Micro exam 4
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Fungi mycology
Chemoheterotrophic- (absorbs food), cell walls contain chitin, lack chlorophyll aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Molds- multicellular - Yeasts- unicellular
Eukaryotic reproduction
DNA packaged as chromosomes in the nucleus
Algae Fungi and some protozoa. reproduce asexually and sexually
Consists of Nuclear and cytoplasmic division
Nuclear division
-Has one or two complete copies of genome
single copy- (haploid)
Two Copies (Diploid)
Cytoplasmic Division
-Cytokinesis
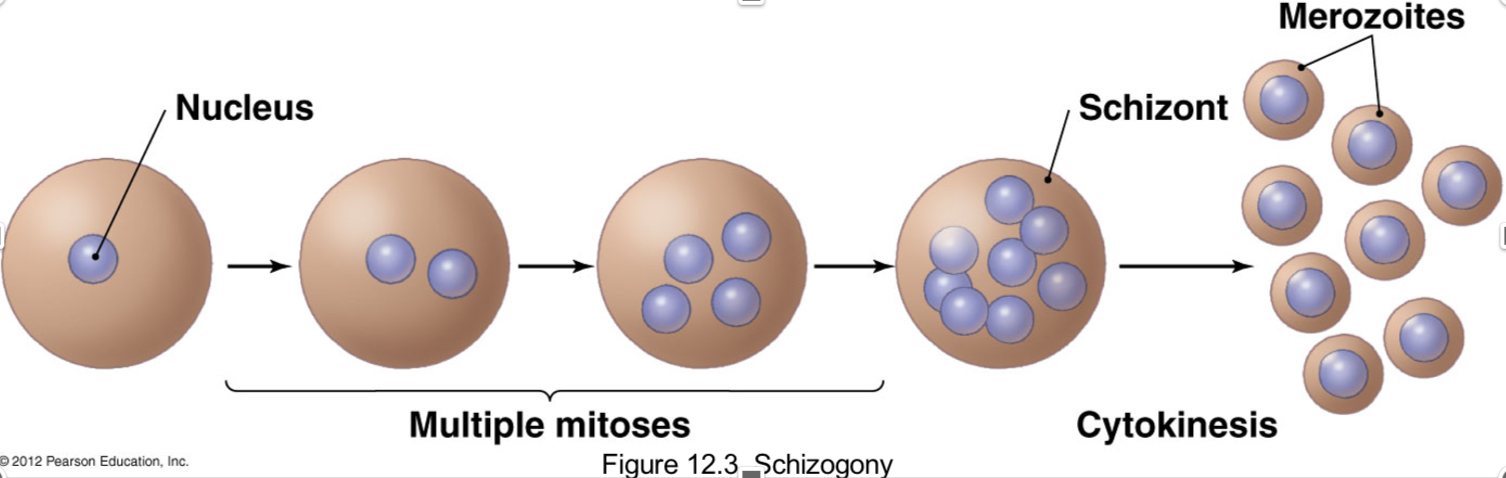
Schizogony
-Produce multinucleate schizont
-after cytokinesis = many daughter cells
Significance of Fungi
-Decompose dead organisms and recycle their nutrients
-help plants absorb water and minerals
-used for food and in manufacture of foods and beverages
-produce antibiotics / serve as important research tools
-can spoil pickles, jelly, and fruit
Fungal morphology
Mold- long filamentous tube can either be septate or aseptate
Yeasts- small globular spore
Mycelium
Intertwined hyphae forms tangled mass
-can spread thousands of acres and go several feet deep
-mushrooms are the vsible portion of mycelium
Dimorphic
-change shape in response to environmental conditions
Spore form
-Disease causing form
Yeasts
-Unicellular fungi
-Fission yeasts
divide symmetrically
Binary fission
-Budding yeast
divide asymmetrically
Budding
-Pseudohyphae is short chins that form when buds don’t completely separate
asexual spores of molds
-Sporangiospore - spores that form inside a sac
-conidiospores - produced at tips or sides og hyphae
-Arthocondia - formed by the fragmentation of hyphae
Blastocondia-formed by budding yeast cells
sexual reproduction (3 phases)
Plasmogamy- (+ )Haploid donor cell nucleus penetrates cytoplasm of recipient cell (-)
Karyogamy - (+) and ( - ) nuclei fuse
Meiosis - Diploid nucleus produces haploid nuclei
Sexual spores
Zygomycota: fusion of haploid cells produces one zygospore
-Fusion of hypha (+) and Hypha (-)
Ascomycota: Sac fungi
-septic hyphae, reproduces sexuallly by acospores in ascus sac
Basidiomycota: formed Externally on a pedestal (basidium)
Fungal divisions Zygomycota
-conjugation fungi
-Sexual repro by Zygospores Asexual repro by Sporangiospores
Genera
-Rhizopus -Black bread mold
Fungal Divisions Ascomycota
-Sac fungi
-Sexual repro by ascospores, Asexual Repro by conidiospores on condia
-Genera
Aspergillus - opportunistic, systemic mycosis
Basidiomycota
-Club fungi
-Septate fungi, sexual repro by basidiospores on basidium pedestal, Asexual Repro by Fragmentation
-important decomposer of lignin - puts nutrients back into soil
-SHROOMIES
Genera-
Cryptococcus neoformans - Systemic mycosis
Anamorphs / deuteromycota
-Produce asexual spores only
-septate hyphae
-asexual reproduction by conidiospores
Genera- Penicillium
Economic effects of Fungi
-Saccharomyces: bread wine HBV vaccine
-Trichoderma: cellulase starch in plants
fungal diseases (mycoses)
Systemic Mycoses- deep within body
Subcutaneous Mycoses: beneath the skin
Cutaneous Mycoses: Affect hair skin and nails
Superficial Mycoses: Localized like hair shafts
Opportunistic Mycoses: caused by normal microbiota or environmental fungi
Algae
-Photoautotrophs
-Food through diffusion
-Vegetative structures
Thallus, holdfasts
stipes,blades
Divisions by:
-pigments, cell wall types, food storage polymers
Brown algae (Phaeophyta)
-cellulose,alginic acid and cell walls
-chlorophyll A and C
-store carbs, harvested for algin-food thickener.
Red algea
-chlorophyll A and D phycobiliproteins
-store glucose polymer, harvested for agar
Green algae
-Cellulose cell walls
-Chlorophyll A and B store glucose polymer
store glucose polymer, gave rise to plants td
Protozoa characteristics
-eukaryotic, unicelular, lack cell wall
-food by ingestion and absorption
-Motile by cilia, flagella, and or pseudopodia
-vegetative form a trophozoite
-Asexual reproduction is by fission,budding or schizogony- sexual by conjugation
-produce cysts (like endospore)
Distribution of protozoans
-Require moist environments
-most live in ponds lakes, some like in moist like beach sand or decaying matter.
Morphology-
2 nuclei, Macro and Micro nucleuses
-contractile vacuoles
(Phyla of protozoans) - Parabasala
-Lack mitochondria
-single nucleus
-Parabasala body- golgi body structure
—Trichonympha- found in gut of termites with digestion
(Phyla of protozoans) - Diplomonadida
-Lack mitochondria, golgi bodies, peroxisomes
-Contain 2 equal sized nuclei
-Multiple flagella
Giardi lamblia
Euglenozoa
-unicellular, rigid cell membrane, no cell wall
move by flagella with crystalline rod
-photoautotrophs, chloroplasts contain chlorophyll
-reproduce by mitosis, ad form cysts
Kinetoplastids:
Trypanosoma brucei
-african sleeping sickness - Tsetse Fly
Vector bite = lesion = necrotic tissue
Alveolates-cilliates
-move by cilia
-chemoheterotrophs
vorticella- whirlpool current w cillia
Didinium-phagocytize other protozoa
Balantidium coli- pathogenic to humans
Amebozoa
-lobe shaped pseudopodia, and lack shells
-Free living- Naegleria Fowleri
Animal parasites- Entamoeba histolytica
Helminths flatworms and roundworms
-Eukaryote, multicellular
Chemoheterotrophic
-Parasitic lifestyles may lack digestive system, have reduced nervous system, and reduced locomotioon
-Reproductive lifestyle
Egg→ Larvae→ Adult
Mono vs Dio -Ecious (Helminths)
-Monoecious -Both Male and Female reproductive systems in one animal
-Dioecious - separet male and female
(parasitic worms)
Kingdom: Animalia
-Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
Trematodes (flukes)
Cestodes (tapeworms)
-Nematoda (roundworms)
Trematodes (flukes)
-Food by oral sucker or absorption by outer layer
Clonorchis sinensis - (asian liver fluke)
Cestodes (tapeworms)
-Scolex- head
-Proglottids- segmented body
-Monoecious
-Taenia Saginata - Beef tapeworm
Nematodes (Roundworms)
-Diecious
-Some infect humans as eggs
-Enterobius - pinworm
Arthropods as vectors
-insect that carries and transmit diseases (vector)
Kingdom: Animalia - Phylum: arthropoda
classes:
Insecta-6 legs Lice fleas and insects
Arachnida- 8 legs-mites and ticks
Symbiosis
-The relationship between normal microbiota and the host
-some normal microbiotas are opportunistic which means an organism that wouldn’t normally cause harm eventually does cause disease like an overgrowth-they take an opportunity
Types of symbiosis
Commensalism - one benefit’s and one is unaffected
Mutualism - both benefit
Parasitism - one benefits at the expense of the other
Normal microbiota and the host
Resident microbiota - permanently colonize the host but do not produce disease under normal circumstances
Microbial antagonism: competition between microbes
Transient microbiota - present but only temporarily
Acquisition of normal microbiota
-Development in womb free of microorganisms (axenic)
-microbiotas begin to develop during birthing process
-much of one’s resident microbiota established during first months of life
Resivoirs of infections
-Site where pathogens are maintained as a source of infection
-Most pathogens cannot survive for long outside their host
-three types of reservoirs
Animal
Human
Nonliving
Animal reservoirs
Zoonoses- diseases that naturally spread from animal to human
can acquire
-them through direct contact with animal or its waste
-eating animals
-bloodsucking arthropods
Human carriers
-Infected individuals who are asymptomatic but infective to others (latent disease)
-transmit from person to person - AIDS, gonorrhea
Non living reservoirs
-Soil water and food can be reservoirs of infection
-Prescence often due to contamination by feces or urine
-Botulism, tetanus, cholera
Exposure to microbes
Contamination- the mere presence of microbes on or in the body
Infection- colonization or invasion of the body by pathogen
Pathology - the study of disease
Etiology - the study of the CAUSE of a disease
Pathogenesis - The development of a disease
Portal of entry
Major pathways
Skin - they enter through natural openings, Hair follicles, sweat glands + Hookworm Larvae
Mucous membranes - Respiratory tract, by inhaling droplets or dust particles containing microbe + common cold, tuberculosis
Placenta - pathogens may cross the placenta and infect fetus
spontaneous abortion, birth defect, premature birth
-Parenteral route - Deposition of microbes directly into tissues beneath skin or mucus membrane
punctures, injections, bites, cuts, surgery
Portals and numbers of microbes
-Not all microbes cause disease - depends on portal of entry
Streptococcus -pneumonia when inhaled (not through skin)
Numbers of invading microbes
-virulence or potency of toxins expressed as
LD50 - (lethal dose) causes death in 50 % of test population
ID50- (infectious dose) for 50% of test population
Role of adhesion in infection
-most pathogens have a method to attach to host cells
necesary step in pathogenicty
attaches by binding surface molecules to complimentary surface molecules on host tissues
Receptors - host cells surface molecules
Adhesions/Ligands - pathogens surface molecules
-Glycocalyx
The Nature of infections diseases
Symptom - a change in body function from a patient as a result of disease
-headache
Sign - a change in a body that can be seen measured or observed as a result of disease
-vomiting
Syndrome - a specific group of signs and symptoms that accompany a disease
Causation of Disease
-Germ theory of disease
Kochs postulates
Virulence factors and Infectious agents
Pathogenicity - ability of microorganism to cause disease
Virulence - degree of pathogenicity
Virulence factors contribute to virulence
Adhesion factors
Biofilms
Extracellular enzymes
Enzymes and Increased virulence
-Some enzymes (exoenzymes) produced by bacteria and ejected from the cell can aid virulence
-Leukocidins destroy neutrophils and leukocytes active in phagocytosis
-Hemolysins cause lysis of erythrocytes
Coagulase / Kinases
Coagulase: coagulates fibrinogen
clotting protect bacteria from phagocytosis
Kinases: Digest fibrin and breakdown clots
-releases the clot
More “ase”
Hyaluronidase: hydrolysed hyaluronic acid
Collagenase: hydrolyses collagen
Lecithinase: destroys plasma membrane
Protease- break down proteins
Toxins
-poisonous substances produced by some microorganisms
toxemia - toxins in the bloodstream
Exotoxins: produced inside bacterium and then released into surrounding medium
Endotoxins: are part of the outer portion of the cell wall of G- bacteria released when killed -Lipid A Shock and fever
Effects of endotoxins
Response of endotoxin-shill, fever, weakness, generalized aches
Shock -life threatening loss of blood pressure
called septic shock when caused by G- organism ]
Pyrogenic response - causes fever
Antiphagocytic factors
Prevent phagocytosis
Bacterial capsule- slippery, foreign chemicals causes capsule to be camouflage
Antiphagocytic chemicals- prevent fusions of lysozyme and phagocytic vesicles
Leukocidins directly destroy phagocytic white blood cells
Plasmids / lysogeny
-virulence factors can be carried on plasmids or lysogenic phages
-plasmid encoded
-phage encoded
Pathogenic properties of fungi
Pathogenic properties of protozoa
pathogenic properties of helminths
pathogenic properties of algae
Stages of infectious disease
Incubation period -
prodromal period -
illness -
convalescence -
Transmission of diease
Direct - close association between infected and a susceptible host
Indirect by fomites - like doorknob, blanket
Vehicle - by inanimate reservoir like food, water
Vector - animals that carry vectors
mechanical arthropod arries pathogen on feet (roach walkin on toothbrush)
Biological - pathogens reproduce in vector
How are diseases classified
the body system they affect
longevity and severity
how the disease is spread
effect they have on population
classifying
communicable disease - disease that is spread from on host to another
Non communicable -
occurance of a disease
incidence - fraction of population that contracts a disease during a specific time
prevalence - fraction of a population having specific disease at a given time
sporadic - disease occurs occasionally
endemic
epidemic
pandemic
Emerging infectious diseases
New or changing disease showning an increased incidence in the recent past or a potential to increase in the near future.
Contributing factors to emerging
genetic recombination
evolution of new strains
inappropriate use of antibiotics and pesticides
changes in weather patterns
Extent of host involvement
Local infection: pathogen are limited to a small area of the body
Systemic infection: aninfection throughout the whole body
bactermia
septecimia
toximia
viremia
focal infection - started locally but now systemic
classification of infection
Primary infection -
Secondary infection -
Subclinical disease -
Predisposing factors
-Make the body more susceptible to disease
short urethra in females
inherited traits
climate and weather
age
lifestyle
Types of nosocomial infections
-means hospital acquired infections
Exogenous - pathogen acquired from health care environment
Endogenous - pathogens arise from normal microbiota
Latrogenic -
Control of Nosocomial infections
good aseptic technique
isolation
use of disposable or carefully sterilized equipment
monitoring procedures to trace causes