Head and Neck Anatomy - Skull and Cranial Cavity
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the anatomy of the skull, including the cranium, facial bones, sutures, fossae, and meninges, for review and exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
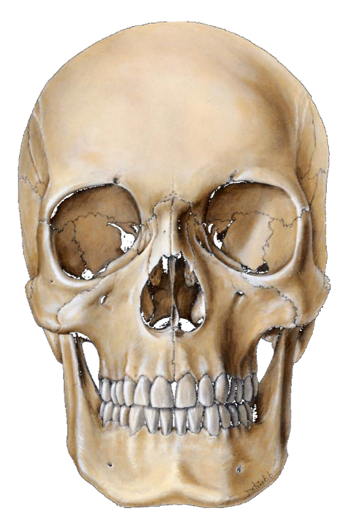
Anterior View
Anterior view of the skull as if you are looking at someone's face.
Maxilla
Upper jaw, holds the soft tissues.
Mandible
The only movable bone in the adult skull.
Neurocranium
Includes cerebrum, cerebellum, and cranial nerves.
Viscerocranium
Includes the soft tissues of the skull, such as the face, orbit of the eye, nasal cavity, and mouth; Includes the mandible
Calvaria/Cranial Cap
The rounded, domed portion of the skull where a hat would sit.
SCALP
Skin, Connective tissue, Aponeurotic layer, Loose connective tissue, Periosteum
Suture
The connecting points or articulation sites between the bones of the skull
Coronal Suture
Joins the frontal bone to the two parietal bones on the sides
Sphenoid Bone
Connects right side to the left side of the skull. Has the greater wing that connects to the frontal, parietal, temporal bones
Pterion
Connecting suture between the frontal bone, parietal bone, temporal bone, and the greater wing of the sphenoid. Naturally weak point of the skull.
Lacrimal Bone
Located inside the orbit of the eye; tears drain through here.
Coronal Suture
Connects your frontal bone to the two parietal bones
Sagittal Suture
Connects the two parietal bones
Lambdoid Suture
Connects the occipital bone to the two parietal bones
Fontanelles
Soft spots on an infant's skull.
Bregma
The intersection of the coronal and sagittal sutures in a child past two years of age
Lambda
Intersection between the sagittal suture and the lambdoid suture
Nasal Septum
Separation between the right and left nasal passages.
Vomer
Part of the bony portion of the nasal septum.
Hypoglossal Canal
Located in the perimeter of the foramen magnum. More transverse positioned hole
Communicating Foramina
Holes that allow structures to pass through the skull.
Incisive Foramen/Fossa
Front teeth, just behind them on maxilla
Greater Palatine Foramen
Located very close to the molars, found on the hard palate
Foramen Ovale
Directly posterior to the greater palatine foramen, slightly lateral
Foramen Lacerum
Directly medial to your foramen ovale
Foramen Spinosum
Pretty much directly lateral to your foramen ovale
Carotid Canal
Starts in the petrous portion of the temporal bone.
Stylomastoid Foramen
An opening located between the styloid process and the mastoid process of the temporal bone
Foramen Magnum
Located in occipital bone; spinal cord transitions away from brainstem here
Anterior Cranial Fossa
The highest cranial fossa, directly above the eyeballs, includes frontal and ethmoid bones. Frontal lobe of the brain sits here.
Middle Cranial Fossa
Level with the tops of your ears. Temporal lobes of the brain are housed here
Posterior Cranial Fossa
Primarily for the cerebellum. Hypoglossal canal and jugular foramen are located here
Crista Galli
Pointed structure coming out of the ethmoid bone in the anterior cranial fossa
Sella Turcica/Dorsum Sellae
Structure of the sphenoid bone shaped like a Turkish saddle that houses the pituitary gland
Dura Mater
Most superficial and thickest layer of the meninges.
Arachnoid Mater
Deep to the dura mater
Pia Mater
Deep to the arachnoid mater
Falx Cerebri
The dura mater folds into itself to protect the two lobes from touching each other.
Superior Sagittal Sinus
Structure on the skull that indicates the vein of the brain
Subdural Space
Potential space that should not exist in a nonpathogenic person. If seen on an MRI or CT scan, it is a bad sign.
Arachnoid Granulations
Outpouching of arachnoid mater that allows cerebrospinal fluid to filter into the venous system.
Tentorium Cerebelli
The dura mater folds in on itself and forms a tent over the cerebellum, separating the cerebellum from the occipital lobe
Cavernous Sinus
Located on either side of the dorsum sellae and the pituitary gland. Nerves and arteries pass through it. Point of drainage for face