Unit 3: Political Geography
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Enforce
to make people obey a rule or law -
to make sure people do what the government requires

Authority
the power to influence or command people's thoughts, opinions or behaviors
(the government can only enforce a law if they have the power to do so. Ex: the money to pay a police force, to hand out tickets, when people drive faster than the law allows)

Policy
A plan adopted or proposed by a government, political party, or business, that establishes goals and determines procedures, decisions and actions.
EX: Neuqua Valley has a “no cell phones in class” policy
EX: The U.S. has a policy of providing a public school education to all children.

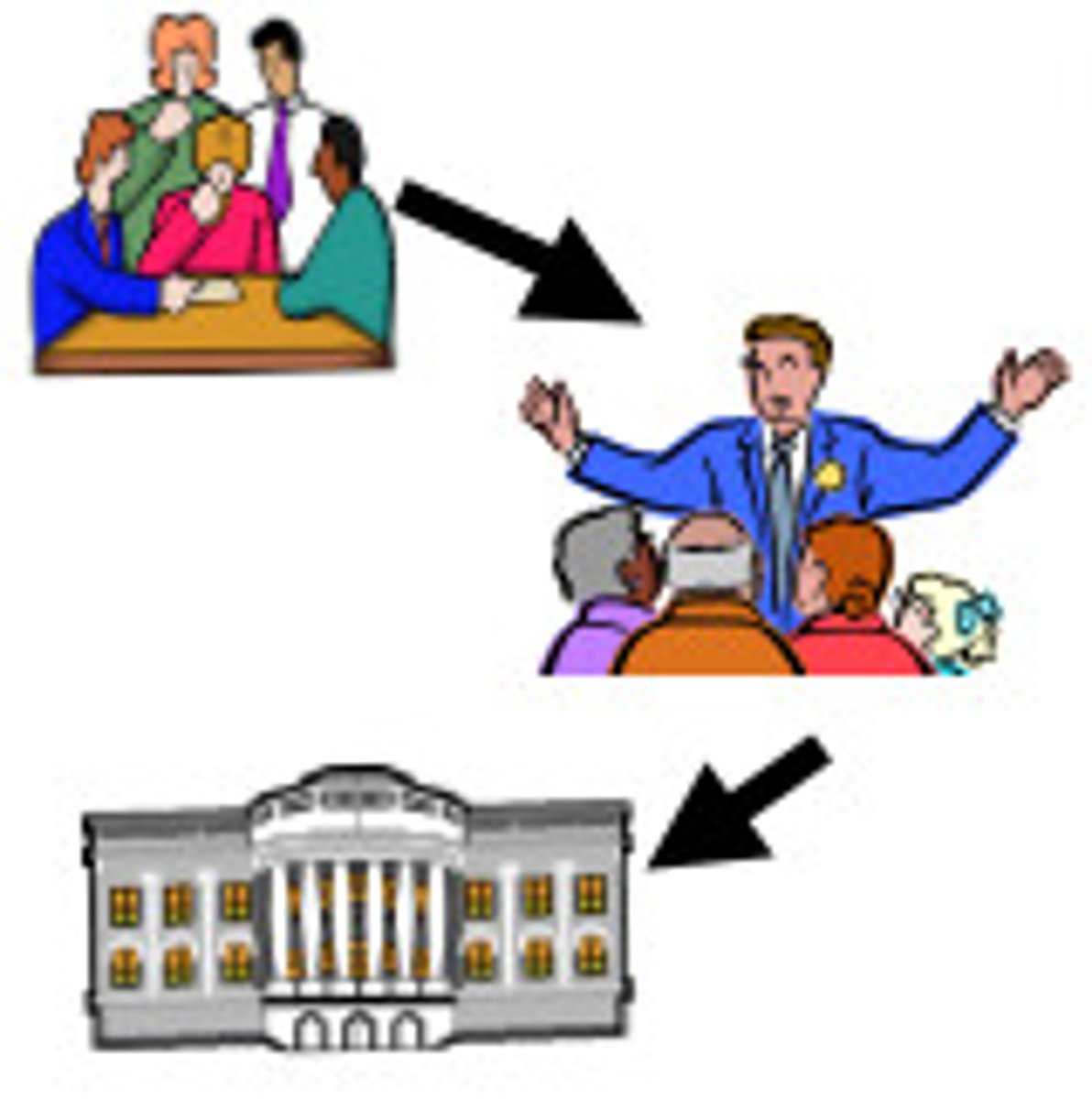
Representative democracy
A system of government in which citizens elect representatives, or leaders, who are trusted to pass laws and maintain order (govern) in line with the desires of the citizens who elected them.
Power is given to those in charge by the people.
Authoritarianism
A system of government where power is concentrated in the hands of a single leader or a small group AND decisions are taken without considering the desires of the people
- Individuals may have some individual rights.
- Lots of variation between authoritarian regimes in different countries when it comes to how many individual rights the citizens have
Ex: Saudi Arabia, China

Totalitarianism
A system of government where power is concentrated in the hands of a single leader or a small group AND those in power seek to control ALL aspects of individuals lives, no individual rights allowed
Ex: Nazi Germany, North Korea
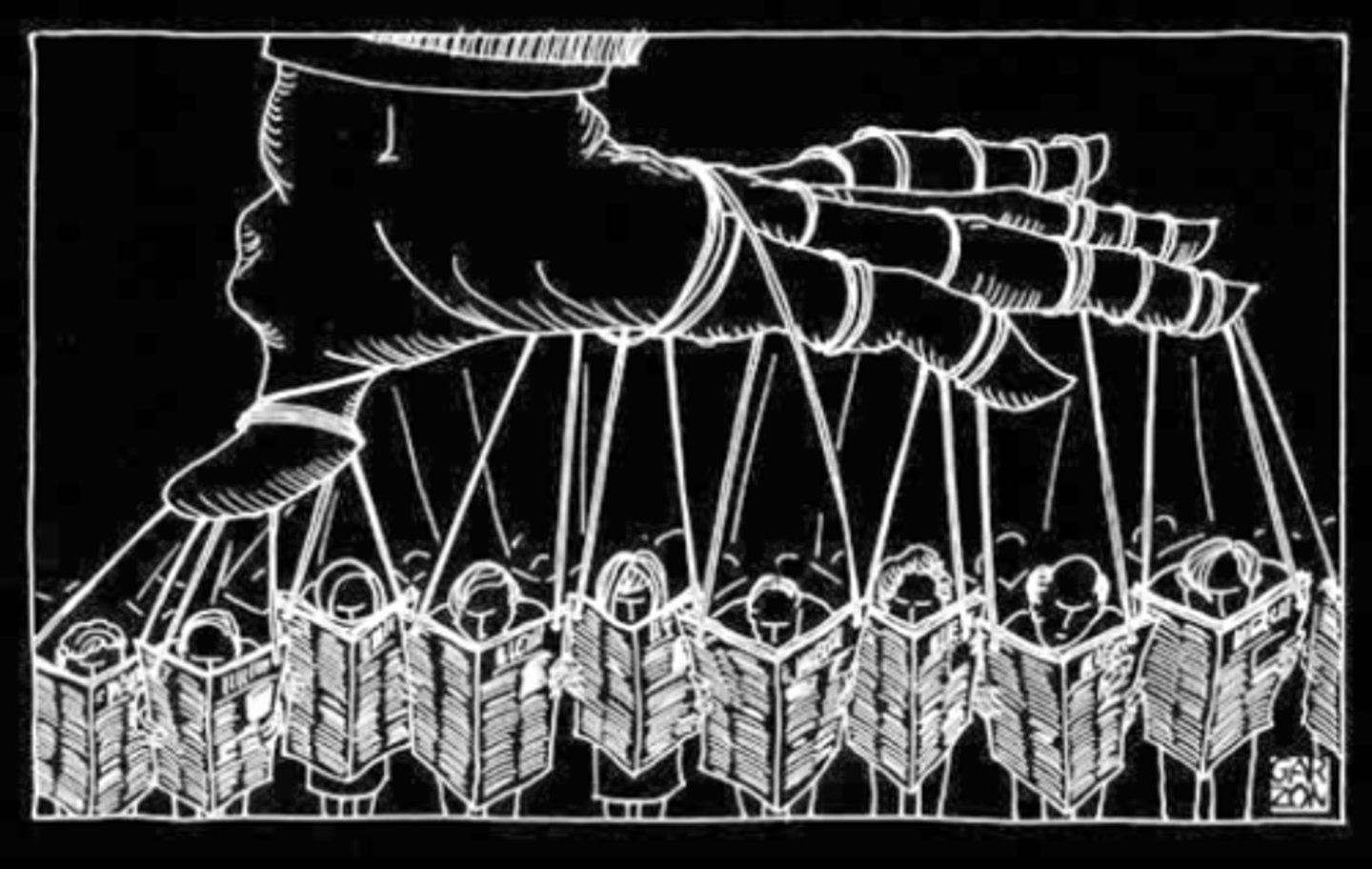
Autocracy
A political system in which one person (autocrat/dictator) has total control over the population.
- While other branches of government may exist, they are only there to give the illusion of a legitimate government. Any rights the people have are determined by the "autocrat."
- Autocrats often come to power by weaponizing fear, and hold onto power through indoctrination & propaganda
- Usually bribe the "elites" or wealthiest in the society to retain their support and keep power
- Free speech must be LIMITED, to control the minds of the people/stop rebellion
- Ex: Russia (which is also "authoritarian")

Monarchy
A form of autocratic government, in which power is in the hands of a single person (king, queen = monarch) who believes that they have "divine right" to rule (a higher power/god has given them the right)
- Monarchs usually inherit their position through royal bloodline
- Any rights the people have are decided by the monarch
- Ex: United Kingdom (Constitutional Monarchy - king/queen is just a figure head with little power)
- Ex: Saudi Arabia

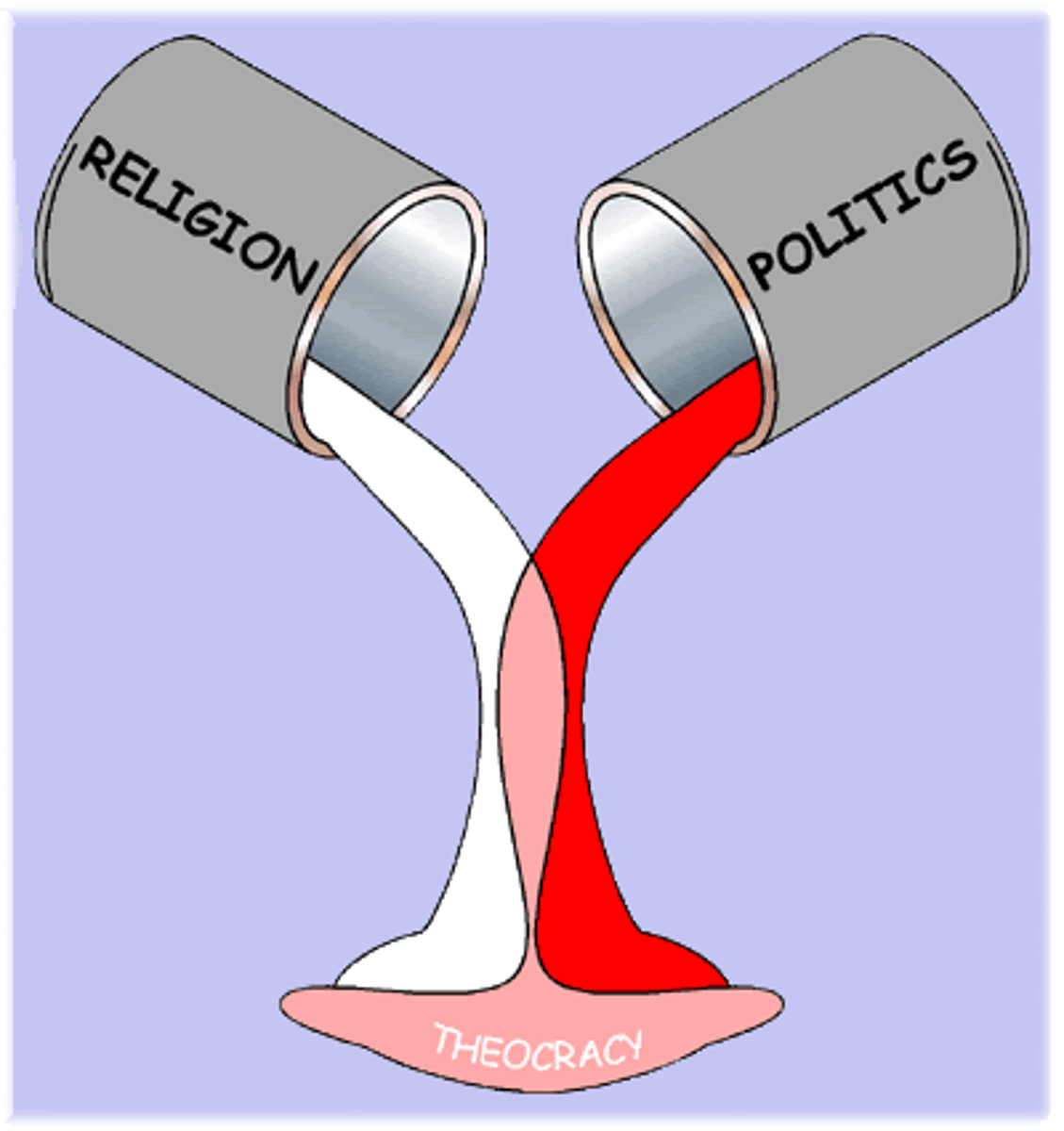
Theocracy
A government controlled by religious leaders whose goal is to govern according to the rules of a religion (as they have interpreted them)
- People's rights are dependent on the rules of the religion (as interpreted by the religious leaders)
- Ex: Iran
Communism
A political and economic system that seeks to create a classless society in which there is no private property, but rather everything (businesses, land, resources) are communally owned (owned by the people)
- Theoretically the people make collective decisions that benefit all of society, but in reality - no government has ever been able to effectively do this...
- In reality communist governments have all been taken over and run by an elite few with a single leader, who end up with most of the power in society, and the people end up with few rights
- Ex: China, the Soviet Union (USSR)

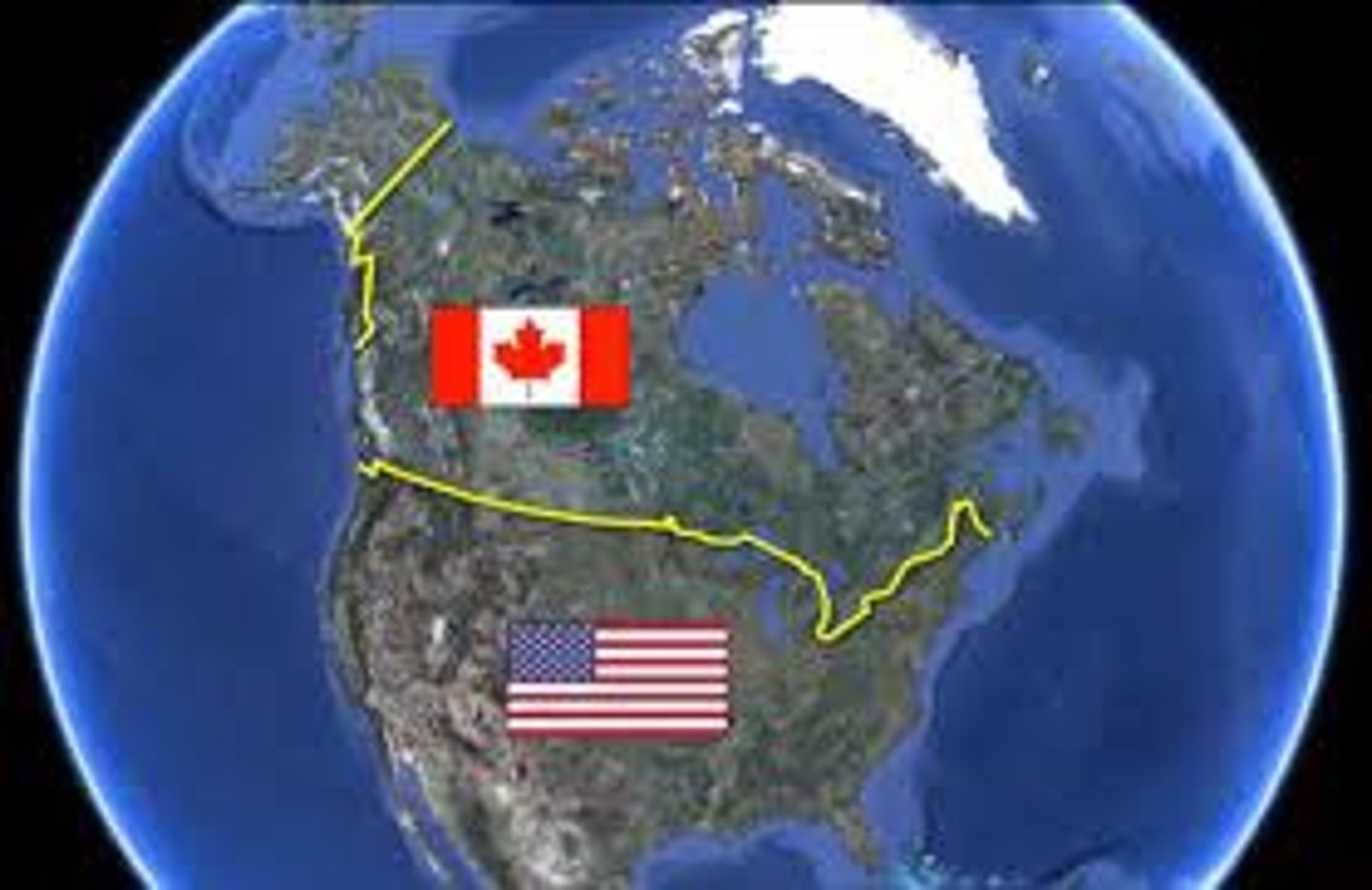
Border/boundary
An invisible line that marks the extent of a state's territory
Natural boundary
follows physical geographic features such as mountains and rivers
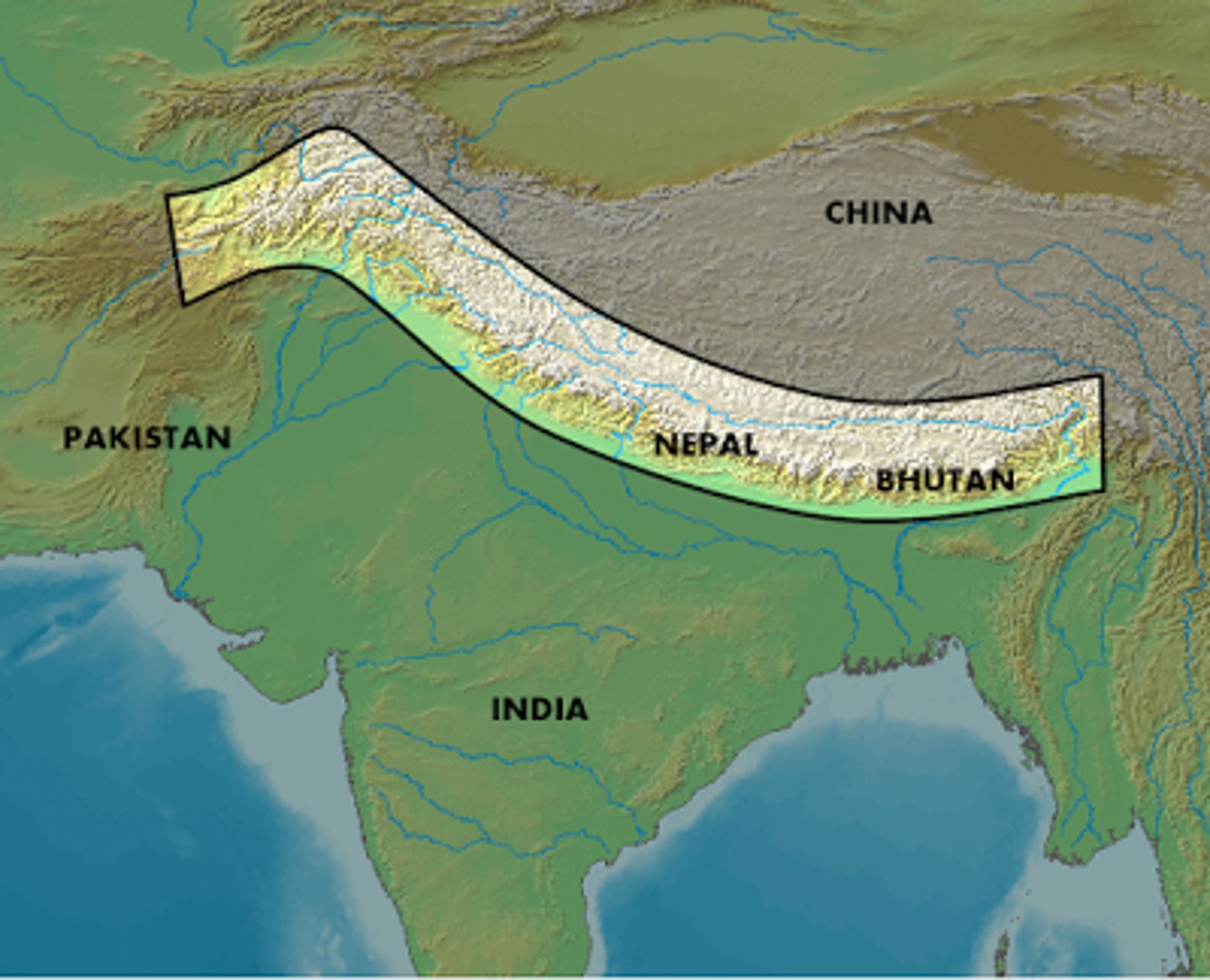
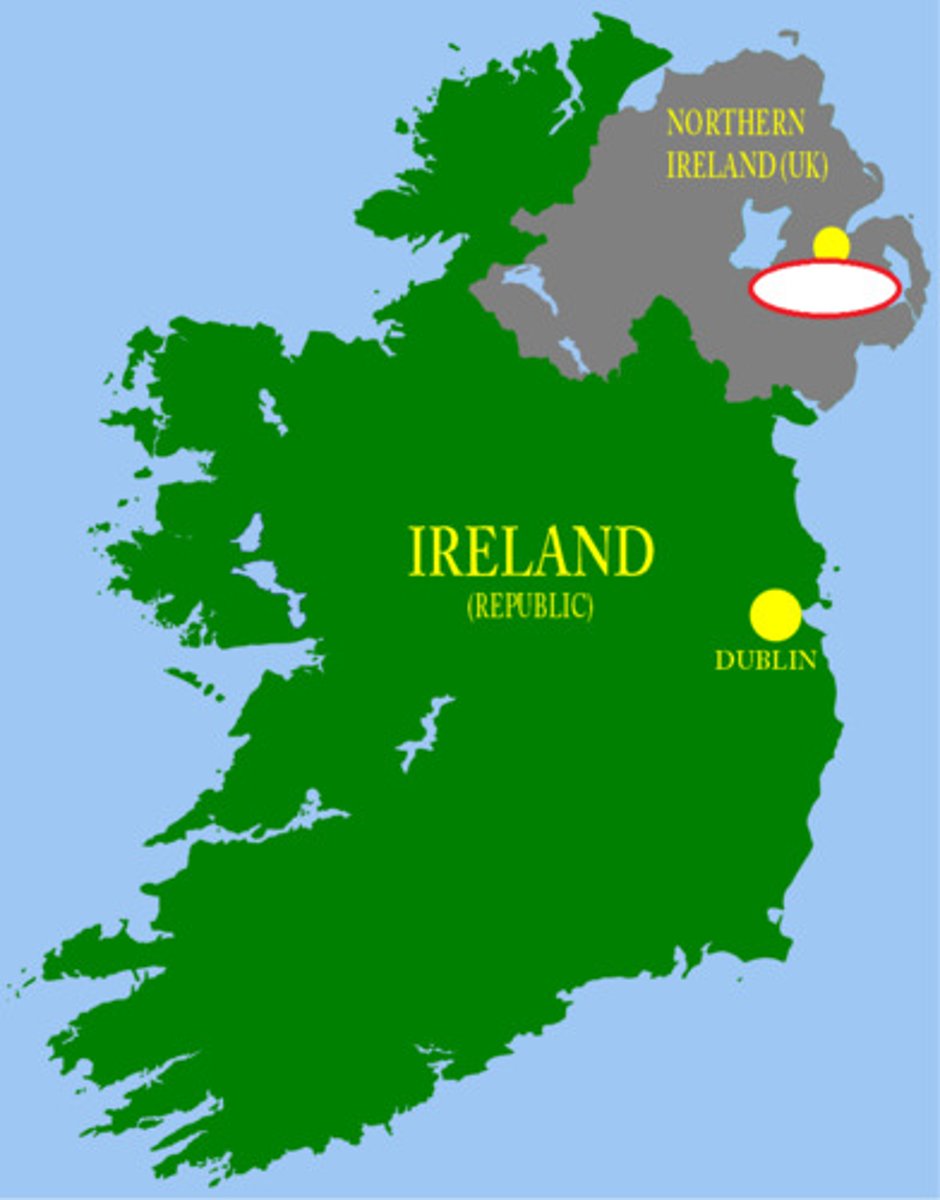
Cultural boundary
a geographic boundary between two different cultures
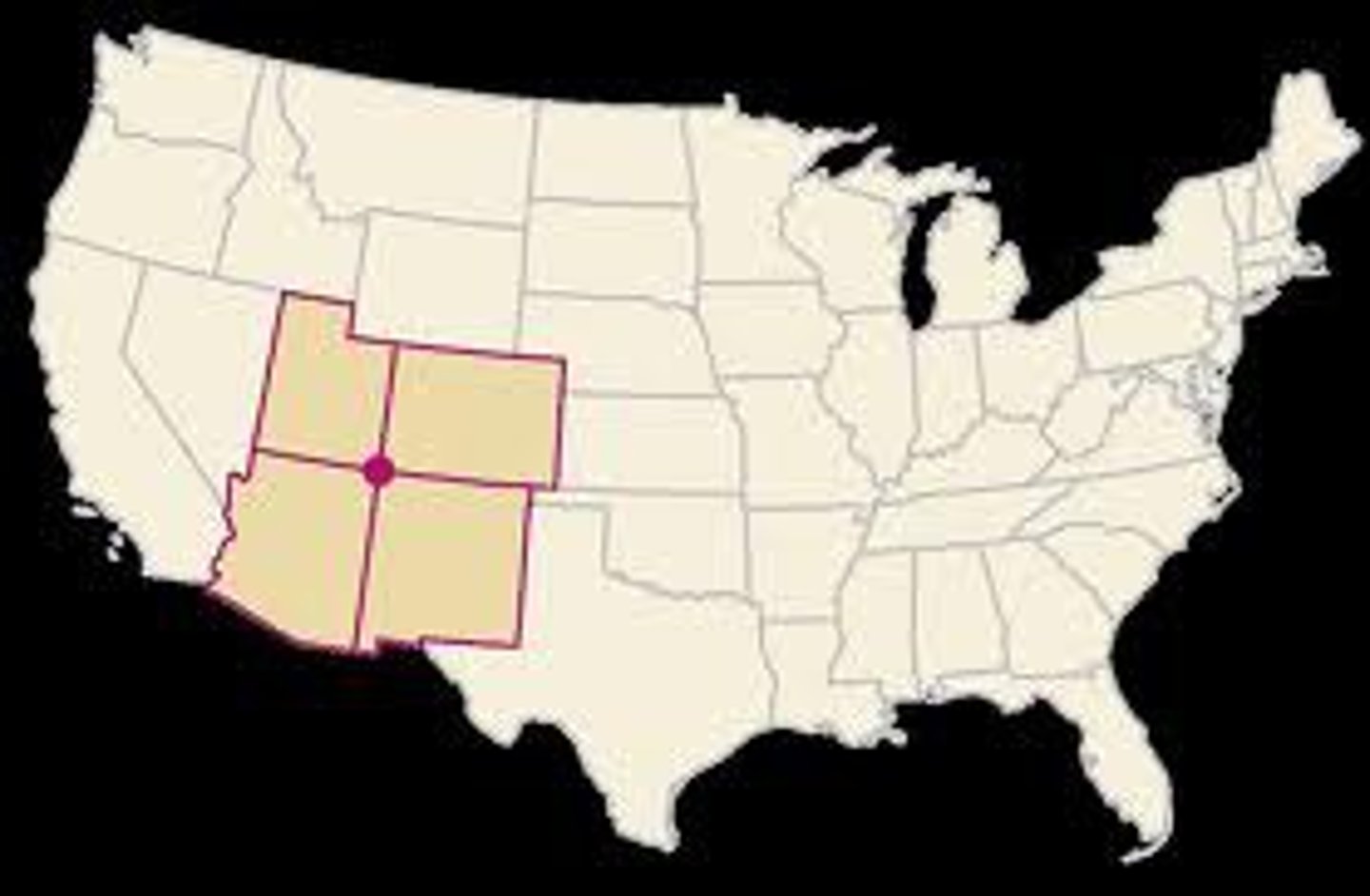
Geometric boundary
a boundary that follows a geometric pattern (usually straight lines, do not account for natural and cultural features)
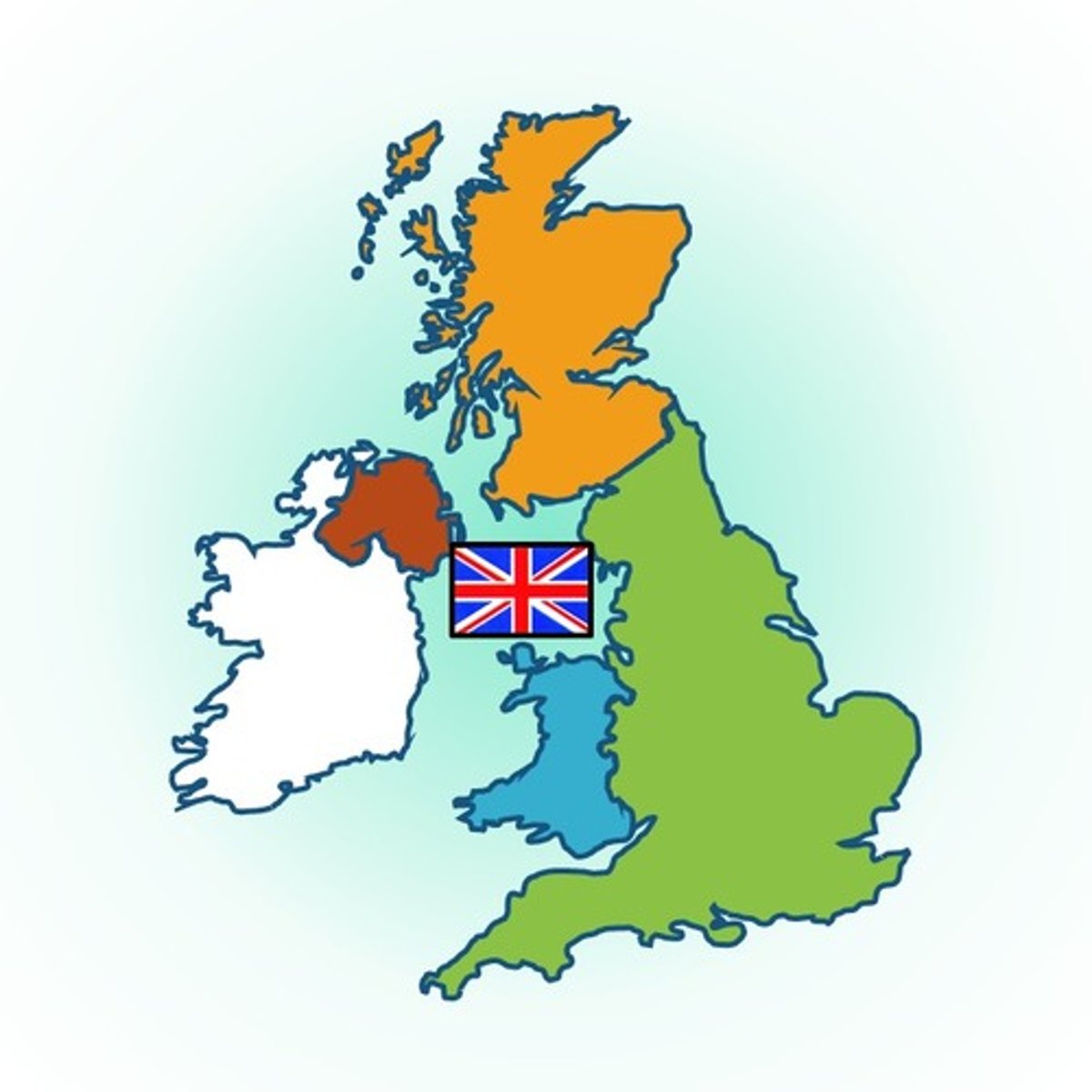
Territory
an area of land under the authority of a government
Sovereignty
the supreme and absolute authority within one's territorial boundaries
(the right for a government to rule over it's territory without outside interference)

Nation
A large group of people with a common culture, sense of unity, AND a desire for self-rule
- They can have their own state (country) or not
Ex: The Japanese (have their own state)
Ex: The Palestinians (do NOTE have their own state)

State
An area organized into a political unit and ruled by an established government that has control over its internal and foreign affairs. (Also known as a country)
Nation-state
A state with primarily one nation of people inside it
Ex: Japan
Nationalism
Belief in the right of each people with a unique cultural identity based on common language, religion, and national symbols (each nation of people) to be independent
- Nationalism can also mean that one strongly identifies with and supports their nation - in the extreme this can lead to conflict with other nations

Colonialism
The policy or practice of acquiring full or partial political control over another country, occupying it with settlers, and exploiting it (taking advantage of it) economically.
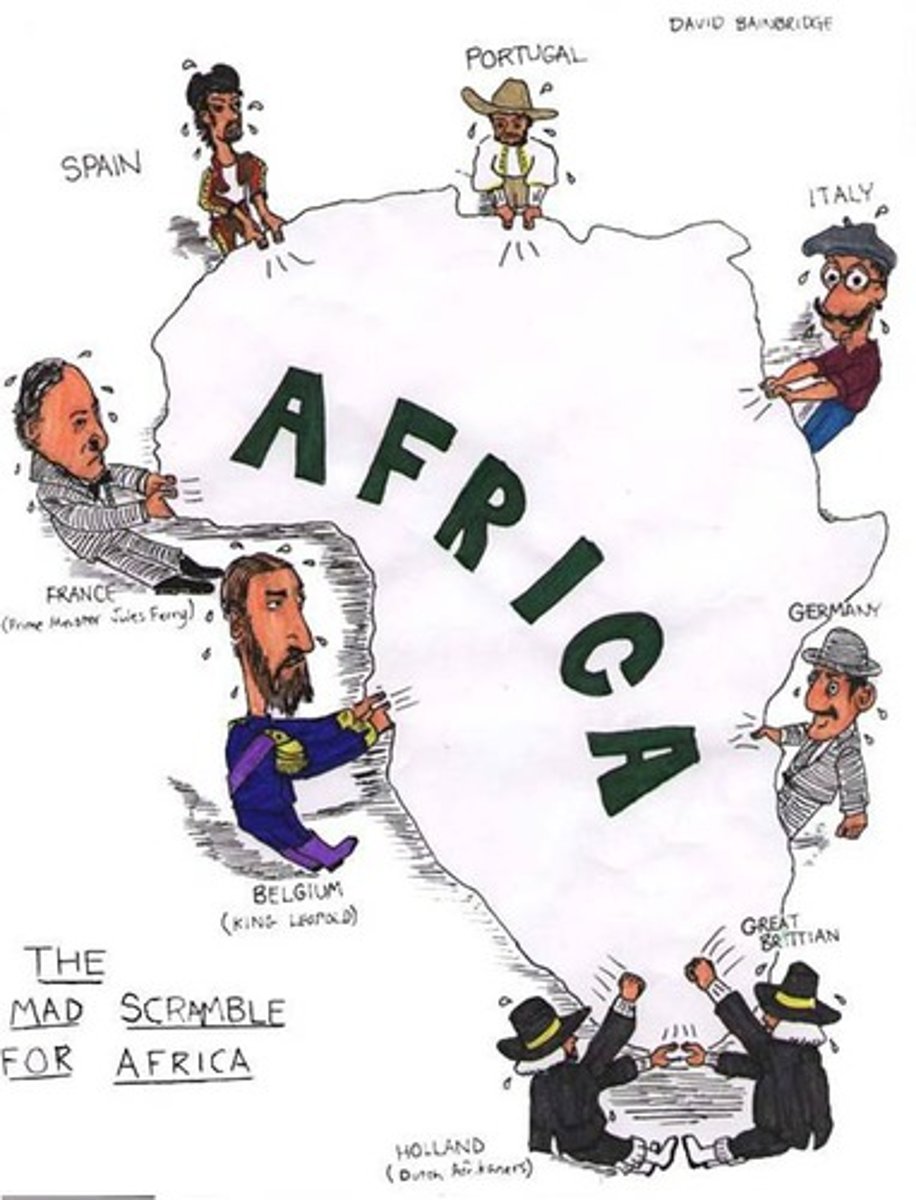
Imperialism
The practice of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy (negotiations) or military force
- The U.S. has used its large military and economic strength to pressure other countries into doing what the U.S. wants
- Ex: Influencing who gains political power in Latin American countries like Nicaragua & Guatemala

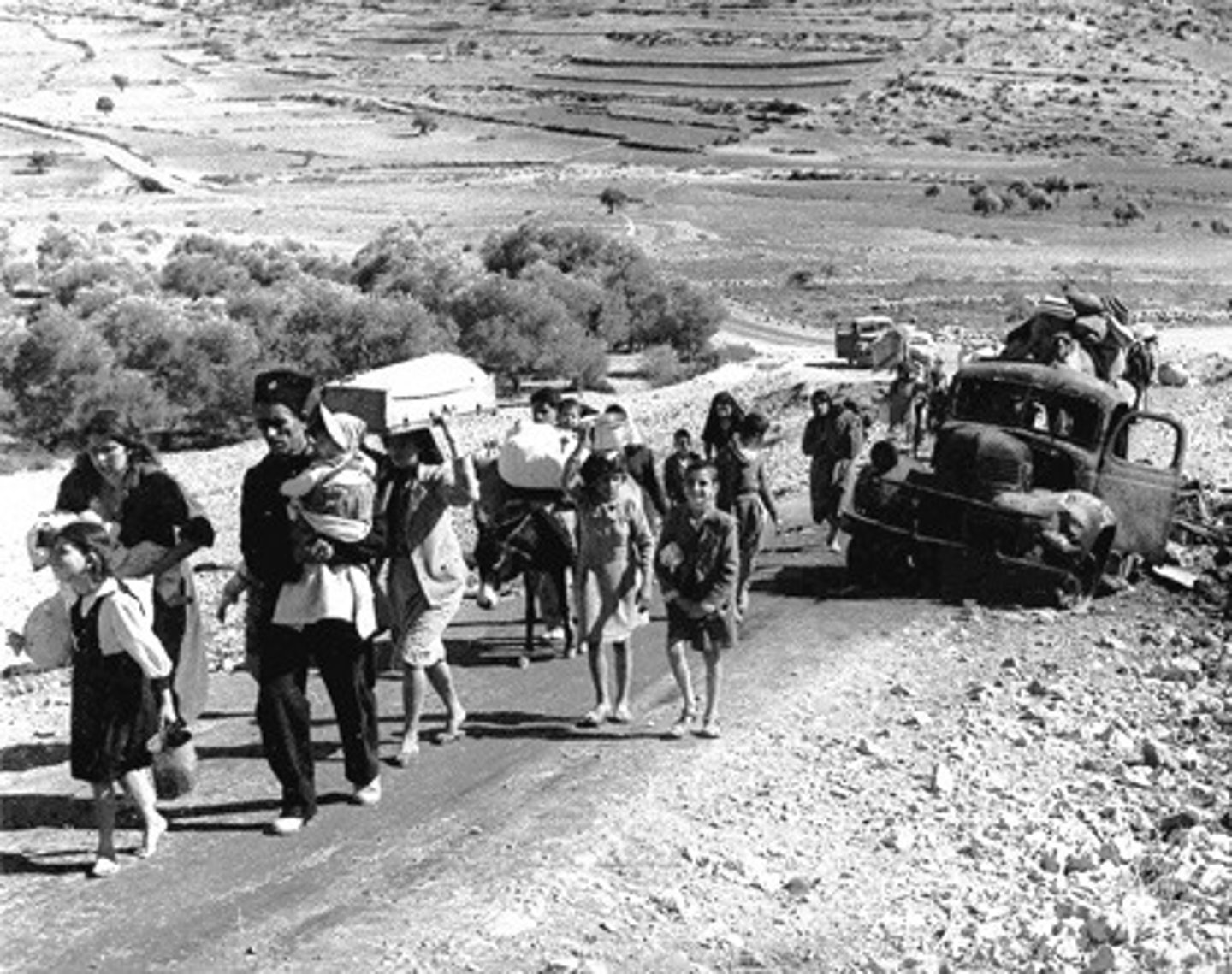
Genocide
The deliberate mass killing of a particular ethnic group or nation, with the goal of eradicating that group

Ethnic cleansing
The mass expulsion or killing of members of one ethnic or religious group in a society by another. It includes:
- ARBITRARY (Random) ARRESTS & INTIMIDATION
- DEPORTATION (kick people out of country) & DISPLACEMENT (segregate people - move them out of homes & to section of a country)
- GENOCIDE: the deliberate killing of a particular group of people, with the goal of eradicating the group

Reconciliation
the process of making peace with another
"to reconcile" = to make up, become friendly again

Human rights
the basic rights to which all people are entitled as human beings
Exs: Life and liberty, freedom from slavery and torture, freedom of opinion and expression, the right to work and education, and many more

Treaty
A formal agreement between two or more sovereign states

Diplomacy
The profession, activity, or skill of managing international relations, typically by a country's representatives abroad.
Supranational organization
Global organization composed of three or more countries that come together for their mutual benefit, in pursuit of shared goals

United Nations (U.N.)
- Supranational Organization created after WWII (1945)
- Hope to prevent future world wars
Goals:
- Help maintain international peace and security
- Develop friendly relations among nations
- Achieve international cooperation on global issues (EX: Climate Change)
The U.S. is 1 of 5 members of the U.N. "Security Council" so the U.S. has a lot of power inside the organization.

World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Supranational organization that tries to reduce trade barriers (make it easier to trade internationally - in between countries)
- Settles trade disputes between countries
- Criticism: It is run by the wealthiest countries, so it tends to benefit them the most

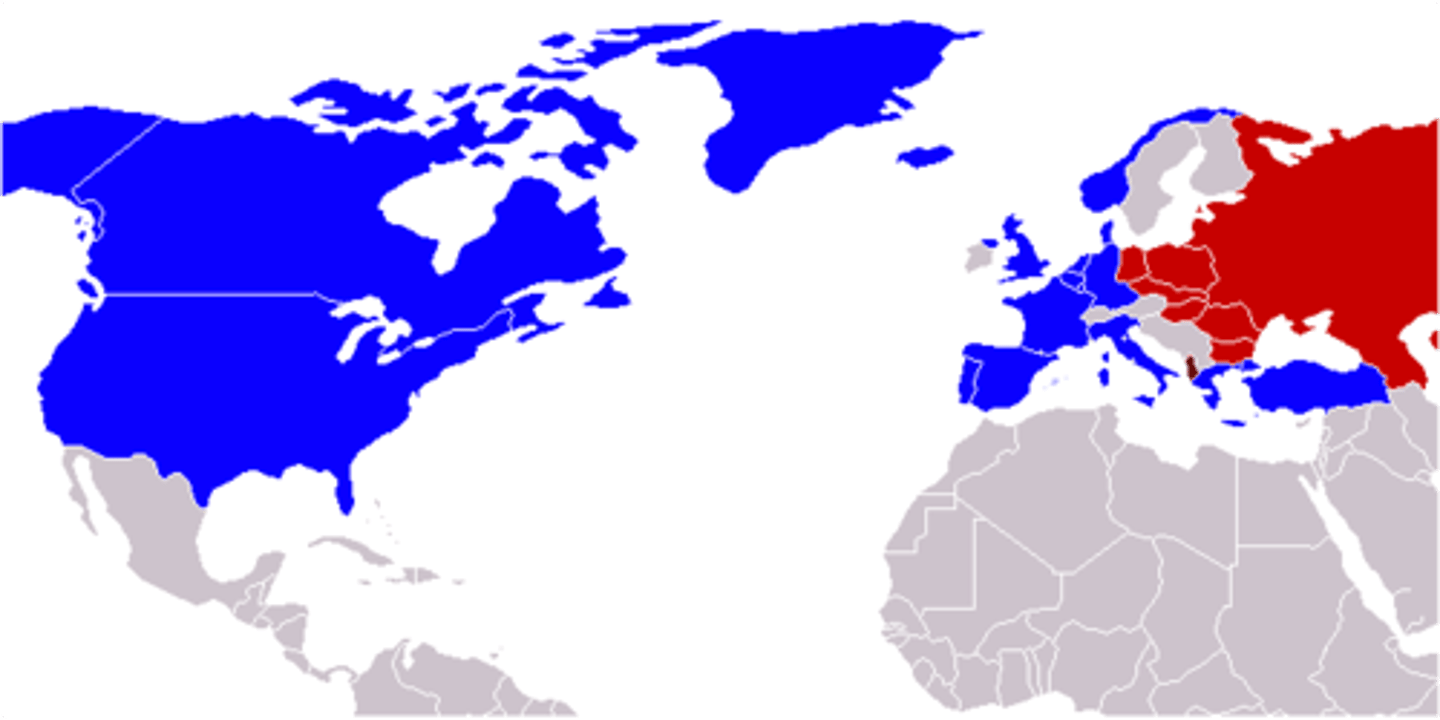
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
A supranational organization formed around a military alliance of European Countries, Canada, and the United States
- Created during the “Cold War” when the Soviet Union (Russia today) wanted to spread communism & authoritarianism around the world, and the U.S. wanted to spread capitalism & democracy
Goal: Maintain & promote democracy abroad
Independence
In political geography, when a group of people gain freedom from outside control - when they gain sovereignty, or the ability to govern themselves

Protest
A statement or action expressing disapproval of or objection to something.

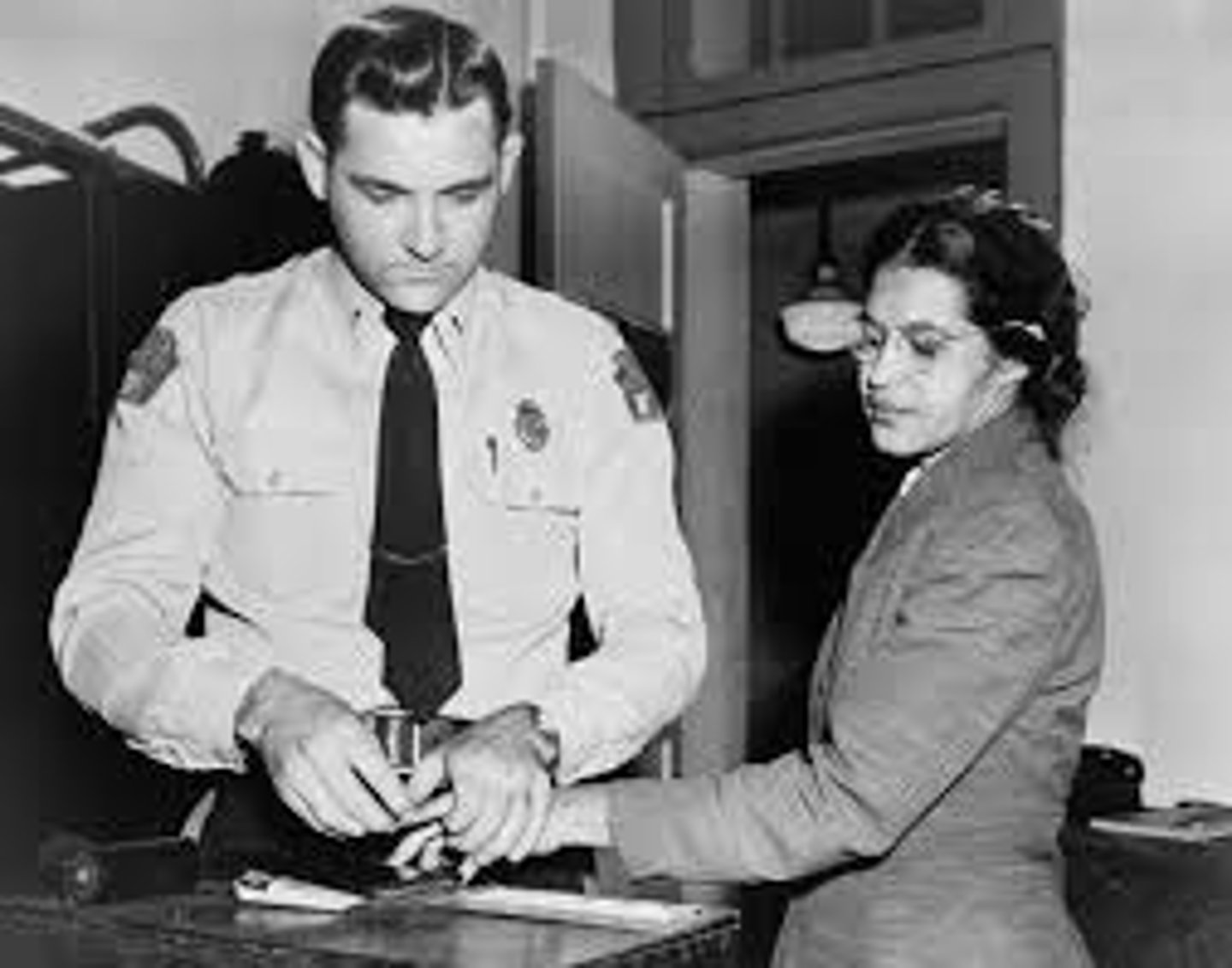
Civil Disobedience
A form of political protest where individuals intentionally break the law to express their discontent with the government, media, or public. It's usually nonviolent and is intended to force concessions from the government or occupying power.
Ex: Rosa Parks, refusing to give up her seat on the bus, to protest segregation in the Jim Crow Era South
