Invertebrates: Sponges to Annelids Overview
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Sponges
Phylum Porifera; habitat: fresh and marine waters, sessile; germ layers: none; no true tissues; body cavity: no; symmetry: asymmetrical; nervous system: none, no cephalization; gas exchange and excretion: diffusion; reproduction: most sponges are hermaphrodites; dispersal: flagellated, swimming larva.
Spongocoel
Cavity in sponges where water is drawn through pores and out through an opening called the osculum.
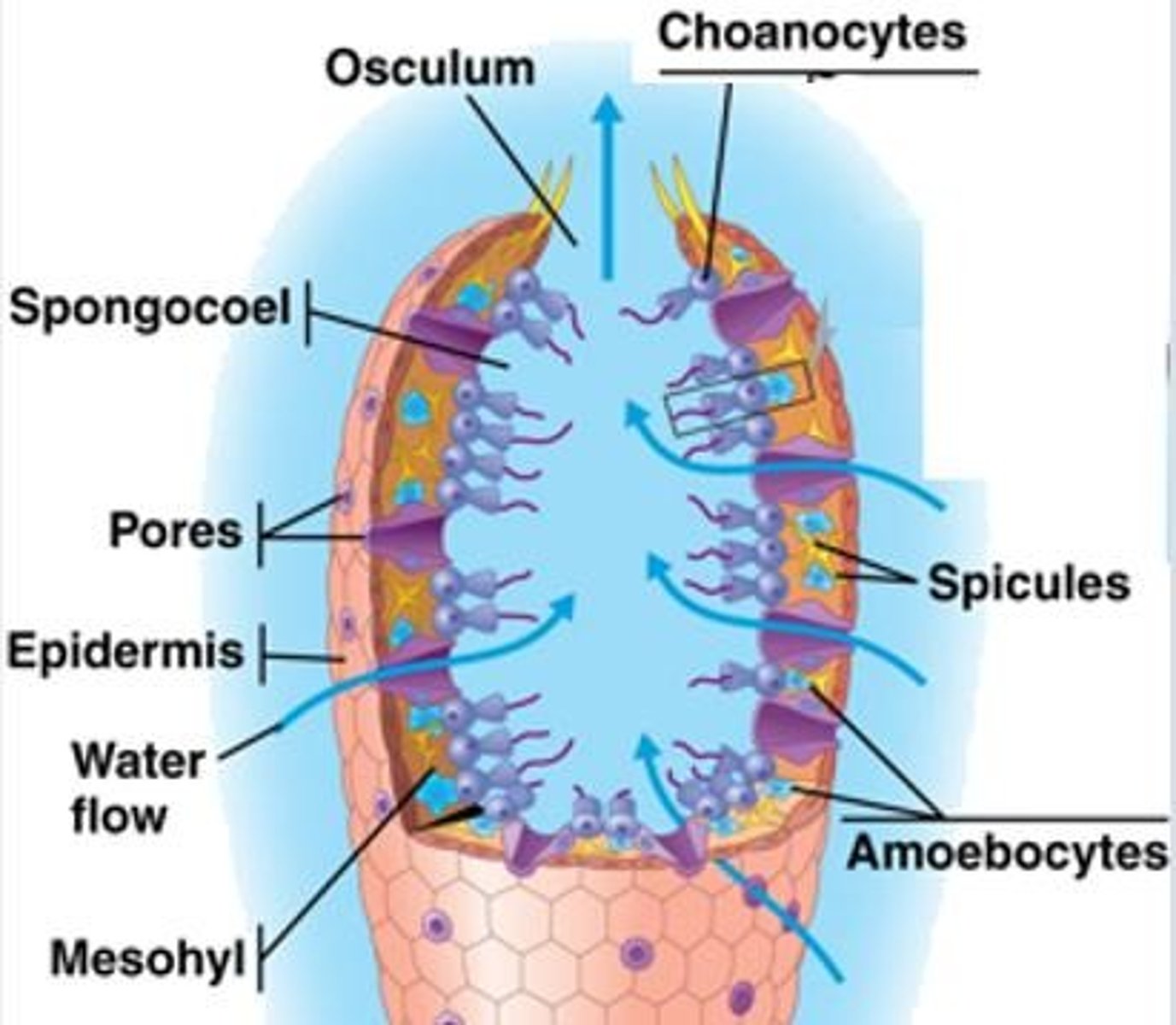
Choanocytes
Flagellated collar cells in sponges that generate a water current.
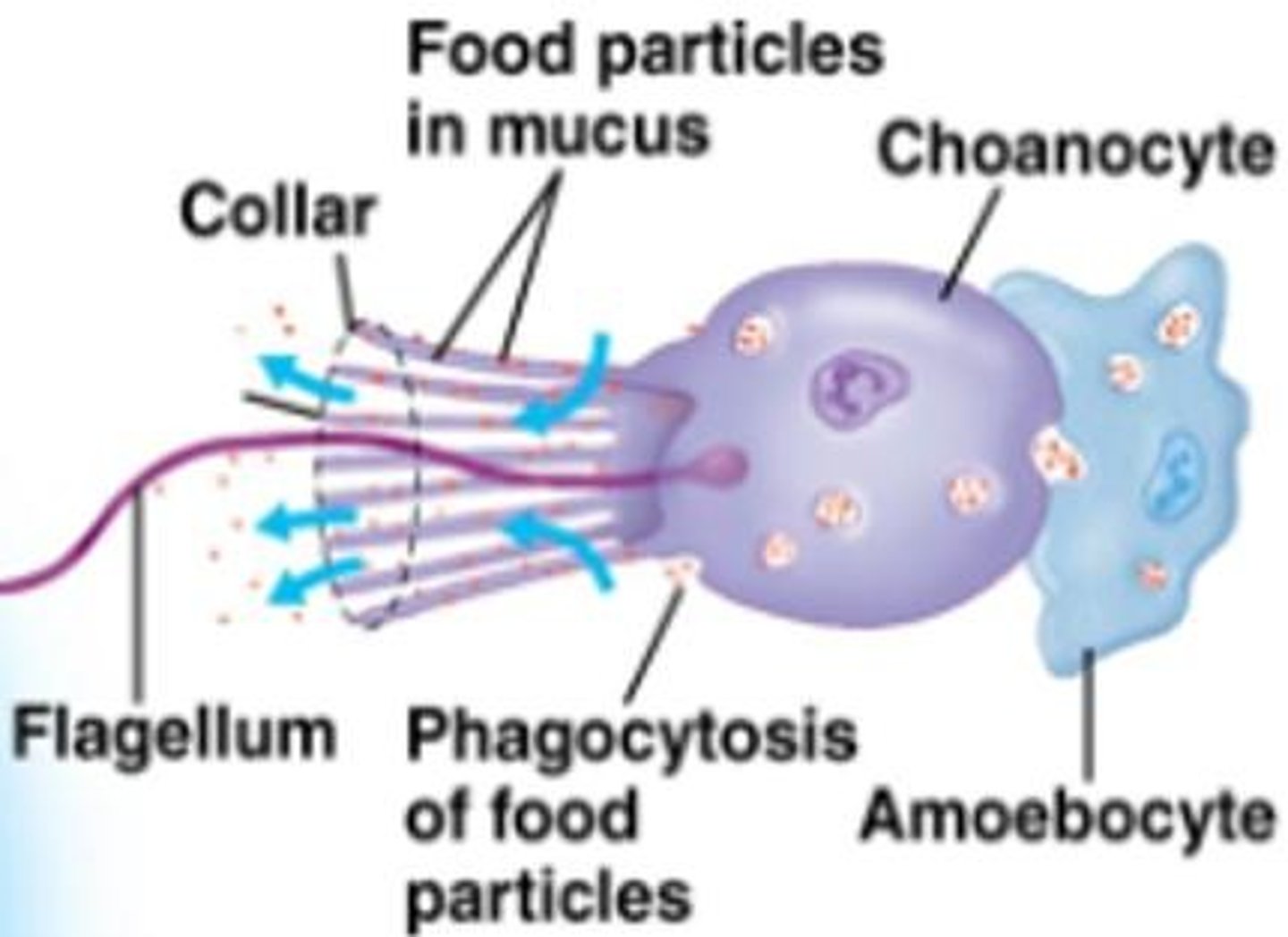
Amoebocytes
Cells in sponges that take up food particles, digest them, and carry nutrients to other cells.
Eumetzoa
Animals with true tissues; all animals except sponges and a few other groups belong to the clade Eumetazoa.
Cnidarians
Oldest Eumetazoans; phylum Cnidaria includes jellyfish, hydra, coral, and sea anemone.
Cnidarian Habitat
Marine and fresh water; includes sessile and motile forms.
Germ Layers in Cnidarians
Diploblastic, consisting of endoderm and ectoderm only.
Symmetry in Cnidarians
Radial body plan.
Body Cavity in Cnidarians
None.
Body Plans in Cnidarians
1) Sessile asexual polyp; 2) Sexual motile medusa.
Nervous System in Cnidarians
No cephalization, no brain; a non-centralized nerve net allows cells to communicate over long distances.
Nematocysts
Specialized stinging cells on the tentacles of cnidarians.
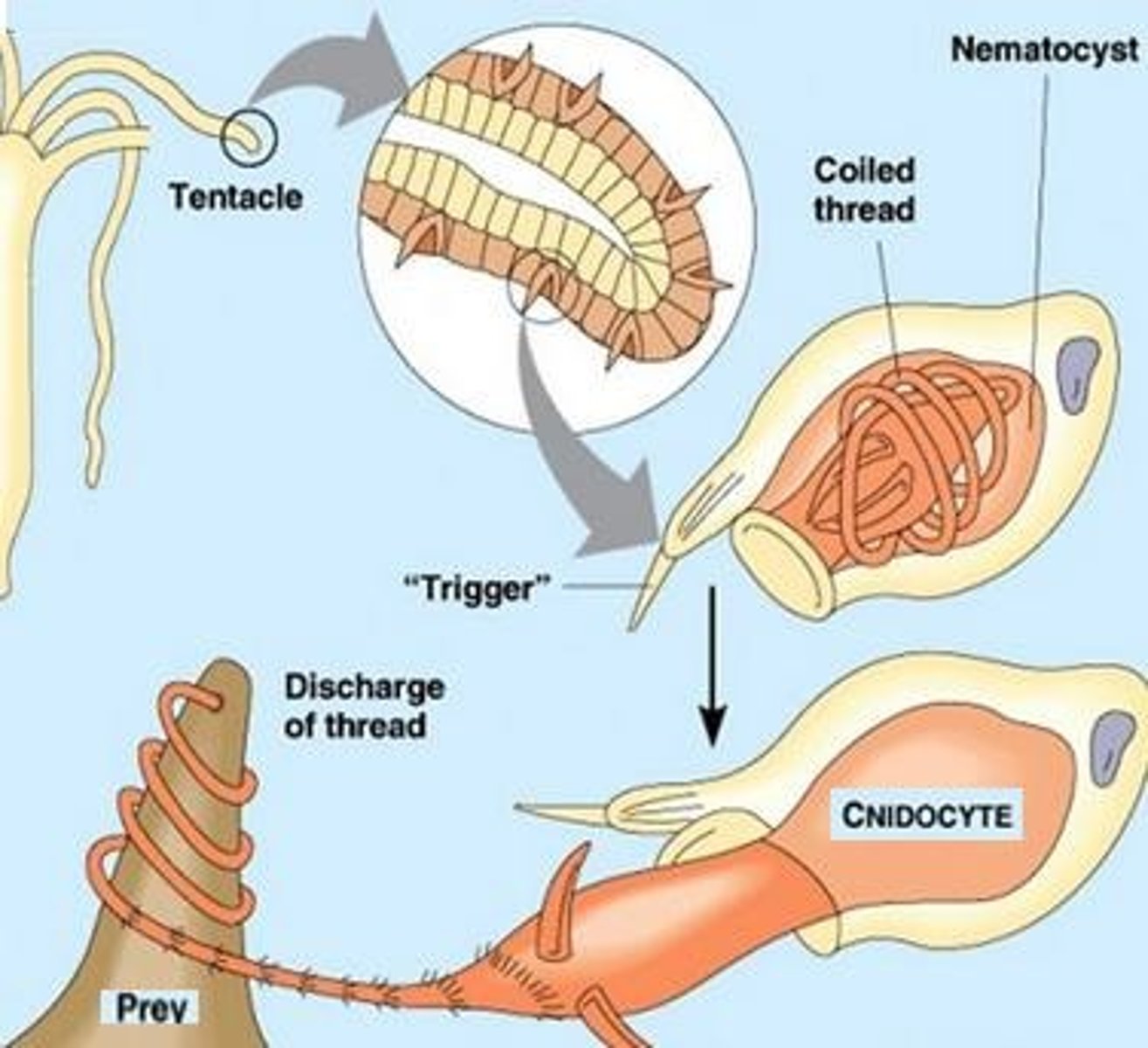
Cnidarian Feeding
Carnivores that use tentacles with nematocysts to capture and ingest prey.
Digestive System in Cnidarians
Incomplete digestive system with a single opening that functions as both mouth and anus; sac with a digestive compartment called gastrovascular cavity.
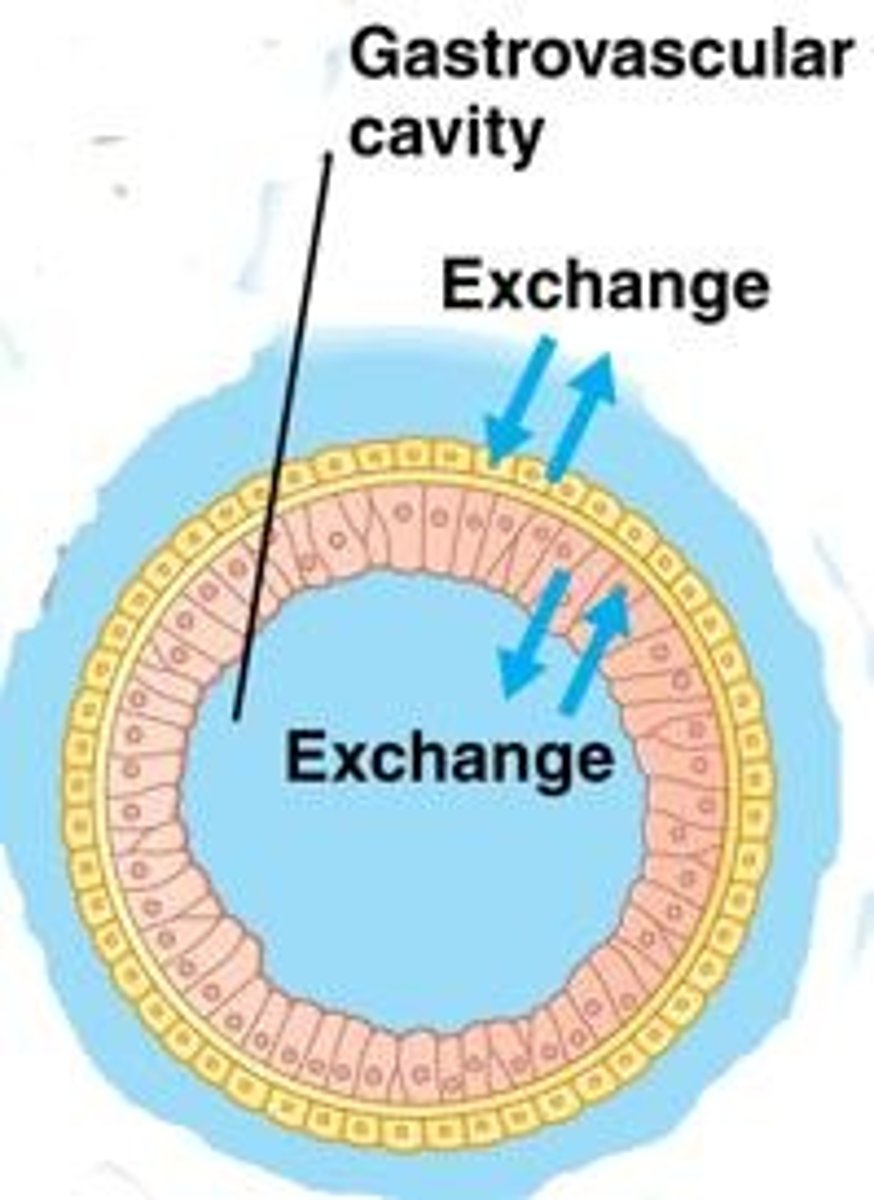
Gas Exchange in Cnidarians
By diffusion; cavity is only 2 cells thick.
Bilateria
Organisms with bilateral symmetry and triploblastic structure.
Lophotrochozoans Characteristics
Bilateral symmetry and 3 germ layers (triploblastic); some have lophophore for feeding; others pass through a trochophore larval stage.
Platyhelminthes
Flatworms; habitat: marine, fresh water, and damp terrestrial environments; can be free-living or parasitic.
Body Cavity in Platyhelminthes
None; Acoelmates.
Germ Layers/Symmetry in Platyhelminthes
Triploblastic/Bilateral.
Gas Exchange in Platyhelminthes
Very thin bodies; transport via diffusion; no circulatory system.
Nervous System in Platyhelminthes
Yes; nerves with a centralized 'brain'.
Cephalization in Platyhelminthes
Yes.
Head
Has light-sensitive eye spots
Digestive System
Gastrovascular cavity (one opening); branching delivers food to worm's cells
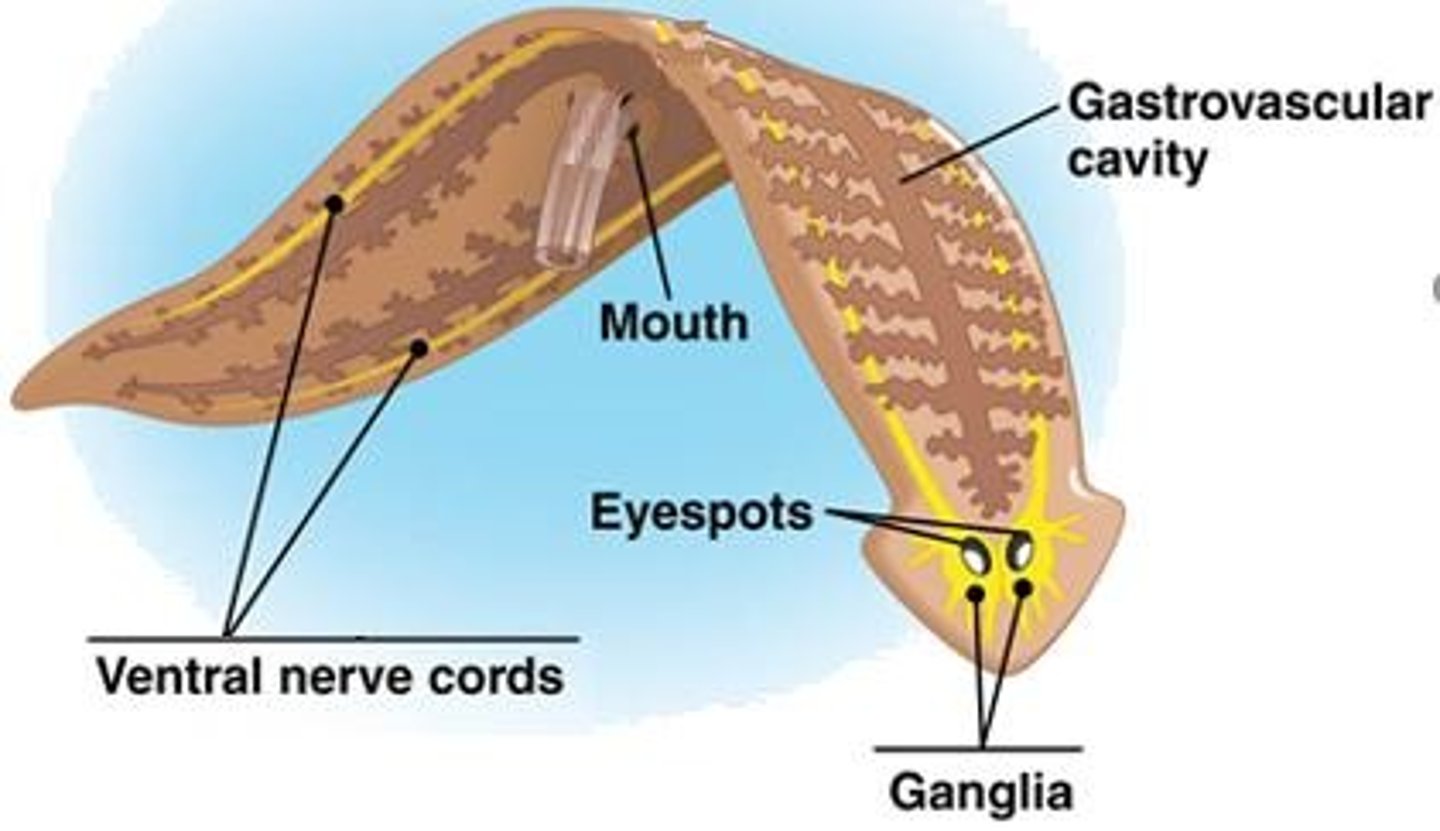
Platyhelminthes
Some free-living and some parasites
Planaria
Freshwater predators/scavengers that move with cilia or muscles
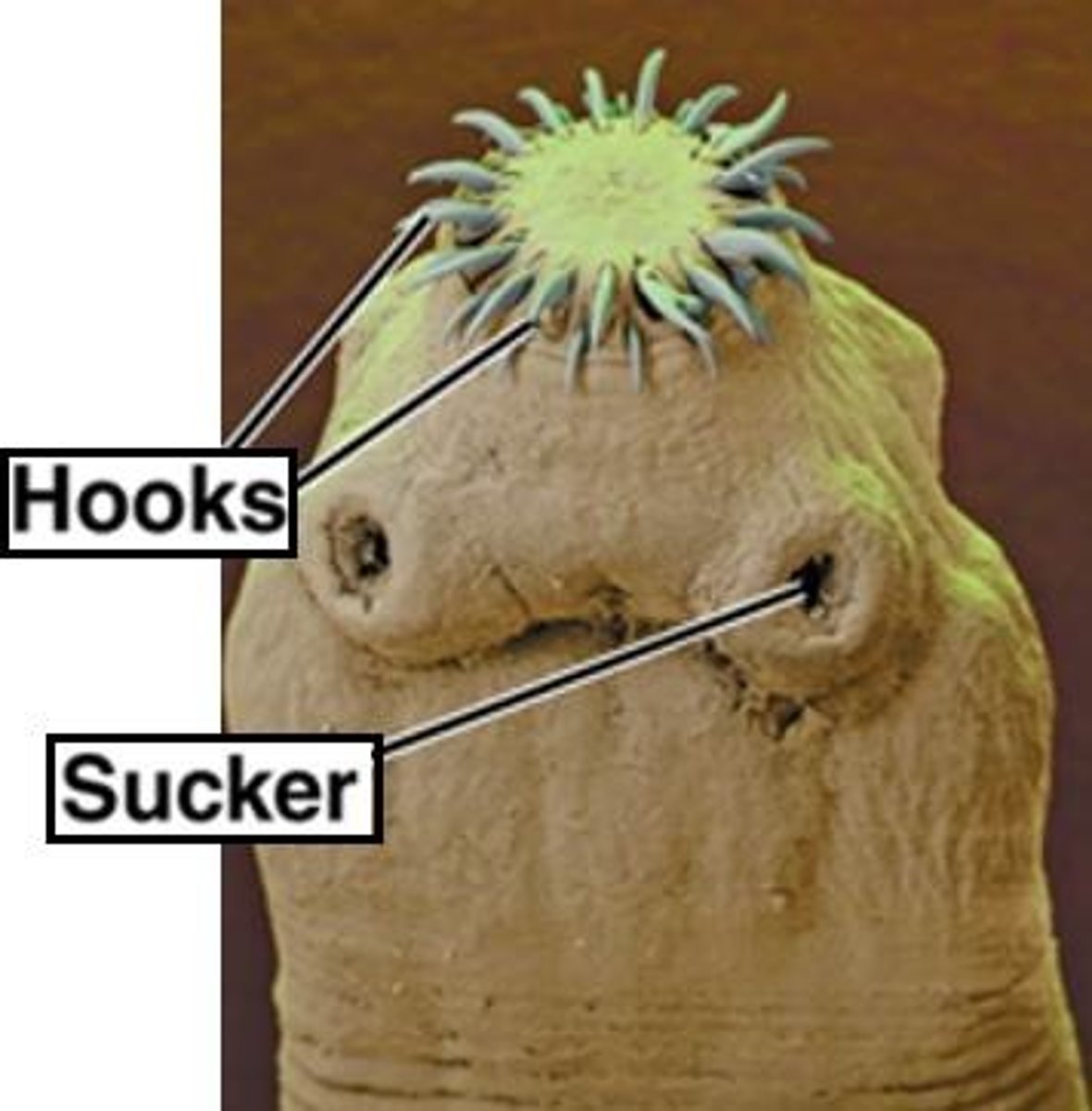
Tapeworms (cestodes)
Mostly parasitize vertebrates and attach to intestinal lining of host to obtain nutrients
Rotifers
Phylum: Syndermata = Rotifers; Protostomes with a body cavity (pseudocoelmates) and an alimentary canal
Mollusca
Includes snails, slugs, oysters, clams, octopuses, and squids; mostly marine, some freshwater & terrestrial
Mollusca Body Plan
Soft-bodied, but most secrete a hard shell; body cavity: Coelmates (hemocoel)
Radula
Organ that scrapes up food in molluscs
Circulatory System in Mollusca
Open (except cephalopods) with hemolymph as the circulatory fluid
Gas Exchange in Mollusca
Occurs through gills or simple lung
Digestive System in Mollusca
Scavengers with a digestive gland containing enzymes
Nervous System in Mollusca
Nerve ring around esophagus with nerve cords and cephalization
Excretion in Mollusca
Excretion organs present
Reproduction in Mollusca
Most have both sexes; snails are hermaphroditic
Mollusca Major Groups
Gastropoda (snails and slugs), Bivalvia (clams, oysters, and other bivalves), Cephalopoda (squids, octopuses, cuttlefish, and chambered nautiluses)
Cephalopoda
Active marine predators with a closed circulatory system, complex brain, and well-developed sense organs
Annelida
Segmented worms found in marine & freshwater and damp soil; coelomates and protostomes
Annelida Orders
1) Sedentaria (burrowers) 2) Errantia (swimmers, crawlers)
Leeches
Mostly freshwater predators & parasites that secrete hirudin to prevent blood coagulation
Earthworms
Class: Oligochaetes; have a complete digestive system and extract nutrients from soil
Gas Exchange in Annelida
Occurs through diffusion across skin
Excretion in Annelida
Nephrostome removes nitrogenous waste
Circulatory System in Annelida
Closed with blood
Reproduction in Annelida
Hermaphrodites that cross-fertilize
Lophotrochozoan
Includes two more phyla: Ectoprocta and Brachipoda, which have lophophores for feeding
Body Cavity in Lophotrochozoans
Yes! Coelomates
Deuterostomes
A classification that includes certain phyla of Lophotrochozoans