Genetics (Unit 2)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Chromatin
made out of DNA and protein, gets organized into chromosomes
Histones
Positively charged proteins that form with negatively charged DNA in the nucleus
Bind to DNA, creates nucleosomes, help give chromosomes their shape, and help control the activity of genes
heterochromatin
highly repeated non coding DNA that is usually tightly packed
euchromatin
coding DNA sequences that are loosely packed
centromere
heterochromatin, is essential for chromosome segregation
4 levels of organizational structure of DNA molecules in eukaryotes
nucleosomes, 30 nanometer fiber, chromatin, and metaphase chromosome
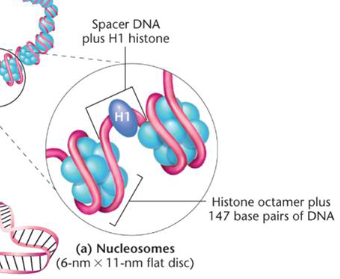
Nucleosomes
A 2 nm diameter DNA molecule coils around an octamer of histones. The resulting nucleosomes are a 6 nm by 11 nm flat disk, which includes spacer DNA plus H1 histone.
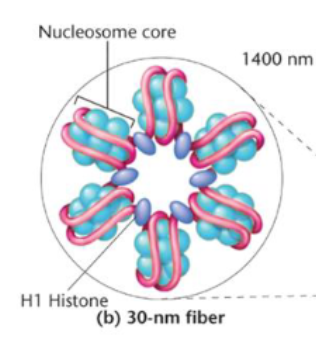
30 nanometer fiber
the nucleosome fiber continues to pack into a thicker structure consisting of multiple bundles of nucleosome cores coiled around and stacked upon one another. The bundles get separated from the next bundle by a H1, then get bundled into looped domains.
Chromatin fiber
the looped domains condense further into a coiled structure 300 nm in diameters
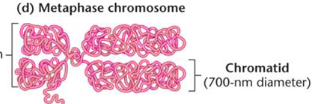
Metaphase chromosome
the coiled chromatin fibers are compacted into the chromosome arms of a chromatid
histone tails
provide potential targets along chromatin fiber for chemical modifications
Acetylation
Enzyme histone acetyltransferase (HAT)
Addition of acetyl group to positivity charged amino acid group on side chain (lysine)
Changes net charge of protein by adding a positive charge
Methylation
Enzyme methyltransferase
Adds methyl groups to arginine and lysine residues in histones
Positive correlation with gene activity
Phosphorylation
Enzyme Kinase
Adds phosphate groups to hydroxyl groups of amino acids serine and histidine
_____ of DNA is another mechanism to regulate
gene expression
Methylation
Methylation of DNA
methylation of the base cytosine in DNA forms a 5-methyl cytosine and is usually negatively correlated with gene activity
Telomeres
is a region of repetative DNA sequences at the end of chromosomes that protect the ends of chromosomes from becoming frayed or tangled
Satellite DNA
is highly repetitive and consists of short repeated sequences, is found in the heterochromatic centromere regions of chromosomes. Not found in prokaryotes
Endogenous retroviruses
Ancient viral DNA inherited by a host and gets inherited like any other gene