Economies of Scale
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
Economies of Scale
Reduction in average cost per unit that a firm benefits from as a result of increasing scale of their business.
2
New cards
EOS Diagram
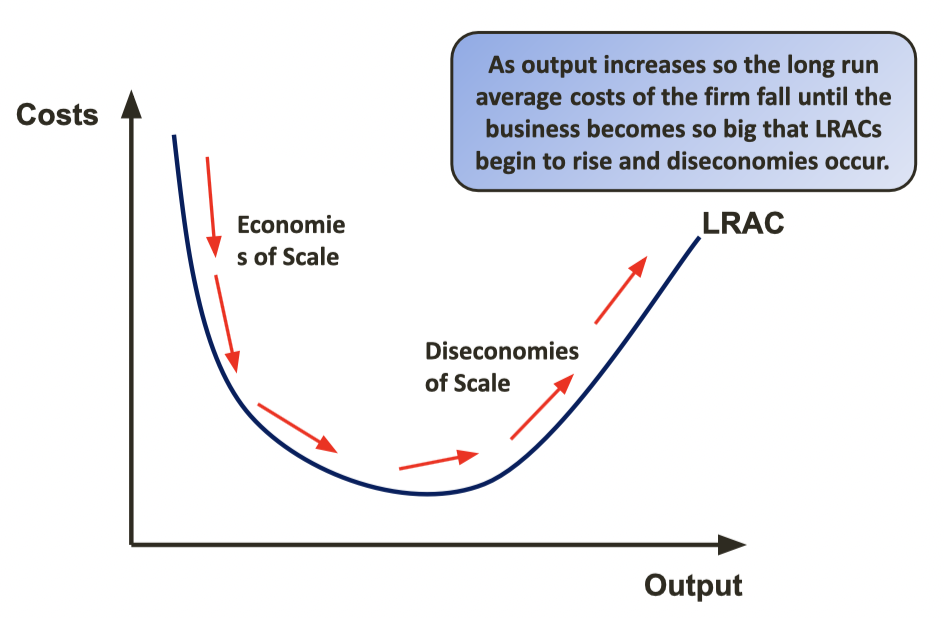
3
New cards
Types of Economy of Scale
Internal - company receives from an increase in size leading to a reduction in their average cost per unit.
\
External - benefits an entire industry, not just an individual business
\
External - benefits an entire industry, not just an individual business
4
New cards
Internal Economies of Scale
* Bulk Buying
* Financial
* Marketing
* Managerial
* Technical
* Financial
* Marketing
* Managerial
* Technical
5
New cards
Bulk Buying
* Known as purchasing an economy of scale.
* Benefit of purchasing in large volumes
* Lower selling prices to consumers or maximise profits.
* Benefit of purchasing in large volumes
* Lower selling prices to consumers or maximise profits.
6
New cards
Financial Economies
As a business grows, acquire more assets.
Used as security against any kind of financial borrowing - reduces risk for lender.
Prepared to offer larger businesses more money and favourable lending than smaller firms.
Used as security against any kind of financial borrowing - reduces risk for lender.
Prepared to offer larger businesses more money and favourable lending than smaller firms.
7
New cards
Technical Economies
Increase levels of production and productivity by making greater use of capital.
Automation - Less waste and greater efficiency than using human capital.
Job losses, lower staff motivation and high initial costs.
Automation - Less waste and greater efficiency than using human capital.
Job losses, lower staff motivation and high initial costs.
8
New cards
Marketing Economies
Increasing growth brings with need for additional marketing and promotional campaigns.
Costs are spread over more units of output, reducing average costs of market.
Costs are spread over more units of output, reducing average costs of market.
9
New cards
Managerial Economies
As business grows in size, so do levels of hierarchy within the business and they employ specialists.
Make fewer mistakes with lowers to costs.
Make fewer mistakes with lowers to costs.
10
New cards
External Economies of Scale
Advantages as a result of growth of the industry
Partially explain the reasons as to why firms within industry cluster geographically near one another.
Partially explain the reasons as to why firms within industry cluster geographically near one another.
11
New cards
Types of External EOS
* Education
* Supplier
* Infrastructure
* Supplier
* Infrastructure
12
New cards
External Diagram
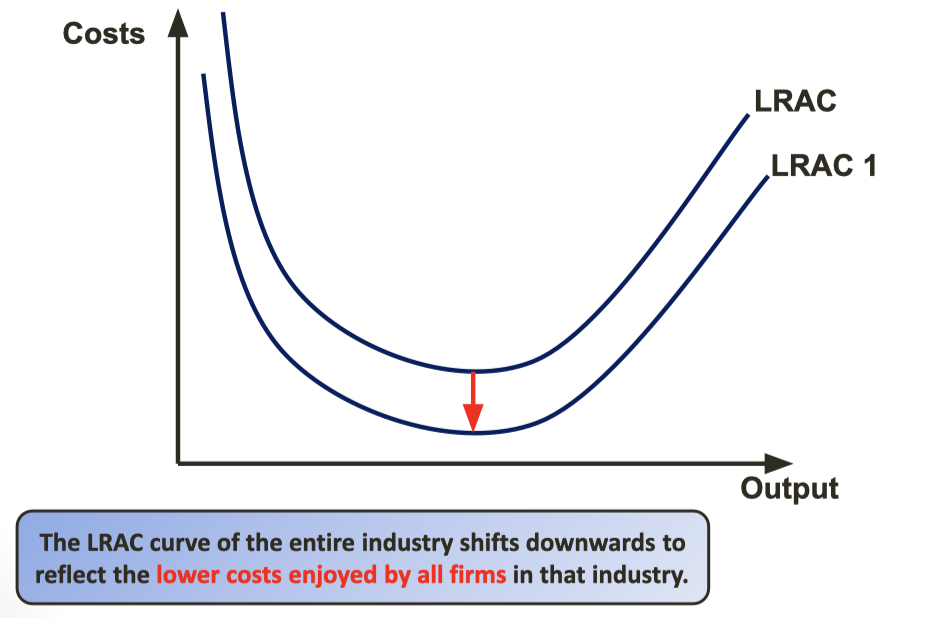
13
New cards
Educational Economies
Local Colleges and Unis assist with developmental of skilled labour force.
14
New cards
Supplier Economies
Relocate themselves closer to industry as to reduce transport costs and improve responsiveness to industry demands.
Benefit from just-in-time resources.
Benefit from just-in-time resources.
15
New cards
InfraStructure Economies
Concentration of an industry and suppliers within a certain geographical area will also encourage the development of local infrastructure.
Result in improve road networks, telecommunications which lower operating costs.
Result in improve road networks, telecommunications which lower operating costs.
16
New cards
Diseconomies of Scale
As a business increases scale of operations, show a rise in costs.
These increases in costs are known as diseconomies of scale and occur as a result of growing inefficiencies.
These increases in costs are known as diseconomies of scale and occur as a result of growing inefficiencies.
17
New cards
DES - Coordination
Different working practices are used and as people spread out across locations.
Difficult for management to monitor all activities and ensure objectives are being followed
As mistakes start to occur, costs of reworking and corrective action increase and leads to a rise in LRACs.
Difficult for management to monitor all activities and ensure objectives are being followed
As mistakes start to occur, costs of reworking and corrective action increase and leads to a rise in LRACs.
18
New cards
DES - Communication
As business grows, levels of hierarchy, staff and branches do
Lead to staff not understanding role
Lower levels of productivity and rise in LRACs
Lead to staff not understanding role
Lower levels of productivity and rise in LRACs
19
New cards
DES - Motivational
Result of poor coordination and communication and become demotivated.
Poor motivation leads to low productivity levels will raises costs and make firms less competitive.
Poor motivation leads to low productivity levels will raises costs and make firms less competitive.
20
New cards
Are Diseconomies Inevitable?
Common for large businesses but with careful planning, impact can be minimised.
Communication - Letters
Motivation - Team Building
Co-Ordination - Training and empowerment
Communication - Letters
Motivation - Team Building
Co-Ordination - Training and empowerment
21
New cards
Stakeholders and Economies
**Customers** - large cost savings, benefit from lower prices
**Competitors** - Hold monopoly power, increase takeover ability
**Suppliers** - put pressure on suppliers
**Shareholder** - low costs means increases profits, higher dividends
**Competitors** - Hold monopoly power, increase takeover ability
**Suppliers** - put pressure on suppliers
**Shareholder** - low costs means increases profits, higher dividends
22
New cards
Why Do Small Firms Survive?
SMEs don’t benefit from EOS
Less efficient and have higher costs
They do have:
* Greater flexibility
* Premium prices
* Markets are small
Less efficient and have higher costs
They do have:
* Greater flexibility
* Premium prices
* Markets are small