meiosis quiz
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
meiosis
cells that undergo meiosis do not undergo mitosis!
meiosis produces reproductive cells with half the number of chromosomes from the parent cell. these cells are only from sex organs (ovaries/testes in animals)
only type of cell undergoing meiosis is germ cells
gamete
the egg or the sperm. meiosis creates gametes
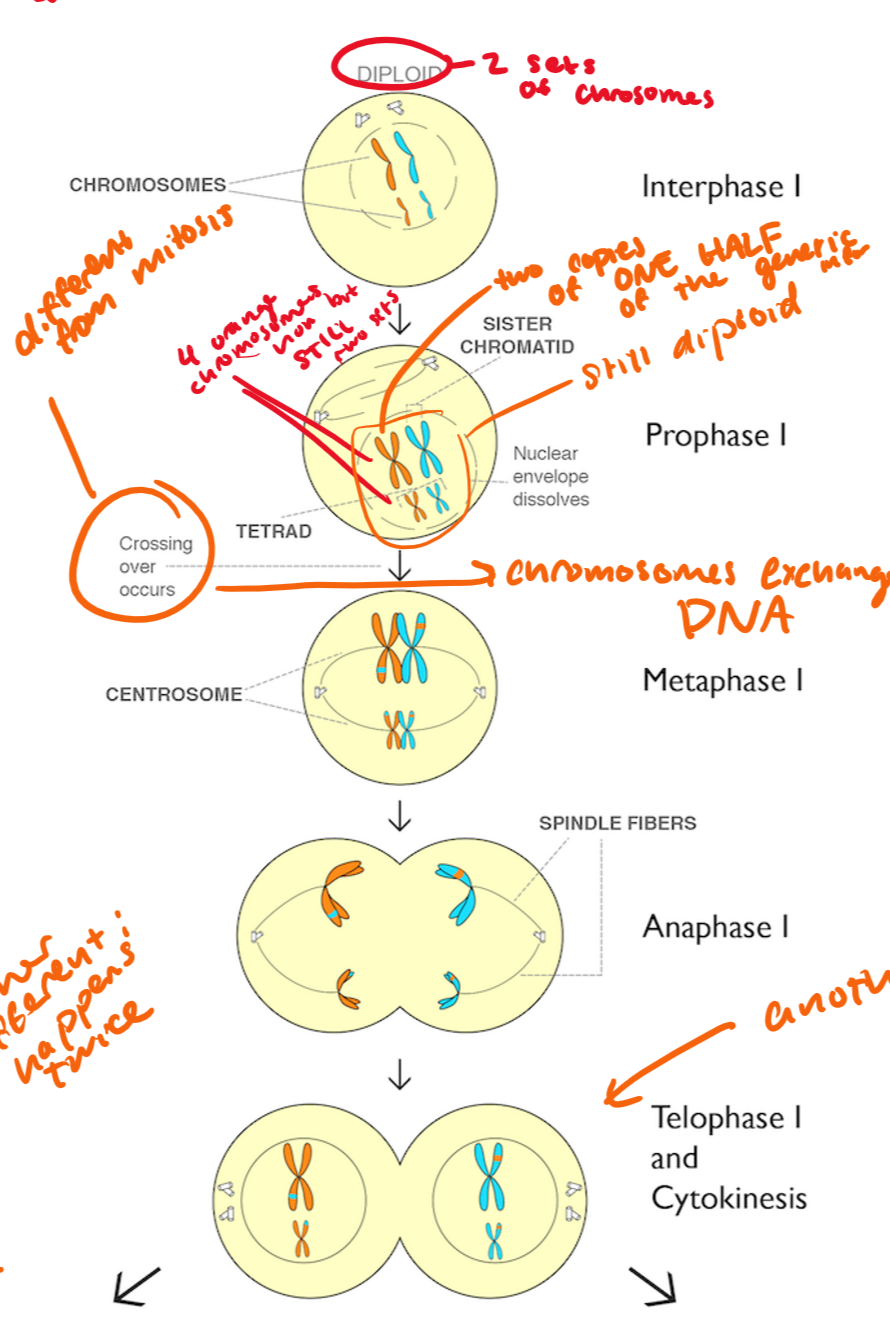
prophase I
chromsomes condense, nucleus dissolves, spindle fibers form
tetrads form, crossing over occurs
tetrad=two “Xs” (2 homologous chromosomes) coming together to form a tetrad
you have two copies of ONE HALF of the genetic material
it is still diploid
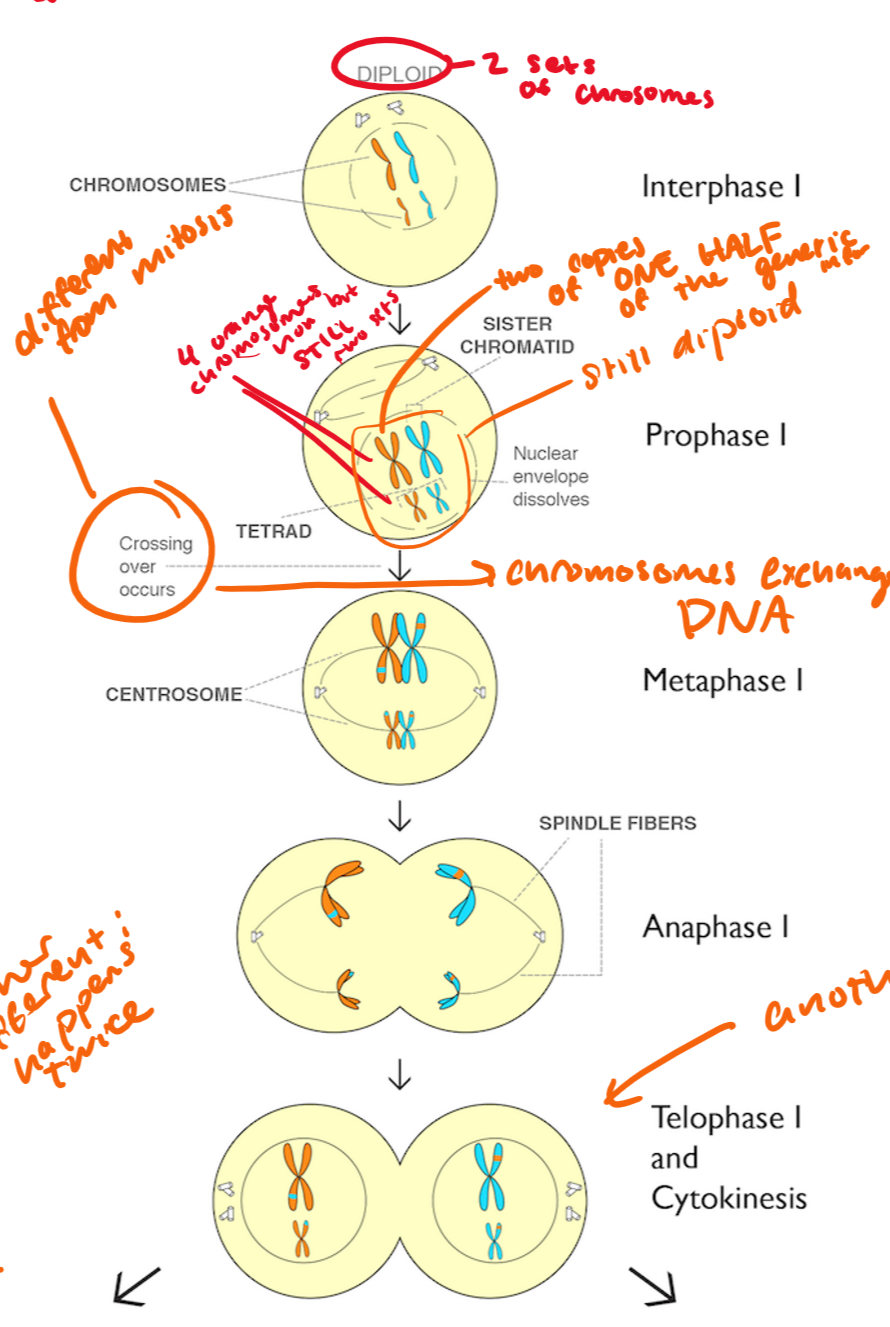
metaphase I
pairs of homologous chromosomes line up on the cell equator
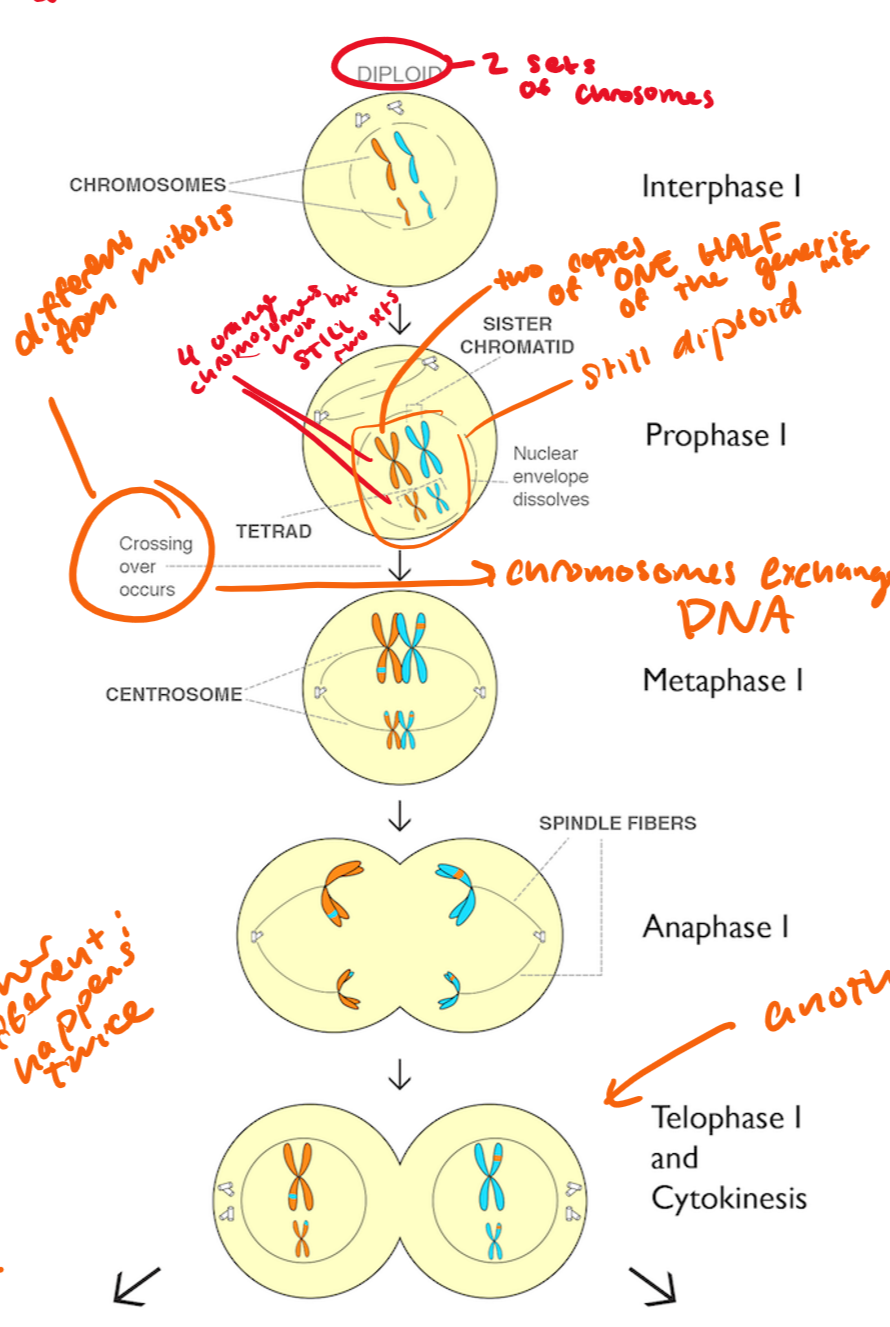
anaphase I
homologous chromosomes are pulled apart (NOT SISTER CHROMATIDS), cytokinesis begins
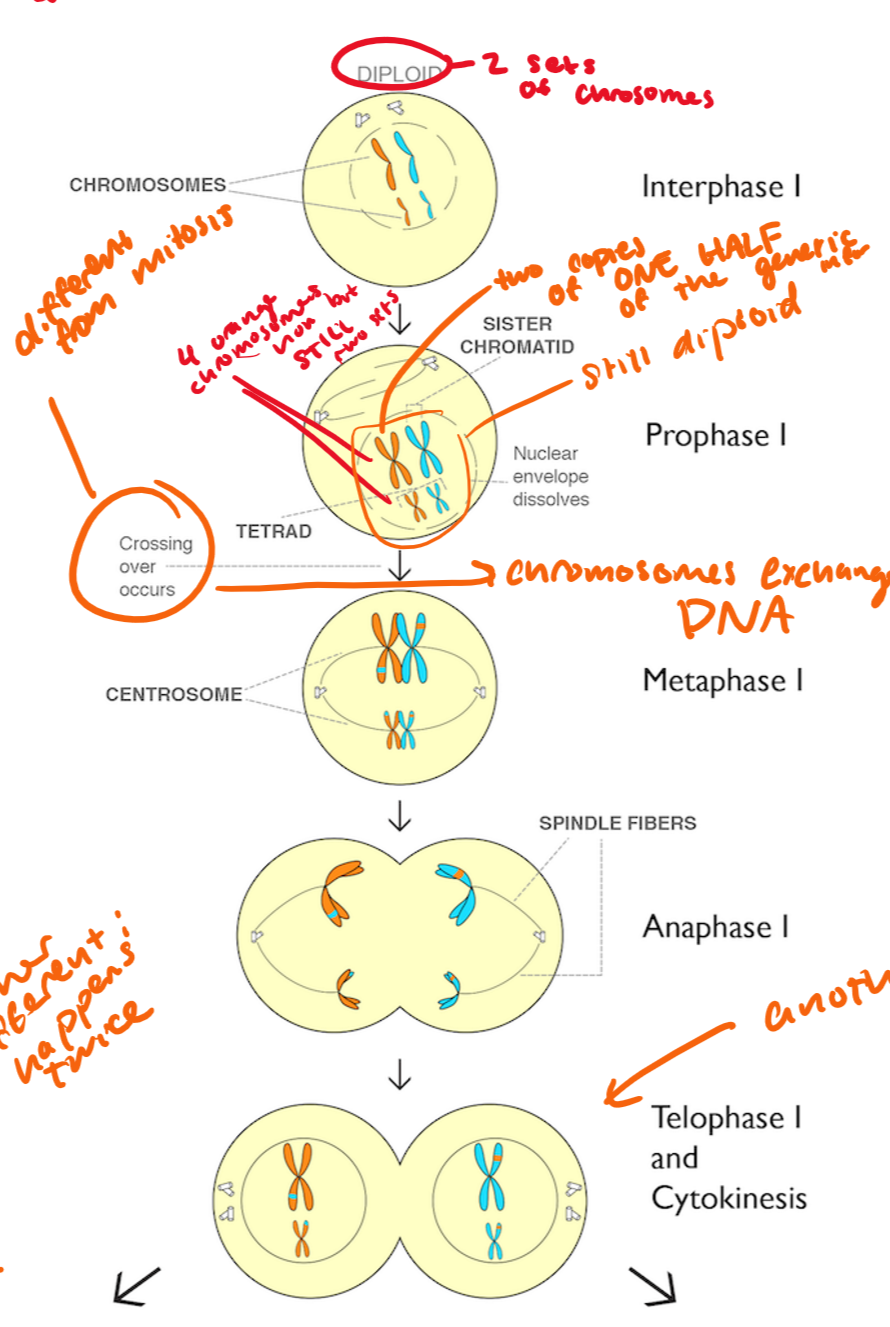
telophase I
chromosomes gather at poles as the cell divides into two
newly forming cells are haploid (n=2), each chromosome has two sister chromatids that are NOT identical (because crossing over just happened)
chromosomes do not decondense
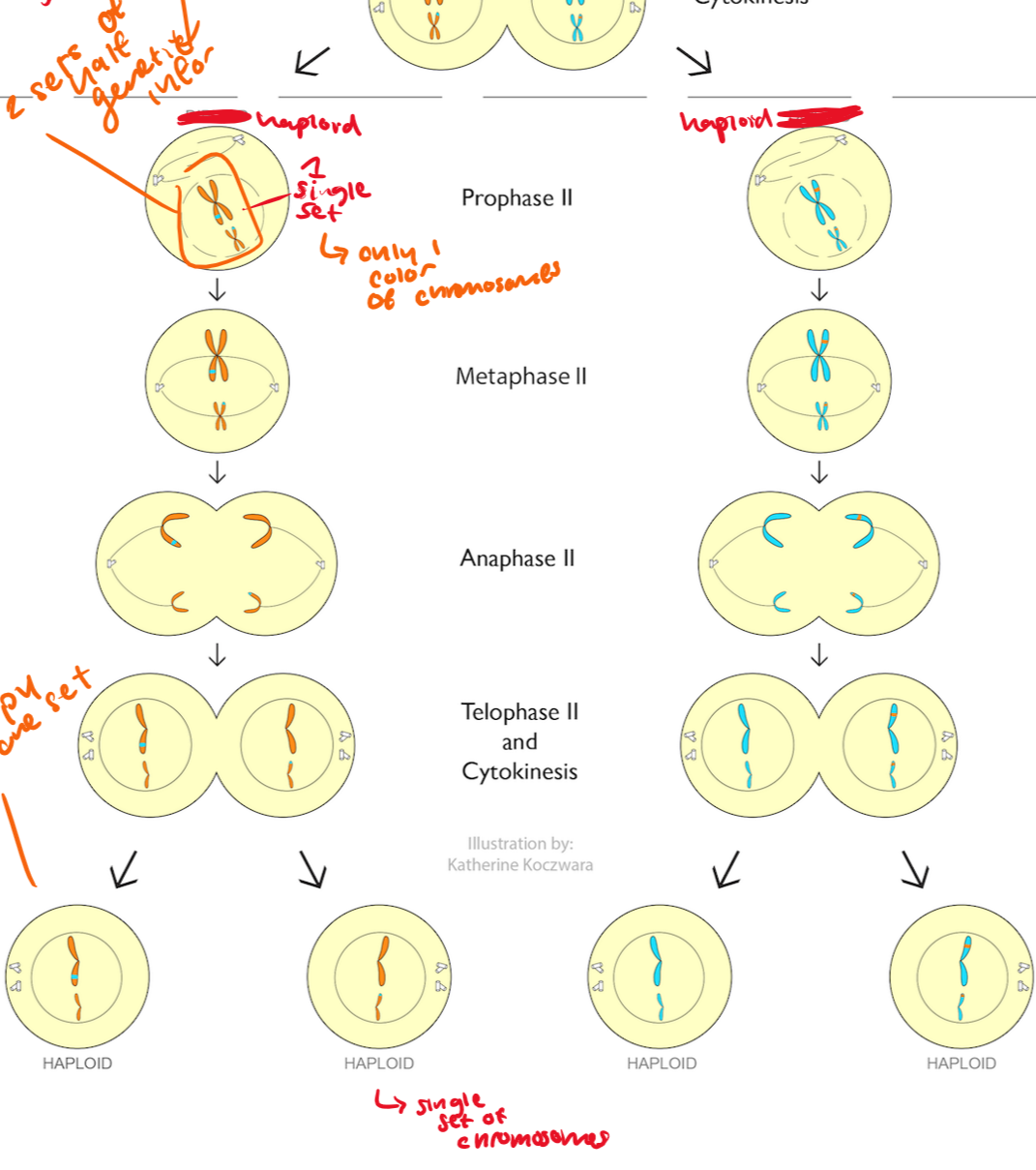
prophase II
a new spindle assembly forms around chromosomes
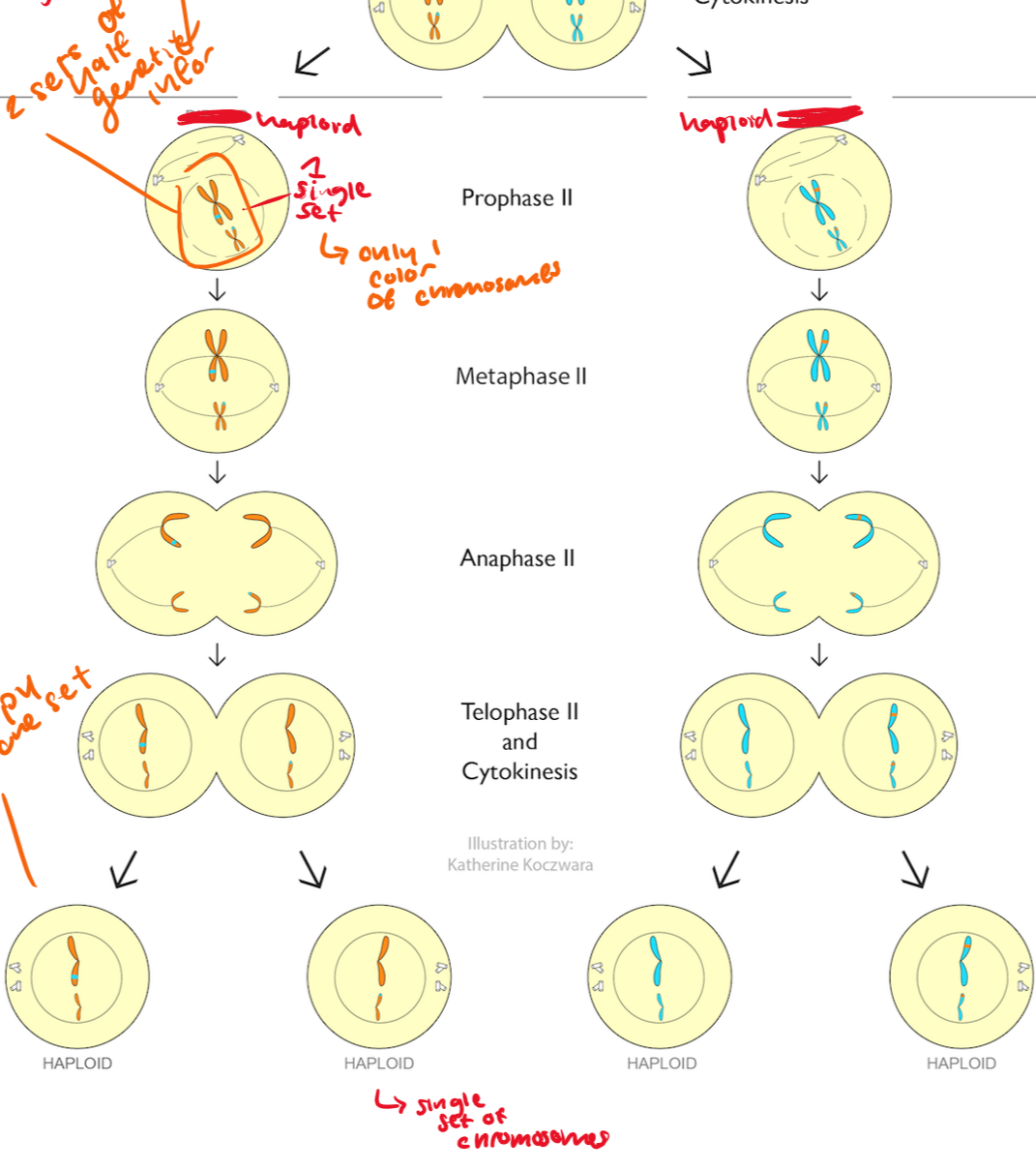
metaphase II
pairs of chromosomes that line up on the cell equator
anaphase II
chromatids move to each pole.
centromeres divide
sister chromatids are finally separated basically
telophase II/cytokinesis 2
nuclear membrane re-forms
chromosomes dissolve
spindle dissolves
cytokinesis finishes the division of the cytoplasm and 4 haploid daughter cells are created
egg/oocyte + sperm
the two germ cell components needed for a zygote
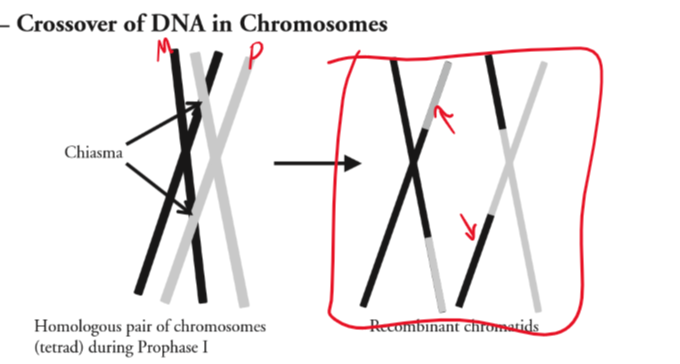
crossing over
a form of recombination that occurs during prophase I. increases genetic variation.
the genes on a recombinant chromatid are the same as the original chromatid, but the alleles (versions of a gene) are different
variation
differences between organisms due meiosis and how it divides DNA to present different alleles and stuff
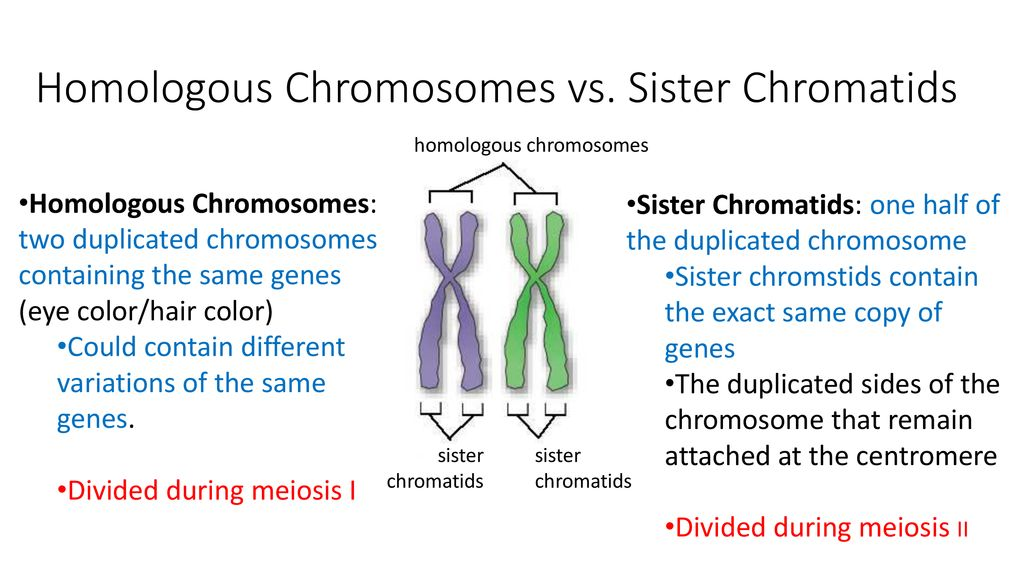
homologous chromosomes
chromosomes that are matching, but not identical. so you have 46 chromosomes originally and 23 different types, so 2 for each type. these 2 per type are homologous to each other so they will interact and cross over to create new combinations
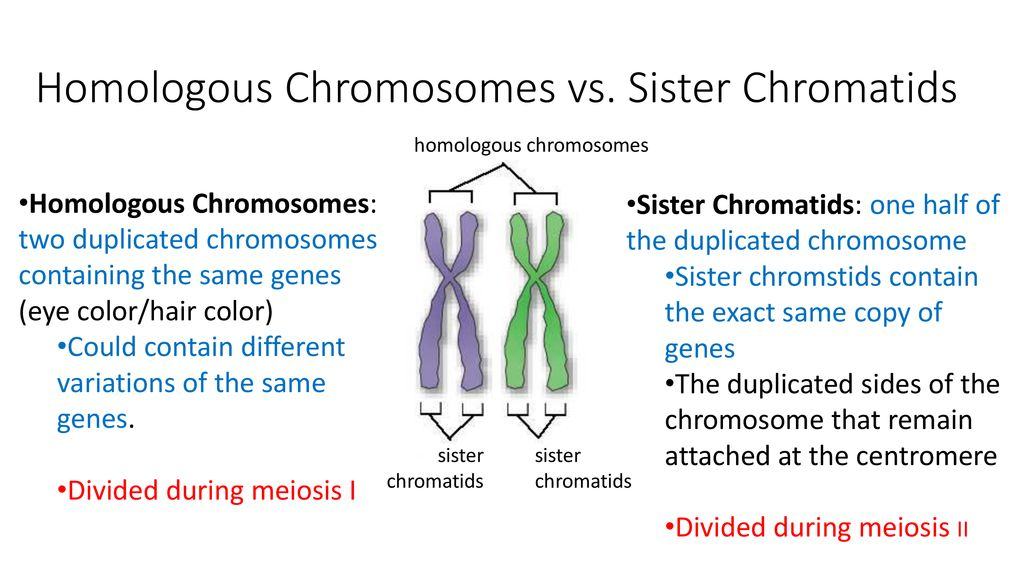
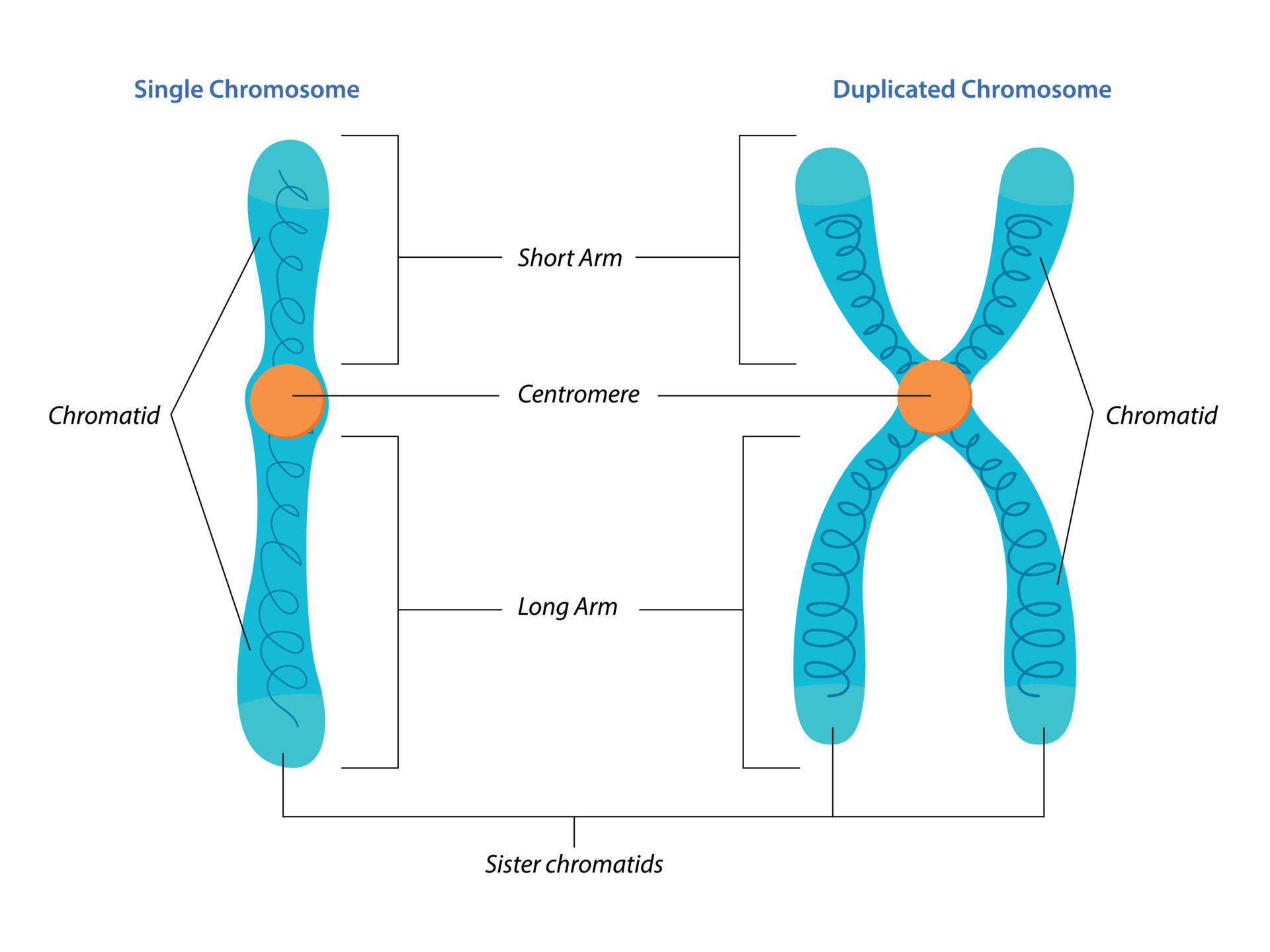
sister chromatids
the two chromatids on a chromsome that are identical to each other.
during interphase 1 the chromatid number duplicates so you have enough DNA
asexual reproduction
one parent
offspring are clones of parent and have same DNA/parental genes passed down
less/no genetic diversity, which could be bad if environment changes
faster
sexual reproduction
two parents
egg+sperm=offspring (each parent passes on half their DNA)
new combinations of genes (not new jeans)
increase of genetic diversity, so offspring better able to evolve and adapt to changing environment
more time and energy needed
egg/sperm produced by meiosis
diploid
“2n”, n=1 set of chromosomes (1 set of genetic material).
1 set refers to 23 chromosomes from the mother or 23 chromosomes from the father. normal cells are diploid because they have 2 sets, or 46 chromosomes total.
cells are diploid until the chromosomes are pulled apart in anaphase I
haploid
“n”, n=1 set of chromosomes (1 set of genetic material).
1 set refers to 23 chromosomes from the mother or 23 chromosomes from the father. normal cells are diploid because they have 2 sets, or 46 chromosomes total.
cells are haploid during meiosis 2 and diploid during most of meiosis 1
chromosomes
a package of condensed DNA containing a part of the genetic code/material of an organism. made of chromatin wrapped around histone proteins
how is the production of gametes different than the replication of somatic (Non-Germ) cells?
gametes undergo meisos, everything else goes through mitosis. mitosis makes direct replicates of the parent cell and meiosis does not
what gets passed on to future generations
DNA
why are babies different than their parents
because you are getting DNA that is different since the chromosomes cross over during meiosis and then the cell divides so that you only have a single set of chromosomes that are a blend of your parents’ dna
what are the important ways of introduction variation into the gametes during meiosis
crossing over, having 2 divisions (idek)
gametes produced by meiosis pair up randomly, producing variation in the offspring
recombinant vs non-recombinant chromosomes
recombinant means chromosomes that have been through crossing over and have a combination of two colors
what are the differences between meiosis and mitosis
crossing over
2 divisions
in mitosis, during telephase chromosomes decondense, but because meiosis has two divisions, the chromosomes dont decondense in telophase I
what is the chromosome number of a cell in each part of meiosis?
basically, there are 23 chromosomes in a cell when there is one color of chromosomes and 46 when you have two different colors
eukaryotes generally have…
paired chromosomes
each chromosome contains many genes, and each gene may have a number of versions called alleles
all multicellular organisms begin with a single cell
what does meiosis produce
four haploid cells
two phases of division for the purpose of sexual reproduction
one egg and three nursery cells OR four sperm are produced depending on the sex of the organism
germ cells diagram
chromatids vs chromosomes
chromatids=represented by how many “arms” on a chromosome you have
chromosomes=counted by the number of centromeres in a cell