equilibrium constants + reaction quotients , Equilibrium Constant Expression and Equilibrium Constant
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What does "Q" represent?
reaction quotient: a value that represents the mass action expression of a reversible chemical reaction, can be used when reaction is not at equilibrium
When will Q=K?
When the reaction is at equilibrium.
When is Q>K?
when the reaction shifts left (the product's [ ] was too large, the reaction wants to make more reactants -> equilibrium.)
When is Q<K?
when the reaction shifts right (the reactant's [ ] was too large, reaction wants to go to equilibrium.)
How do you calculate Q?
Q=[products]/[reactants]
What factors change the equilibrium position?
concentration, pressure, temperature
How does increasing temperature (exothermic) affect the equilibrium position?
the reaction shifts left
reactants <> products + heat
How does decreasing temperature (endothermic) affect the equilibrium position?
the reaction shifts right
reactants + heat <> products
How does increasing the pressure of an equilibrium reaction mixture affect the reaction?
It would shift towards the side of the reaction with fewer moles of gas
How does decreasing the pressure of an equilibrium reaction mixture affect the reaction?
It shifts towards the side of the reaction with more moles of gas.
What does ICE stand for in ICE tables?
Initial, Change, Equilibrium
What is the equilibrium constant expression?
Kc = [products]/[reactants]
How do you calculate Kp?
partial pressures of products/reactants (all to the power of their coefficient)
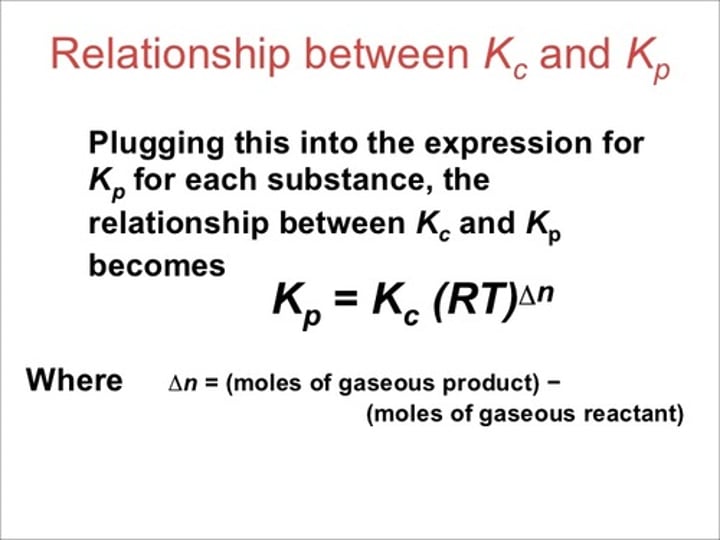
How do you calculate △n?
△n = # moles products - #moles reactants
Equilibrium
When the forward and reverse reaction rates are equivalent
Equilibrium constant expression
Written with products multiplied together and raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients divided by the reactants multiplied together raised to their stoichiometric coefficients
Equilibrium constant (K)
The value of the equilibrium constant expression
Dynamic equilibrium
Equilibrium where both the forward and reverse reactions are occurring but there is no net change in chemical concentrations
Kc
Equilibrium constant expression using concentration values (molarity)
Kp
Equilibrium constant expression using pressure values (atm)
Le Chatelier's Principle
A system at equilibrium will shift in the direction to oppose the stress on the system
Factors affecting equilibrium: Concentration
Changing concentrations of chemicals in the equilibrium expression
Factors affecting equilibrium: Pressure
Changing the pressure by changing the volume of a system
Factors affecting equilibrium: Temperature
Heating or cooling a system
Factors affecting equilibrium: Add Solvent
Shifting a reaction by changing the chemical concentrations as the solvent is added
K reverse
The equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction is the reciprocal of the equilibrium constant for the forward reaction
K multiply
The equilibrium constant for a reaction multiplied by a constant is raised to the power of that constant
K add
The equilibrium constant for the sum of two reactions is the product of the equilibrium constants for the individual reactions
Kc for reversed reaction
The equilibrium constant for a reversed reaction is the reciprocal of the equilibrium constant for the original reaction
Kc for multiplied reaction
The equilibrium constant for a reaction multiplied by a constant is raised to the power of that constant
Kc for added reactions
The equilibrium constant for the sum of two reactions is the product of the equilibrium constants for the individual reactions