clinical biochemistry exam 1 - collagen related diseases
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
describe beta sheets
hydrogen bonding between adjacent peptide chains
parallel or antiparallel
exhbit right-handed twist
describe alpha helices
repeating spiral, righthanded
little steric hindrance
forms repeated hydrogen-bonds along backbone
what is the secondary structure of collagen
3 left-handed helicies form a right-handed triple helix configuration
which amino acids are involved in the synthesis of collagen
proline and lysine which are hydroxylated to form hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine
what is the amino acid composition of collagen structure
1/3 gly, 15-30% pro or hyp
what does the presence of hyp do for the collagen structure
confers stability through intramolecular hydrogen bonds that involve bridging water molecules
what amino acid can lie near the center of the triple helix and why
gly because all other amino acids are too bulky
what is the purpose of the pro in collagen
prevents formation of an alpha helix so the collagen polypeptide assumes a left-handed helical conformation
how are the collagen chains cross-linked
covalently through links between lys and his side chains near the N and C terminals
what is scurvy
deficiancy of vit c which leads to deficiancy of ascorbic acid
how does ascorbic acid affect collagen formation
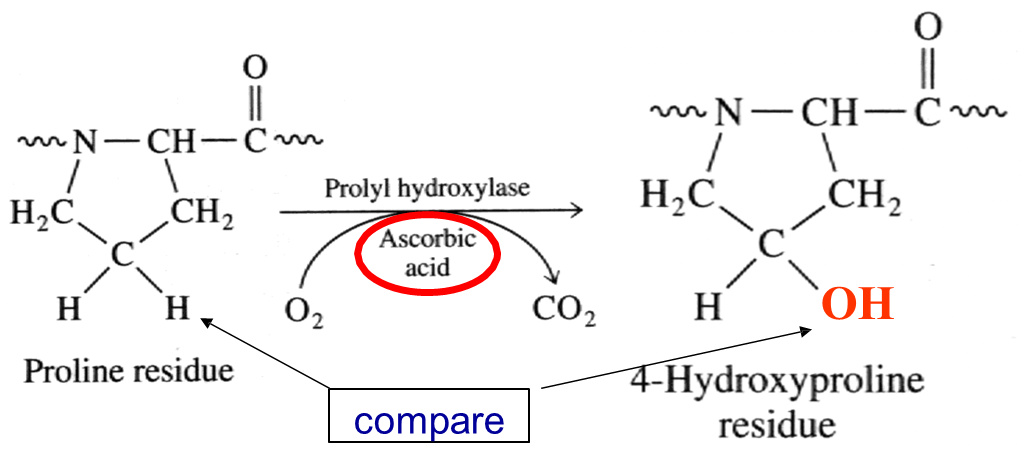
Hyp is needed for collagen stability, ascorbic acid is used to make Hyp if there is a deficiancy of vit c (ascorbic acid) then the collagen structure doesnt form properly
what does ascorbic acid do
reduces iron so thatit can continue to serve as a cofactor for proline and lysyl hydroxylases
in the case study what was the treatment for the pt with scurvy
vit c and iron
what happens if collagen is not properly hydroxylated
ER stress
misfolded procollagen
weaker collagen fibers
what is “brittle bone diease”
autosomal dominant genetic disease that affects the bones
what are the clinical features of brittle bone diease
fragility of bones
pale blue sclera and deafness
abnormal shape of skull and ligaments
what is the biochemical abnormality of brittle bone disease
frequently defective synthesis of type 1 collagen
how many a2 and a1 chains does a normal collagen helix have
2 a1 and 1 a2
what is a ‘null allele’ mutation for brittle bone diease
mutations in COLA1 in which the cells make half of normal amount of collagen; if mutations in COLA2 collagen has 3 a1 chains
what is a structural mutation for brittle bone disease
either gene produces abnormal type 1 collagen
what leads to structural mutations that lead to brittle bone disease and what do they do
subsitutions of another amino acid leads to affects on
protein stability
slower folding
post translational over modifications
how can changes to collagen structure be detected
using differential scanning calorimetry
what are bisphosphonates used for
increasing bone density and thickness; prevent tumors from removing bone and spreading
how are bisphophonates used for OI (brittle bone disease)
reduce fractures and enhance longitidinal bone growth
block mevalonte pathway inhibits osteoclast activity and hence helps preserve bone
doesn’t improve collagen synthesis
what are the three drugs used for OI
anti-resorptive (bisphosphonates): control osteroclats
anabolic: stimulate osteroclats
dual