APSC 100 Midterm (if anyone mentions typos ur dead)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Stakeholder
anyone who is influenced by the project, or who can influence the project
Universal Design
creating solutions that are inclusive of as many different people as possible, work for all users without requiring modifications or special training
Design Process: Stage 1
Study and clarify problem; define the problem we are going to solve, including what determines if a solution is acceptable and of high quality
Needs
stakeholder wants or expectations of what the final design should be or do
Expressed Needs
what stakeholders will actually say if you ask them
Threshold needs
often obvious things stakeholders expect but will forget to say
Latent needs
unexpected things stakeholders may have not considered but would delight them if done
Target Design Specification
a precise description of what the final design has to be or do
quantifiable or testable
developed from the need
an unambiguous agreement on what the team will attempt to achieve in order to satisfy the customer needs
Two Types of Design Specification
requirements
evaluation criteria
requirements
the limits of acceptability for a design which are passed/failed
evaluation criteria
measures that distinguish between levels of performance or stakeholder satisfaction
validation in the design process
do the specifications accurately capture the stakeholder needs?
verification in the design process
does the final design solution meet the specifications?
Design Process: Stage 2
Generate potential solutions
Guidelines for generating solutions
Don’t fixate or anchor on any specific ideas; resists developing on the first or favourite idea
Don’t evaluate ideas
Quantity > Quality; encourage variety of ideas
Wild or unusual ideas are encouraged
Design Process: Stage 3
Identify most promising solution
Screening
eliminate ideas that will never work
Engineering Design
the systematic process through which engineering knowledge and skills are applied to solve real-world, open-ended problems.
Iteration
continuously reviewing and revising previous work
Design Process: Stage 4
Develop and test solution
Design Process: Stage 5
implement the solution; final construction or detailing of the solution
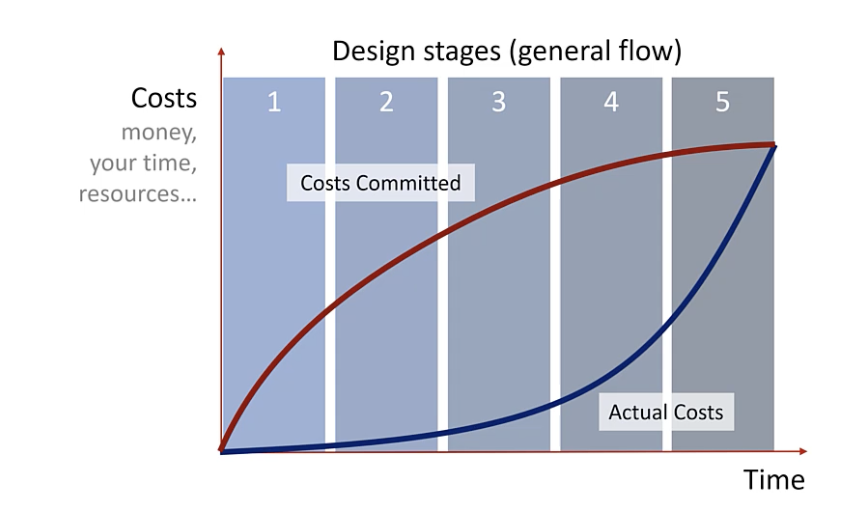
Costs Committed
the actual costs to date plus the anticipated future costs from the decision
the decisions we make early in the project determine most of our spending that occurs later in the project
actual cost
the money, effort, and resources we have spent or consumed in a project
Screening
eliminating concepts that cannot be made to meet all requirements
Ranking
the process of qualitatively comparing ideas in order to narrow down to a small number worth investigating further; quickly and roughly rank from strong to weak; look for consistently strong ideas
Scoring
a detailed and resource-intensive process to quantitatively evaluate a small number of ideas; aim to identify the one idea to be pursued
Individual Voting
Ranking method; each person has a set number of votes which they can distribute among concepts
pairwise comparison
Ranking method; comparing each concept against every other concept, one at a time; a concept receives one point each time it is favoured in comparison, half a point if it is tied, and no points otherwise
criterion-based ranking
ranking method; concepts are qualitativey evaluated using each of the evaluation criteria from the deign specifications; a concept receives +1 if it performs above average, -1 if it is expected to perform below average, and 0 if it is average
weighted decision matrix
scoring method; a common tool used in scoring based on rating multiple options against each evaluation criterion with a weight applied
sensitivity analysis
a process where weights and scores are adjusted in a cWDM to assess the consistency of the results
prototypes
simple models of representations of a final design which reduce risk; sketches, computer drawings. foam models etc
focused prototypes
only capture one or two aspects of the design
comprehensive prototypes
all encompassing and near complete representations of the final design
dimensions to classify protoypes
focused to comprehensive, virtual to physical
3 elements of a presentation
audience, context, purpose
What should you know about your audience?
already know, need to know, and not know
think/opinion on topic
hope to get out of your presentation
purpose
describes the goals and reasons in delivering the presentation; what are you trying to convey
2 categories of presentations
Inform - describe, review, instruct, explain
Persuade - convince, influence, recommend, change, justify
context
situational factors which led to you developing the presentation
the setting
other factors such as time, tools, and space
AAA designations stands for..
all ages and abilities
scales
consider a problem at different levels to determine the real issue and to identify all key stakeholders and potential solutions
What should we expect to change when we view a problem at a different scale?
The context and details of the problem
The group of key stakeholders
Potential Solutions
Danger(s) of viewing a problem at only one scale?
we might not be aware of the optimal solution
key stakeholders to the problem may be neglected
we might commit resources to solving the “wrong” problem
Salience
the measurement of how prominent and important a stakeholder is in a given project.
3 main elements to salience
power, urgency, legitimacy
power
the ability to influence a project (decision making authority, financial or resource contribution, expertise, etc.
urgency
has important or time-sensitive needs in the project
legitimacy
has a right to have a say in the project (they are directly impacted or they are legally entitled to give input)
rights holder
a stakeholder with addition legal or human rights which could be impacted by a project
primary stakeholder
stakeholder with power, urgency, and legitimacy
secondary stakeholder
stakeholder with two of the elements of salience
tertiary stakeholder
stakeholder with one of the elements
we use the salience model to classify stakeholders into which of the following categories?
primary, secondary, tertiary
bearable
both environment and society
viable
both environment and economy
equitable
both economy and society
sustainability
supporting the human world of people, society, culture, and the economy, while protecting and preserving the natural world right now and being able to continue to do this indefinitely;
the capacity of human society to continue indefinitely within the earth’s natural cycles
dimensions of sustainability
environment, society, economy
four principles of sustainability
Avoid consumption rates greater than the replenishment rate of resources.
Avoid making things and releasing things at a rate faster than it takes for them to break down.
Avoid degrading ecosystems, at a rate faster than they can naturally regrow
As a society, move towards happiness, wellbeing and meeting the needs of all people.