Prehistoric Art
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
C. or ca.
When you see c. before a date (c. 500 BCE), this means circa or around. It indicates that we may not know the exact date
BCE
we will use BCE in this course which means Before Common Era (this is the same as BC)
CE or AD
CE refers to Common Era, which we are in now (this is the same as AD)
Prehistoric and Bronze Age Art c.____-____
c.25,000BCE-c.30BCE
lintel
in architecture a horizontal block that spans the space between two vertical supports (posts).
Horizontal support beam
Just the horizontal element
Ex) a concrete beam over a window
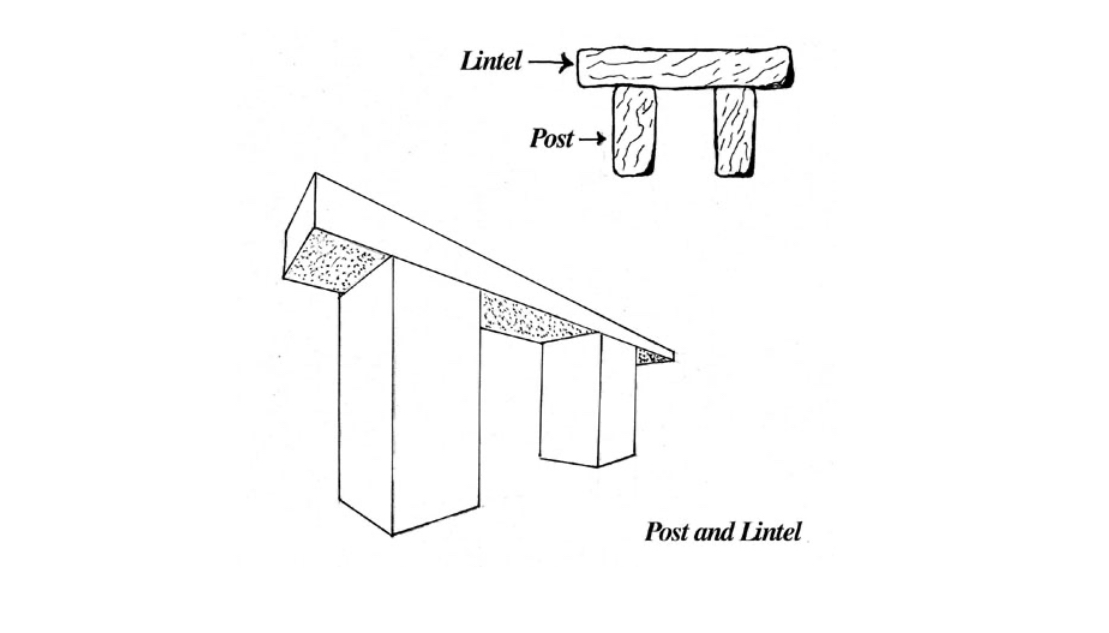
post and lintel
A method of construction where a horizontal lintel is supported by two vertical posts, often used in ancient structural designs.
structural system
vertical posts + horizontal lintel
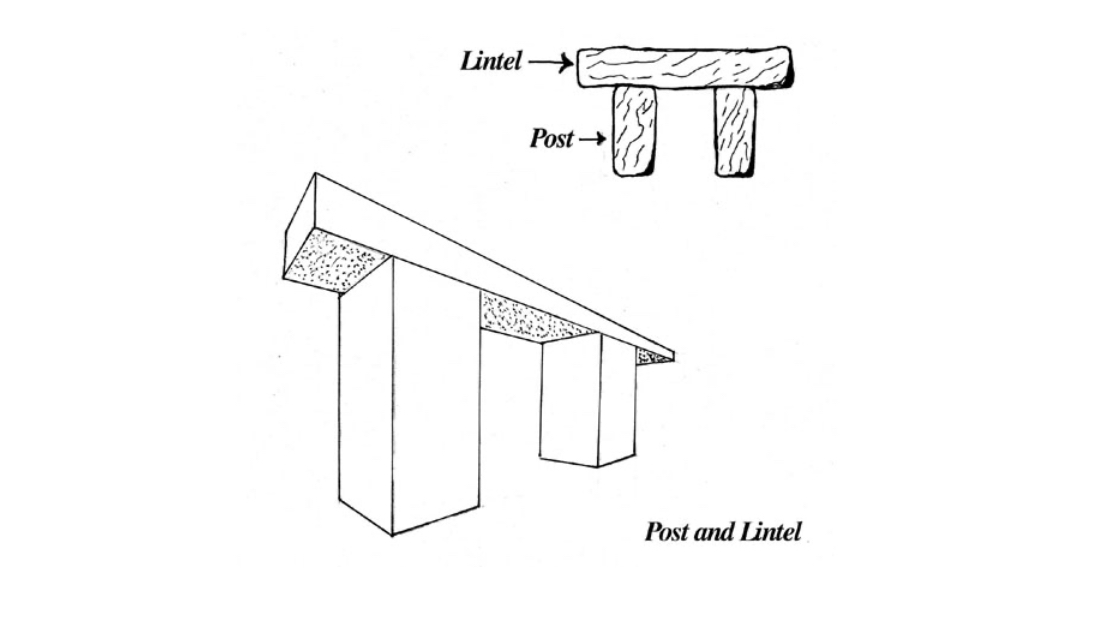
what era is the post and lintel system used in?
Prehistoric period and Bronze Age in ancient architecture
Megalithic architecture
A large stone used to construct a structure or monument, such as a tomb or a stone circle. The term megalithic describes structures made of such large stones, especially during the Neolithic period in Europe.

Cuneiform
An ancient Mesopotamian writing system using wedge-shaped characters. Cuneiform characters were normally impressed on clay tablets using a pointed tool called a stylus

Register
A horizontal band containing decorative or narrative imagery. The term is normally used when a work os art is organized in multiple horizontal bands.

Hierarchic scale
The use of differences in size to show relative importance: the large the figure, the greater his or her importance

Stela/Stele
An upright stone slab decorated with inscriptions or relief sculpture. Stelae (plural) were used as commemorative monuments or tomb markers
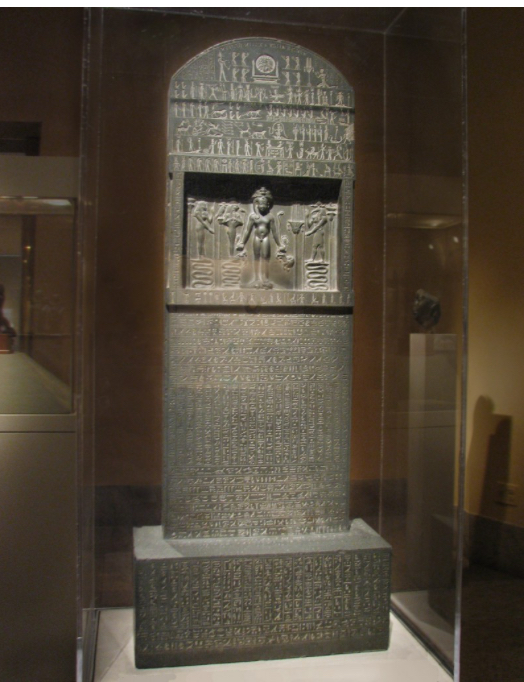

Composite Pose or View/Twisted Perspective
A pose that combines two or more viewpoints in a single representation, a convention common in ancient Near Eastern and Egyptian art. A figure in composite pose usually appears in profile with feet, legs, hips, and head turned to the side, but torso facing forward.
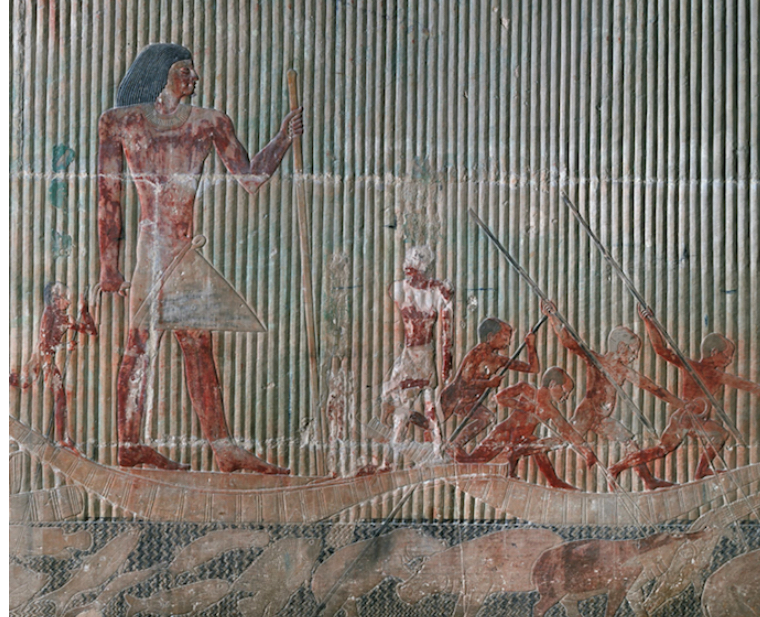

Relief sculpture
Sculpture in which the images have been carved or modeled on a surface so as to stand out from the background. Because it cannot be viewed from all sides, relief sculpture is distinct from sculpture in the round. Relief sculpture can be described as high relief or low relief, depending on how far it projects from its background
High relief is a sculptural technique where the design projects significantly from the background surface.
Low relief is a sculptural technique where the design is only slightly raised from the background surface.

Hieroglyphics
An ancient Egyptian pictographic writing system in which many of the symbols are stylized, recognizable pictures of the things and ideas represented

Necropolis
The translation from Greek means “city of the dead.” An ancient cemetery site usually located outside a city and featuring monumental tombs
Colonnade
A row of columns supporting a roof or entablature
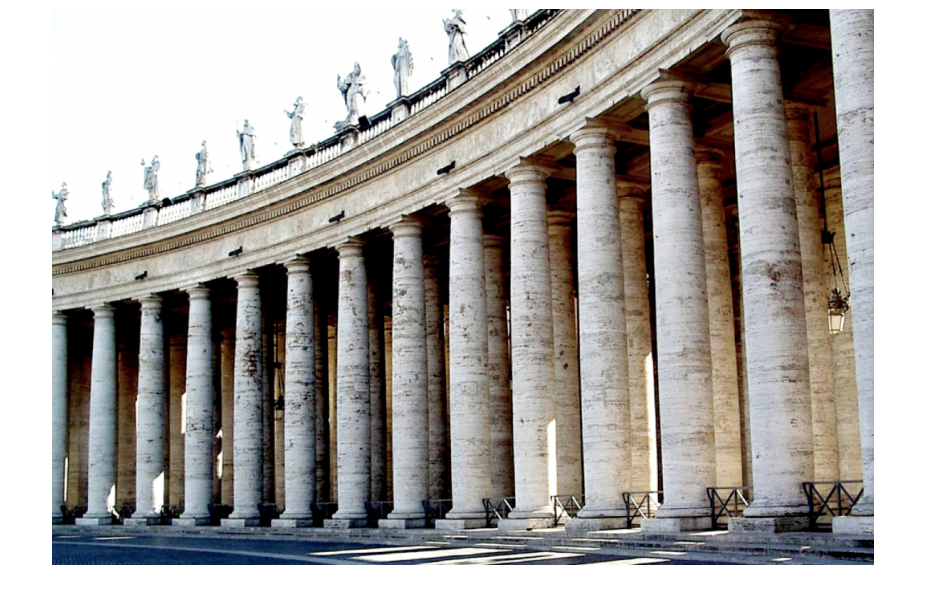

Iconography
The study of the significance and interpretation of the subject matter or art
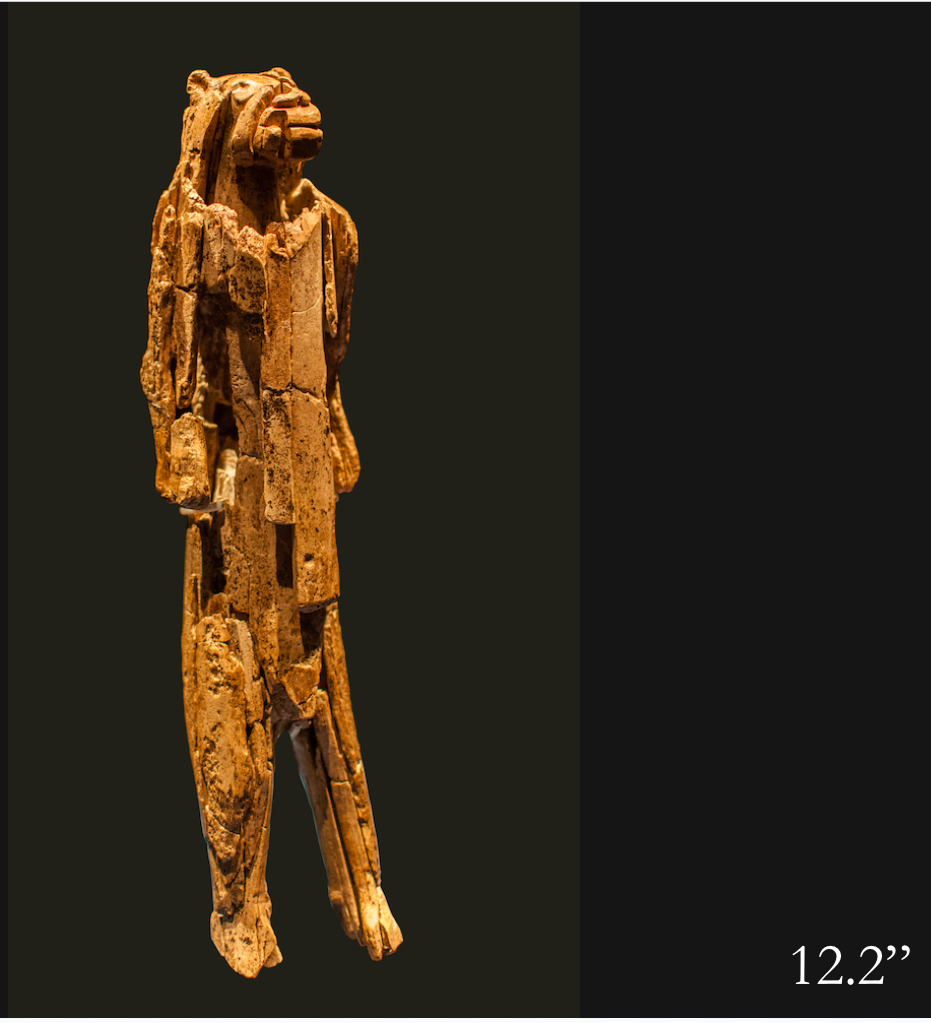

Lion-Human figure (Löwenmensch of Hohlenstein-Stadel), Germany, c. 35,000 BCE, Paleolithic
gaze is powerful and directed at the viewer
he’s the oldest known representation of a being that symbolizes ideas about the supernatural
The wear on his body suggests that he was passed around, possibly as part of a ritual
Found in Stadel Cave in a dark inner chamber, which suggests that this cave was only used on special occasions
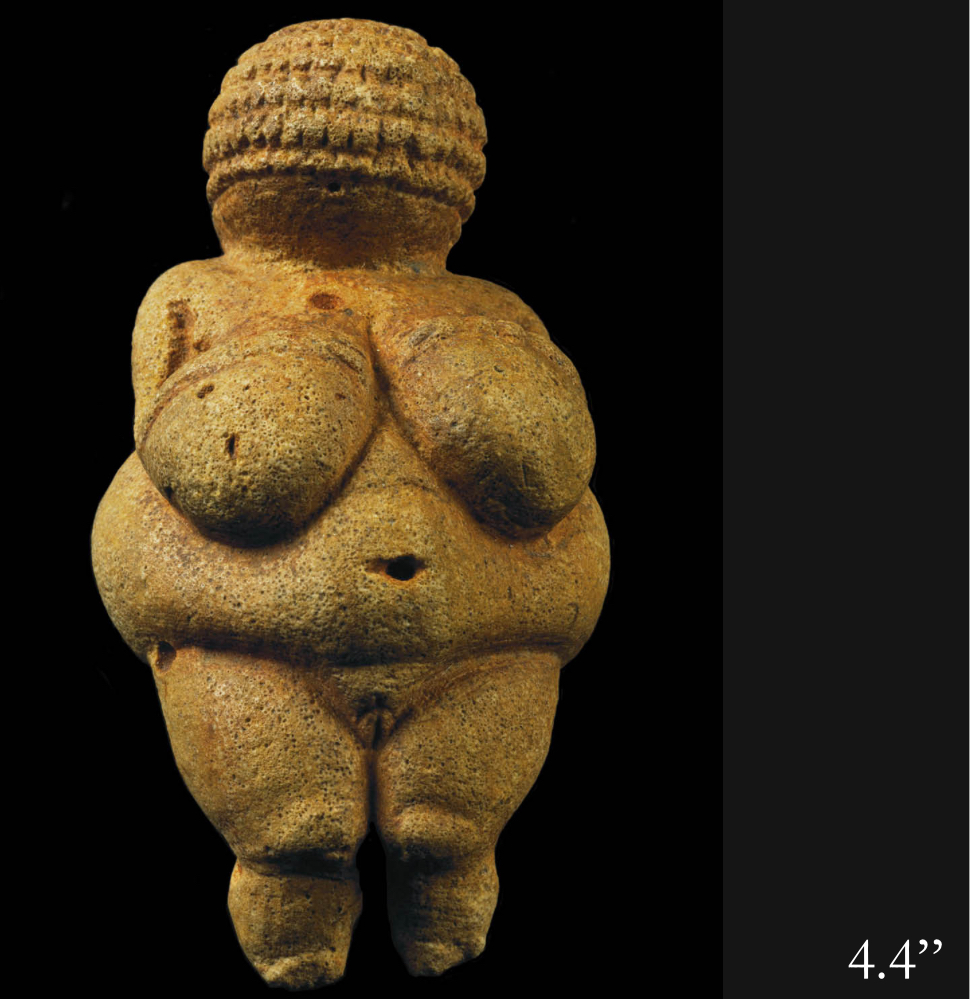

Nude woman (“Venus” of Willendorf), Austria, c. 25,000 BCE, Paleolithic
It’s one of the oldest and most famous surviving works
most noticeable parts of her anatomy deal with reproduction and childbirth and symbolizing fertility and femininity
no eyes or mouth. artist paid little attention to non-reproductive parts of the body
this women takes up a lot of space
she’s diamond shape
maybe she’s pregnant
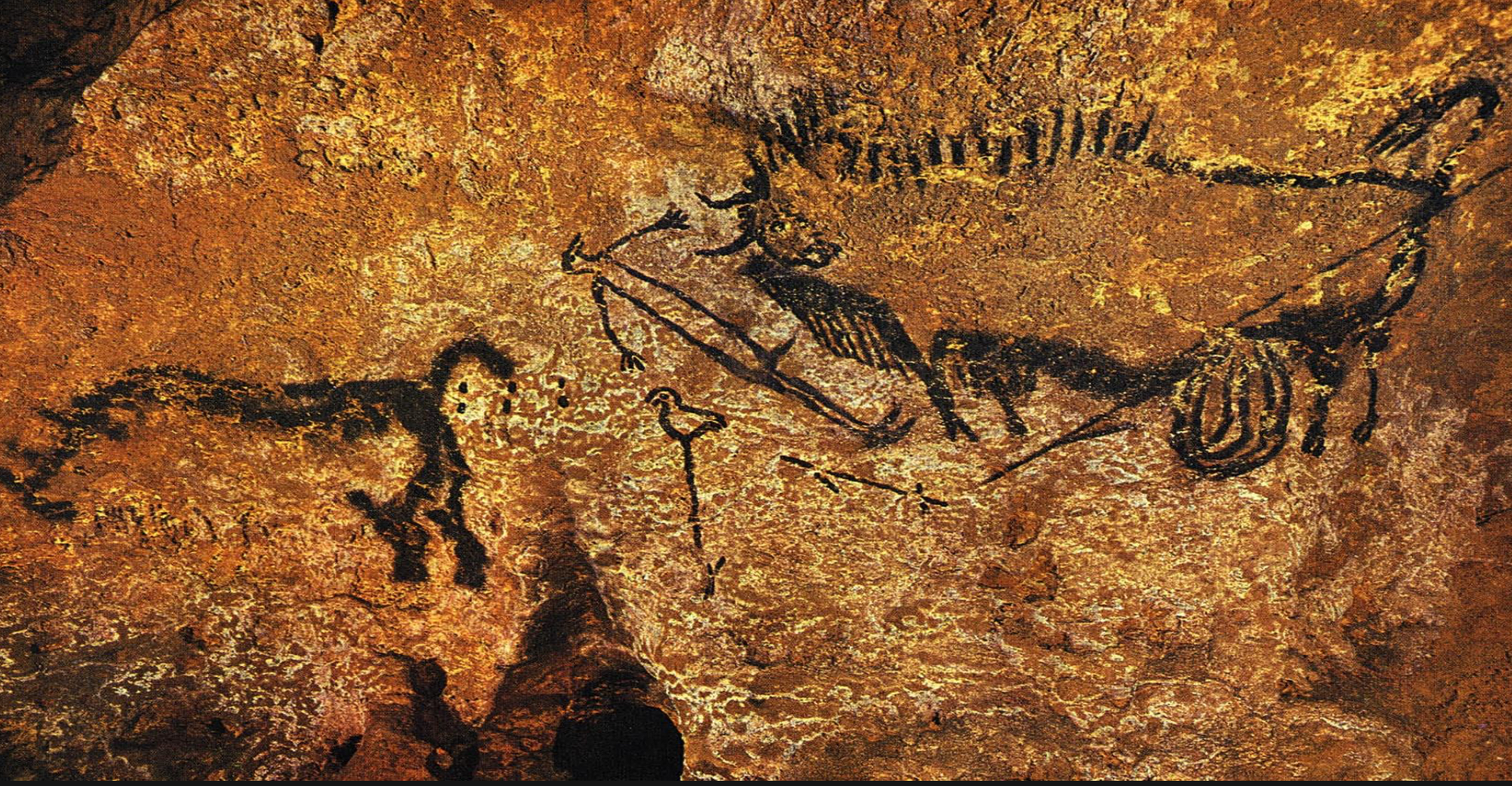

Rhinoceros, wounded man, and bison, Lascaux Cave, c. 15,000 BCE, Paleolithic
to paint, they used charcoal and other stuff
images on the wall are like an encyclopedia of the area’s prehistoric wildlife
the Caves of Lascaux are the most famous of all known caves in the region.
twisted perspective/composite view
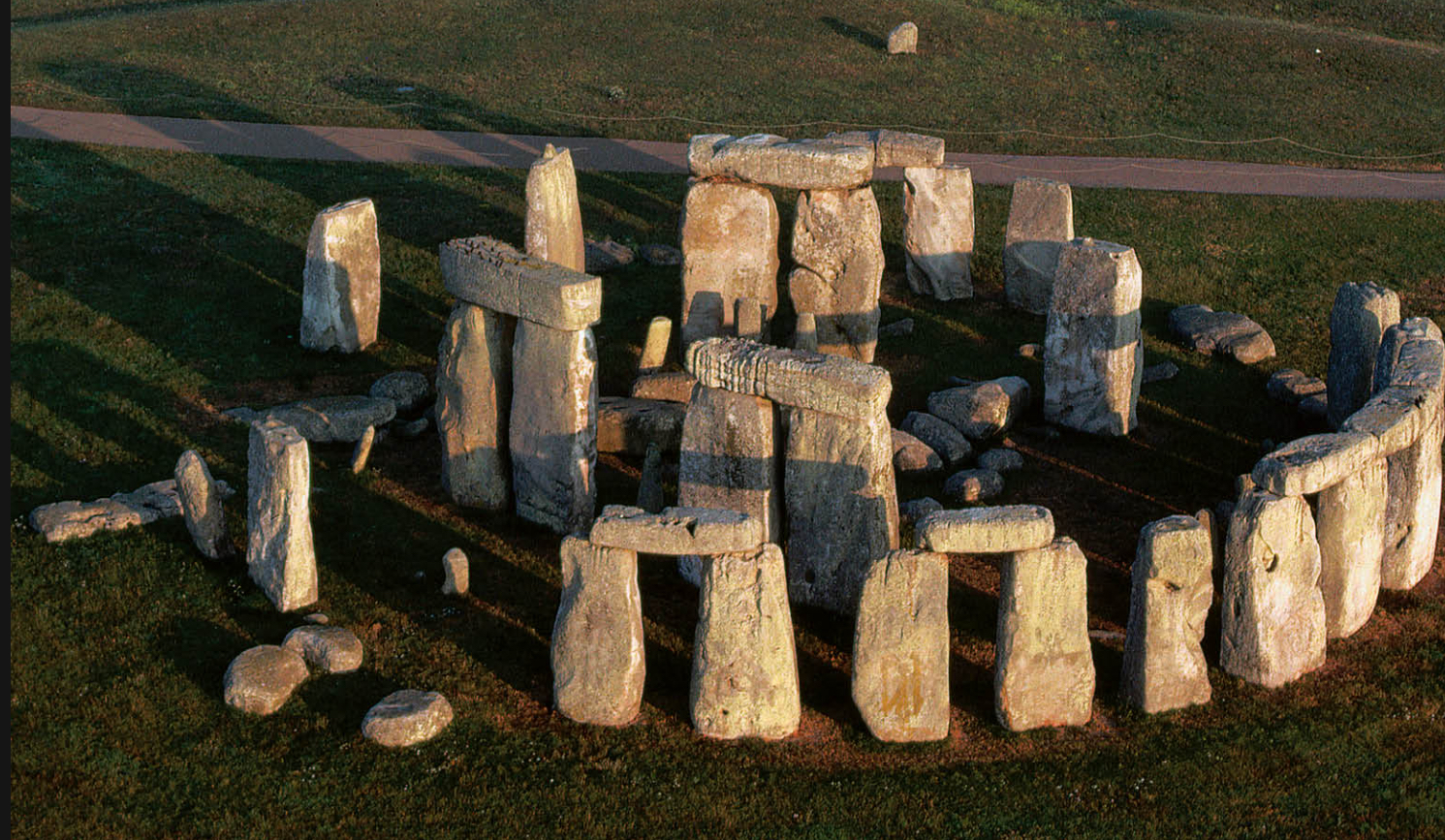

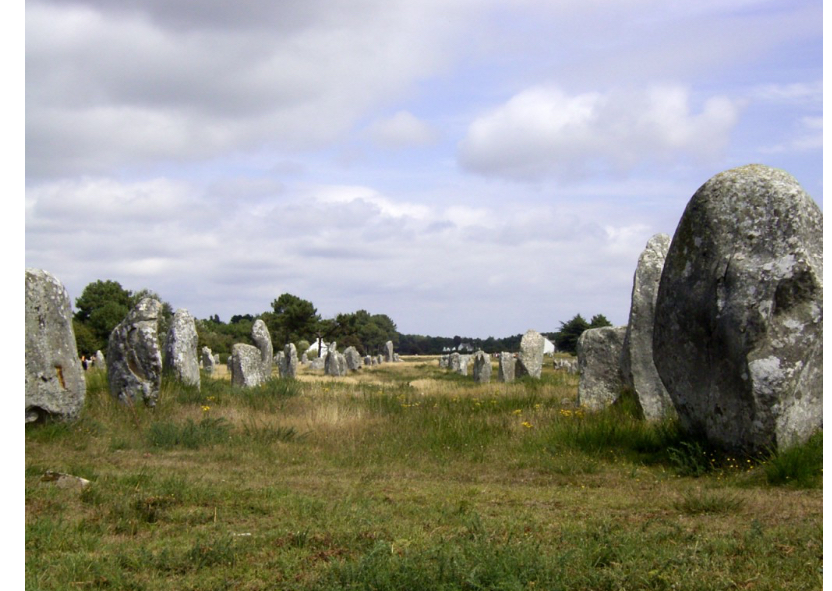
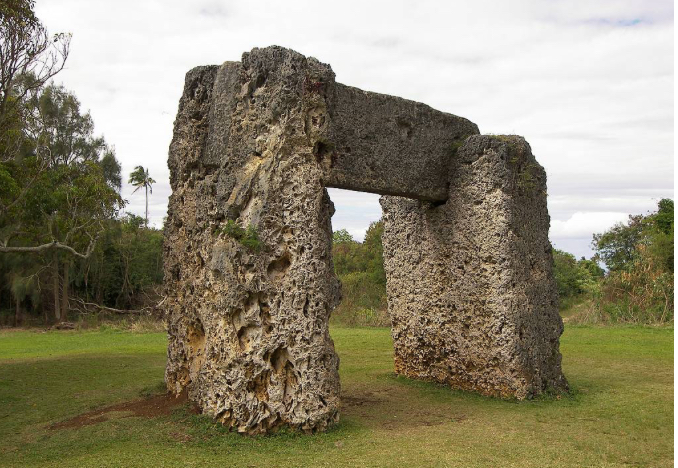
Stonehenge, England, c. 3000-1600 BCE, Neolithic to Bronze Age
built over several 1000s years bc they had to transport the stone
Henge=stone circle
Megaliths
trilithons
post and lintel system
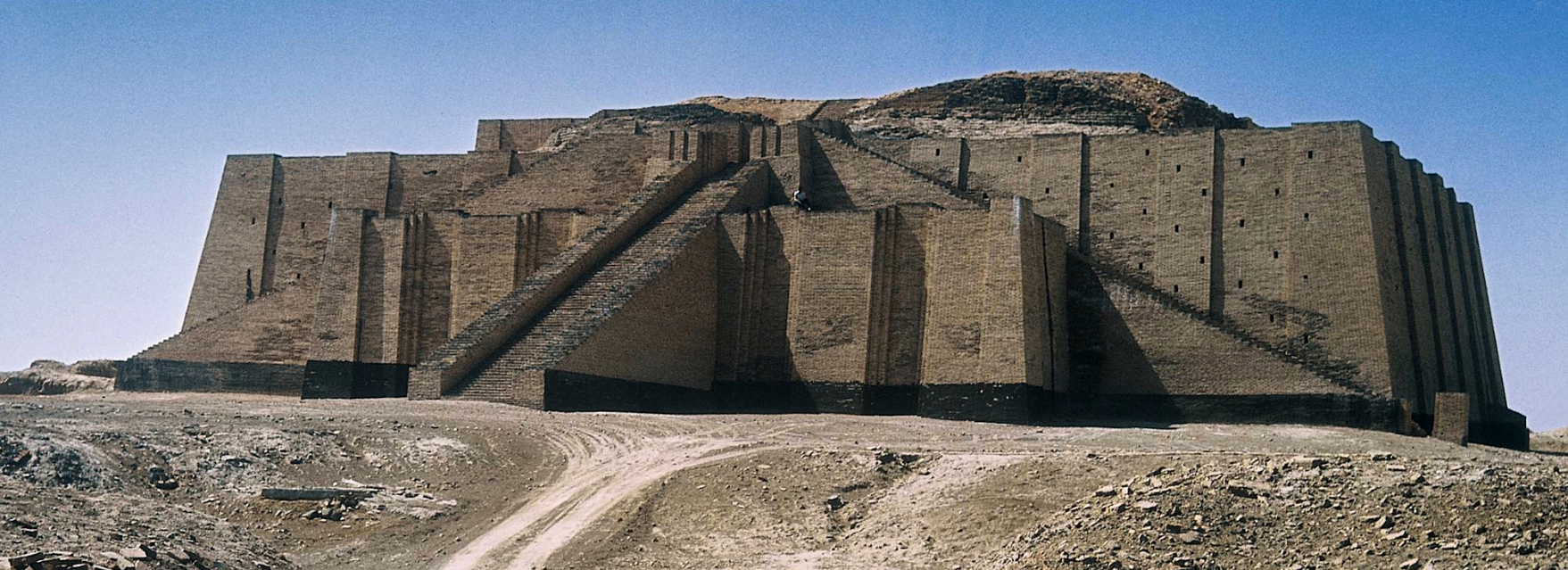

Ziggurat of Ur, c. 2100 BCE (Mesopotamia) [partially reconstructed, 1980s CE]
unlike Egyptian pyramids, the exterior wasn’t smooth.
build for the moon goddess Nanna. The Ziggurat was built high to get close to their Goddness
stimulates mountains
white temples
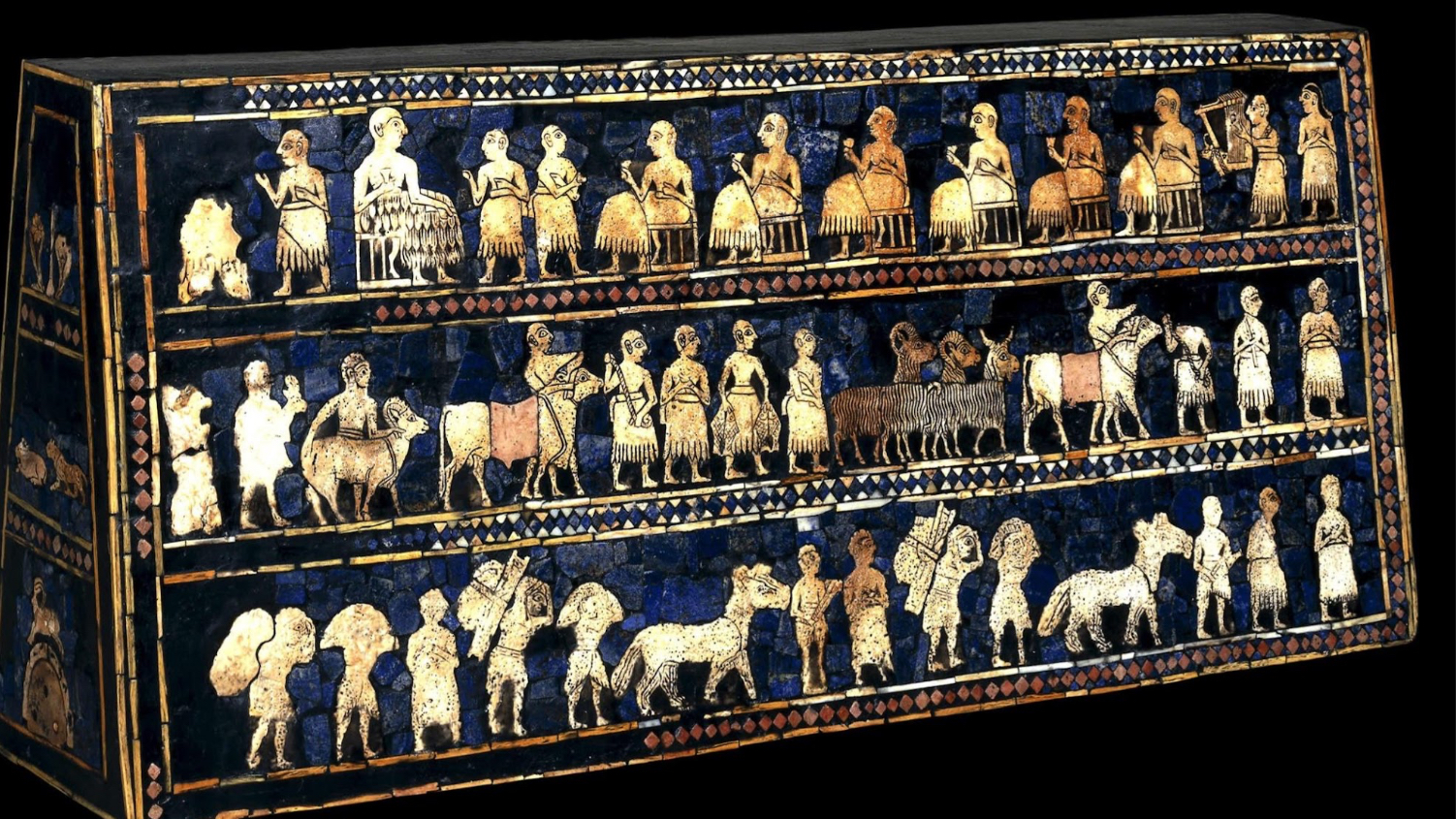

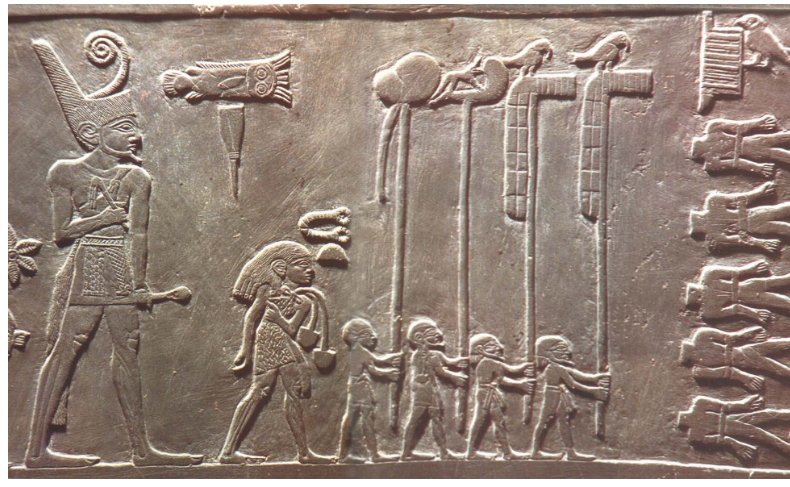
Standard of Ur: (this is the) Peace side, c. 2600 BCE (Mesopotamia)
war side and a peace side
thought to have been used in battle: a visual object held high on a pole
represents hierarchy of scale
made of materials of many areas shows that places where connected
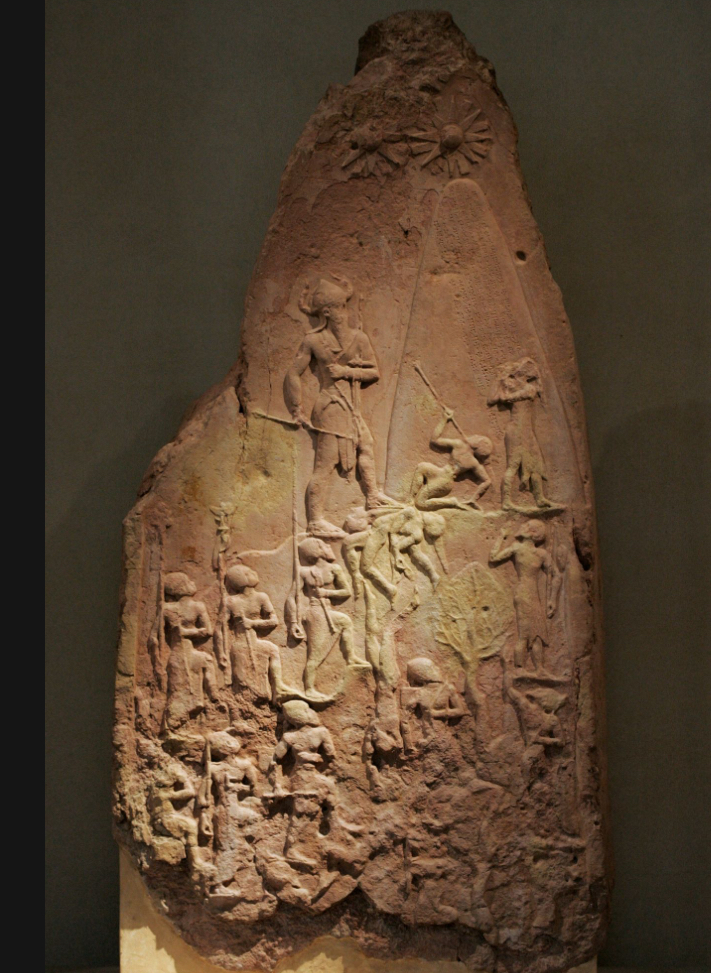

Stele of Naram-Sin, c.2200 BCE (Mesopotamia)
Victory Stele of Naram Sin
Naran Sin leads his victorious army up a mountain
Earliest surviving representation of a King deity
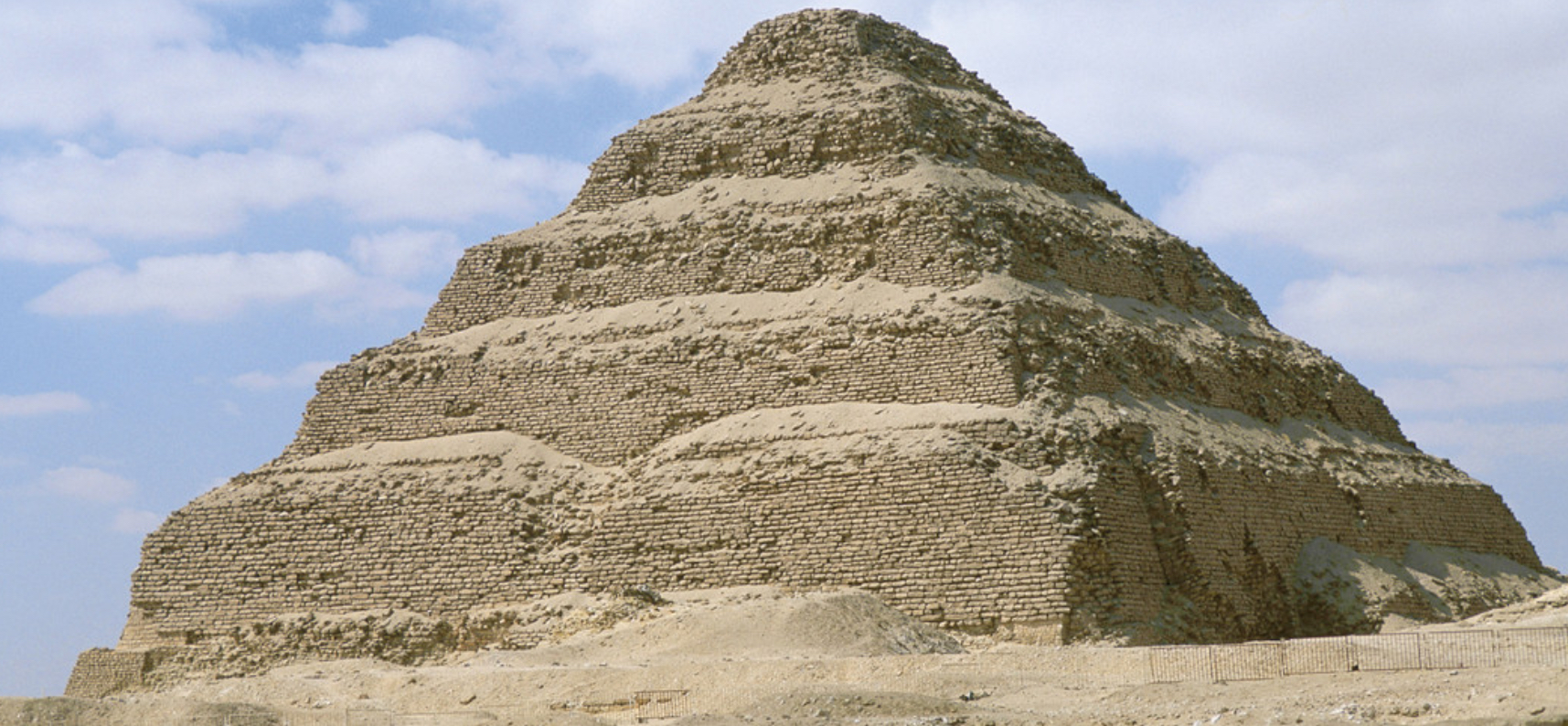

Stepped Pyramid, mortuary precinct of Djoser at Saqqara, c. 2600 BCE: Architect Imhotep (Ancient Egypt)
Pyramid of Djoser
is important for the history of art because it’s the first artist’s name we have recorded
It’s the earliest large-scale monument
the 1st time Egyptians experimented with cut stone blocks instead of mudbrick
Its towering form showed the divine statue of the pharaoh and his connection to the Gods
The step form may have symbolized a stairway to heaven.
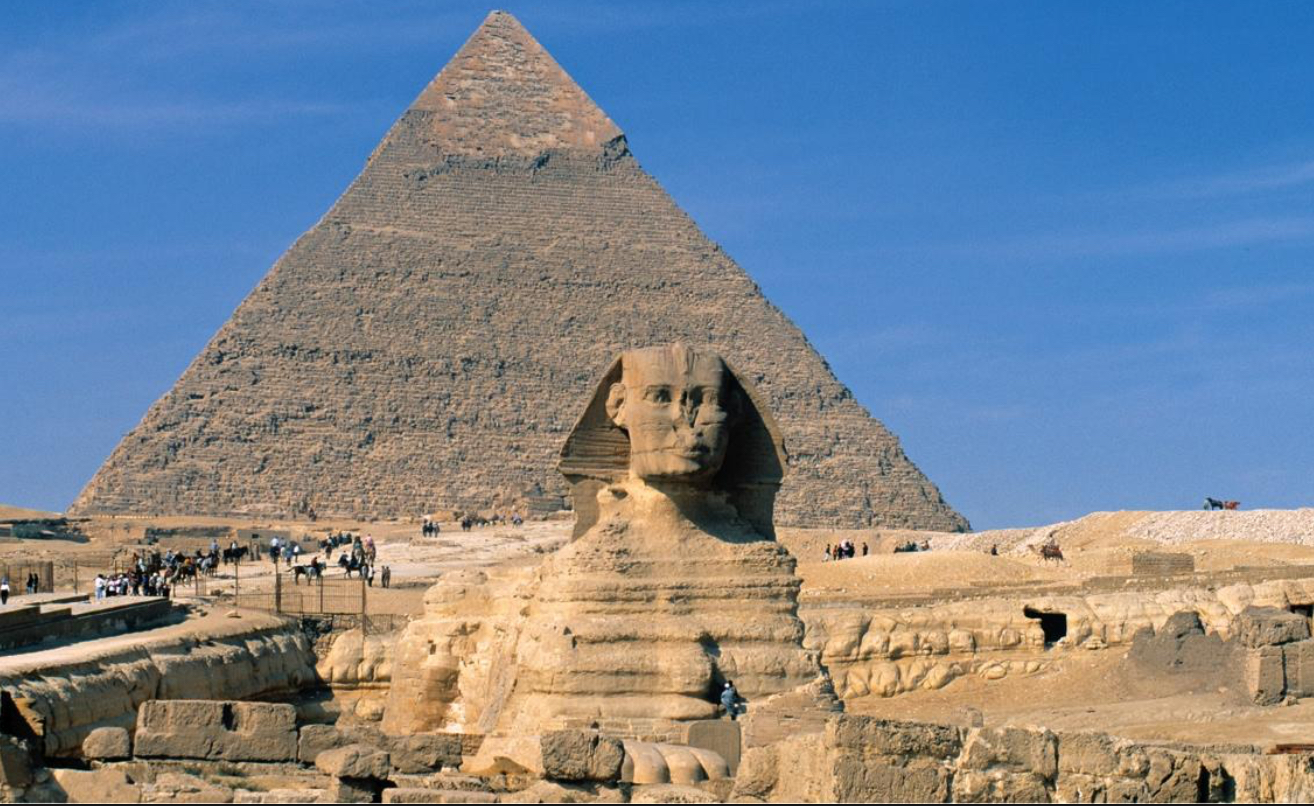

Sphinx and Great Pyramid of Khafre at Giza, c. 2500 BCE (Ancient Egypt)
The pyramid symbolizes rebirth
The Sphinx at Giza faces east towards the rising sun
the first truly colossal sculpture in Egyptian history, the Great Sphinx
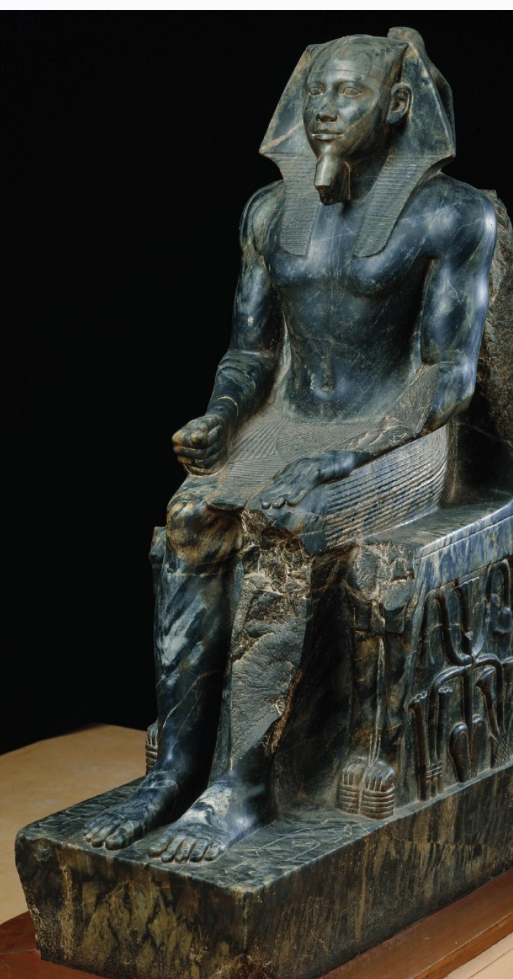

Khafre enthroned, from Giza, c. 2500 BCE (Ancient Egypt)
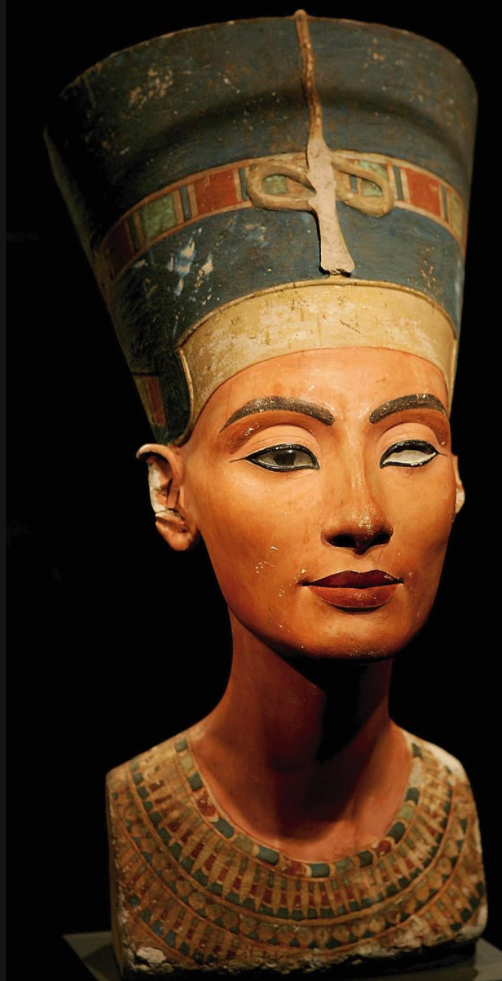

Nefertiti, mid-14th century BCE (probably by Thutmose) (Ancient Egypt, Amarna Period)
this bust exemplifies a change in style, maybe this was a prototype
more naturalistic compared to other pieces. More modern.

Book of the Dead Hunefer, Judgment of Hunefer (papyrus scroll) late 14th century BCE (Ancient Egypt)
Prehistoric art is
what humans made before written language, beginning around 3,000 BCE (the end of the 4th millennium BCE)
prehistoric era is often separated into different eras of the ‘stone age’
including
Paleolithic period (paleo/old + lithic/stone)
most sculptures were hand held
ppl would decorate cave walls
Neolithic period (neo/new + lithic/stone)
humans began to settle
domesticate plants and animals
Megalithic structures
Bronze Age
began around 6,000 BCE when ppl learned how to melt copper with tin or other materials in order to make bronze.
This is when people started to write down history
Art vs. Artifact
Art refers to creative works intended for aesthetic or expressive purposes, while artifacts are objects made by humans, often serving a practical function and providing insights into past cultures.
What are the two main types of Paleolithic art
Caves
Portable
Relative dating
is a technique used to determine the age of an artifact or fossil by comparing its placement in sediments to surrounding layers, helping establish a timeline without providing an exact date.
involves comparing an object whose day is uncertain to others that are firmly established
ethnography
A qualitative research method used to study cultures through direct observation and interaction. It provides insights into social practices and cultural norms.
Bust
It is a sculpted representation of a person or animal from the neck or shoulders up, including the head and chest.
Henge
a prehistoric monument consisting of an arrangement of stone or wooden uprights, usually circular, and often surrounded by a bank or ditch.

Provenance
Information abt the origin and ownership history of a work of art, often used as a clue to authenticity.
Trilithon
two upright megaliths supporting a horizontal lintel

In the Paleolithic period
most sculptures were…
ppl would decorate … walls
hand held
cave walls
Neolithic period
humans began to..
… plants and animals
… structures
settle
domesticate plants and animals
Megalithic structures
Bronze age
began around 6,000 BCE when ppl learned how… in order to make bronze.
This is when people started to… history
6,000 BCE to around 1,200 BCE, when ppl learned how to melt copper with tin or other materials in order to make bronze
write down
Death Pit
was an open square-shaped space, serving as the graveyard for bodies of armed men that were laid along with other corpses thought to belong to women or young girls
What way did the pyramid complex at Gizeh face
east
sum of attriutes=
iconography
Khafre enthroned from Gizeh c.
2500BCE
Compare and contrast pyramid of giza and the ziggurat de Ur
The Pyramid of Giza was supposed to be a big burial. They used a river system to bring their materials. Tomb monument
pully and level method. Made to be closer to the Gods. Temple platform to the Gods.