Organic Chemistry 2 Exam 2
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Conjugated system
Any double-single-double bond
Allene
Double-double bond
NBS
Good source of bromine
hv required
CCl4 solvent
Allylic bromination
Allylic position
-C=C-C (the C on the right is the Allylic C)
Conjugated dienes
More stable
Shorter bond length
Types of reactions of conjugated dienes
Electrophilic Addition
Diels Alder Reaction
(Has Markovnikovs addition)
Electrophilic addition of conjugated Dienes has which products
Kinetic
Thermodynamic
Kinetics product
1,2- adduct
Has more % at Room temperature
Thermodynamics product
1,4- adduct
Has more % at high temperature
Formal charge formula
(# of valence electrons) - (lines + dots)
Diels-Alder Reaction
Diene
Dienophile
Diene
Has 2 carbons with 2 double bonds
One Double bond is used to form bond with dienophile while other moves to single bond to form double bond ( 1 will go away)
Dienophile
Has 2 carbons with a double bond and an Electron withdrawing group
Conditions of Diene
s-trans → s-cis
locked in s-cis
locked in s-trans
hard to reach/react
Diene that goes from s-trans to s-cis
Reactive but slow reaction
Diene that is locked in s-cis
Best position for dienes
Very reactive
Dienes locked in s-trans
Unreactive
Dienes that are unable to reach Dienophiles
Cannot adopt s-cis conformation because of steric hindrance
Unreactive
If there is no electron withdrawing group then the molecule is not a…?
Dienophile
T or F- having more electron withdrawing groups on the Dienophile is better
True
T or F- The stereochemistry of Dienophile changes after reacting with dienes
False
Axial position
Straight
Endo
Equatorial position
Slanted
Exo
T or F- endo position is more favorable than exo position
True
Toluene
CH3
Phenol
OH
Aniline
NH2
Benzoic acid
CO2H
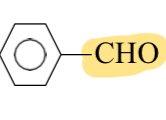
Benzaldehyde
CHO
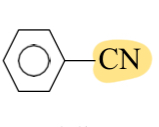
Benzonitrile
CN
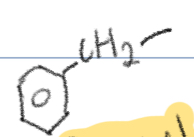
Benzyl
-CH2–
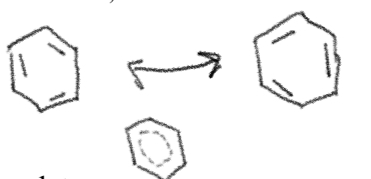
Benzene
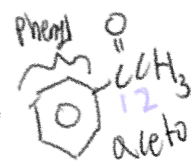
Acetophenone
COCH3
Nitrobenzene
NO2

Phenyl
Name for when benzene is connected to something else
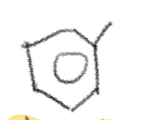
Ortho
1,2
Meta
1,3
Para
1,4
Benzene is…?
Unusually very stable
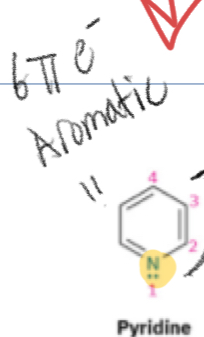
Huckel’s rule
Benzene is a conjugated aromatic compound, aromatic compounds are:
Planar
Cyclic
Conjugated
Has a total of 4n+2(pi) electrons (where n= whole numbers)
4 pi electrons means the compound is..?
Anti aromatic
Anti aromatic
Less stable than aromatic
Very reactive
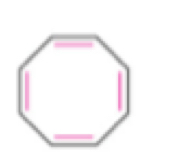
Cyclooctatetraene
Anti-aromatic because it is not planar and is flat
What contributed to the pi electron system besides pi bonds(double bonds)
Electrons and lone pairs
+, .., and .
Leave empty sp2 orbital To make molecule aromatic
Heterocycles
When carbon is replaced by a nitrogen, sulfur, etc. which makes the molecular not similar
When a nitrogen has lone pairs but is near a double bonds, it…?
Is not in the pi system
T or F- A (+) sign adds a pi electron
False
If lone pair is in sp2 orbital, it is..?
Not a part of the pi system
Aromatic vs anti-aromatic
Aromatic is stable and not a solvent because it is not reactive whereas anti-aromatic is the opposite
Lewis acid
Electron accepter
Types of reactions for alkenes vs aromatics
Alkenes: Electrophilic addition
Aromatics: Electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS)
Bromination
—Br2/FeBr3 →
Product is Br attached to benzene
Chlorination
—Cl2/FeCl3–>
Product is Cl attached to benzene
Iodination
—I2/CuCl2—>
Product is I attached to benzene
Electrophile
Lewis acid
Accept electrons
Has a Positive charge
Base
Has the negative sign
The catalyst after gaining an atom
Nitration electrophile
NO2 with 2 double bonds attached to each O and a positive charge on N
Nitration
—HNO3/H2SO4–>
Product is NO2 attached to benzene
Sulfonation
—SO3/H2SO4–>
Product is SO3H
Electrophilic is HSO3+ (sulfanyl)
Friedle-Crafts Alkylation
—alkyl halide/AlCl3–>
Product is alkyl halide attached to benzene
Friedel-Crafts Acylation
—Acyl Halide/AlCl3–>
Product is acyl halide attached to benzene
Nitric acid
Used as the first step/reaction in nitration
HNO3

Prep step
Always required
Before the first step in an EAS reaction
X2 breaks bond and attached to Lewis acid catalyst and forms a strong Electrophilic and base
Resonance creates a stable…?
Carbocation
Catalyst
Speeds up a reaction
Shown in first step and comes back as a product because it is not used up
The energy of addition reactions are ___ than the energy of substitution reactions
Greater
Friedel Crafts Limitations
Only works with alkyl Halides (not Aryl halides, double bonds, or cyclo structure)
Difficult to stop reaction after a single substitution (no alkylation)
Electron rearrangement may occur (primary → secondary)
Acyl
RCO
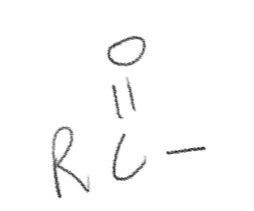
Ortho and para-directing
Activating
Meta-directing
Deactivating
Halogens
Weakest out of the ortho para directing
F,Cl,Br,I
Sigma Donors
Second strongest out of the ortho para directing
-R
Alkyl (ex. CH3)
Aromatic ring/benzene
Aryl (RCO)
Pi donors
Strongest out of ortho para directing
NH2
OH
OR
NHCOCH3
Non-binding electron pairs
Carbonyls
Weakest out of the meta-directing
COR
COOH
COOR
Other in the meta directing
Strongest in meta directing
SO3H
C (triple bond) N
NO2
N+R3
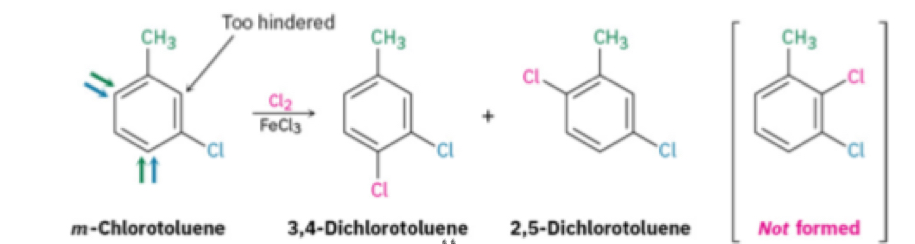
Steric hindrance when doing additivity of effects
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
Occurs in 2 steps
Not SN2
Forms carbanion (intermediate)
Halogen(Good leaving group)
EWG in ortho or para position to the leaving group
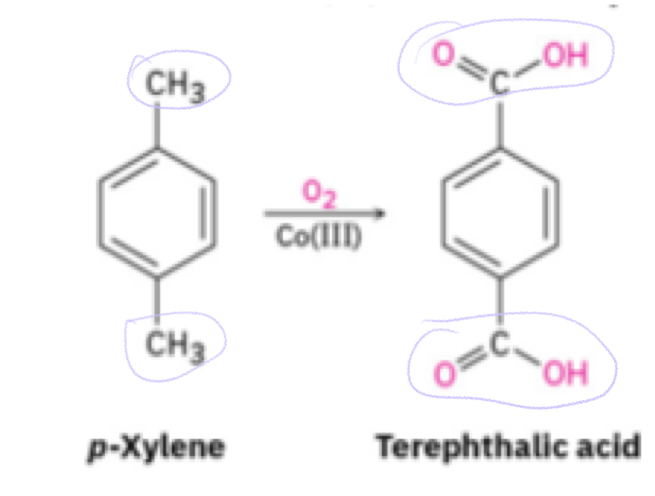
Oxidation of aromatic compounds
KMNO4 (strong oxidizing agent)
Benzylic hydrogen
Benzylic hydrogen
Hydrogen that is attached to the first carbon
If there are 2 Benzylic hydrogens, reaction happens twice
Bromination of alkylbenzene side chains
Considered to be oxidation
Adding a halogen
NBS (N-Bromosuccinamide)
Radical reaction
Reduction of aromatic compounds
Changes all oxygen to Hydrogen when friedel crafts acylation is involved (RCO)
—H2, Pd/C or Pt or Rh/C/ ethanol—>