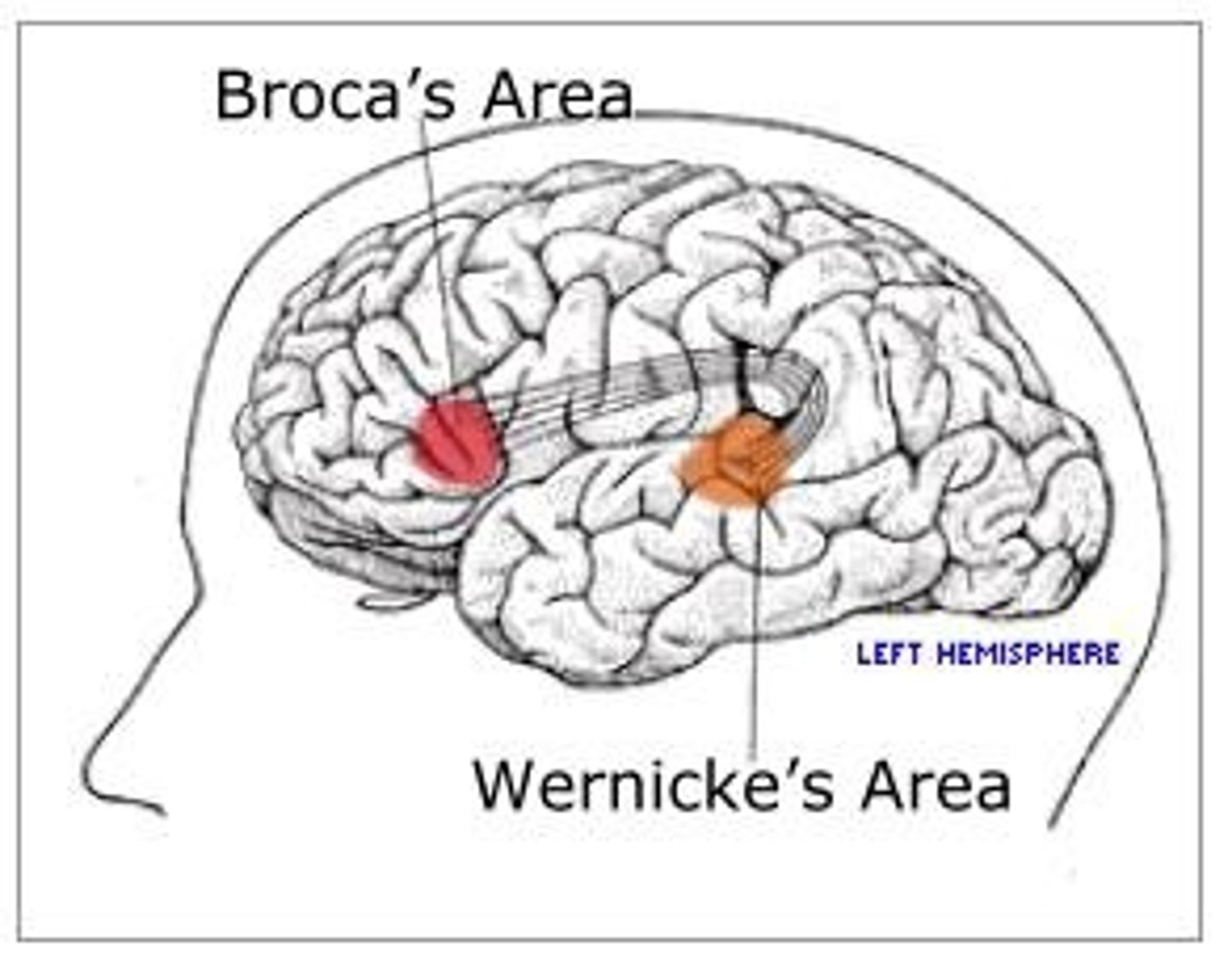
Wernicke's Area
Located in the left temporal lobe, responsible for understanding speech.
Cerebral Peduncle
Part of the midbrain involved in motor control.
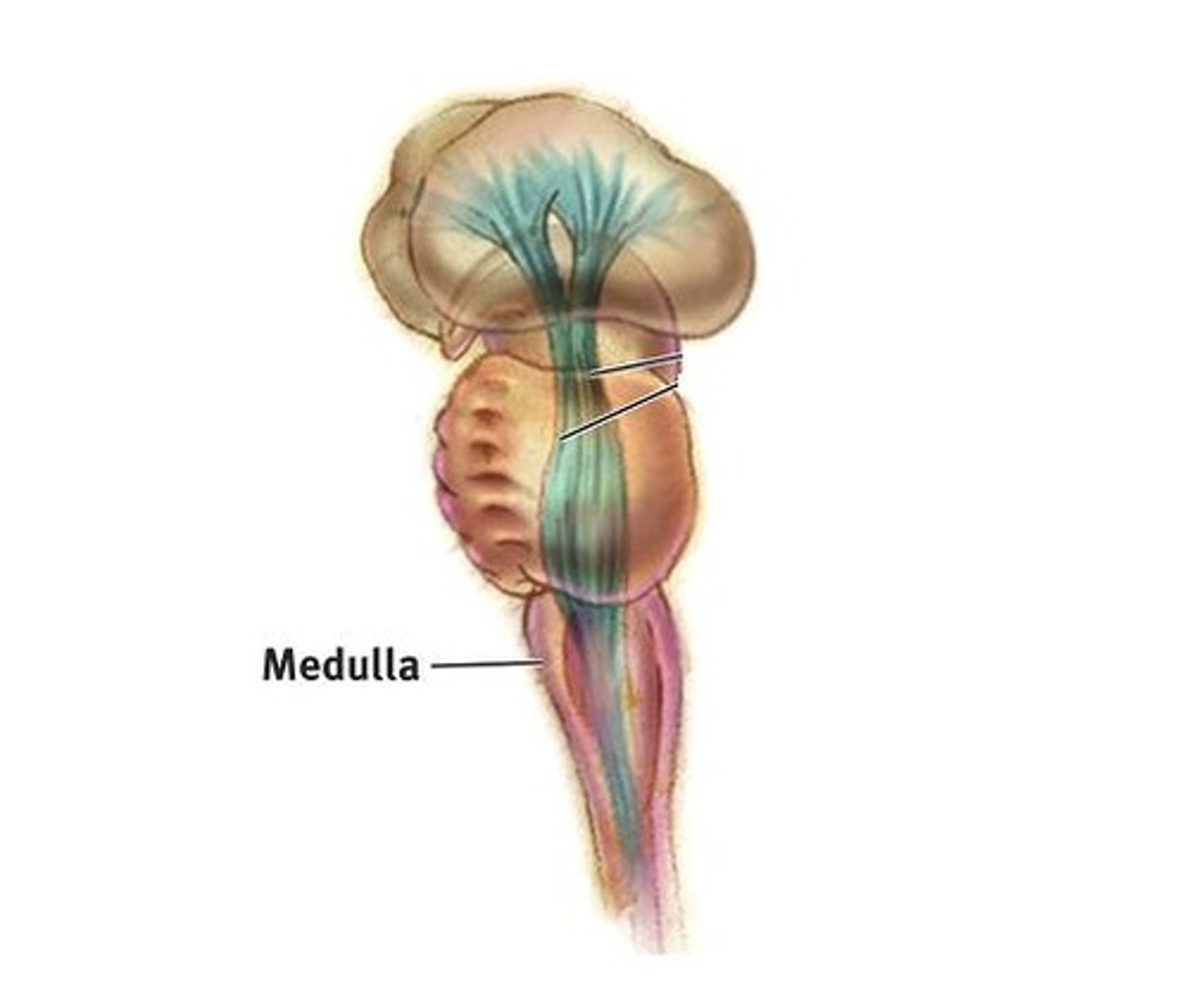
Medulla
The base of the brainstem that controls heartbeat and breathing.
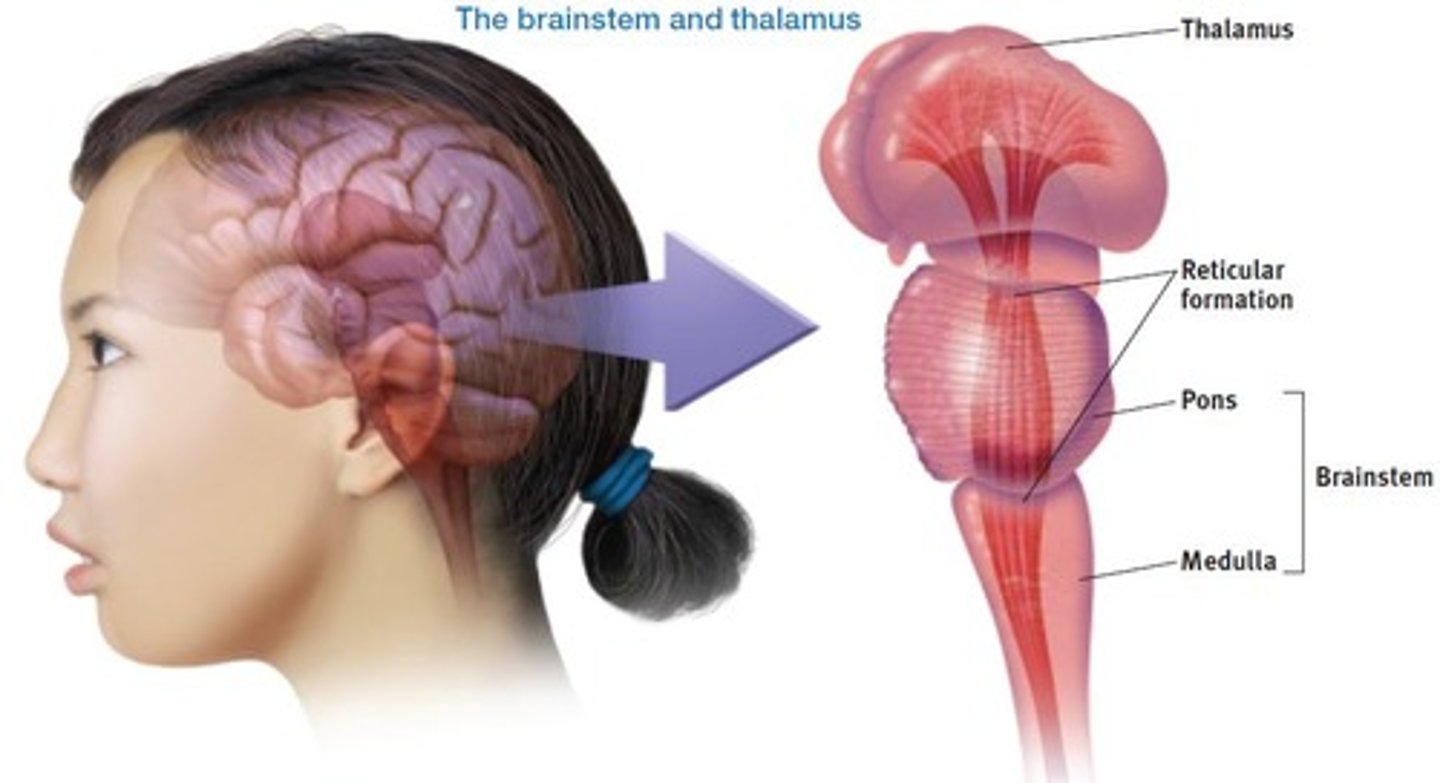
Pons
Involved in motricity and helps coordinate movement; directly linked with the cerebellum.
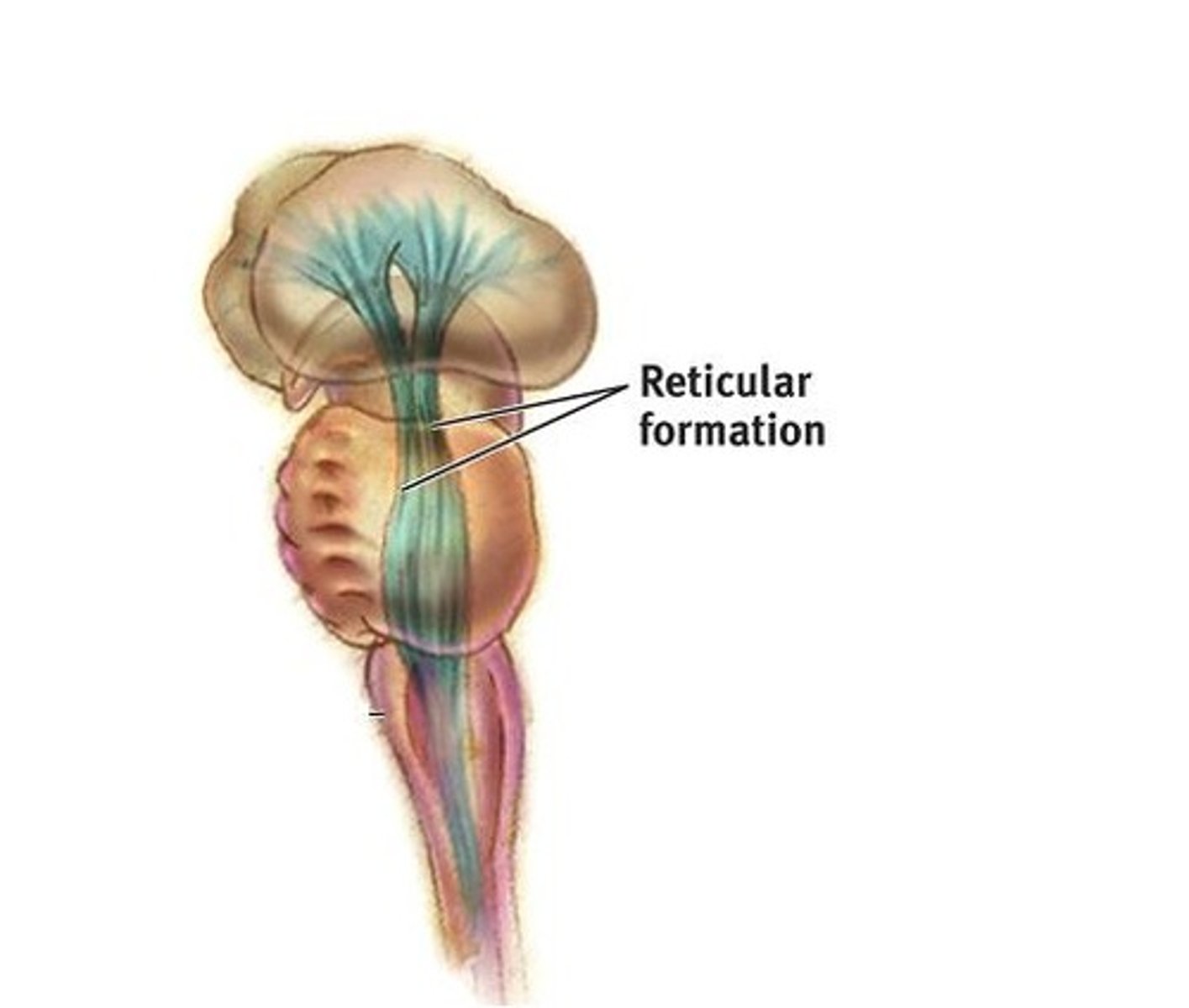
Reticular Formation
A nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal.
Thalamus
The brain's sensory switchboard that directs messages to sensory areas in the cortex.
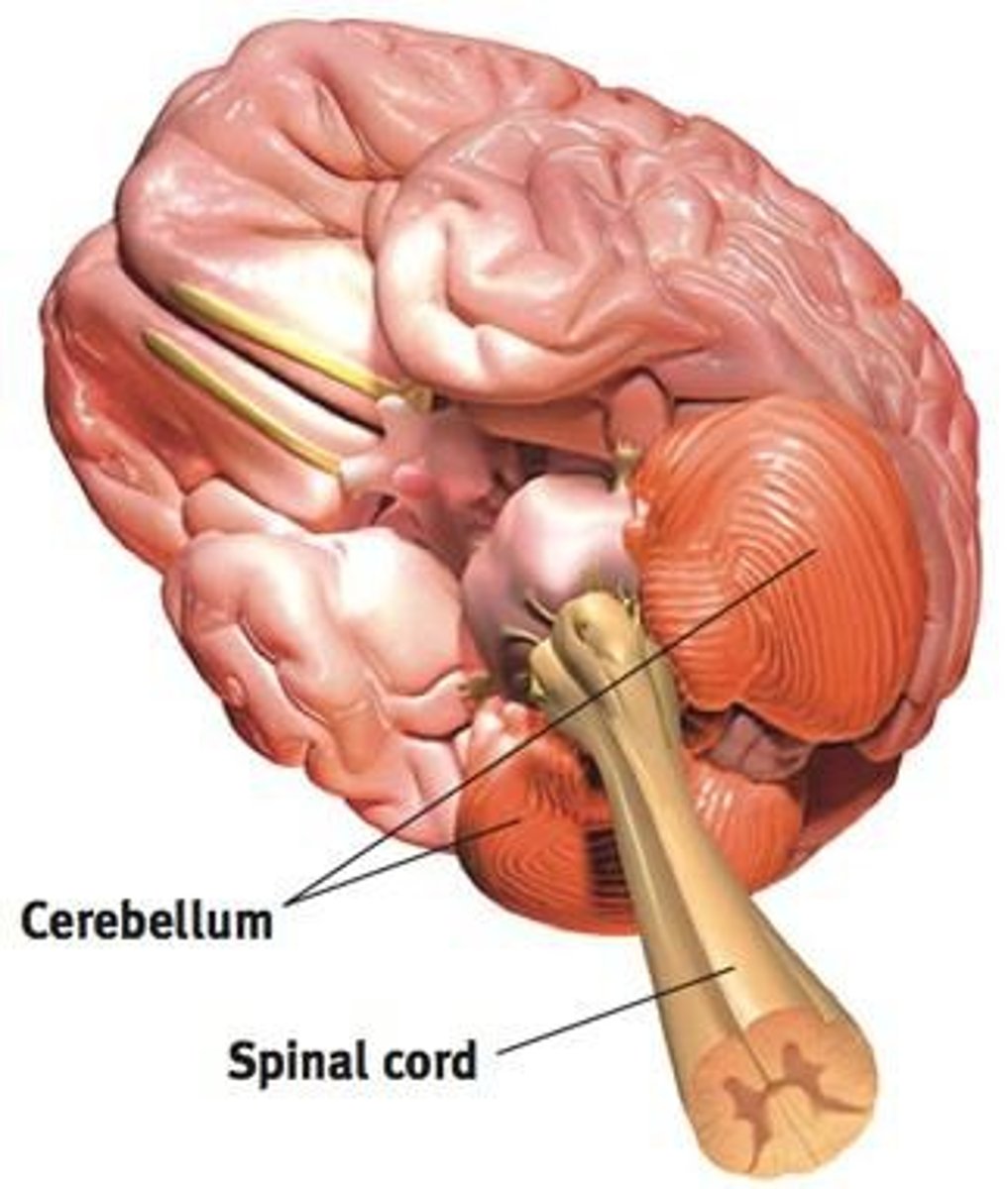
Cerebellum
Controls balance, agility, and voluntary movement, working with the pons.
Limbic System
A doughnut-shaped system of neural structures associated with emotions such as fear and aggression.
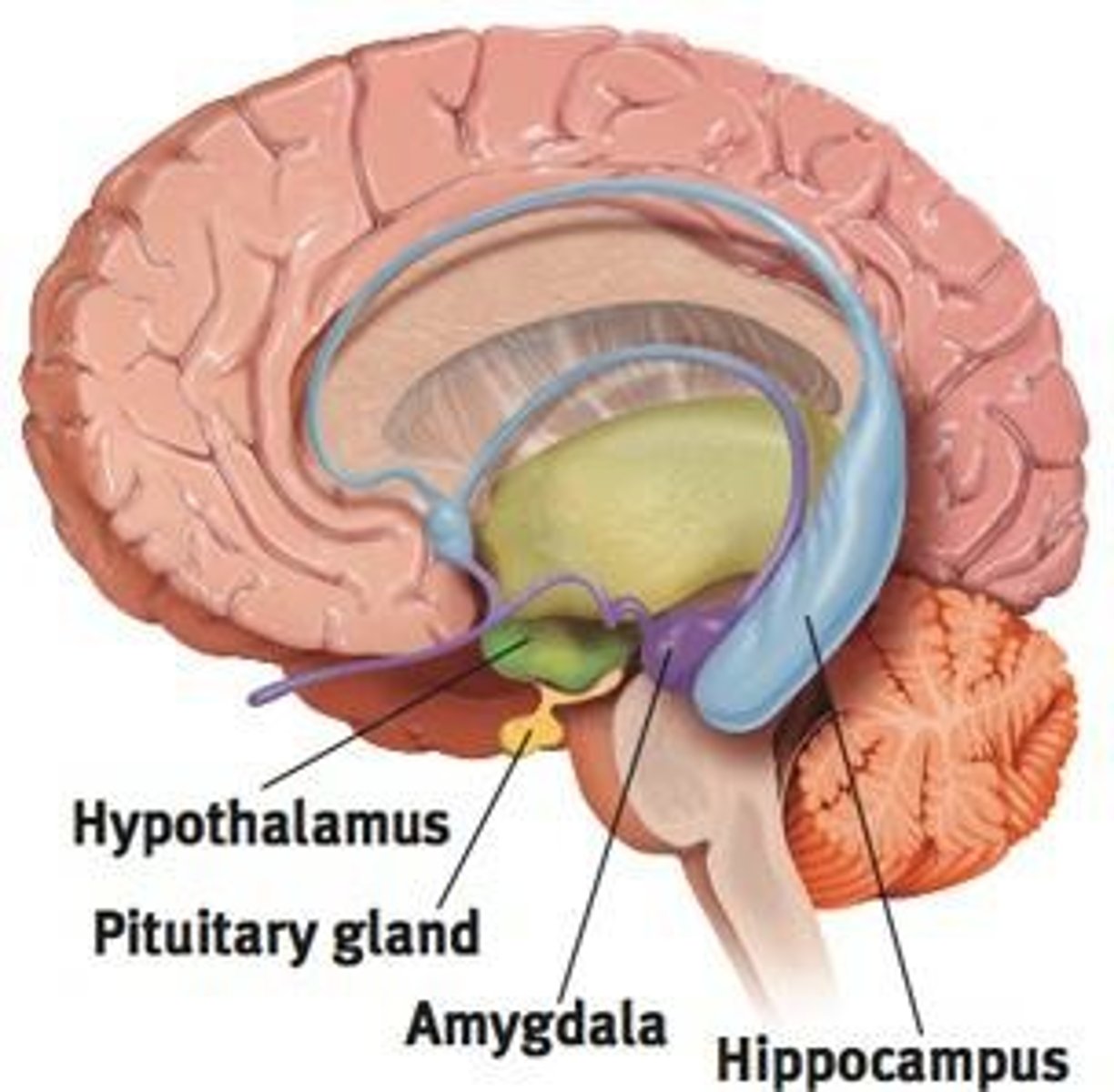
Amygdala
Involved in aggression, fear, and emotional memories.
Hypothalamus
Influences the pituitary gland.
Hippocampus
Supports long-term explicit memory (new information).
Neuron
A nerve cell that consists of many different parts.
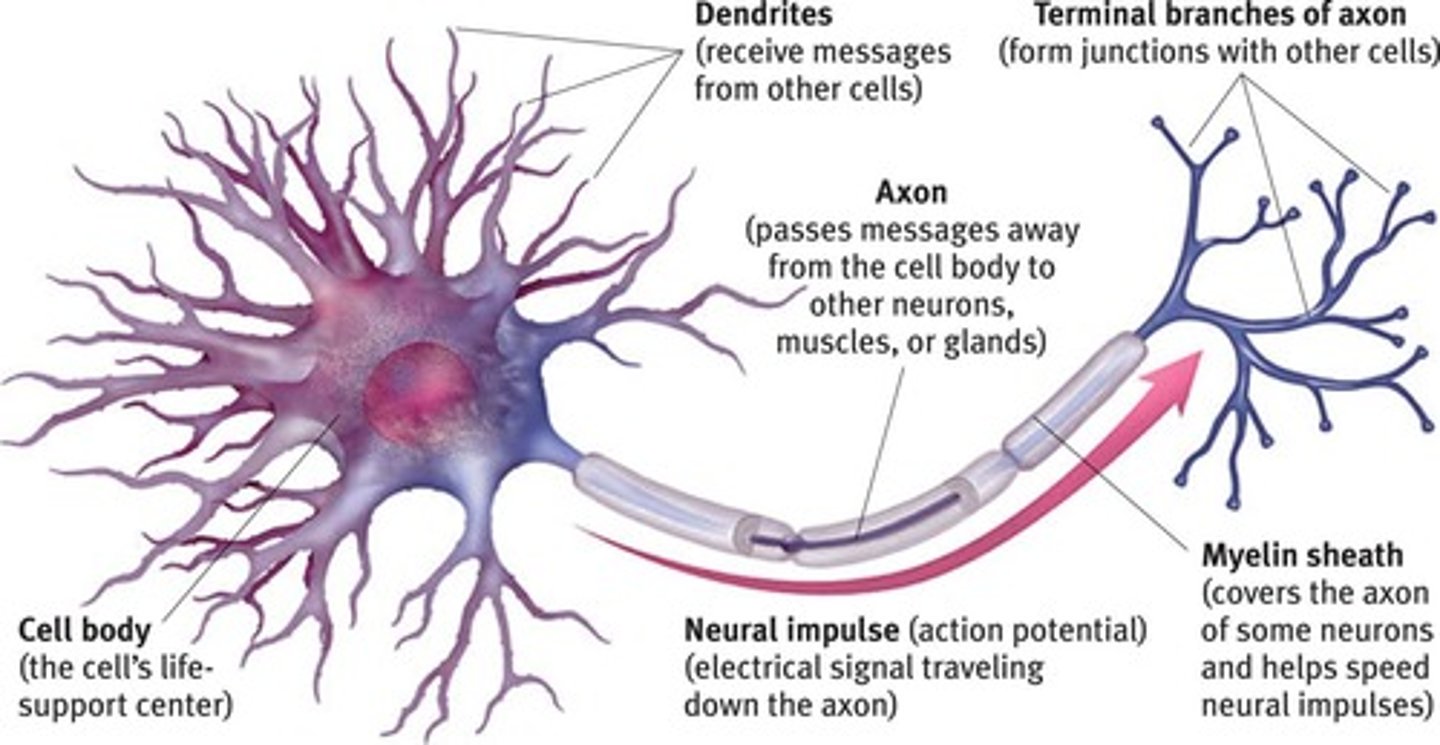
Cell Body
The life support center of the neuron.
Dendrites
Branching extensions at the cell body that receive messages from other neurons.
Axon
A long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin sheath to insulate and speed up messages.
Terminal Branches of Axon
Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons.
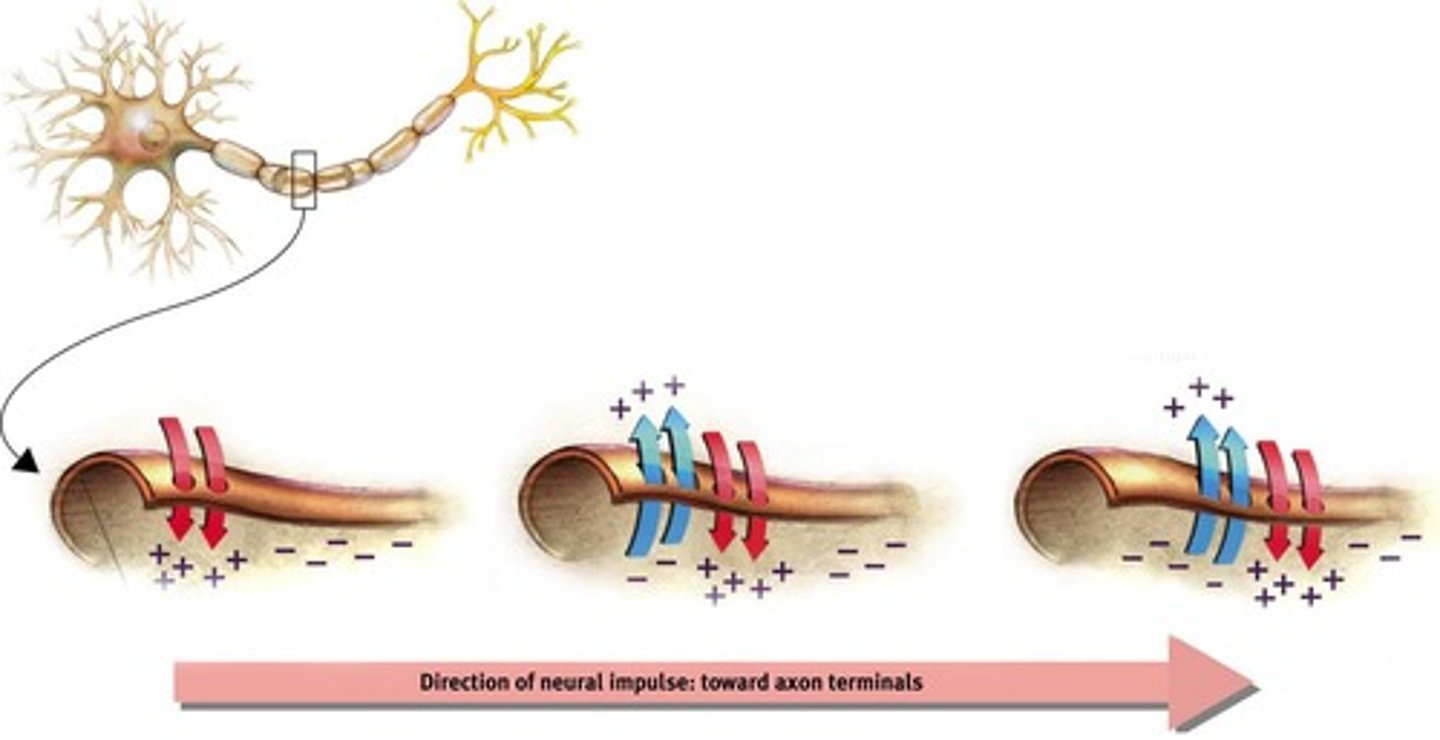
Action Potential
A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon, generated by the movement of positively charged atoms.
Synapse
A junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron.
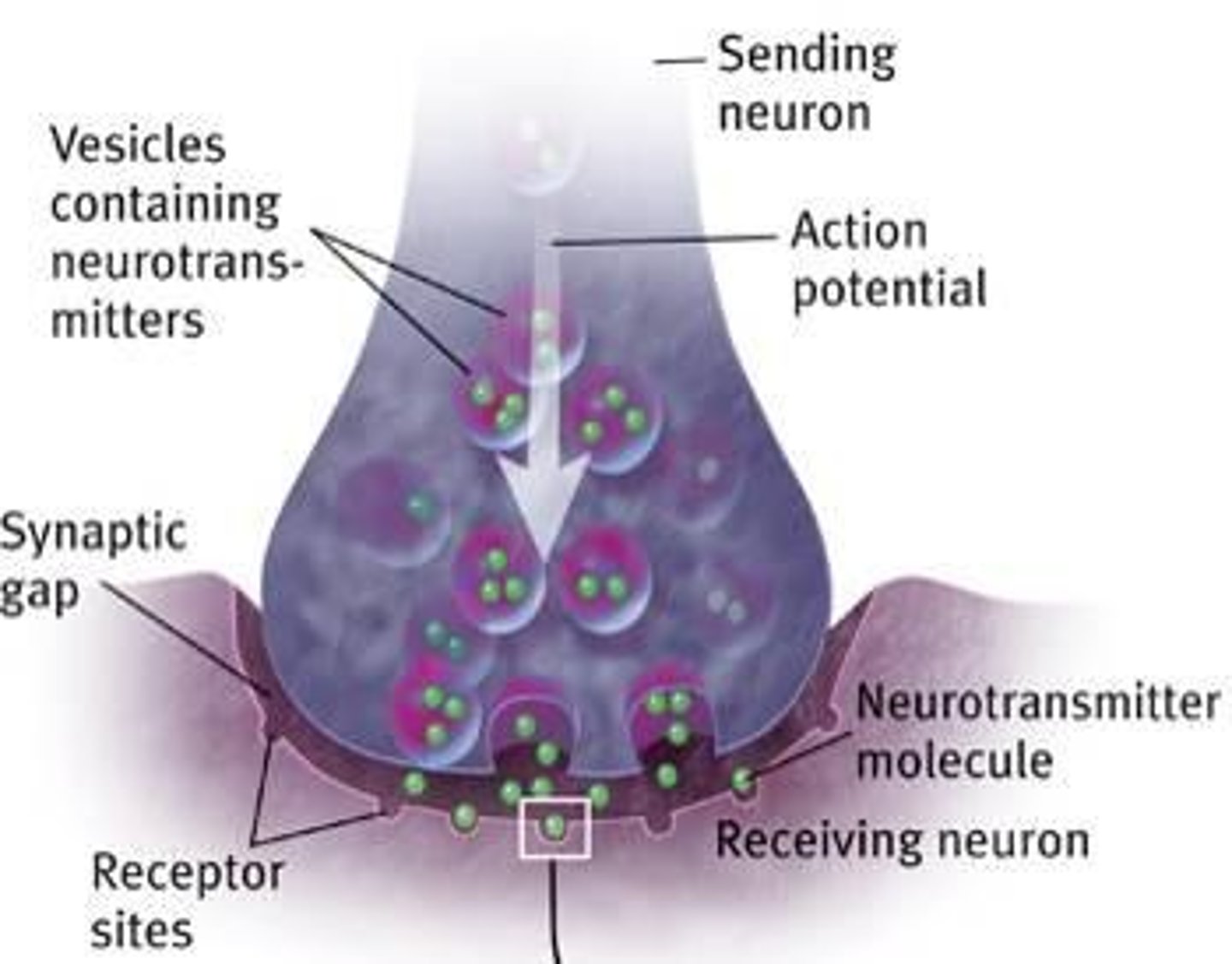
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals released from the sending neuron that travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron.
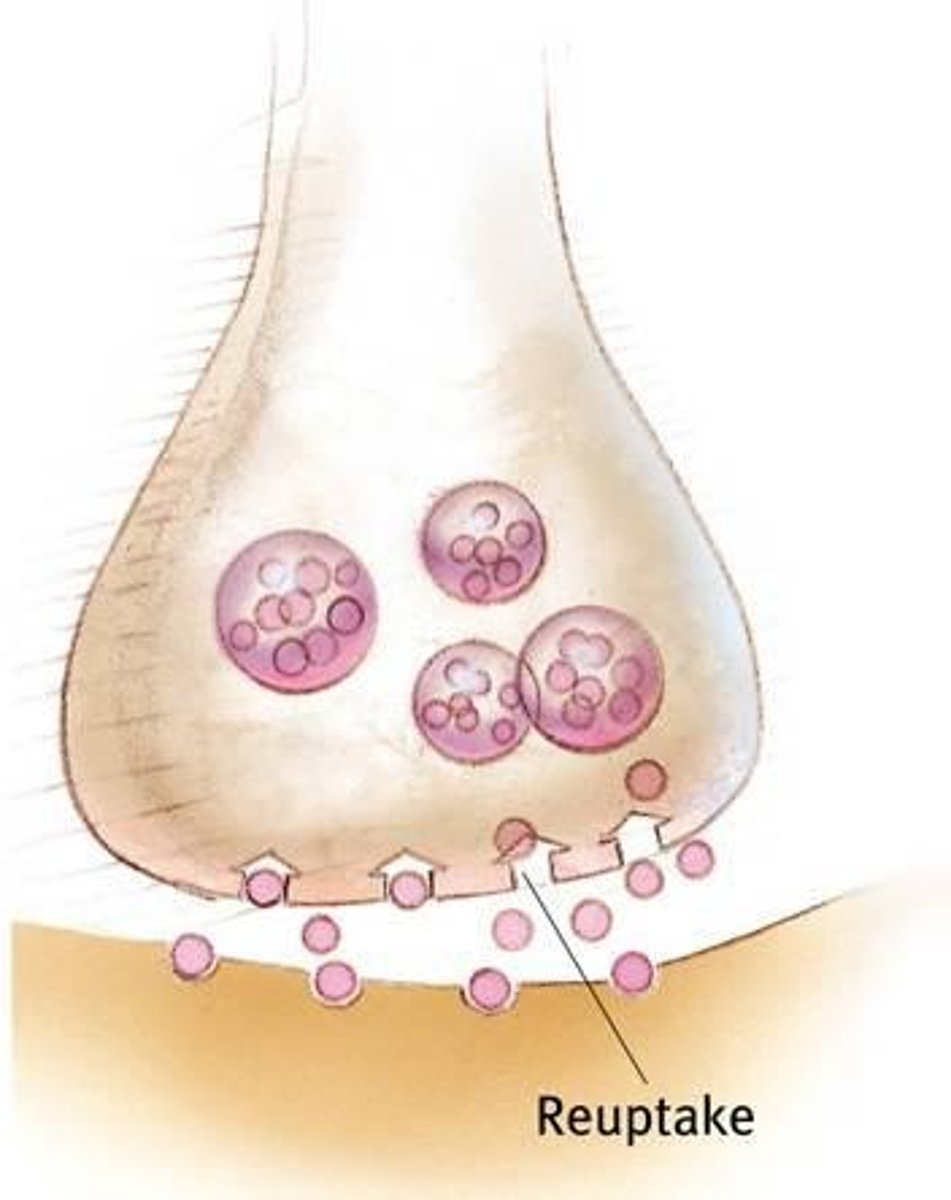
Reuptake
Neurotransmitters in the synapse are reabsorbed into the sending neurons through the process of reuptake.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another.
The Endocrine System
The body's "slow" chemical communication system carried out by hormones synthesized by a set of glands.
Hormones
Chemicals synthesized by the endocrine glands that are secreted in the bloodstream and affect the brain and many other tissues of the body.
Epinephrine
A hormone that increases heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, and feelings of excitement during emergency situations.
Pituitary Gland
Called the "master gland," it releases hormones that regulate other glands and regulates water and salt balance.
Forms of Consciousness
An awareness of ourselves and our environment.
Dual processing
The principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks.
Selective Attention
Our conscious awareness processes only a small part of all that we experience, and our attention is limited.
Inattentional Blindness
The inability to see an object or a person in our midst, as demonstrated by Simons & Chabris (1999) with a gorilla-suited assistant.
Change Blindness
A form of inattentional blindness where individuals fail to notice a change in the individual asking for directions.
Circadian Rhythms
Biological rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle, including sleep and wakefulness, and can be altered by artificial light.
Biological Clock
The internal mechanism that regulates circadian rhythms, triggered by light to decrease or increase melatonin.
Stages of sleep
The different phases of sleep, with a link between REM sleep and dreaming.
90-Minute Cycles During Sleep
With each 90-minute cycle, stage 4 sleep decreases and the duration of REM sleep increases.
Psychoactive Drug
A chemical substance that alters perceptions and mood, affecting consciousness.
Depressants
Drugs that reduce neural activity and slow body functions, including alcohol, barbiturates, and opiates.
Alcohol
A depressant that affects motor skills, judgment, and memory, increasing aggressiveness while reducing self-awareness.
Barbiturates
Drugs that depress the activity of the central nervous system, inducing sleep and reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgment.
Opiates
Opium and its derivatives (morphine and heroin) that depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety.
Stimulants
Drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions.
Caffeine
A stimulant that increases heart and breathing rates and other autonomic functions to provide energy.
Nicotine
A stimulant that increases heart and breathing rates and other autonomic functions to provide energy.
Cocaine
Induces immediate euphoria followed by a crash; can be smoked (crack), sniffed, or injected; inhibits reuptake of dopamine.
Ecstasy
A stimulant and mild hallucinogen that inhibits reuptake of serotonin, producing a euphoric high and potentially damaging serotonin-producing neurons.
Hallucinogens
Psychedelic drugs that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input.
LSD
A powerful hallucinogenic drug also known as acid.
THC
The major active ingredient in marijuana that triggers a variety of effects, including mild hallucinations.
Sensation
The process of detecting physical energy from the environment and converting it into neural signals.
Perception
The process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting sensations.
Transduction
The conversion of one form of energy into another that the brain can use.
Bottom-up Processing
Analysis of the stimulus that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the level of the brain and mind.
Top-Down Processing
Information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, drawing on experience and expectations.
Absolute Threshold
The minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time.
Subliminal Threshold
When stimuli are below one's absolute threshold for conscious awareness.
Sensory Adaptation
Diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation.
Vision
The most studied sense that transduces light energy into neural messages to the brain.
Wavelength
The distance from the peak of one wave to the peak of the next, determining the hue (color) of light.
Hue
The dimension of color determined by the wavelength of light.
Intensity
The amount of energy in a wave determined by the amplitude, related to perceived brightness.
Cornea
Transparent tissue where light enters the eye.
Iris
Muscle that expands and contracts to change the size of the opening (pupil) for light.
Lens
Focuses the light rays on the retina.
Retina
Contains sensory receptors that process visual information and sends it to the brain.
Retina
The light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing receptor rods and cones.
Rods
Peripheral receptors in the retina that detect black, grey, and white.
Cones
Foveal receptors in the retina that detect color.
Optic nerve
Carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain.
Blind Spot
Point where the optic nerve leaves the eye because there are no receptor cells located there.
Fovea
Central point in the retina around which the eye's cones cluster.