Psych disorders exam 3
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Class poll on sex-related disorders
How do we define normal?
Main point → have to ask many other clarifying questions, and identity what we define as normal
Main difference between men and women (sex related disorders)
Frequency of masturbation
Other U.S. gender differences
Males are more permissive regarding premarital sex, but gap shrinking
Frequency of sex, number of partners, slightly greater in males
Females are more likely to report passion and romance important for sexuality
Females are more likely to have self-conscious and negative schema about sex
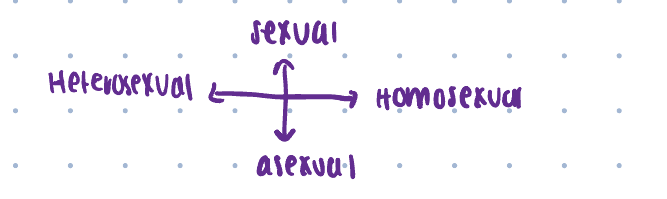
Sex spectrum
Homosexual used to be in DSM
Not a binary thing
Have to also think about gender identities
At what point is there a disorder
Sex
Biological characteristics to delineate male and female
Genitalia
Sex chromosomes
Internal organs
Also on a spectrum → ex: intersex: born with characteristics that are not male nor female
Gender, gender identity, gender expression, sexual orientation
Constructs, not as biological
Gender identity: make sense of own gender
Gender expression: how you convey to the world (cultural restraints)
Sexual orientation: what gender you are attracted to
Gender dysphoria
Controversial: and should it be a “disorder”? A DSM-5 change from gender identity disorder
Biological sex does not match gender identity and distress is the focus
Independent of sexual orientation
In what duration and severity should these lead to labels and transitions? No easy answers
Higher risk for mood disorders and suicide
Stages of sexual response
Desire
Arousal
Plateau
Orgasm
Revolution
Sometimes shortened to desire, arousal, orgasm
Sexual dysfunction
Something is going wrong in one of the phases of the sexual response
Treatment of sexual dysfunction
Education
Increased communication
Sensate focus (non demand pleasuring)
Dysfunction involves performance anxiety
Performance plummets
Pleasure/be pleasured without demand of needing an orgasm
CBT for performance anxiety
Ex: negative schemas about sex, shame, insecurities
Self-pleasuring → exploring own body
Possible medication
Erectile dysfunction drugs (psych disorder related)
Prescribed a lot so we have to ask if we have to change norms, does this change performance anxiety
Paraphilic Disorders
Definition: arousal to something deemed inappropriate, causing distress
Fetishistic disorder
Attraction to (typically object) that is problematic
Voyeuristic and exhibitionistic disorder
V → someone looking at someone against their will
E → actual exposure of yourself to someone against their will
Transvestic disorder
Sexual gratification from clothing
Sexual sadism and masochism disorder
S → infliction of pain
M → receiving the pain
Frotteuristic disorder
Sexual gratification from rubbing up against someone who is unsuspecting and not consensual
Sadistic rape
Violence and infliction of harm is whole point of sexual gratification
Pedophilic disorder and incest
P → attraction to prepubescent children (attraction itself, do not always act on it)
I → attraction to someone to whom you are in a familial relationship with
Causes of paraphilic disorders
Genetics? still unclear
Difficulty forming “normal” relationships
Deficits in typical sexual experiences
Relationship difficulties in childhood or adolescence
Early experiences may lead to sexual associations by chance > then reinforced through masturbation
Often have very high sex drive
Suppressing unwanted fantasies may paradoxically increase them
Treatment of paraphilic disorders
Covert sensitization
Creating aversive stimuli
Negative effects of object and fantasy
Ex: mild electric schools - very controversial
Orgasmic reconditioning
Insert a more positive and sexual stimulus
Last second → switch to a more positive stimulus
Will be gradually conditioned
Coping and relapse prevention (most important) as there is a high rate of relapse
Keep in mind → high comorbidity with mood, anxiety, and substance related disorders
Modern technology role in sex related disorders
Ex: chat-roulette → placed randomly with a stranger on video chat
A lot of exhibitionist
Larger problems now than what it used to be due to access of technology
Causes of paraphilic disorders → book chart
Gender non-conformity in children
Phenomenon in which prepubescent children do not identify with their biological sex, but instead identify strongly with the gender of the opposite sex and display varying degrees of behavior more characteristic of the opposite sex
Types of sexual dysfunction
Desire
Men → male hypoactive sexual desire disorder (little or no desire to have sex)
Women → female sexual interest/arousal disorder (little or no desire to have sex)
Arousal
Men → erectile disorder (difficulty attaining or maintaining erections)
Women → female sexual interest/arousal disorder (little or no desire to have sex)
Orgasm
Men → delayed ejaculation; premature (early) ejaculation
Women → female orgasmic disorder
Pain
Women → Genito-pelvic pain/penetration disorder (pain, anxiety, and tension associated with sexual activity; vaginismus, that is muscle spasms in the vagina that interfere with penetration
Cultural differences in sexuality
The Sambia in Papau New Guinea believe semen is an essential substance for growth and development in young boys of the tribe
They also believe semen is not produced naturally; that is, the body is incapable of producing it spontaneously
Therefore all young boys in the tribe, around age 7, become semen recipients by engaging exclusively in oral sex with teenage boys
Masturbation is forbidden and absent
Then will switch roles
Heterosexual relations are prohibited until boys become teenagers
In contrast, the Munda of northeast India require adolescents and children to live together
But in this group, both male and female children live in same setting, and sexual activity is all heterosexual
Western cultures there is still variation
Premarital sexual behavior is culturally accepted and encouraged in about half of 100 societies surveyed
Sexual orientation
Some reports suggest that sexual orientation is mediated by early actions of sex steroids, the direct actions of sex specific genes, and epigenetic mechanisms
In two twin studies, same-sex sexual orientation was shared in approximately 50% of identical twins, compared with 16% to 22% of fraternal twins
Other studies reveal that genes account for approximately 34% to 39% of the cause in men and 18% to 19% of the cause in women, with the remainder accounted for by environmental influences
Overall some genetic basis but not overly strong
Some of the identified genetic loci are linked to hormone regulation identified with male patterned balding
Some support to the theory of differential hormone exposure in utero
No factor, biological or psychological, can predict the outcome
Likely that sexual orientation can change over time
Substance abuse statistic
Abuse of drugs and alcohol kills 500,000 annually
Substances
Chemical compounds that are ingested to alter mood or behavior
Psychoactive
Have an effect on the mind, typically can lead to intoxication or being high, possibility of addiction
Levels of interaction with substance use
Use, with different methods of ingestion
Intoxication → under influence somehow
Abuse → clear DSM disorder → used in a way that causes distress and impairment
Dependence/addiction → physiologically and psychologically need drug
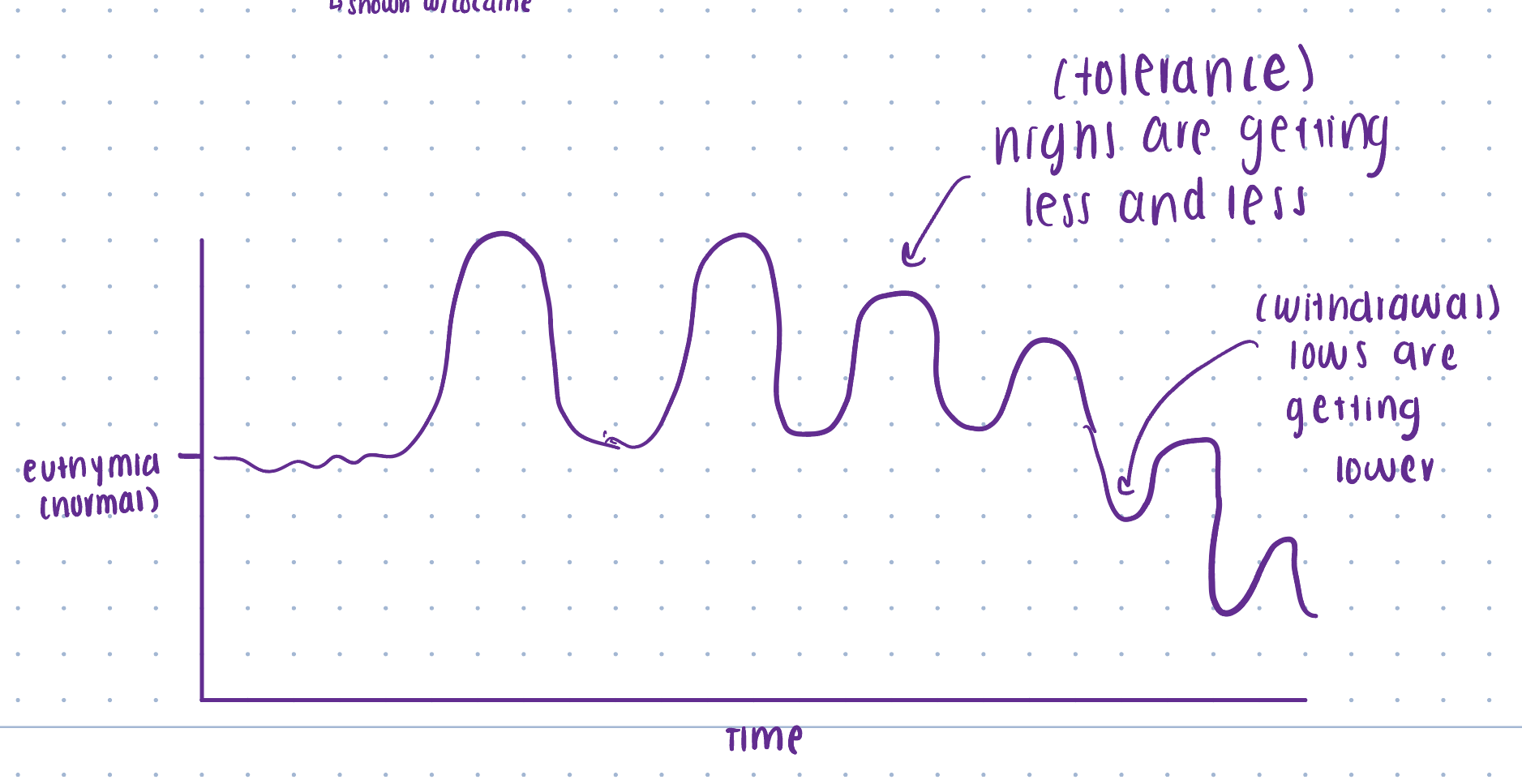
Dependence
Physiological: tolerance and withdrawal
Tolerance → feel less over time → need more to get same effect, matter of conditioning
Withdrawal → no substance in system - system cannot get back to normal → nervous system out of control trying to compensate
Psychological: drug-seeking behavior
Shown with cocaine
Diagram of tolerance and withdrawal
Ultimately tolerance and withdrawal work together to get someone really stuck → video of bird example
Five categories of substance
Depressants “downers'“: include sedation (sedatives, alcohol, muscle relaxers, benzodiazepine, some sleeping pills)
Stimulants “uppers”: increase alertness (caffeine, nicotine, adderall, cocaine)
Opiates: produce analgesia (pain reduction), induce feeling of wellbeing/euphoria such as heroine
Opioids include synthetic drugs as well such as Percocet and oxytocin
Hallucinogens: alter sensory perception (LSD, ketamine, marijuana, psychedelics)
Other: a variety of effects
Inhalants, anabolic steroids, cough syrup with DMX, ecstasy, MDMA, Molly)
Substance related disorders
New DSM-5 term
Sometimes other disorders can interfere with symptomology
Gambling disorder is now added in within this (develop tolerance and withdrawal)
Amount of substance are not specific
11 symptoms that presents the range of severity
2-3 symptoms are mild
4-5 moderate
6 or more severe
Symptoms of substance related disorders
Substance taken in larger amounts or over longer period than intended
Persistent desire to cut down/unsuccessful efforts
Lots of time on activities related to obtaining, using, or recovering
Strong cravings
Disruption in fulfilling obligations, due to use
Social or interpersonal problems due to use
Activities given up or reduced because of use
Use when physically hazardous
Use despite knowledge of having physical or psychological problems related to it
Tolerance (may vary by substance)
Withdrawal (may vary by substance)
Method of ingestion does…
Affect potency - getting into bloodstream
Alcohol
A depressant, but initial depression of inhibitory centers
Central nervous system → relaxed muscle tension, less coordinate, bad reaction times
Body → heart, lungs, liver
Brain → glutamate, GABA, serotonin, neuron communication
Fetal alcohol syndrome is an issue → facial development, developmental delays
Long term-effects on brain like dementia, but does it cumulatively kill brain cells?
Data is mixed
Lately → data shows even small amounts are not good
Hard because there is no controlled randomized experiments, most of time it is correlational
Brain effects (alcohol)
Glutamate → encoding memory
GABA → inhibitory neurotransmitter
Serotonin → sleep, mood, eating
Neuron communication → alcohol slows this down
Combination of alcohol + other classes of drugs
Ex: four look → caffeine + alcohol = poisoning can happen more easily
Caffeine: stimulant (artificially prop you up) to probably keep drinking
Alcohol: depressant
If in same class → could magnify effects
Alcohol use in the United States
Most adults: light drinkers or abstainers
Overall use has done down since mad men area, but binge drinking has gone up
Current use = around 50% of Americans drink
Binge drinking = around 24.6% of Americans had 5+ drinks one on occasion in past month
Rates are higher in males than females
Millions of American Adults Alcohol Dependent
Cultural differences worldwide
Role of genetics and alcohol dehydrogenase
Ex: “Asian flush”
Heaviest drinking 10% of Americans
This group of adults, over age 18, consume on average, 74 alcoholic drinks per week, that works out to a little more than four and a half 750 mL bottles of Jack Daniels, or 18 bottles of wine, or three 24 Cana cases of beer in one week
Or 10 drinks per day
Alcohol withdrawal effects
Body is trying to compensate
Tremors
Nausea/vomiting
Anxiety
Transient hallucinations
Agitation
Insomnia
DTs (delirium tremors) are life threatening → likely to go into seizures or cardiac arrest)
The Pickle Hypothesis
Once you turn something into a pickle you cannot unpickle it
Does tolerance ever go back down?
Opioids/opiates
Opioid dependence is considered an epidemic, especially in certain hard hit areas
Prescription painkiller abuse a serious problem
Uptick in heroin deaths related
Overdose happens when breathing slows to a stop
Withdrawal effects: nausea/vomiting, chills, muscle aches, diarrhea, insomnia
Naloxone (narcan) can save lives in overdose disputations, but availability is controversial
Some believe that people will not help if narcan is available
Marijuana (hallucinogen)
Potency depends on THC levels - what we have now is a lot larger than before
Some research linking teenage use with increased risk of psychosis
Research is hard to come by
Mixed data on tolerance, but psychological addiction can occur
Often used to mask depression and anxiety
Can still impair driving skills, but many variables exist
Other hallucinogens
LSD, mescaline, psilocybin, PCP, DXM (active compound in cough syrup), ketamine (potential role for depression therapy)
Psilocybin (shrooms)
Potential therapeutic role → clinical usage
Problem: hard to get rid of confounds because there are no placebos
Stimulants
Turning up nervous system
Ritalin and adderall abuse is a major issue
Tolerance and withdrawal can happen in non therapeutic doses (fatigue, sluggish, not motivated)
Methamphetamine is a growing problem in rural areas → potent, gives buzz/high energy - bad for heart
Ecstasy and MDMA not typical of this category, more of a hallucinogen
Cocaine shows a different early pattern of tolerance and dependence, but boredom and apathy at withdrawal
Not great longitudinal research on e-cogs, but some major concerns (not just used with stimulants)
Issues with e-cigs
Amount of nicotine + additives
In theory: remove what makes smoking bad for lungs by vaporizing, removing carcinogenic effects, and people would stop smoking cigarettes
Companies hooked in new people who would not have smoked in the first place → overall not universally better from a lungs and cardiovascular standpoint
Also harder to regulate since it is easier to do in secret
This was a way that the government was able to regulate behavior on smoking cigarettes in the 80s → taxations, laws, warning messages
Behavioral techniques for quitting (nicotine)
Gradually cutting down is best way to go
Nic withdrawal → sluggish, uneasy, headaches
But tend to save for when they most need it → psychological conditioning worsens
Much more advise a random schedule to eventually, learn to break conditioning and find new coping mechanisms
Amphetamines physiological effects
Effects of amphetamines:
Produce elation, vigor, reduce fatigue
Such effects can be followed by extreme fatigue and depression
Amphetamines stimulate CNS by
Enhancing release of norepinephrine and dopamine
Reuptake is subsequently blocked
Kratom
Properties of both an opiate and a stimulant
Comes from leaves from a topical tree
Toxicity is possible - death has occurred in high dosages
Withdrawal symptoms are possible
Often chewed, powder, liquid form
Tianeptine
Tricyclic antidepressant - risk of overdose
Recreationally used for potential effects as an opioid agonist
“gas station heroin”
2C-B
Synthetic psychedelic
“Nexus” “Bromo” “Venus” “Pink cocaine”
Powder, pills, sometimes mistaken for ecstasy
Not a lot of research but there seems to be similar psychological risks as other psychedelics and physical risks as stimulants such as cardiovascular issues and stroke
Poppers - Alkyl nitrates
Inhalants
Liquid, but then inhaled as vapor
Other category
Vasodilators: relax and widen blood vessels
Fast acting and short lived effects, sometimes paired with sexual activity
Been around for decades as club drugs
Chemical burns, eye damage
Cardiovascular effects
Not sold as recreational drugs to try to get around regulations
Etiology of substance abuse disorders
Diathesis stress and gene environmental correlation model
Psychosocial stressors
Social and cultural expectations for use
Exposure to drug
Psychological influences:
Positive reinforcement (feel good and confidence), negative reinforcement (removing anxiety), cognitive influences (what you believe you need and how you view the substance)
Biological influences: sensitivity to drug, rate of metabolism, base levels of arousal, co-occurring disorders, personality
Treatment for substance abuse disorders
Biological treatments: agonists (e.g. methadone - substitute drug and suboxone- treat opioid dependence), antagonists (e.g. naltrexone- blocks feeling), aversive treatments (Antabuse)
Psychological treatments: counseling, 12 step programs
Much controversy, and one size does not fit all
Many treatments should be tried, relapse risk can be high
Co-existing disorders need to be treated
Alcoholic anonymous: a 12 step program
A lot in common with CBT
Abstinence: learn to give up substance
Meeting with other people who struggle as well
Decentralized and deregulated
Social connection model
Integrative model for substance abuse disorders

Hallucinogen- related disorders (book)
Albert Hoffmann → created and recorded first trip of LSD
LSD (also known as acid) is the most common hallucinogenic drug
Synthetically produced
Used to be used as truth serum by CIA
Psilocybin (shrooms), DMT, PCP
Perceptual changes such as subjective intensification of perceptions, depersonalization, and hallucinations
Physical symptoms: pupillary dilation, rapid heartbeat, sweating, and blurred vision
Increased reports of mystical experiences
Tolerance developed quickly
No withdrawal symptoms are reported
Possibility of psychotic reactions
Chemically similar to neurotransmitters
Role of prevention (substance abuse disorders)
Education about drug risks
DARE program → encourages a no drug use message through fear of consequences, rewards for commitments not to use drugs, and strategies for refusing offers of drugs → not always helpful
More comprehensive programs that involve skills training to avoid or resist social pressures (such as peers) and environmental pressures (such as media portals of drug use) can be effective in preventing drug misuse among some
Etiology of impulse control disorders
neurotransmitter dysfunction
stress
genetics
Impulse control disorders - related to substance abuse
Intermittent explosive disorder
Exploding with rage
Adults
Cannot manage impulse to act out on anger
Kleptomania
Steal because they cannot stop
Rush of stealing
Pyromania
Spark from starting fires
Impulse to be around fire
How psychological factors affect biology and physical health
Through underlying physiological process
Ex: bp, immune system, inflammation, gut microbiome
Through behavior and lifestyle factors
Ex: accident control, smoking cigs, exercice
Lifestyle factors
Account for as many as fifty percent of deaths from the top 10 leading causes of death
Smoking, substance overdose, poor nutrition, lack of exercise, inadequate safety
For some health issues, both mechanisms at work
Ex: genital herpes, shingles
Stress levels can worsen outbreaks
Behavioral medicine
Knowledge derived from behavioral science is applied to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of medical problems
Health psychology
Study of psychological factors that promote and maintain health as well as healthcare systems and health policy
Stress
Boys response to a stressor
Ex: cannot sleep well, getting rashes
Bridge analogy:
Bridge around for 50 years
Dust, crack, fractures (stress)
Cars going over, wind, rain (stressor)
General adaptation syndrome
Alarm: detected a stressor, under threat
Resistance: how body manages and withstand threat, coping mechanisms
Exhaustion: depleted damage (too severe and too long)
HPA axis
Stress activates HPA axis
Hypothalamus releases CRF and stimulates pituitary gland
Pituitary gland activates adrenal glands, secreting cortisol (stress hormone)
Ordinarily hippocampus turns off stress response, but can be damaged by excessive or chronic stress
What determines your stress response
Psychosocial factors: predictability and controllability (ex: having a schedule)
Ability to find coping mechanisms → social connection is key
Physical health: a vicious cycle (already in exhaustion phase, harder to get back)
Attributions/ability to be optimistic
Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI)
Very hot field
Studies psychological influences on the neurological responses and its relationship to the immune system
HIV (virus) and AIDs (syndrome from HIV, life threatening)
High priority of public health system
Exclusively lifestyle related - not just if you get it, but lifespan after
A lot of medications developed now
Because some promising medications can extend life, awareness/concern has plummeted
HIV in DC remains an extremely serious problem (1 in 20 people)
Median time from HIV infection to development of AIDS 7-10 years, with great variability
In developing countries, death occurs frequently even within a year
Cancer
Psychoncology
Psychological factors play role in development in disease
Psychological factors play role in treatment and recovery
Psychological and behavioral contributions to the etiology and maintenance of cancer
Perceived lack of control
Poor coping responses (e.g. denial)
Stressful life events
Life-style risk behaviors
Mechanism: psychological factors impact cancer risk by impacting functions such as:
Immune function
Viral activity
DNA repair processes
Gene expression
Younger people are getting colon cancer more frequently
Psychological treatment implications
Psychosocial treatment for cancer improve:
Health habitats
Treatment adherence
Endocrine function
Stress response and coping
May lead to better remission and decreased mortality
Cardiovascular issues and hypertension (high BP)
Psych factors like personality, coping style, social support, and levels of stress can explain individual differences in bp
Warm touch and laughter can reduce bp
Type A behavior, especially hostility and impatience, matters, but maybe it is more about chronic negative emotions
Coronary heart disease also linked to chronic negative affect, low socioeconomic status, and stressful experiences
Psychological and social aspects of pain
Severity of the pain does not seem to predict the reaction to it, primarily as a result of psychological factors
Same factors as those in stress response and other negative emotional states
Determining factor → individuals general sense of control over situation
Positive → associated with active attempts to cope and exercise
Phillips and Grant example → lookout at patients who suffered from back and neck pain after an injury
Almost all expected to recovery quickly, but 40% of them still reported substantial pain in 6 months (chronic pain)
Related to personality, socioeconomic differences, lawsuits
Phantom limb pain: people who have lost a limb still feel pain there
Changes in sensory cortex of brain
Social factors:
Family members who were formerly critical and demanding may become caring and sympathetic (operant control of pain behavior)
Strong network of social support may reduce pain
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Originally neurasthenia (ack of nerve strength)
Prevalent throughout the Western world
Symptoms initially attributed to XMRV (xenotropic murine leukemia virus related virus) a retrovirus with some similarities to HIV
Suffer considerably and often must give up their careers
Less use of sedating medications and a more psychological approach led to better outcomes
Attributed to extremely stressful environment, changing roles of women, rapid dissemination of new technology and information
Nonspecific response to stress
Michael Sharpe → developed one of the first models of the causes
Theorizes that individuals with particular achievement oriented lifestyles undergo a period of extreme stress or acute illness → results in behavioral avoidance, helplessness, depression, and frustration
Genetic factors influence as well
Core beliefs → beliefs → lifestyle → trigger → symptoms → thoughts, mood, behavior, physiology
Tensing and relaxing muscles
People purposefully tense different muscle groups in a sequential fashion followed by relaxing each specific muscle group → learn to recognize tension in different muscle groups and how to reduce it
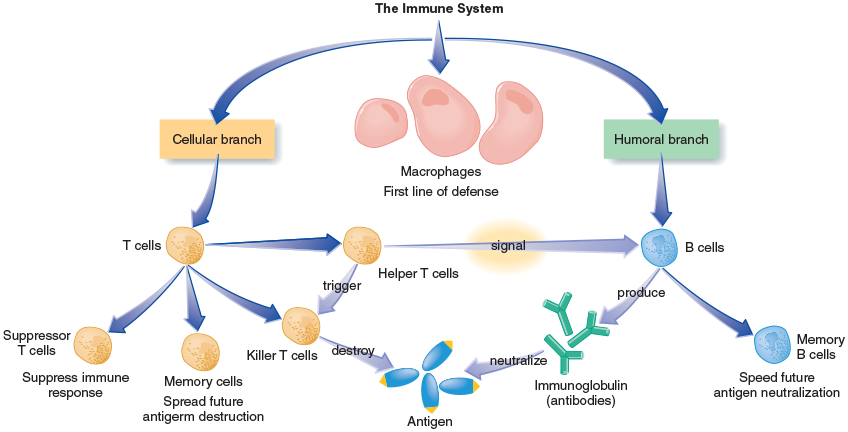
Antigens
Immune system identifies and eliminates foreign materials called antigens in the body
Antigens can be any of a number of substances, usually bacteria, viruses, or parasites
Antibodies
B cells produce highly specific molecules called immunoglobulins that act as antibodies which combine with the antigens to neutralize them
Leukocytes
White blood cells
Multiple types:
Macrophages might be considered one of the body’s first line of defense
They surround identifiable antigens and destroy them
Also signal lymphocytes which consist of two groups, B cells and T cells
Branches of immune system
Cellular branch
Humoral branch
Treatments → health disorders
Biofeedback → ex: watch BP monitor as you do muscle tension relaxation practices, some video games
Be cautious of wearables that track what you do
Relaxation techniques (including progressive muscle relaxation)
Slow and deepen breath, reduce stress response
Breathing through nose (inhale)
Meditation
Love and kindness → putting goodness out into world
Associated with slowing of aging process
Controlled trial experiments - telomere length
A lot of pain in labor and delivery
Why zebras do not get ulcers
Personality disorders is study of
Why individual people behave differently - opposite of social psych
Personality
Characteristic ways that people think and behave
Distinction between personality and disorders
Personality:
Enduring patterns of perceiving, relating to, and thinking about the environment and oneself that are exhibited in a wide range of social and personal contacts
Disorders:
Such patterns are also inflexible, maladaptive, harmful, and cause either significant functional impairment or subjective distress
Personality disordes and childhood
Personally disorders originate in childhood and continue but cannot be diagnosed as a kid since personality is still forming
Five factor model
Neuroticism (renamed emotional stability)
If you scored high before, now score low (valence has changed)
How easily distressed, anxious, angst, easily upset
Extraversion
Are you energized by other people
Agreeableness
How polite, do not want conflict
Not just about being nice
Conscientiousness
Punctual, tidy, organized
Openness to experience
Willingness to try new things, risk taking
Only factor that has correlation with intelligence
What other factors could be involved?
Independence, passive/active, sense of humor, honesty, humility/arrogance
Three personality disorder clusters
A: odd or eccentric
B: dramatic, emotional, or erratic
C: anxious or fearful
Gender bias for personality disorders
Criterion gender bias (criteria is biased)
Assessment gender bias (measures are biased)
A → Paranoid personality disorder
Mistrust
So suspicious of other people - causing problems
Not psychosis
Inherently mistrustful, suspicious without reason
Might lose job after job, relationship with family tanked
Pretty unhappy
A → Schizoid personality disorder
Detachment
Severe detachment from other people and emotions
Cannot make a living, no relationships
Not social anxiety
No desire/completely detached
Anhedonia typically
Some think has something to do with autism
Pretty unhappy because narrow emotional range
A → Schizotypal personality disorder
Odd
Distress and impairment
A lot of magical thinking
Not psychosis
Likely to be homeless
Might be a different type of psychotic disorder, but data unsure now
B → Antisocial personality disorder
Violation
Violating others to get what they want
Many are slick charmers
Lack empathy and remorse
Not “antisocial” in the stereotypical sense
Substance abuse heavily prevalent
Not just psychopathy but also need behavioral component
Under arousal hypothesis → act in cold blood, will not get distressed or feel guilt
Hard to treat because they will manipulate therapist, been like this their whole life
Need to create prosocial relationships
Prevention is the most important
Psychopathy, sociopath, conduct disorder
Psychopathy: personality trait - do not naturally have level of thinking of other people, feeling guilt
All on a spectrum
Also involves arousal
Sociopath: not a clear definition in the way that psychopathy does
Conduct disorder: in children, precursor to antisocial personality disorder
Richard Lee McNair
Shot someone in a robbery and escaped prison
When caught, able to talk his way out of it
Under arousal hypothesis in play
B → Borderline personality disorder
I hate you do not leave me
Erratic relationship history
Not bipolar
Reactive to other people (external)
Most common personality disorder (50% of personality disorders)
More treatable → we have more longitudinal data, more likely to go to therapy, but likely to turn on therapist
Might be a gender bias
Tumultuous and unstable relationships
Rage to a deep depression
Fear of abandonment
Pushing people away out of fear
Cutting is common
How did BPD get its name
Used to be thought of as border of neurosis and psychosis
Comborbid disorder - BPD
80% borderline patients also have major depression; 10% suffer from bipolar
Suicide attempts - 10%
67% are diagnosed with at least one substance use disorder
Eating disorders
25% of bulimia patients have borderline personality disorder
20% have anorexia
Etiology potential - BPD
Strong genetic component
Also linked to depression genetically
High emotional reactivity may be inherited
May have impaired functioning of limbic system
Early trauma/abuse increase risk
Many BPD patients have high levels of shame and low self-esteem
More female but gender bias?
From reactivity standpoint (more reactive)
Treatment for BPD
Antidepressant meds provide some short term relief
DBT (dialectical behavior therapy) → most promising
Focus on dual reality of acceptance of difficulties, and need for change
Focus on interpersonal effectiveness and coping mechanisms
Focus on distress tolerance to decrease reckless and self-harming behavior
Ex provided in class
Someone with BPD dating someone
Date is late to restaurant → thoughts are spiraling → he then comes in → but relationship already wrecked
DBT would have her shit with feelings, increase distress tolerance in that moment, effective coping mechanism, less likely to damage relationship
Case study on BPD
Young women came in for problems with dating
Saw 7-8 therapists - said they were all fraud, elevated new one at first
Trauma in her life
Start establishing relationship
Introducing DBT
Leaves session, confirm next appointment, no availability within a week
End of day - 7 messages from her raging
Returned call calmly → no response → eventually gets a message back
3 months of no therapy because her reactivity → have her realize and see this, but also not shaming her
She was able to see how she had wrecked the situation and relationship
B → Histrionic personality disorder
Dramatic
Attention seeking - even if they do not believe it themselves
Black and white
Exaggerate everything
Lying and grandiosity
Impulsivity and sexually provocative
Won’t have meaningful relationships
Love therapy (built in audience)
Barrier to therapy
No vulnerability