Genetics 3 Quiz
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Mutation
Heritable change in genetic material
3 types of mutations: Gene Mutations
Relatively small change in DNA that affects a single or few genes
3 types of mutations: Chromosome mutations
Changes in chromosome structure
3 types of mutations: Genome mutations
Changes in chromosome number
De novo spontaneous mutations are
more likely to be harmful than beneficial to the individual and more likely yet to be neutral
Mutation rate
is the likelihood that a gene will be altered by a new mutation
Mutation rates vary…
substantially between species and even within different strains, groups, or variants of the same species.
Hot spots
Locations within the chromosome that are more susceptible to mutation
Somatic hypermutation (SHM)
Mutation affect regions of immunoglobulin genes which diversifies B cell receptors to expand their recognition range.
Mutation Frequency
Number of mutant alleles divided by the total number of that allele in a population.
Mutation frequency depends on:
mutation rate
Timing of mutation
Likelihood that the mutation will be passed on to future generations
Point Mutation
Change in a single base pair.
Transition
Change of a pyrimidine (C,T) to another pyrimidine (C,T) or a purine (A,G) to another purine (A,G).
Transversion
change of a pyrimidine to a purine or vice versa
Silent mutations
do not alter amino acid sequence of polypeptide
Missense mutation
base substitutions in which an amino acid change occurs
nonsense mutation
base substitutions that change a normal codon to a stop codon
Frameshift mutation
The addition or deletion of bases not divisible by three.
Forward mutation
changes the wild-type genotype into a new variation
Reverse mutation
Changes mutant allele back to the wild-type allele.
Deleterious mutation
Decrease the chances of survival
Beneficial mutation
Enhance the survival or reproductive success of an organism
Suppressor mutations
a second mutation that counteracts the effects of a first mutation.
Suppressor mutation types: Intragenic
Second site is within the same gene as the first mutation
Suppressor mutation types: Intergenic
Second site is in a different gene from the first mutation.
Chromosomal rearrangement can affect a gene by:
Chromosomal breakpoint occurring within a gene
Position Effect
A gene is left intact but the expression is altered because of its new location.
Two common reasons for position effects:
Movement to a position next to regulatory sequences
movement to a heterochromatic region.
Germ-Line
Mutation can be passed on to future generations because it occurs in sperm or egg cells.
Somatic cell
Mutation can’t be passed on to future generations because occurs directly in a body cell.
Spontaneous mutations
Result from abnormalities in cellular/biological processes
Induced mutations
Caused by environmental agents, like chemical or physical agents.
Spontaneous mutation arise by three types of chemical changes
Depurination
Deamination
Tautomeric shift
Spontaneous mutations can occur by mispairings or “slipping” during DNA replication
Simple mispairing not corrected by proofreading
Wobble Pairing
Additions/deletions due to slippage and looping out
Depurination
Removal of a purine (guanine or adenine)
Apurinic site
Covalent bond between deoxyribose and purine base is somewhat unstable and it undergoes hydrolysis (beta-N-glycosidic link) that releases the base from the sugar.
Readily repaired and happens very frequently
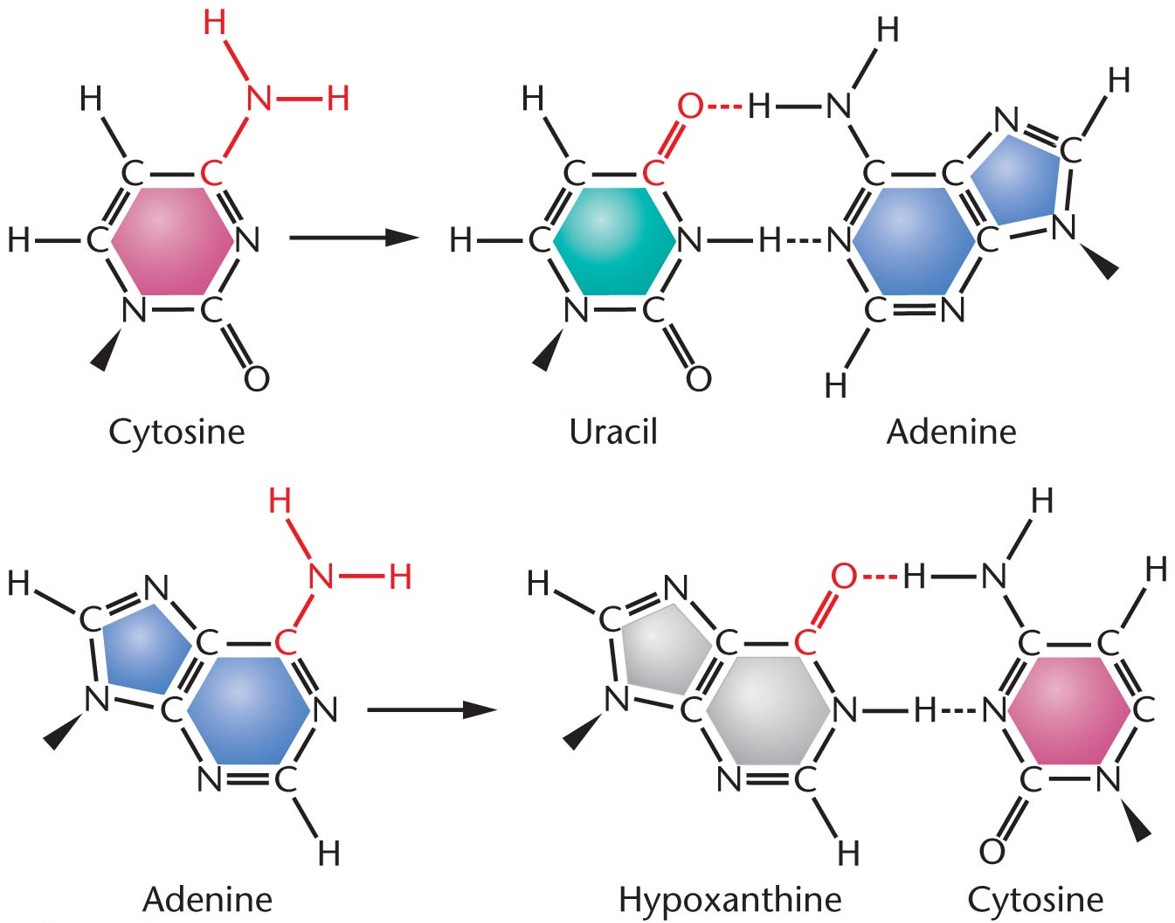
Deamination
Removal of amino group from cytosine (C) resulting in uracil (U)
Tautomeric shift
Temporary change in base structure
Stable form of thymine and guanine is
Keto form
T and G can interconvert to an enol form
Stable form of adenine and cytosine is
Amino form
A and C can interconvert to an imino form
If DNA loops out on template strand
Pol III skips bases
If DNA loops out on daughter strand
Pol III adds random bases
Slipped Strand Mispairing
DNA strand loops out and becomes displaced or if DNA polymerase slips then small insertions and deletions can occur resulting in mutations during replication.
Trinucleotide repeat expansion (TNRE)
Number of 3 nucleotide repeat sequences can increase from one generation to the next
IF TNRE located in noncoding regions then:
May cause abnormal changes in RNA structure
Produce methylated CpG islands which may silence the gene
TNRE disorders
Severity of disease tends to worsen in future generations, called anticipation.
Chemical mutagens are categorized as:
Base analog
Base modifiers
Intercalating agents
Base Analog
May change pairing
Base modifiers
Change one base into another
Intercalating agents
Alter shape of DNA and cause deletion or addition
Physical mutagen types
Ionizing radiation
Nonionizing radiation
ionizing radiation
X-rays and gamma rays
Short wavelength and high energy
Penetrate deeply into biological molecules
Create chemically reactive molecules (free radicals)
Ionizing radition can cause
Base deletions
Oxidized bases
Single nicks in DNA strands
Cross-linking
Chromosomal breaks
Nonionizing radiation (includes UV light)
Lower energy than ionizing
Cannot penetrate deeply into biological molecules
Causes formation of cross-linked pyrimidine dimers (C or T)
Pyrimidine dimers may cause mutations when that DNA strand is replicated
Common test for mutagen
Ames test
Ames test
Uses a strain of Salmonella typhimurium that cannot synthesize the amino acid histidine and has a point mutation in a gene involved in histidine biosynthesis. Second mutation may occur resotring ability to synthesize histidine. This test monitors rate at which second mutation occurs.