Intramolecular forces (BondingCharacteristics of Crystals)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is intramolecular force?
bonds within a molecule that hold the atoms together
What are lattice structures?
repeating, periodic 3D arrangements of interconnected unit cells found in nature and engineering
What are lattice points?
represents the position of a repeating unit (like an atom, ion, or molecule) in a crystalline
(type of solid material where the atoms, ions, or molecules are arranged in a highly ordered, repeating pattern that extends in all three spatial dimensions.)
What are the 4 types of crystals?
ionic, covalent network, metallic, covalent molecular
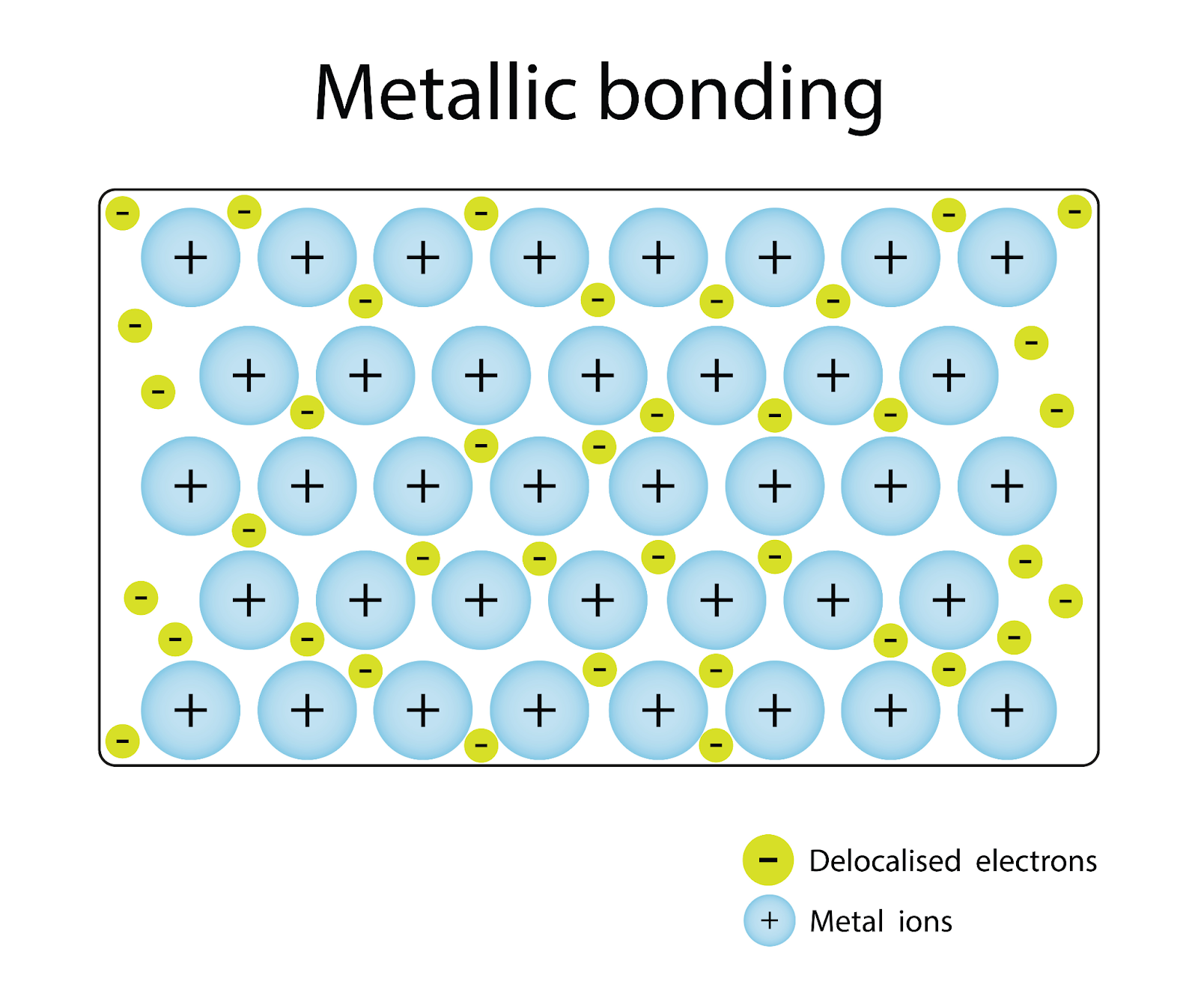
What is metallic bonding?
bonds between a metal and metal
Describe metallic bonding (2)
atoms have low IE, it takes very little energy to remove an e- (e.g. being at room temp creating cations)
atoms have low EA, means that other atoms are not willing to take in the lost e-
thus, the lost e- “wonders around”
Lattice structure of metallic bonds
cations form the lattice points of a network with the e- floating in a sea around them
The structure is held together by electrostatic forces (attraction between opposite charges) between the cations and e-
6 metallic crystals properties
metallic bonds (50-800 kj/mol)
high melting and boiling points
very high electrical and thermal conductivity
usually malleable and ductile
hard
insoluble
4 factors affecting metallic crystal properties
charge on cation
cationic radius
# of electrons in the “sea”
impurities (alloys)
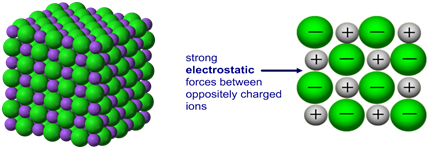
What is ionic bonding?
bonds between metal and non-metal
Describe ionic bonding (2)
metal has low IE and will readily giving up its e- to form a cation
non-metal has high EA which means that it will take loose e- to form an anion
cation and anion are then bonded together by electrostatic force of attraction
Lattice structure of ionic bonds
lattice structure that is created alternates cations and anions (ions) at the lattice points
These bonds lock the ions into place so that they don’t move freely
6 ionic crystals (salts) properties
ionic bonds (600-4000 kj/mol)
high melting point and boiling point
electrical and thermal conductivity depends on the state of the ionic crystals
poor conductors as solids (when ions are locked in place)
good conductors as aqueous (when ions are free to move)
brittle
ionic crystals are not malleable because the ions are locked into place
when a force is applied, it can push the ions down one row, so that the anions are lined up (and the cations are lined up)
this causes the crystal to repel and shatter
hard
because ionic bonds are quite strong
generally soluble in polar solvents
5 factors affecting ionic crystal properties
charge on cation
charge on anion
packing of ions
ratio of ions involved
impurities
What is covalent bonding?
bonds between non-metal and non-metal
Describe covalent bonding (2)
since both atoms are non-metals they:
both have high IE, neither is willing to give up any valence e-
both have high EA, both try to grab onto additional e-
This results in the sharing of e- between the 2 nuclei
What are the 2 types of lattice point a covalent molecular can have?
non-polar and polar covalent
non-polar covalent
ΔEN < 0.4
pure covalent bond
equal sharing of electrons between the 2 nuclei
polar covalent
0.4 < ΔEN < 1.7
unequal sharing of electrons between the 2 nuclei
partial positive charge (δ+) on the atoms with lower EN
partial negative charge (δ-) on the atom w/ higher EN
6 non-polar covalent crystals properties
dispersion forces (0-50 kj/mol)
very low melting and boiling points
extremely low electrical and thermal conductivity
extremely fragile (in terms of malleability and ductility)
very soft (in terms of hardness)
soluble in non-polar and slightly polar solvent
6 polar covalent crystals properties
hydrogen bonding or dipole-dipole
low melting and boiling points
very low electrical and thermal conductivity
fragile (in terms of malleability and ductility)
soft (in terms of hardness)
generally soluble in polar solvent
6 covalent network properties
covalent bonds 300-800 kj/mol
very high melting and boiling points
low electrical and thermal conductivity (with some exceptions)
not malleable or ductile
very hard (in terms of hardness)
insoluble
(lattice points are atoms)
What are the 4 bonds intramolecular can form?
single bond
double bond
dative bond/ coordinate covalent bond
triple bond
What are allotropes? (2)
Different structural forms of the same element
Exist in the same physical state, but have different arrangements of atoms and have different properties
What are 3 allotropes of carbon?
diamond, graphite, and fullerenes (buckyball)
What are 3 allotropes of silicon?
asbestos, mica, and quartz