PMI Exam 2
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
The best tool to use for perceptual assessment of speech, resonance, and voice is
A) Videofluoroscopy
B) Nasoendoscopy
C) the examiner's ear
D) Electropalatography
the examiner's ear
You evaluate a 3 year old in the clinic who is demonstrating consistent hypernasality during connected speech. Which professional would you refer the client to for further medical examination?
ENT
GI
Cardiovascular
Physical Therapist
ENT
Which series of numbers is best to use when testing for HYPOnasality?
50s
90s
70s
80s
30s
90s
If you use the nasal cul-de-sac test and you hear a difference on production of a vowel, this confirms the diagnosis of which of the following?
Hypernasality
Hyponasality
Cul-de-sac resonance
Nasal emission
Hypernasality
Which of the following instruments is the least reliable in assessing hypernasality and nasal emission?
Straw
Listening tube
Dental mirror
Stethoscope
Dental mirror
What is the most common cause of the spread of infection in healthcare settings?
Providers not wearing gloves when appropriate
Providers not following proper handwashing guidelines
Medical equipment that is not properly disinfected
Medical equipment that is not properly sterilized
Providers not following proper handwashing guidelines
The shape of the palate should be evaluated in relationship to which of the following?
The position of the mandible
The position of the maxilla
The size and movement of the tongue
Dental occlusion
The size and movement of the tongue
When do tonsils create a concern for speech production?
When they extend beyond the faucial pillars
When they are absent
When they are asymmetrical
When they are visible
When they extend beyond the faucial pillars
Surgery is NEVER indicated for which of the following:
Velopharyngeal Mislearning
Velopharyngeal incompetence
Velopharyngeal Insufficiency
Nasal Emission
Velopharyngeal Mislearning
At what age does an SLP usually complete a more comprehensive speech, language, and resonance evaluation for a patient with a history of cleft palate?
Birth
3-4
18
1-2
3-4
Aerodynamics
an indirect measure of airflow
Nasometry
can measure nasality in speech (nasalance score)
Nasopharyngoscopy
provides a high resolution view of the VP port
Videofluoroscopy
an X-ray imaging technique with simultaneous audio for speech
All the following are true about interpretation of nasalance EXCEPT
A) Normal oral resonance is typically under 20 percent
B) Clear Hypernasality is > 40%
C) Mild hypernasality is indicated by a score of 30%-40%
D) The higher the contour is on the screen, the more hyponasality to expect
D) The higher the contour is on the screen, the more hyponasality to expect
Abnormally low data points on a nasogram are indicative of:
A) Upper Airway Obstruction
B) Hyponasality
C) Both A & B
D) Hypernasality
C) Both A & B
Which videofluoroscopy view is done to only view the lateral pharyngeal walls?
A) Lateral view
B) Frontal view
C) Base view
D) Oblique view
B) Frontal view
All the following are easily viewed through videofluoroscopy EXCEPT
A) Relationship between the posterior pharyngeal wall and velum
B) Length of the velum and its upward movement
C) Small or unilateral gaps
D) Posterior wall of the pharynx during closure
E) Movement of the tongue
C) Small or unilateral gaps
Where should you insert the scope when evaluating velopharyngeal function when completing a nasopharyngoscopy?
A) Inferior meatus
B) Superior meatus
C) Middle meatus
C) Middle meatus
Nasopharyngoscopy can be used:
A) During a treatment session for biofeedback
B) To assess swallowing issues
C) During surgery
D) During nasometry
A) During a treatment session for biofeedback
A disadvantage of nasopharyngoscopy is that it allows the examiner to see all the following EXCEPT
A) Adenoid tissue
B) Nasal surface of velum
C) Length of the posterior pharyngeal wall
D) Oronasal fistula
E) Vocal cords
C) Length of the posterior pharyngeal wall
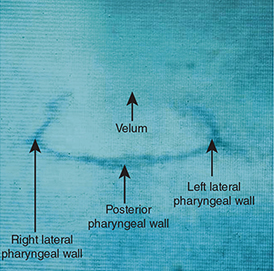
Which videofluoroscopy view is shown in the following picture?
A) Lateral view
B) Frontal view
C) Base view
D) Oblique view
C) Base view
What is the biggest advantage of using a standardized passage to gather nasometric data?
A) The passage can be read by the individual rather than repeated
B) It is easier to administer because it is well-known by the examiner
C) The patient's score can be compared to normative data
D) The passage is designed to contain only certain sounds to make it easier to produce
C) The patient's score can be compared to normative data
Why is palate surgery more difficult than lip surgery?
A) It is technically more demanding
B) There is a greater risk of dehiscence
C) There is a greater risk of fistula formation
D) All of the above
D) All of the above
What is a common secondary surgical procedure for correction of velopharyngeal insufficiency?
A) Palatoplasty
B) Pharyngeal flap
C) Abbe flap
D) Palatal lift
B) Pharyngeal flap
Which type of cleft palate surgery does NOT focus on the velum?
A) Von Langenbeck
B) Wardill-Kilner
C) Both A & B
D) Furlow Z-palatoplasty
C) Both A & B
The earliest age that a pharyngoplasty for VPI is usually done is:
A) Age 1
B) Age 2
C) Age 3
D) Age 4
C) Age 3
All of the following are potential complications of cleft palate surgery EXCEPT:
A) Airway Compromise
B) Oral Aversiveness
C) Post-op Dehiscence
D) Cleft Lip
D) Cleft Lip
The timing of a bone graft is dependent on which of the following?
A) Type of cleft
B) Child’s dental and maxillary development
C) Presence of a crossbite
D) Presence of a nasolabial fistula
B) Child’s dental and maxillary development
Which term refers to the surgical repair of a cleft palate?
A) Le Fort advancement
B) Palatoplasty
C) Bone graft
D) Osteotomy
B) Palatoplasty
Which term refers to surgical repair of cleft lip?
A) Pharyngoplasty
B) Palatoplasty
C) Cheilorraphy
D) Orthognathic surgery
C) Cheilorraphy
A prosthetic device that covers or fills a cleft or fistula to improve speech is called:
A) Pharyngeal flap
B) Palatal Lift
C) Dental Bridge
D) Palatal Obturator
D) Palatal Obturator
All of the following can improve VPI EXCEPT:
A) Pharyngeal Flap
B) Alveolar Bone Grafting
C) Pharyngeal Wall Augmentation
D) Sphincter Pharyngoplasty
B) Alveolar Bone Grafting
What speech sound should be inserted between the consonant and the vowel when trying to eliminate glottal stops? (Think continuous speech to eliminate a stop).
A) /m/
B) /s/
C) /h/
D) /z/
C) /h/
Which of the following can be corrected with speech therapy?
A) Hypernasality due to VPI
B) Compensatory productions secondary to VPI
C) Obligatory distortions secondary to VPI
D) Nasal emission due to VPI
B) Compensatory productions secondary to VPI
Which of the following is appropriate for correction of compensatory errors following correction of VPI?
A) Blowing exercises
B) Sucking exercises
C) Velopharyngeal exercises
D) Articulation therapy
D) Articulation therapy
All these rules are usually correct for correction of speech sound errors EXCEPT
A) Begin with anterior sounds
B) Change one feature at a time when moving from one sound in a group to the next sound
C) Establish correct placement and manner of productions in isolation
D) Begin with the sound in the final word position
D) Begin with the sound in the final word position
What is the best way to correct phoneme-specific nasal emission on /s/?
A) CPAP
B) Blowing and sucking exercises
C) Oral-motor exercises
D) Changing articulation placement
D) Changing articulation placement
Pushing under the child’s chin may help the child to achieve appropriate placement for which group of sounds?
A) Sibilants
B) Lingual-alveolars and /l/
C) Velars
D) Plosives
C) Velars
Which of the following should never be used to treat speech sound disorders?
A) Auditory feedback
B) Tactile feedback
C) Oral-motor exercises
D) Visual feedback
C) Oral-motor exercises
A feeding obturator is capable of all the following EXCEPT
A) Helping an infant to achieve lip closure
B) Keeping the tongue from resting inside of the cleft
C) Covering an infant’s unrepaired cleft during feeding
D) Separating the oral cavity from the nasal cavity
A) Helping an infant to achieve lip closure
Based on ACPA recommendations, which professionals must be on a Cleft Palate Team as a very minimum?
A) Craniofacial surgeon, Orthodontist, speech-language pathologist
B) Plastic surgeon, orthodontist, speech-language pathologist, and one other professional
C) Plastic surgeon, ENT, speech-language pathologist
D) Plastic surgeon, oral surgeon, speech-language pathologist, one other professional
B) Plastic surgeon, orthodontist, speech-language pathologist, and one other professional
The members care for patients independently, with limited communication
A) Consulting team
B) Interdisciplinary team
C) Multidisciplinary team
D) Transdisciplinary team
C) Multidisciplinary team