Oral Cavity Adaptations
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
herbivore diet
plants
describe herbivore dentition
dental pad instead of upper incisors
grasp plants with tongue and pinch it off with lower incisors against dental pad
no canine teeth
thoroughly grind food and mix it with lots of saliva
continually growing molars that are worn down by silica in the plant material they eat
herbivore dentition diagram

what do herbivores have instead of upper incisors?
a dental pad
differences between carnivore and herbivore dentition
carnivores - have canines, no dental pad, carnassial teeth
herbivores - no canines, dental pad, no carnassial teeth
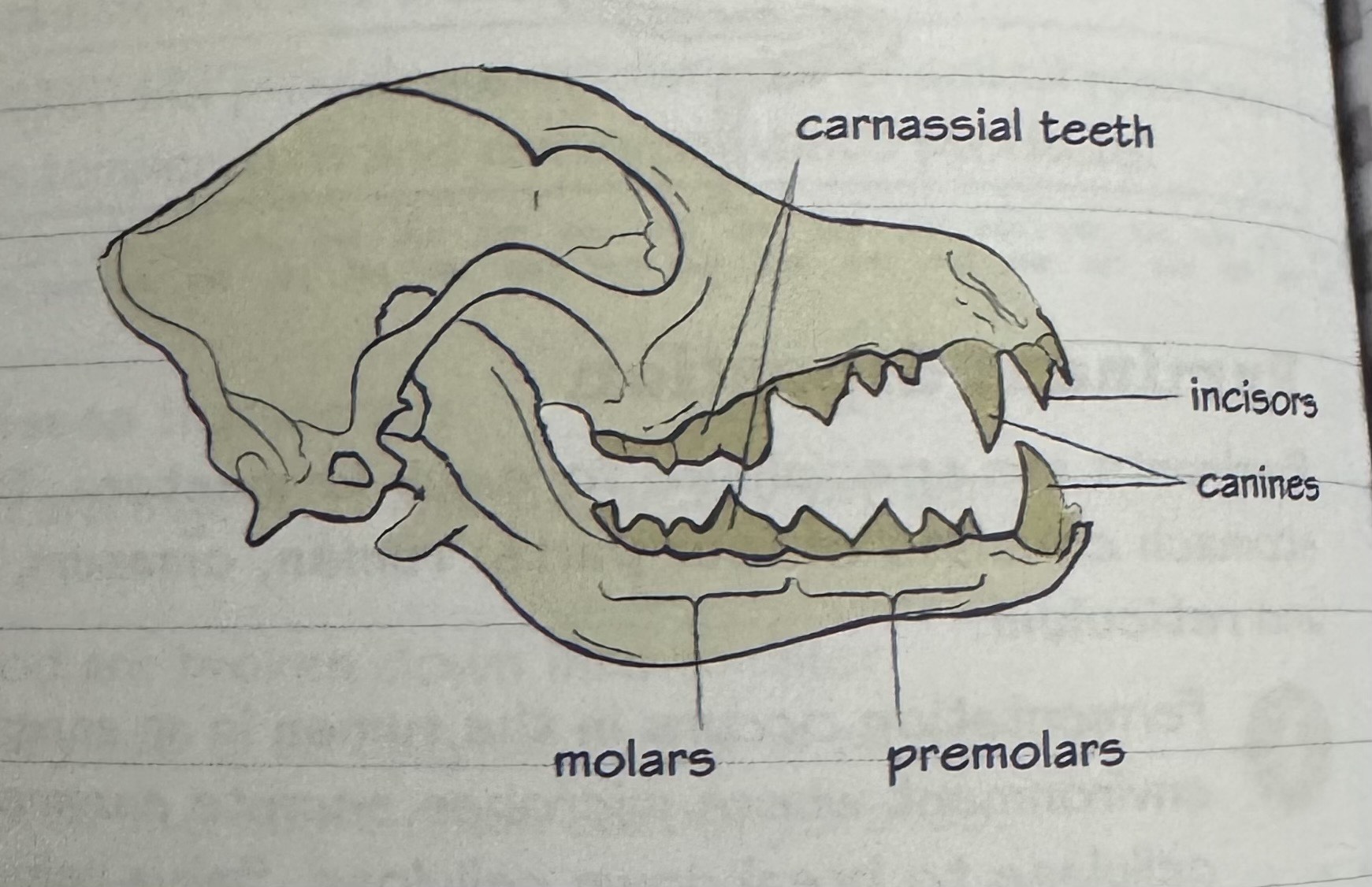
describe carnivore dentition
canines - to rip meat
carnassial teeth - paired modified molars to shear meat
do not have the ability to digest cellulose as they lack the enzyme cellulase
difference between shearing and tearing meat
shearing is more efficient
why can’t carnivores digest cellulose?
they lack the enzyme cellulase
carnivore diet
meat
carnivore dentition diagram
what are bird beaks made up of?
keratin, bone and blood vessels
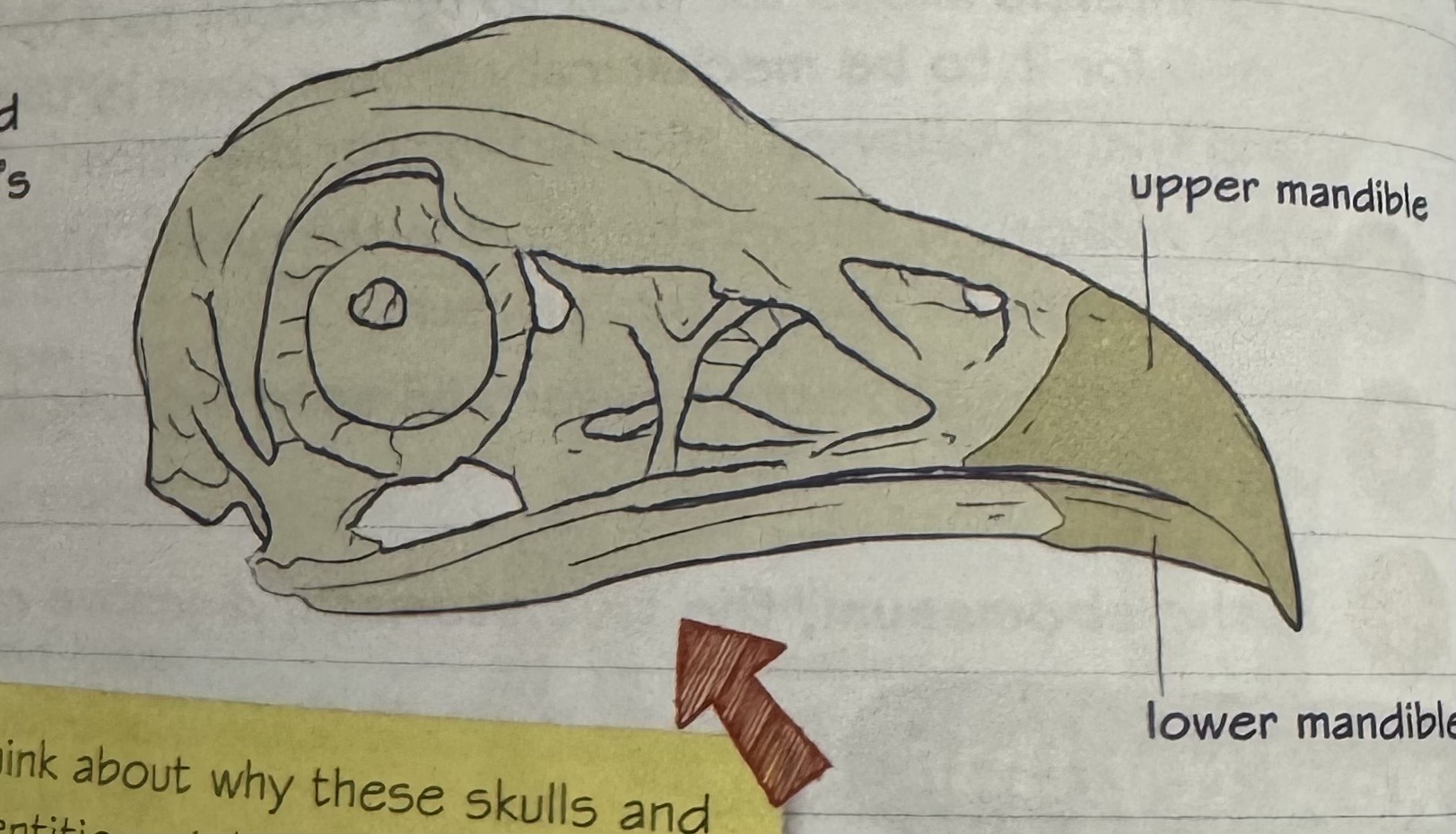
describe oral cavity of birds
beak that grows continually and is worn down by grooming, feeding, rubbing and climbing
beak shape adapted to the type of food the bird eats e.g. pelican has a large lower beak for scooping fish
no teeth in mouth as they do not chew food
bird oral cavity diagram
mastication
chewing food with teeth
types of teeth
incisors, canines, molars, pre-molars
incisor function
cutting
canine function
piercing
molar function
crushing and grinding
pre-molars function
cutting and crushing
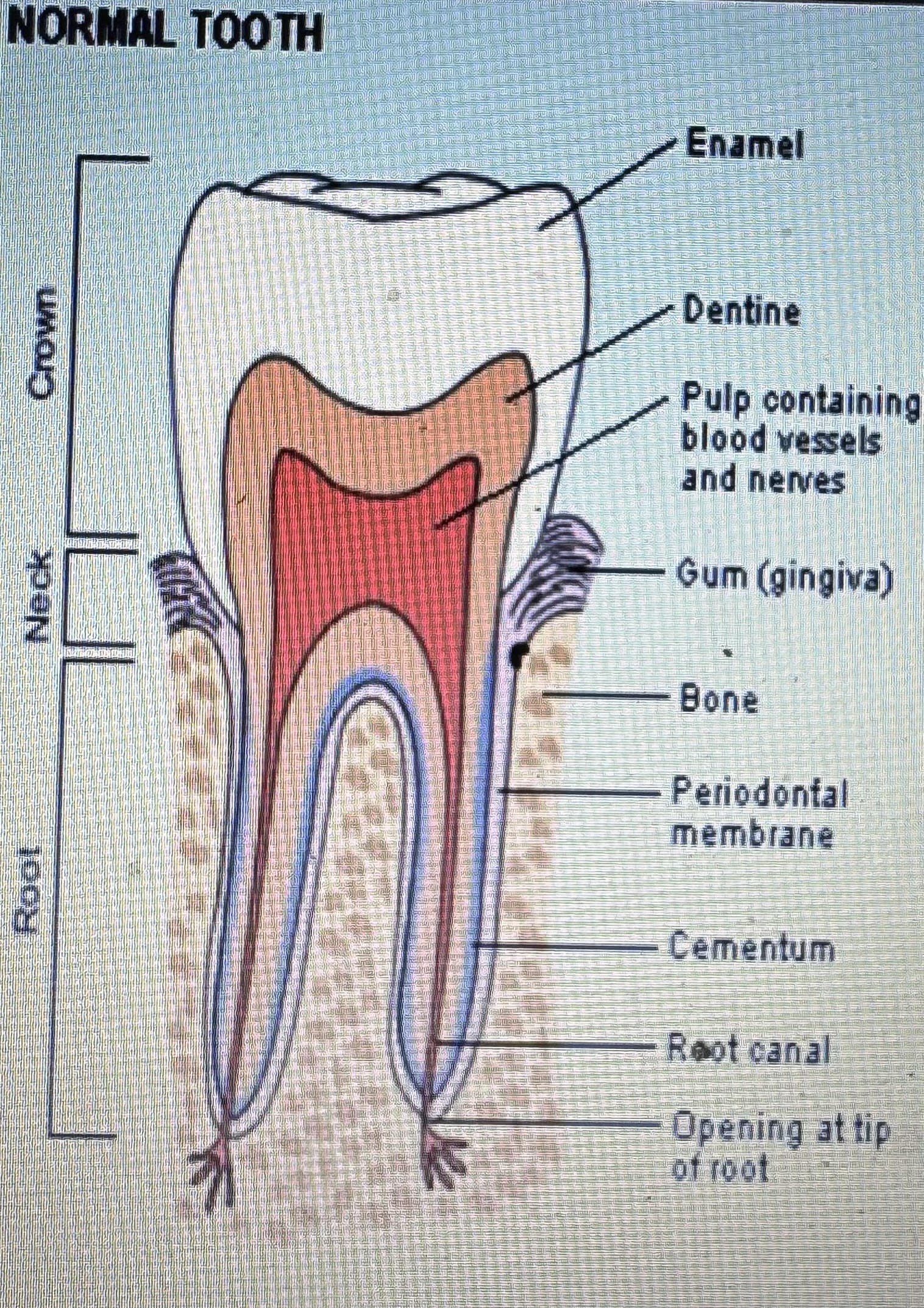
main sections of a tooth
crown, neck, root
further sections of a tooth
enamel, dentine, pulp, gum (gingiva), bone, periodontal membrane, cementum, root canal, opening at tip of root
tooth diagram
dental formulae
a way of writing how many different types of teeth an animal has
bird diet range
fruits, plants, seeds, carrion, nectar, invertebrates, vertebrates (i.e. small mammals and birds)
examples of different birds and how their beak is adapted to eat
woodpecker - long, chisel-shape beak for drilling into wood to find insects
hawks - shark, hooked beak for tearing meat from prey
hummingbirds - long, thin beak for reaching deep into flowers to drink nectar
describe a type of foraging mode in ducks
dabbling
filter feed using specialised structures in their bills called lamellae
lamellae
fine comb-like structures found in rows along the inside of the bill
lamellae function
Filter out inedible material for birds, while trapping invertebrates, seeds or grazing on aquatic plants
how many lamellae on dabbling ducks lower and upper bills?
50-70