Biology and Behavior Ch 1-3 Study Guide
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is the mind-brain problem?
“what is the mind, and what is it’s relationship to the brain?”
What is empiricism?
information through observation
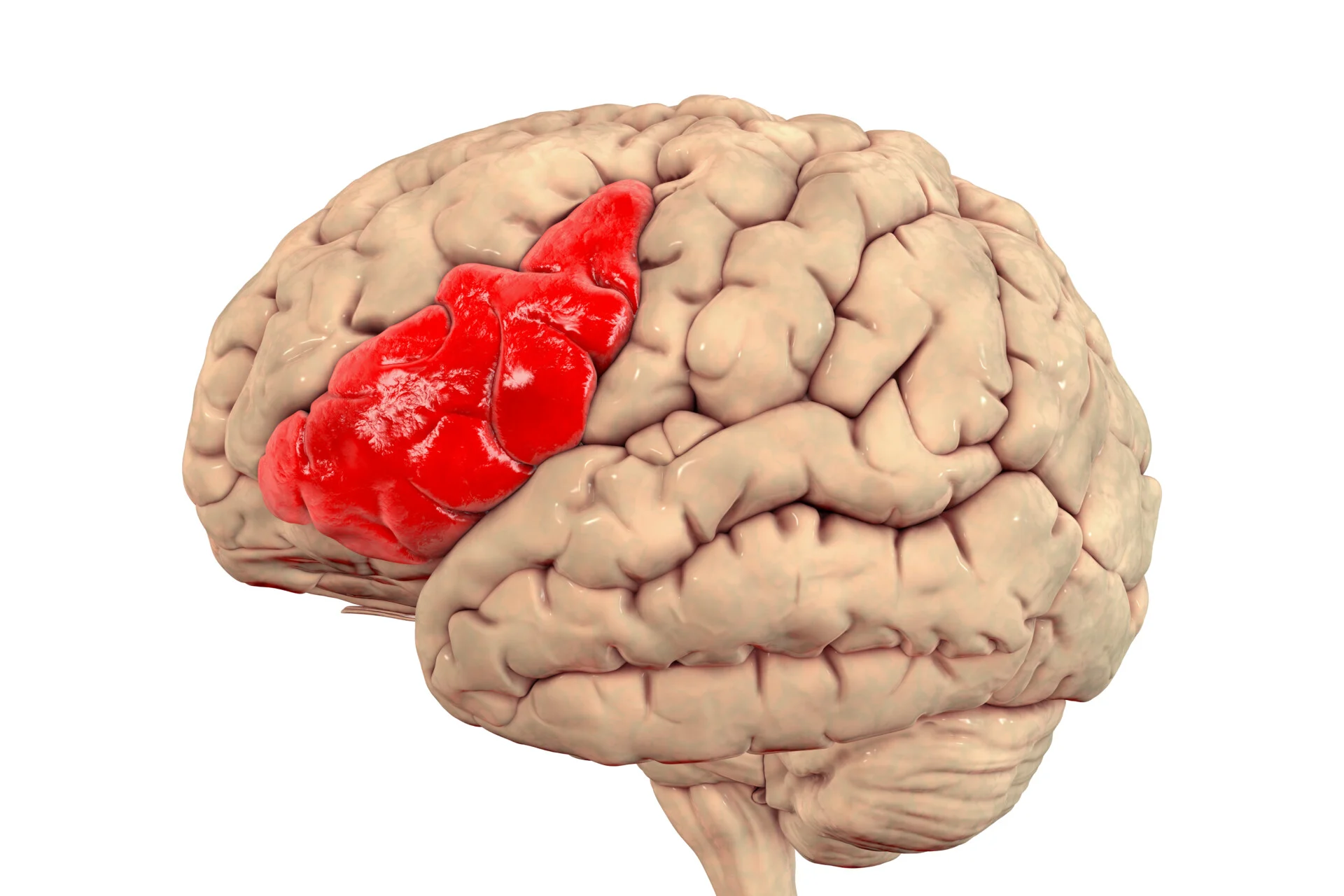
Where is the area responsible for speech in the brain, and who discovered it?
Broca’s area, only on the left side of the brain, frontal lobe; Pierre Paul Broca
What is phrenology?
believed that the brain has specific regions were specialized; Francis Gall; now considered pseudoscience
Left side vs right side of the brain
corpus callosum connects together; left side has Broca’s area, right side processes music
What did Descartes believe was the soul in the brain?
pineal gland since it wasn’t split into hemispheres; “mind interacted with the body”
What did Helmholtz study?
the speed of nerve inpulse, vision and hearing
Nature vs. Nurture
Nature
genetic predisposition
can be used to identify genetic disorders that are heritiable
DNA
Nurture
environmental influences and exposure
Monism vs. Dualism
Monism
mind and body are single substance (mentalistic monism: all mind) (materialistic monism: all physical)
Dualism
mind and brain are separate
one can exist without the other
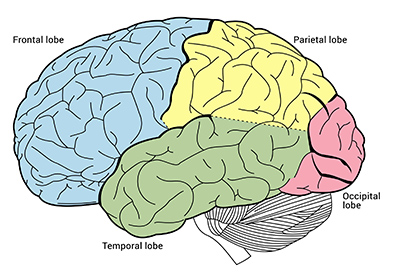
What are the lobes in the brain and their specialization?
Frontal
reasoning
Motor
movement
Temporal
hearing
Parietal
Sensory
Occipital
vision
What makes up the cell membrane?
Lipid bilayer
head and tail
helps with structure and keep items out of neurons
Hydrophillic and hydrophobic
What causes multiple sclerosis?
The loss of myelin (secreted by glial cells, surrounding the axon), neurons lose the ability to send signals
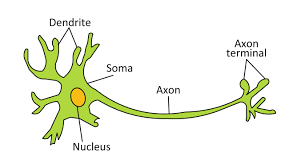
Describe the function and parts of a neuron
dendrites: collect messages from other neurons
soma: cell body
axon: carries nerve impulses away from the cell body
axon terminal: end of axon that releases neurotransmitters insulating la
myelin sheath: insulating layer that forms around the axon; allow fast transmission
synapse: junction between neuron and its target
What is released from the axon terminal that facilitaes communication between neurons? Chemical or electrical?
Neurotransmitters
chemical signals that bind to proteins to create an electrical charge
What is resting membrane potential?
difference in electrical charge between the inside and outside of the cell (-70mV)
Excitatory vs Inhibitory signal
Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP))
open sodium channels
more likely to fire
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP)
opens potassium or chloride channels or both
less likely an action potential will occur
What is the all or nothing law of neuron communication?
must reach threshold of electrical charge or no signal will be sent
What is the purpose of myelin?
to increase speed and strength of conductivity; interneurons are less likely to have myelin because their circuit is short
Sodium and potassium pump ratio?
know how this system works and creates action potentialresti
Describe the process of action potenials
neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body; created by a depolarizing current
What is a lobotomy?
surgical procedure where the front of the brain is damaged or disconnected; used as a treatment for mental disorders for many years before being banned
Which structure connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain?
corpus callosum
Which structure processes sensory information?
thalamus - relays all sensory signals except smell
Which brain structure controls hormones?
hypothalamus through the pituituary gland
How are cells in the brain organized?
columns and rows; cells grouped by function
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for planning and decision-making?
frontal cortex
What makes up a nerve?
bundle of axons travelling together is called a nerve (neuron is not a nerve)
Size or convolution?
convolution (brain wrinkles) predicts a species’ intelligence; brain is proportional to body size
Which area of the brain sustains basic life functions?
hindbrain - controls automatic responses like breathing and heart rate
CNS vs. PNS
CNS
brain and spinal cord
PNS
motor neurons
somatic nervous system - controls voluntary movements
automatic nervous system - controls involuntary movements
sympathetic division - fight or flight
parasympathetic division -
sensory neurons