Earth Science Star Test, The Solar System, Sem 2 4.06 Quiz Galaxies, Environmental Review Meteors
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Because the ____ contains 99% of the mass in the solar system, it controls the motion of the planets.
Sun
_____ is a state of matter in which particles have an electrical charge.
plasma
The ____ has a low density making it very dim.
corona
The _____ flows outward from the corona to the entire solar system. This is what causes the northern lights
solar wind
Earth is bombarded with particles and radiation after violent eruptions from the Sun's surface called
solar flares
more sunspots = ?
higher temps, more frequent and intense northern lights, and potential satellites being destroyed
What does the magnetosphere do?
This layer protects Earth from a majority of solar wind and its charged particles.
Where is energy PRODUCED in the sun?
the core
What process causes the energy in the sun to be produced?
fusion
How does the Suns energy get out of the core?
it is a mixture of radiation and convection
In order for a convection to work you need what?
a difference in temperature
Do you need light for radiation to work?
No, because radiation is when energy travels through wavelengths, and visible light is not the only form of wavelengths.
you started with two hydrogens, and now you have 1 helium, what happens in the core of the sun
fusion
you started with 1 helium, and now you have two hydrogens
fission
Why would conduction be an inconvenient way for the sun to transfer energy to Earth?
If the sun transferred energy to Earth through conduction Earths atmosphere would be destroyed, increasing temperatures, and killing us quickly. Conduction is direct contact with one item and a heated item. Earth cannot get any closer to the sun than it already is because of how hot the sun is.
the lowest layer of the suns atmosphere. visible surface of the sun, 400km thick, 5,800 k(10,000F)
Photosphere
the layers above the photosphere, 250 km thick, 30,000k(53,000F), only visible during a solar eclipse because it covers photosphere, appears red
Chromosphere
top layer of the sun, 3.6 millionF, only visible during eclipse, forms solar winds, made of ions, low density, does not end abruptly
Corona
formed by gas flowing outward from the corona at high speeds
Solar wind
dark spots on the surface of the photosphere
sunspots
violent eruptions of particles and radiation from the surface of the sun
solar flare
Arc of gas ejected from the photosphere
prominence
areas of low density in the gas of the corona
coronal holes
zone above the core of the sun, where the energy is generated due to fusion
radiative zone
where the energy is moved to the suns surface through convection
convective zone
Compare and contrast solar flares, coronal holes, and prominence
solar flares, coronal holes, and prominence all occur because of sunspots. Coronal holes lead to solar flares which lead to prominence, so they are all connected. These are different, however, because coronal holes occur in the corona because of areas with low density which allow solar flares to escape. solar flares are the light that comes out of the coronal hole and prominence is the arc of the gas particles that are ejected from the photosphere which rain back down onto the sun.
Why is the energy difference between the suns core and the photosphere needed for energy to escape?
The photosphere is so much colder then the suns core the energy from the core is able to exit without any collisions or the attempt to trap the energy. Also known as convection, which would not happen without the temperature difference.
What is the relationship between temperature and luminosity? Does it apply to all stars?
the relationship between temperature and luminosity for stars are indirect but this is not true for all stars. For a white dwarf it is indirect because the surface temp is high but the luminosity is low. But main sequence stars are direct. The luminosity and temp are direct.
what features of a star does the stars mass control?
The stars mass controls temperature, luminosity, and diameter. After a star leaves the main sequence the stars mass takes over and determines what happens next in the stars life.
What elements do all stars begin with?
Hydrogen and Helium
What is the order of elements a star will fuse together?
Hydrogen, Helium, Carbon, Oxygen, Silicon, and Iron
What phase is always in a stars life?
nebula and protostar
Low mass stars life cycle
nebula, protostar, low mass star, white dwarf, black dwarf
average mass stars life cycle
nebula, protostar, average star, red giant, planetary nebula, white dwarf, black dwarf
high mass stars life cycle
nebula, protostar, high mass star, red supergiant, supernova, neutron star
very high mass stars life cycle
nebula, protostar, very high star, red supergiant, supernova, black hole
what kind of relationship exists between AA index and sunspots?
direct
What is the suns fusion cycle like?
4 hydrogen elements turn to 1 helium and creates energy for the sun
What do you need to know about magnitude for stars?
the absolute magnitude of
What can an HR diagram help predict?
it will predict the stars next stage in life. What kind of star it will become next, how much energy it will release, how hot it is, etc.
What star colors are hottest to coldest?
blue, white, yellow, orange, red
star has a surface temp of 5,000 k and an energy output of 10^2. What type of star is it?
Red giant
If a star is in the main sequence, it will always be in the main sequence
false
stars in the "White Dwarf" stage are the youngest
false
Stars with the most mass are always the coldest
false
Solar activity cycle. How long? What's measured? Lasting affects?
22.4 years, sunspots, and more solar flares
Why does the solar activity cycle start over?
The polarity of the magnetic field because it flips after 11.2 years.
What are the basic properties of the sun?
Diameter, mass, brightness, energy output(power), surface temp, composition.
a range of visible light based on wavelengths
Spectrum
group of stars
constellation
two stars that are gravitationally bound together and orbit a common center of mass
binary star
an apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from different locations
parallax
how bright a star appears to be from Earth
apparent magnitude
how bright a star actually is
absolute magnitude
energy output from the surface of a star per second
luminosity
A graph relating mass, luminosity, temperature, and diameter of stars
Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram
where 90% of stars fall on the H-R diagram
Main sequence
a cloud of interstellar gas and dust
nebula
a contracting cloud of gas and dust with enough mass to form a star
protostar
A star that has collapsed under its own gravity
neutron star
A gigantic explosion in which a massive star collapses and throws its outer layers into space
Supernova
Small, extremely dense remnant of a star whose gravity is so immense that not even light can escape its gravity field.
black hole
What can be found in the Asteroid Belt?
Asteroids or rocks, ice, and dust
Why are the models of solar systems that you can purchase in stores not to scale?
The comparison between the size of the planets and the Sun do not represent the actual mathematical scale
The sun consists of _____________ % of the mass in our solar system.
99.8
Earth is found in a region of space called the _________________________________________________ zone.
Habitable
What can be found in the Kuiper Belt?
Dwarf planets, rocks, and ice
Why do the planets stay in their orbit around the Sun?
The gravitational pull of the Sun holds them in orbit.
What are the planets called that are mostly made of gas?
Gas giants
What constitutes a solar system?
A sun or star and all the objects that orbit it.
Why are scientists studying Mars?
Scientists believe that humans will land on Mars in our lifetime.
Why was Pluto reclassified as a dwarf planet?
Pluto did not clear the neighborhood around its orbit of other objects.
The universe is made up of __________.
Thousands of galaxies
Which number best describes the number of stars you would find in a galaxy?
billions
Which kind of galaxy has arms of gas and dust?
spiral galaxy
Which category of galaxy does not have a distinctive shape?
an irregular galaxy
Which unit is used to measure the distance between galaxies?
light years
Which statement best describes how galaxies exist in the universe?
They form clusters that are light years away from other clusters.
The distance from the sun to Earth would be ___________.
less than one light year
How long does it take for light from a star that is 8 light years away to reach Earth?
8 earth years
A light year is a measurement of ___________.
distance
What is a light year?
the distance light travels in one earth year
small pieces of an asteroid or a comet
Meteoroid
when it gets into Earth's atmosphere and enters at high speeds...it burns up & produces a streak of light. They are often called a shooting star. (Smaller than asteroids)
Meteor
The rocky pieces that survive Earth's atmosphere and lands on Earth
Meteorite
Rocky pieces that revolves around the Sun (larger than meteors)
Asteroid
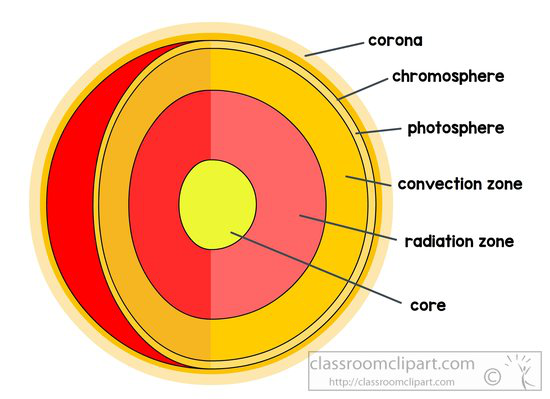
What are the layers of the sun?
core, radiation zone, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona
What are two pieces of evidence that support the Big Bang Theory?
red shift of light and cosmic background radiation
The approximate age of the universe is estimated to be __________.
13.8 billion years
Compared to our solar system, the universe is…
older, larger, and contains more stars
Cosmic background radiation detected from all directions in space provides evidence for the ______________.
Big Bang theory
The red shift of light from distant galaxies provides evidence that these galaxies are _______________.
increasing in distance from Earth
In which sequence are the celestial objects correctly listed in order from the smallest mass to the largest mass?
Milky Way
Saturn
Universe
solar system
Saturn, solar system, Milky Way, universe
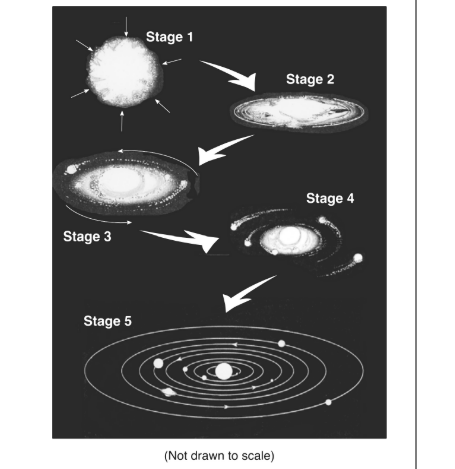
Which force was mostly responsible for the contraction of the gas cloud?
Friction
Magnetism
Gravity
Inertia
gravity
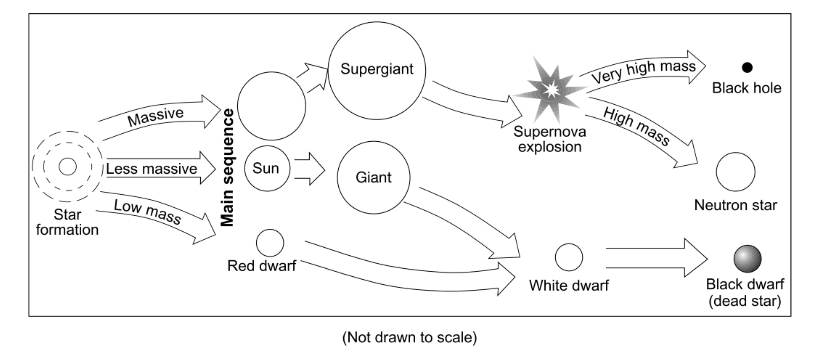
The final stage in the life cycle of the most massive stars is a…
Black hole
Black dwarf
supergiant
white dwarf
black hole
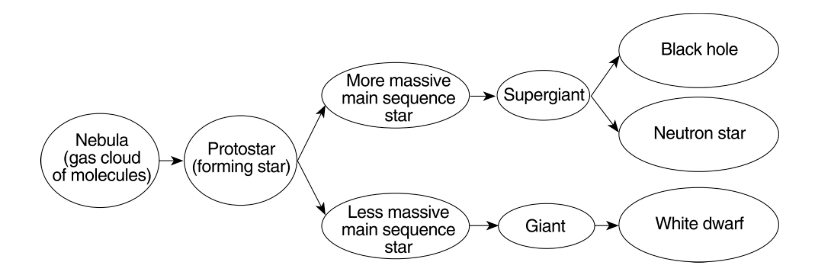
Based on this flow chart, identify the characteristics of a main sequence star that determines whether the star becomes a giant or a supergiant.
mass
Why is the surface of Mercury covered with meteor impact craters, while Earth’s surface has relatively few craters?
Earth’s hydrosphere and atmosphere destroyed or buried most meteor impact sites.
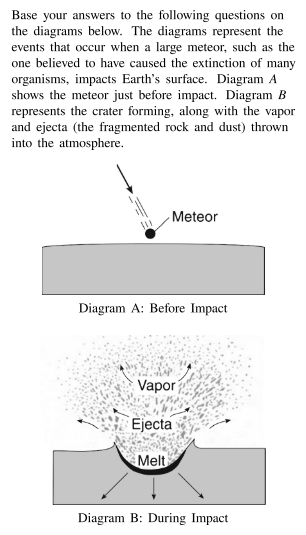
Which statement best explains how global climate would most likely be affected after this large meteor impact?
A. Large quantities of ejecta in the atmosphere would block insolation and lower global temperatures
B. An increase in vapor and ejecta would allow radiation to escape Earth’s atmosphere and lower global temperatures.
C. Ejecta settling in thick layers would increase the absorbtion of insolation by Earth’s surface and raise global temperatures.
D. Forest fires produced from the vapor and ejecta would raise global temperatures.
Large quantities of ejecta in the atmosphere would block insolation and lower global temperatures
Why is evidence of asteroids striking Earth so difficult to find?
Weathering, erosion, and deposition on Earth have destroyed or buried most impact craters.
Earth, the Sun, and billions of stars are contained within ____________.
the Milky Way galaxy