Chemistry criteria A final
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
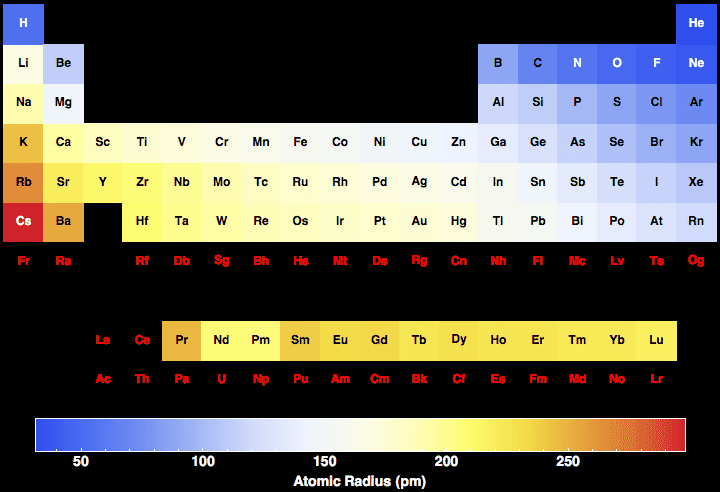
Atomic Radius
The size of the atom
Ionization Energy
How much energy taken to remove an outer electron
Electron Negativity
How much energy taken to add an electron
Atomic radius pattern
the more protons (the higher atomic number) the smaller the radius is due to the high positive charge pulling the electrons in. The bigger the atomic number though the more shells it has and the less effective the positive charge is. So the smallest radius is in the top right corner.
Electronegativity pattern
The more protons the higher the electronegativity but the further away the outer shell is the lower as the charge i less effective
Ionization energy pattern
The more protons there are the higher the energy needed to remove an electron however the further the outer shell is the lower the amount of energy is required to remove an electron
Period
horizontal
Group
vertical
Alkali metals
the red section, first group on the periodic table
Alkaline earth metals
the second group in the periodic table
Halogens
The yellow section, 17th group
Noble gasses
18th group
anion
A negative atom, occurs when an electron is gained
Cation
A positive atom, occurs when an electron is lost
Atomic structure (amount of electrons in shells)
2,8,8
Isotopes
When an atom has more or less neutrons
atomic mass
The weight of the average atom of an element (Amu)
Mass of an electron
1/1800
Factors that affect reaction rates
Temperature- Kinetic energy increases chance of collisions
Concentration- more of the solute increases chance of collisions
Surface area-Increases chance of collisions
Amount of catalysts-can create more of the correct collisions in the right positions
Collision theory
For a reaction to occur, the particles must collide with enough energy in the correct orientation.
Reaction rate
Change in mass of reactant(or product)/time
Activation energy
he minimum energy required for a reaction to occur.
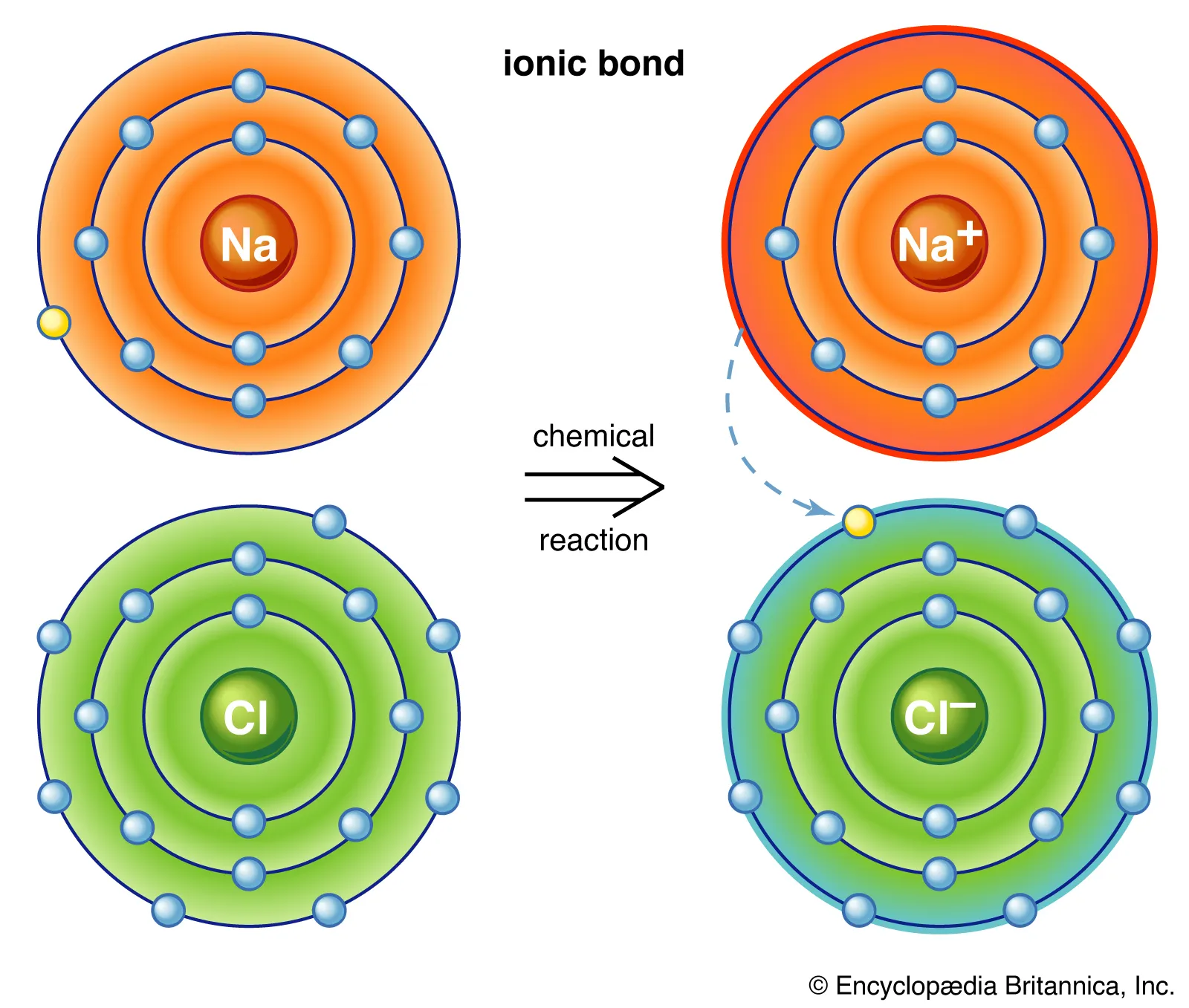
Ionic bonding
metal to non metal, transfer of electrons to another atom
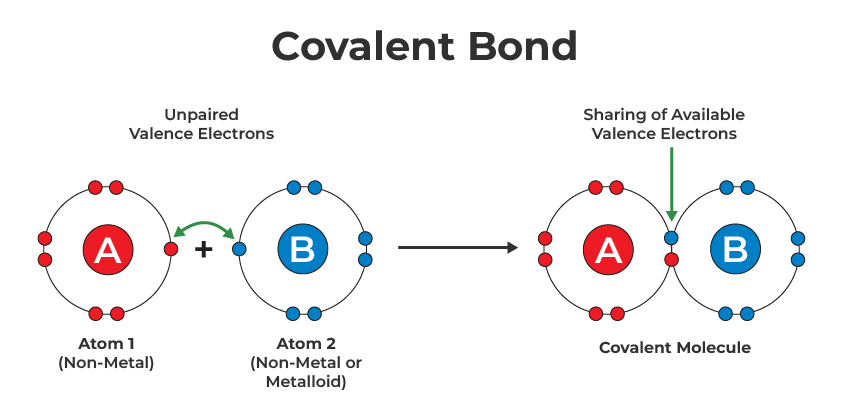
Covalent bonding
non metal to non metal, sharing of electrons between atoms
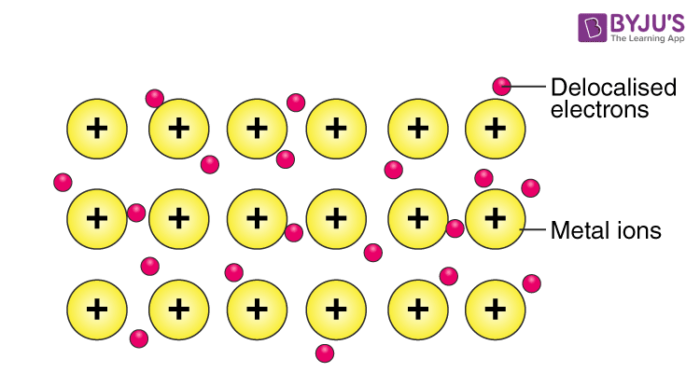
Metallic bonding
Metal to metal, a sea of shared electrons.
Acid
any hydrogen-containing substance that is capable of donating a proton
base
a substance that can accept hydrogen ions in water
pH scale
A scale from 1 to 14 showing how acidic or basic solution is. Lower being more acidic and higher being more alkali, 7 being neutral.
neutralization with bases
If an acid is added to a basic solution, the solution becomes less basic and moves toward the middle of the pH scale
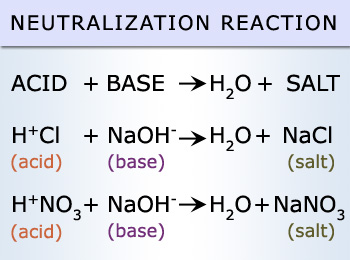
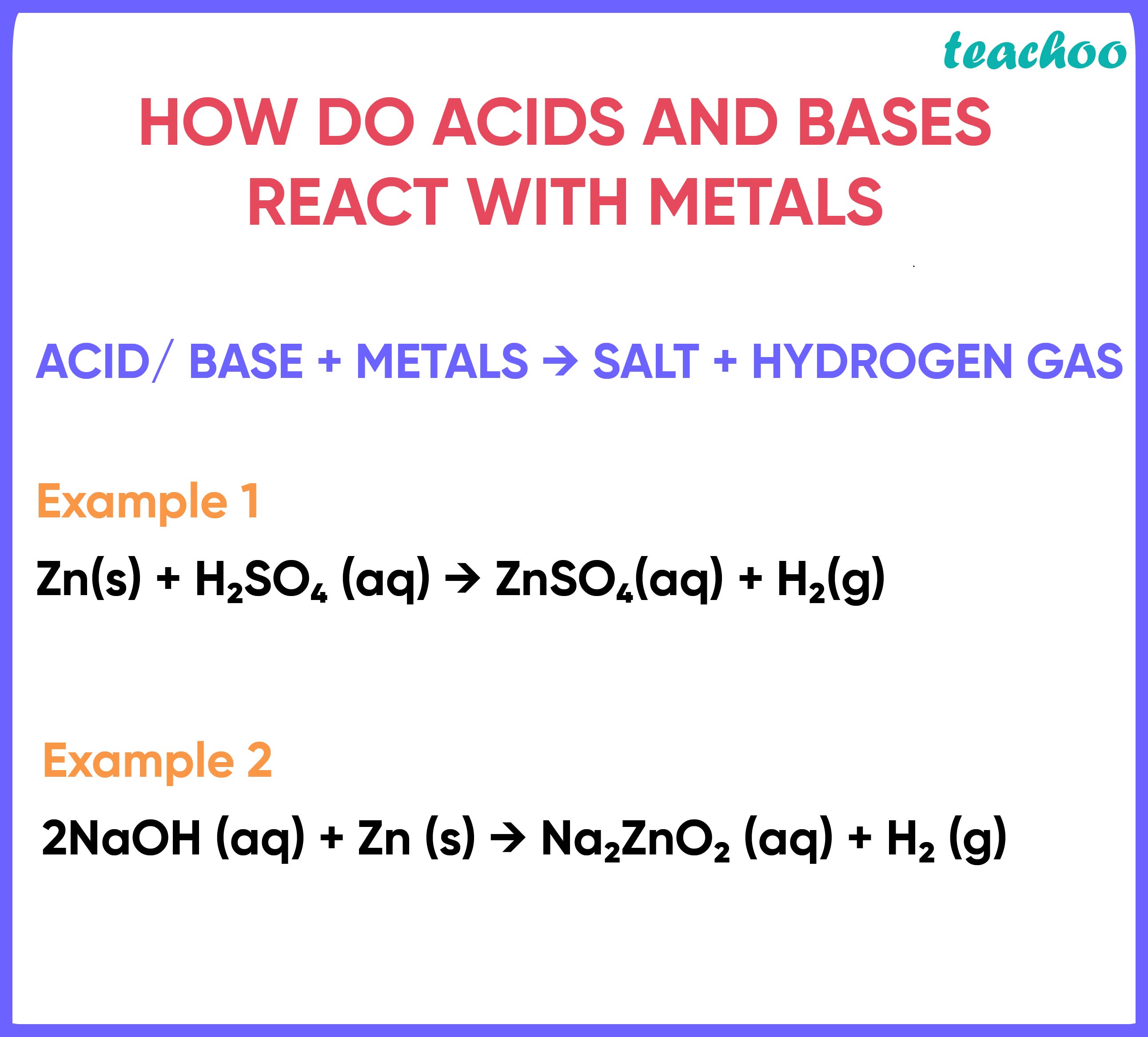
an acid’s reaction with metals
forms a salt and hydrogen gas
acid Reaction with carbonates
Result in water carbon dioxide and salt

basic titration
process of chemical analysis in which the quantity of some constituent of a sample is determined by adding to the measured sample an exactly known quantity of another substance with which the desired constituent reacts in a definite, known proportion.
Indicator
A chemical compound that changes color and structure when exposed to certain conditions and is therefore useful for chemical tests