Cardio Q2- autonomics/capillaries-lymph
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
what are the two divisions of the peripheral nervous system
somatic and autonomic
somatic nervous system includes…
links brain and spinal (CNS) w voluntary muscles and sensory receptors of skin
autonomic nervous system is divided into…
parasympathetics and sympathetic
the autonomic nervous system regulates…
bodily funx and is under unconscious/involuntary control
sympathetic neural system location
T1-L2
parasympathetic neural system location
cranial and sacral regions
does the sympathetic neural system have a short/long pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic
short pre-ganglionic, long post-ganglionic
does the parasympathetic neural system have a short/long pre-ganlionic and post-ganglionic
long pre-ganglionic and short post-ganglionic
is the ganglion closer to the spinal cord in the sympathetic or parasympathetic
sympathetic
do both sympathetic and parasympathetic work at the same time? explain
yes, but one tone is stronger than the other
what are the two neurotransmitters involved in the sympathetic tone
norepinephrine and epinephrine
what are the four receptors involved in the sympathetic tone
alpha and beta 1, 2
what neurotransmitter is involved with parasympathetic tone
acetylcholine
what 2 receptors are involved with the parasympathetic tone
muscarinic and nicotinic
which receptor involved in the parasympathetic tone is specific to the heart
muscarinic
medicines that are _____________ cause xerostomia
anti-cholinergic
muscarinic agonist can be used to tx ________, and example of this medication is ____________
xerostomia; pilocarpine
____________ agonists are the opposite of anti-cholinergic medicines
muscarinic
muscarinic antagonist are used to tx…
COPD, lung disease
muscarinic antagonist have what type of side effects
anticholinergic side effects
do muscarinic antagonists have sympathetic or parasympathetic manifestations
sympathetic manifestations
do muscarinic agonists have sympathetic or parasympathetic manifestations
parasympathetic manifestations
alpha 1 receptor location
vascular smooth muscle
alpha 1 receptor action
inc vascular tone to raise resistance- vasoconstrict
alpha 2 receptor location
not completely known- probs presynaptic nerve terminals
alpha 2 receptor action
dec affect of alpha 1; vasodilate- Modulates the response to NE on vascular smooth muscle
beta 1 receptor location
myocardial cells- HEART
beta 1 receptor action
inc hr and contractile force
beta 2 receptor location
smooth muscle in lung- vascular and nonvascular
in vascular smooth muscle, there are typically more __________ receptors than ___________ receptors
alpha 1; beta 2
beta 2 receptor action
relaxes smooth muscle- bronchodilation, vasodilation
beta 1/2 antagonist tend to __________ (inc/dec) sympathetic tone
dec
beta 1/2 antagonists are also known as
beta blockers
beta blocker medications often end in…
-olol
what affect do beta blockers have on the body
control heart rate (dec), constrict lungs, can use for headache, performance anxiety, and others
beta 1/2 agonists tend to __________ (inc/dec) sympathetic tone
inc
what are beta 1/2 agonists commonly used for
COPD- lung disease, asthma
beta 1/2 agonists are also known as
short and long-acting beta agonists (SABA/LABA)
what affect do beta 1/2 agonists have on the body
vasodilate, bronchodilate
where are baroreceptors located
carotid sinus and aortic arch (arterial tissue)
baroreceptors send fibers to the CNS to regulate…
the autonomic nervous system
if the blood pressure is high, how do baroreceptors respond
will dec sympathetic and inc parasympathetic activity
if the blood pressure is low, how do baroreceptors respond
will inc sympathetic and dec parasympathetic activity
what is tachycardia
elevated resting heart rate; >100 bpm
heart rate is primarily regulated by the…
ANS- parasympathetic
what is autonomic neuropathy
where you do not have enough parasympathetic input (tachycardia can be a sign + diabetes)
what is postural/orthostatic hypotension
medical term for dizziness and light-headedness (can be a sign for neuropathy)
uncontrolled diabetes can lead to diabetic autonomic neuropathy, what are some signs (6)
resting tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, exercise intolerance, impaired baroreflex, gastroparesis, anhidrosis
what is gastroparesis
stomach does not empty (from parasympathetic)
what is anhidrosis
inability/dec in sweating
during anaphylaxis the hr inc and the bp dec, explain this
histamine and other factors cause ALL arterioles to vasodilate at the same time→ drops bp, heart tries to compensate by pumping blood harder and faster → inc hr
what is the importance of the autoregulatory range
when a person is out of this range, their life is in jeopardy
what are some characteristics of capillaries that are unique
no smooth muscle innervation, do not constrict or dilate, have a greater total-cross sectional area
where is the site of edema
at the capillaries
what is edema, what can cause this
excess fluid in the tissues; can happen due to infection or problems w lymphatic system
what are the methods of exchange across capillaries
paracellular and transcellular
what is paracellular exchange
high to low gradient: pass through fenestrations in capillary endothelial cells / leak through space between endothelial cells
what is transcellular exchange
transcytosis using vesicles (LUNGS); how meds get into tissues, diffusion
what can the starling force equation be used for
finding fluid movement across the capillary wall
the starling forces equation includes…
hydrostatic pressure gradient and the osmotic pressure gradient in the capillaries vs the interstitial fluid
a positive net filtration means…
getting filtration out of the capillary
negative net filtration means
getting absorption into the capillary
what is hydrostatic pressure
the difference between the capillary blood pressure outward and the interstitial fluid pressure inward at a given capillary
what is osmotic pressure
the tendency of water in the blood to collect in areas of higher solute (in the capillaries)
what solutes contributes to osmotic pressure in capillaries
albumin
in edema, what could be happening to the factors in the starling forces
inc in Kf, inc in hydrostatic pressure, and dec in osmotic pressure
what is the lymphatic system responsible for
drains excess fluid in the interstitium back into the circulatory system
only one system takes blood to capillaries:
arteries
two systems take blood from the capillaries:
veins and lymph vessels
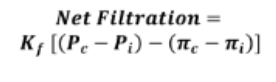
what equation is this
starling forces
what effects does epinephrine on receptors
acts on adrenergic receptors: alpha-1 to inc bp via vasoconstriction, beta-1 to inc hr and inc contractions, beta 2 to bronchdilate