L7 Conjunctivitis
1/202
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
in both viral AND bacterial pathophysiology, it begins with exposure to pathogen through _____ contact or _____ of air bone particles
direct, inhalation
______ proliferates via colonization into conjunctival epithelium and adjacent tissue through break in the epithelium or ability to invade. whereas _____ proliferates multiplying within the cell of the conjunctival epithelium cell. When the cell dies and it releases it contents to continue replication
Bacterial, viral
in the pathophysiology of bacterial conjunctivitis, host immune system activates the ______ immune response. Similarly, the pathophysiology of viral conjunctivitis, the host immune system activates the ____
innate, innate
in the process of pathophysiology of the immune response of bacterial conjunctivitis, the innate response directly engulfs _____ and recruits other immune cells such as PMN and macrophages presenting as lid or conj. vascular dilation. whereas in viral conjunctivitis activation of the innate immune response would lead to _____ of cells via interferons and destroy infected cells via NK cells, macrophages & neutrophils causing similar presentation as lid/ conjunctival vascular dilation
bacteria, protection
bacterial conjunctivitis pathophysiology activates the innate response to activate the _____ system which leads to inflammation contributing to lid edema, papillae, conjunctival hyperemia and purulent discharge. On the other hand, innate immune system of viral conjunctivitis activates the _____ system which utilizes B and T cells
complement system, adaptive
In bacterial conjunctivitis when the complement system is activated it _____ outs pathogen and causes inflammation contributing to lid edema, papillae, conjunctival hyperemia and purulent discharge. when all this occurs, it creates risk for ____ of adjacent structures such as intraocularly or cornea
clears, infection
in viral conjunctivitis, adaptive system uses T and B cells. T cells are used to destroy __-__ cells whereas B cells are used to bind to free viral particles to ____ new host cell infection
virus- infected, prevent
pathophysiology of ____ conjunctivitis activates the innate system and using the interferons and NK cells. This leads to presentation of lid/ conj vascular dilation. it can worsen to appear as lid edema, follicles, conj hyperemia, conj chemosis and serous discharge and then worse of all have _____ involvement
viral, and corneal
follicles are seen in viral or bacterial conjunctivitis
viral
papillae are seen in bacterial or viral conjunctivitis
bacterial
papillary response will present in _____ conjunctivitis and _____ conjunctivitis
hyperacute, neonatal
hyperacute conjunctivitis includes Neisseria ____ and Neisseria _____
meningitis, gonorrhea
neonatal conjunctivitis includes Neisseria _____ and chemical trauma, bacterial such as _____, ____ and _____
gonorrhea, staph, strep, HSV
both hyperacute and neonatal conjunctivitis share ___ ___
Neisseria gonorrhea
inclusion conjunctivitis is
serovars D-K
trachoma is
serovars A-C
parinaud oculoglandular syndrome is
Serovars L1-L3
all of inclusion conjunctivitis, trachoma, parinaud oculoglandular syndrome is all considered
chlamydia trachomatis
FDA approved fluoroquinolones drugs for conjunctivitis consists of (6)
1. Besifloxacin 0.6%
2. moxifloxacin 0.5%
3. Gatifloxacin 0.5%
4. levofloxacin 0.5%
5. Ofloxacin 0.3%
6. ciprofloxacin 0.3%
FDA approved Macrolides drugs for conjunctivitis consists of (2)
azithromycin 1%
erythromycin ointment
FDA approved Aminoglycosides drugs for conjunctivitis consists of (2)
tobramycin 0.3%
gentamicin 0.3%
FDA approved combo drops drugs for conjunctivitis consists of (2)
10,000 u/g polymyxin/ bacitracin
polymyxin B / trimethoprim
Besifloxacin 0.6%
moxifloxacin 0.5%
dosing is
BID or TID x 5-7 days
Gatifloxacin 0.5% dosing is
BID or TID x 5 days
levofloxacin 0.5% dosing is
1 gtts Q2 hrs while awake for 2 days then QID for 5 days
Ofloxacin 0.3% is
Q2h x 2 days then QID for more days
ciprofloxacin 0.3% dosing is
1 gtts Q2 hrs while awake for 2 days then for 5 days
azithromycin 1% dosing is
BID for 2 days then once daily for 5 days
erythromycin ointment dosing is
4-6 times daily for 1 week
Tobramycin 0.3% dosing is
1 gtts Q1-4hrs depending on severity
ung: 1 gtts Q3-12 hrs until improved and then taper
gentamicin 0.3% dosing is
1 gtts Q1 1-4 hrs based on severity; ointment BID - TID
10,000 u/g polymyxin / bacitracin dosing is
Q3-6h x 7-10 days
polymyxin B / Trimethoprim dosing is
1 drop Q3- 4 hrs x 7-10 days
for papillary conjunctivitis, acute papillae tends to be ____ etiologies
infectious
bacterial conjunctivitis, hyperacute conjunctivitis and neonatal conjunctivitis are all ____ papillary conjunctivitis
acute
staph, strep, and Moraxella are all _____ conjunctivitis
bacterial
Neisseria spp. is ____ conjunctivitis
hyperacute
ophthalmia neonatorum is _____ conjunctivitis
neonatal
papillary conjunctivitis with presence of red eye can be considered
bacterial
papillary without the presence of red eye can be considered
allergic
_____ papillae tends to be due to inflammation, toxicity to by byproducts, and/or mechanical processes
chronic
chronic consists of (4)
lacrimal infections, floppy eyelid syndrome, keratoconjunctivitis sicca, blepharoconjunctivitis
fine papillae
giant papillae
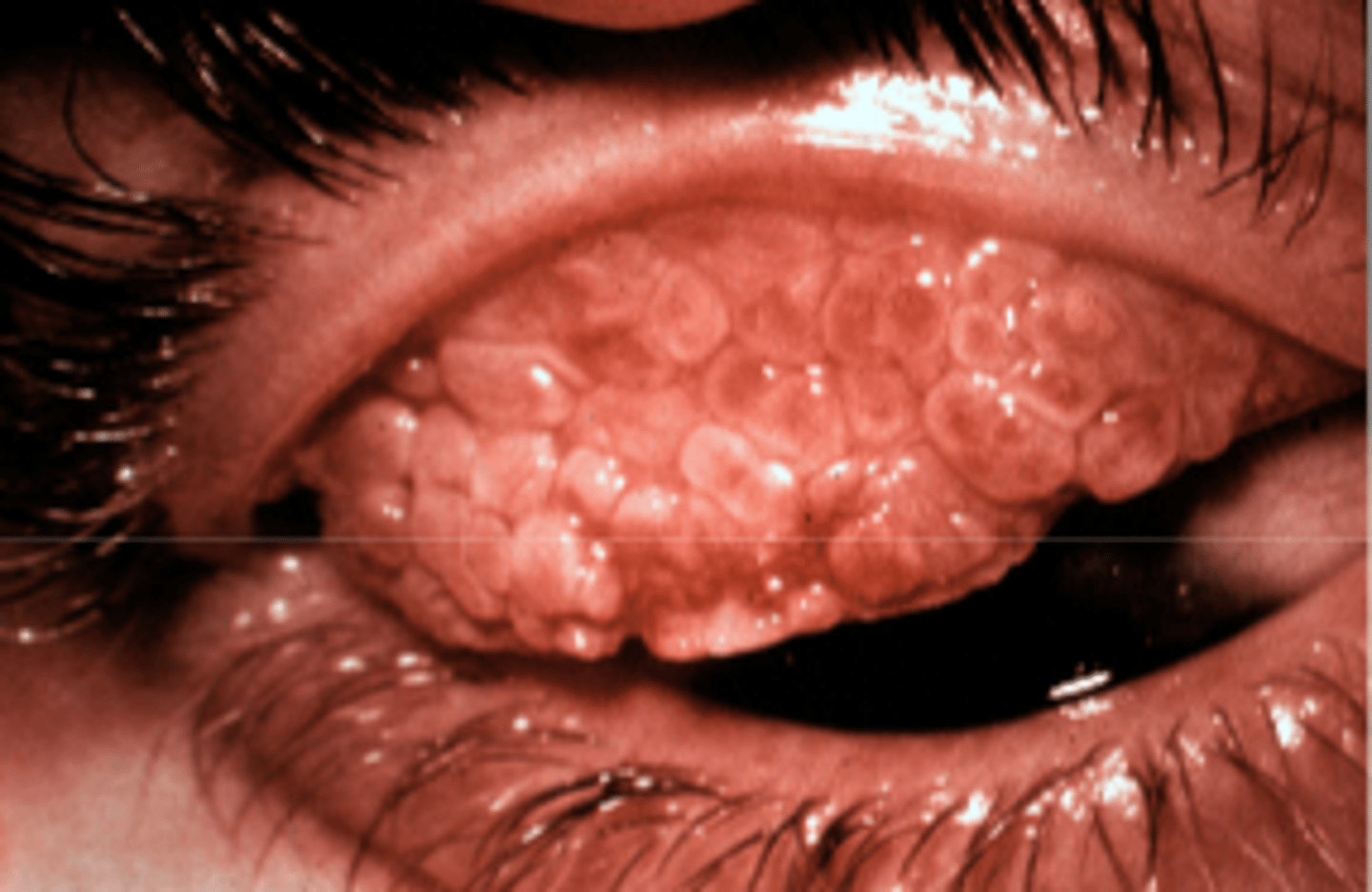
bacterial infections, chronic inflammation, and allergic conditions will have _____ papillae
fine
_______ papillae presents with chronic CL over wear, VKC, and AKC
giant
the beam in slit lamp should be ___ ____ to see whether it is follicles or pappilae
optic section
papillae is uniform in size until it break then it is ______
GPC
_______ sit more medially compares to ______ that sit more inferior-temporally
papillae, follicles
_____ is the acute or hyper acute inflammation of the conjunctiva in newborns within the first 28 days of light because of the chemical insult or microbial infections
neonatal conjunctivitis or neonatal ophthalmia
which microbes causes neonatal conjunctivitis or neonatal ophthalmia (3-5)
N. gonorrhea, C. trachomatis, HSV orr staph/strep
____ can present with purulent discharge and eyelid edema
neonatal ophthalmia/ neonatal conjuctivitis
neonatal ophthalmia/ neonatal conjunctivitis
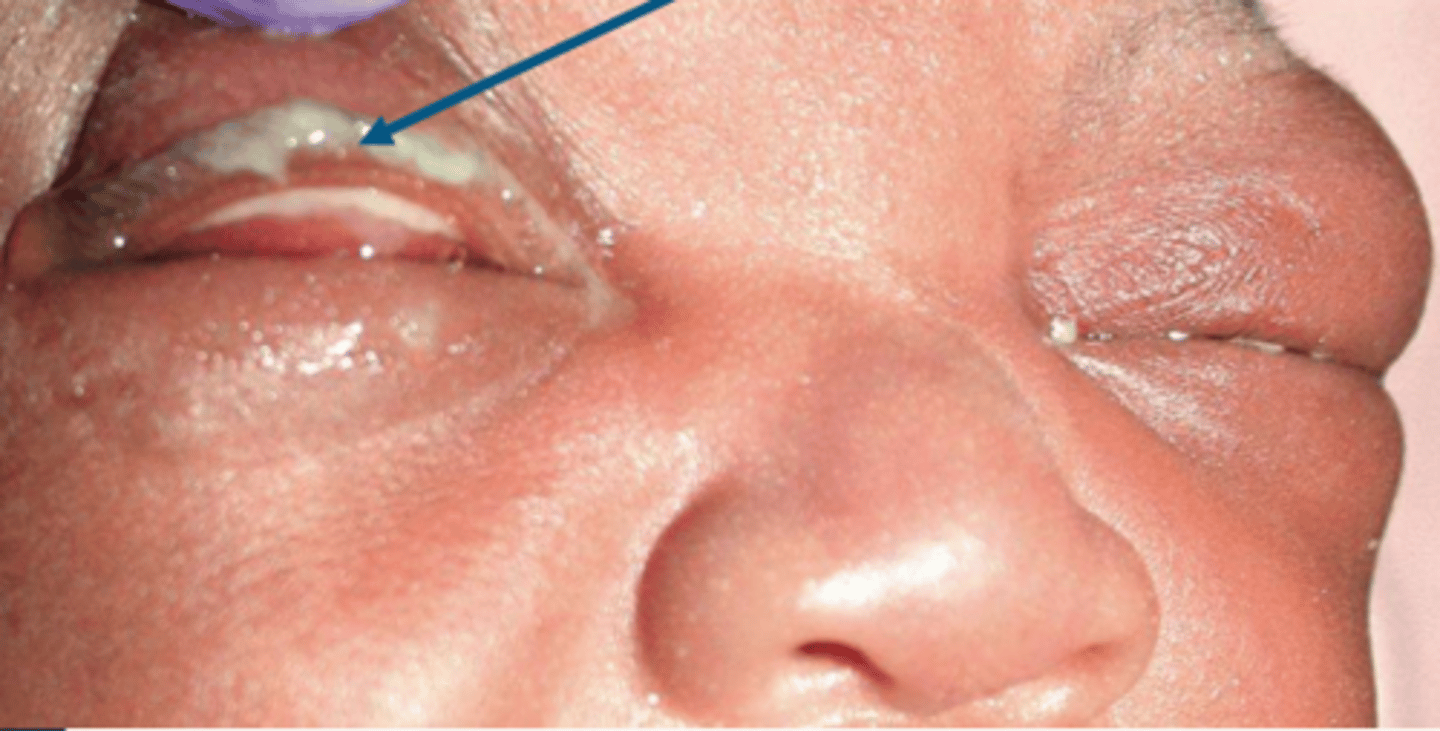
what tx method can be used to prevent neonatal ophthalmia/ neonatal conjunctivitis and what was it replaced by
silver nitrate replaced by erythromycin ung
what tx method can be used to manage neonatal ophthalmia/ neonatal conjunctivitis
infectious disease management
chlamydia _____ is the most common cause of neonatal conjunctivitis in U.S
trachomatis
to treat chemical (silver nitrate exposure) is done immediately after _____
delivery
neissera gonorrhea onset is from ____to ____days after delivery
birth to 5 days
herpes simplex virus occurs __ -___ weeks after delivery
1-2
_____ risk factors are conjunctivitis affects newborns, infected mothers, young females, and ocular trauma during delivery, and silver nitrate exposure
neonatal conjunctivitis
someone with neonatal conjunctivitis would experience (5)
pain, discharge, tenderness, redness, and eyelid crusting
a 22WF comes to you complaining of pain and tenderness. upon slit lamp you see redness, edematous lids, discharge and what looks to be some corneal involvement. what is your diagnosis?
neonatal conjunctivitis
to check if your diagnosis of neonatal conjunctivitis is correct what ancillary testing can you do? (3)
staining, culture or PCR
neonatal conjunctivitis tx if its chemical
avoid or discontinue offending agents. monitor for 2-4 days
neonatal conjunctivitis tx if its infectious
treat based on pathogen detected
what is the most common cause of hyperacute conjunctivitis
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
_____ is rapidly progressive severe conjunctivitis characterized by copious purulent discharge and lid edema accompanied by (+) ___ node
hyperacute conjunctivitis, PA
what happens to cornea in hyperacute conjunctivitis?
erosions, infiltrates, edema and ulceration
if the cornea is involved during hyperacute conjunctivitis you should
change tx and management
in hyperacute conjunctivitis, the presentation is
1. diffuse conjunctival hyperemia & chemosis
2.purulent discharge which is made of pathogen, wbc, dead cells
in hyperacute conjunctivitis, there is a risk of ___ and ____ which is the severe inflammation of the eye affecting all layers including retina, cornea, and sclera
perforation, panophthalmitis
hyperacute conjunctivitis
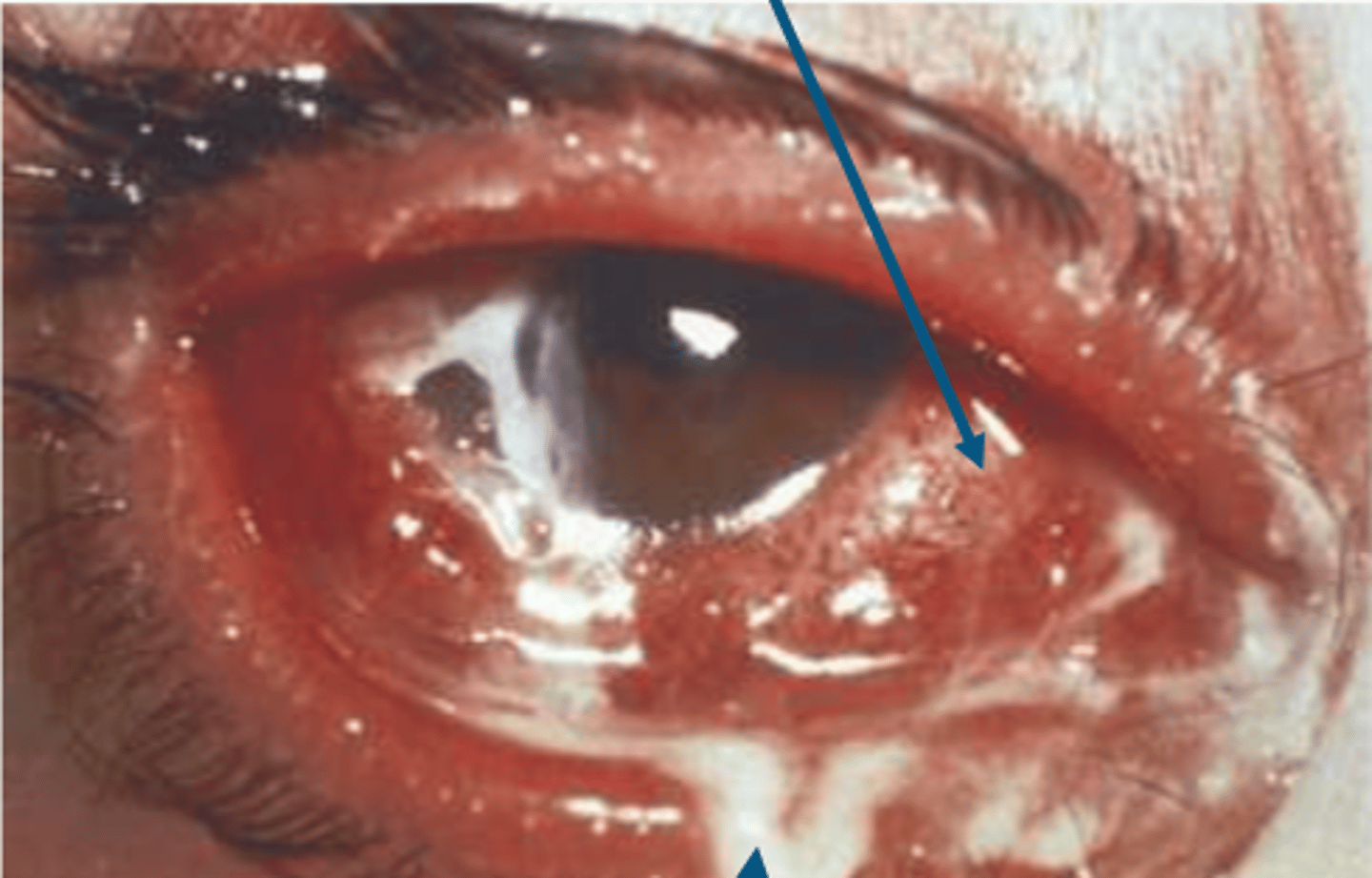
to test for hyperacute conjunctivitis, you can do (3)
gram stain, plate culture, and PCR
hyperacute conjunctivitis is in ages less than ___ as well concurrent ___ or more than sexual partner as well as MSM
25, STI
____ ___ sx include pain, significant white-green discharge, tenderness, blurry vision, photophobia, redness and eyelid crustins
hyperacute conjunctivitis
clinical signs for hyperacute conjunctivitis includes (7)
1. severe purulent discharge
2. + PA node
3. papillae
4. severe lid edema
5. SPK/erosions
6. infiltrates
7. risk for rapid corneal ulceration which lead to perforation
a patient comes in presenting with significant white discharge, tenderness, and photophobia. upon slit lamp you see SPK and infiltrates. you think its hyperacute conjunctivitis. what are some ancillary testing to confirm or deny this thought (3)
gram stain, geimsa stain, pcr
you want to treat a patient with hyperacute conjunctivitis. what is the drug of choice and dosing
1 gm ceftriaxone IM single dose
you want to treat a patient with hyperacute conjunctivitis. what is the conservative option
saline lavage + topical antibiotics such as fluoroquinolones
you want to treat a patient with hyperacute conjunctivitis but they have allergies to the drug of choice which is a cephalosporine group. what is the alternative
gentamicin 240 mg IM single dose
for tx of hyperacute conjunctivitis you should also tx the patient's __ ____ and consider ____ treatment with doxycycline 100mg po bid x7 days
sexual partners, chlamydial
what is the most common cause of acute bacterial conjunctivitis in adults
staph aureus
what is the most common cause of acute bacterial conjunctivitis in pediatrics
Hemophilus influenza
_____ ____ ____ is the sudden unilateral or bilateral with asymmetry rapid onset of inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by bacteria
acute bacterial conjunctivitis
acute bacterial conjunctivitis
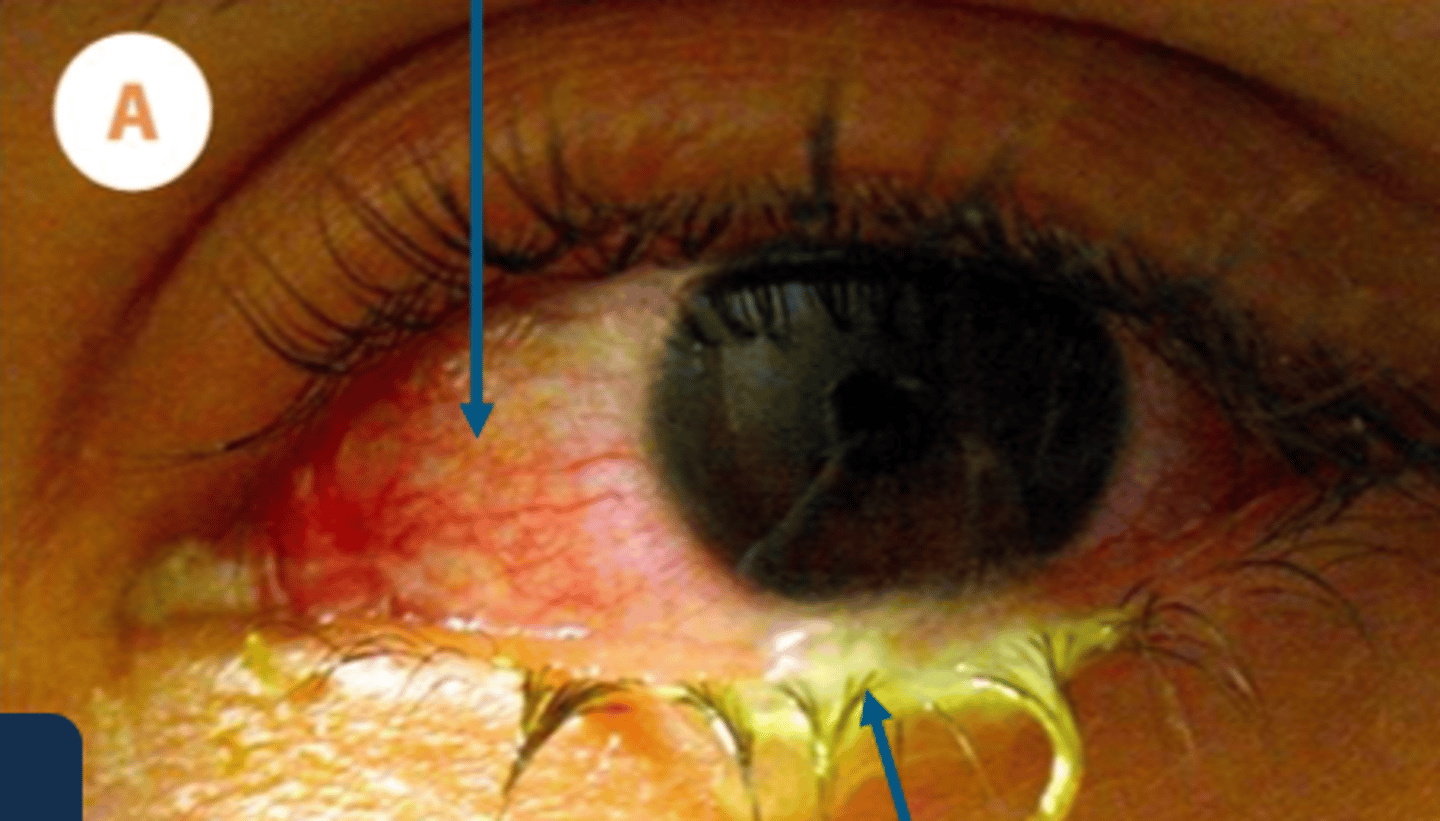
what are most common microbes leading to acute bacterial conjunctivitis
staph. spp
strepto pn
hemo influenza
n/ gonorrhoeae, Corynebacterium dipertheria, strepto pyogense and B hemolytic strepto can produce conjunctival _____/_____
membranes, pseudomembranes
___ ___ ___ presents with beefy red injection (bacterial) and its greater on the palpebral and peripheral bulbar conj as well as scant discharge that can be purulent or mucopurulent
acute bacterial conj
the demographics for acute bacterial conjunctivitis is ____ less than 12 but common in __-___ yros. as well as contact lens users
peds, 0-4
acute bacterial conjunctivitis sx include (7)
1. irritation
2. pain
3. swelling
4. stuck eyelids
5. redness
6. photophobia
7. tearing
a patient comes to you experiencing pain, swelling, tearing and feels like their eyelids are stuck. under slit lamp, you see a variety of things red injection but other things like papillae, + pa node sign, pseudomembrane, and follicles. what is their ddx
acute bacterial conjunctivitis
a patient is diagnosed with acute bacterial conjunctivitis. what is their tx options
1. topical antibiotic therapy
and follow up
a patient is diagnosed with acute bacterial conjunctivitis. their pathogen is H. influenza. what is added to their tx plan
oral amoxicillin/clavulanate because their systemic involvement
what is the most common cause of chronic bacterial conjunctivitis
staph spp
___ ____ ___ is inflammation of the conjunctiva lasting longer than 3 weeks. often associated with blepharitis
chronic bacterial conjunctivitis
chronic bacterial conjunctivitis common microbes are(2)
staphylococcal aureus and Moraxella lacunata
chronic bacterial conjunctivitis
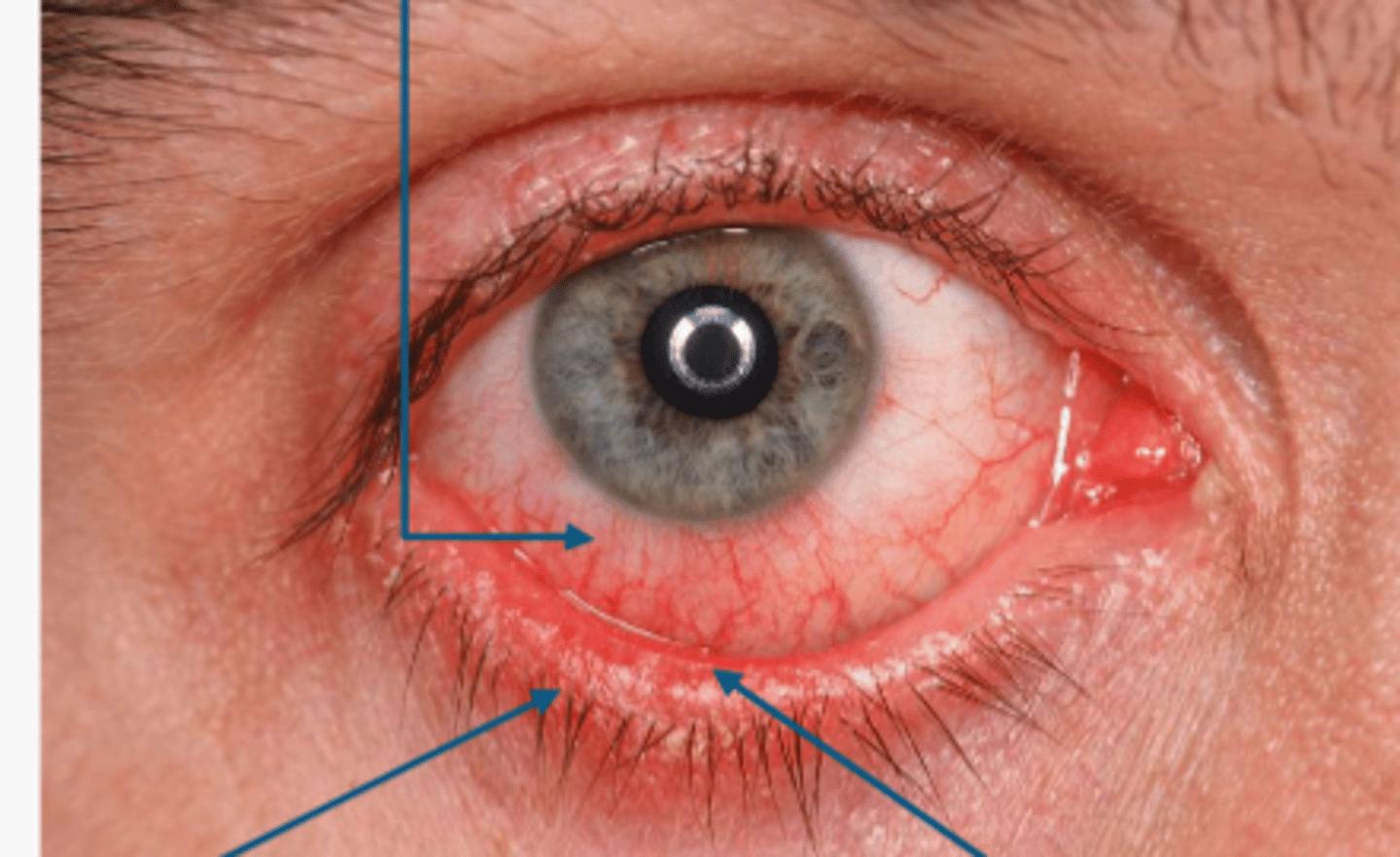
if you have blepharitis you can develop...?
chronic bacterial conjunctivitis
in addition to staph and moraxella, what are other microbes that can cause chronic bacterial conjunctivitis
enteric spp: proterus mirabilis, E.coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, serratia marcescens
chronic bacterial conjunctivitis sx includes (7)
irritation
swelling, redness
FBS, eyelid crusting
photophobia and tearing