BIOCHEMISTRY carbohydrate metabolism
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
08-11-25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Mouth
Start of the digestion process is always the ?
Salivary α-amylase
hydrolysis of some α-glycosidic linkages;
an enzyme found in human saliva that plays a role in the digestion of carbohydrates, specifically breaking down starch into smaller sugar molecules
Gastric juice
no effect on digestion
Stomach
an organ that helps the conversion of solid food to liquid
Intestine
resumes the enzymatic degradation using the pancreatic digestive enzyme
Pancreatic digestive enzymes
hydrolysis of polysaccharides to disaccharides
Brush border of intestines
disaccharides reaches further hydrolysis when it reaches ?
Intestinal Lining (Villi)
Where products of monosaccharides get absorbed
Salivary enzyme α-amylase
An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of α-glycosidic linkages of starch and glycogen to produce smaller polysaccharides and disaccharide — maltose
Stomach
Part of the carbohydrate digestion where very little carboydrate is digested
No carbohydrate digestion enzymes present in ?
Salivary amylase gets inactivated because of ? acidity
Stomach acidity
In the stomach, Salivary amylase gets inactivated because of ?
Small intestine
The primary site for the carbohydrate digestion is within the ?
Where Pancreatic α-amylase breaks down polysacccharide chains into disaccharide — maltose
Outer membranes
The final step in carbohydrate digestion occurs on the ? of intestinal mucosal cells
Maltase
hydrolyses maltose to glucose
Sucrase
hydrolyses sucrose to glucose and fructose
Lactase
hydrolyses lactose to glucose and galactose
Bloodstream
Glucose, galactose, and fructose are absorbed into the ? through the intestinal wall
Liver
Galactose and Fructose are converted to products of glucose metabolism in the ?
Galactose and Fructose
are not actually used, usually gets converted to get used by the body
Oxidized to CO2 and H2O (ATP)
Converted to fat
Converted to muscle glycogen
The glucose in the tissues may be:
Blood-sugar level
The proper functions of the body are dependent on precise control of the glucose concentration in the blood.
Glucose concentration
In blood-sugar level, The proper functions of the body are dependent on precise control of the ? in the blood
70-90 mg/100 mL.
The normal fasting level of glucose in the blood is ?
Hypolgycemia
condition resulting from a lower than the normal blood-sugar level (below 70 mg/100 ml)
extreme hypoglycemia, usually due to the presence of excessive amounts of insulin, is characterized by general weakness, trembling, drowsiness, headache, profuse perspiration, rapid heart beat, lowered blood pressure and possible loss of consciousness.
Loss of consciousness is most likely due to the lack of glucose in the brain tissue, which is dependent upon this sugar for its energy.
Hyperglycemia
higher than the normal level (above 120 mg/100 mL); when the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin
may temporarily exist as a result of eating a meal rich in carbohydrates.
extreme hyperglycemia, the renal threshold (160-170 mg/100 mL) is reached and excess glucose is excreted in the urine
Hormones
Besides enzyme inhibition, carbohydrate metabolism may be regulated by ?
Insulin, Glucagon, Epinephrine
Three major hormones control carbohydrate metabolism:
Insulin
51 amino acid polypeptide secreted by the pancreas
Promotes utilization of glucose by cells
The release of insulin is triggered by high blood-glucose levels
Its function is to lower blood glucose levels by enhancing the formation of glycogen from glucose (glycogen synthesis)
Aids in glycogen synthesis
High blood-glucose levels
The release of insulin is triggered by ?
mom Insulin
involves insulin binding to proteins receptors on the outer surfaces of cells which facilitates entry of the glucose into the cells
Glucagon
29 amino acid peptide hormone produced in the pancreas
Released when blood glucose levels are low
Principal function is to increase blood-glucose concentration by speeding up the conversion of glycogen to glucose (glycogenolysis) in the liver
elicits the opposite effects of insulin
Epinephrine
also called adrenaline
Released by the adrenal glands in response to anger, fear, or excitement
Function is similar to glucagon, i.e., stimulates glycogenolysis
Primary target of epinephrine is muscle cells
Promotes energy generation for quick action
Glycogenesis, Glycogenolysis, Gluconeogenesis, Hexose Monophosphate Shunt, Glycolysis, Citric Acid Cycle
Six major metabolic pathways of glucose
Glycolysis
A series of reactions in the cytoplasm which converts glucose (C₆) to two molecules of pyruvate (a C₃ carboxylate), and ATP and NADH are produced.
Also called Embden-Meyerhof pathway, after the scientist who elucidated the pathway.
An anaerobic process; each step takes place without O₂; one of its advantages, the body can obtain energy from glycolysis quickly, without waiting for a supply of O₂ to be carried to the cells.
Occurs in cells lacking mitochondria, e.g., erythrocytes and in certain skeletal muscle cells during intense muscle activity.
Embden-Meyerhof pathway
Glycolysis is also called ?, after the scientist who elucidated the pathway
Phase 1 of Glycolysis
“energy investment phase”
Phosphorylation of glucose and conversion to 2 molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; 2 ATP are used in these reactions
Phase 2 of Glycolysis
“energy payoff phase”
Conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to pyruvate and coupled formation of 4 molecules of ATP.
Hexokinase
an enzyme that transfers phosphate group
an enzyme that catalyzes the phosphorylation of hexoses, particularly glucose, using ATP
2
How much phosphate does ADP have?
3
How much phosphate does ATP have?
1,3 and 10
In steps of Glycolysis, which steps were irreversible?
-1
In Glycolysis, ATP Change per Glucose in Step 1 and step 3 is ?
+2
In Glycolysis, ATP Change per Glucose in Step 7 and Step 10 is ?
Krebs cycle
In glycolysis, if there is adequate oxygen, an aerobic pathway is followed, and pyruvate enters the ?
Lactic acid
In Glycolysis, If there is insufficient oxygen available, the anaerobic pathway is continued and pyruvate undergoes a series of reactions to produce ?
Lactic acid
is the end-product of glycolysis, and if there not some mechanism for its removal, it would accumulate in the muscle cells & cause muscle “cramps”
Muscle cramps
If there not some mechanism for the removal of lactic acid, it would accumulate in the muscle cells and cause ?
Lactate fermentation
What bacteria uses in the production of yogurt and cheese?
Identical
In glycolysis, Reactions 1 → 9 are ? for glycolysis and alcoholic fermentation for pyruvic acid, the crossroads compound, its metabolic fate depends on the conditions (aerobic or anaerobic) and upon the organism under consideration.
Three common fates for pyruvate
Conversion to acetyl CoA, Conversion to Lactate and Conversion to ethanol. Generated by glycolysis
Aerobic conditions
an environment where oxygen is present and utilized by humans, animals and microorganisms
Anaerobic conditions
an environment where oxygen is present and utilized by (humans, animals and some microorganisms) or (some microorganisms)
Acetyl CoA
When pyruvate is exposed to aerobic conditions in humans animals and microorganisms, it becomes ?
Lactate
When pyruvate is exposed to Anaerobic conditions in humans animals and some microorganisms, it becomes ?
Ethanol
When pyruvate is exposed to Anaerobic conditions in some microorganisms, it becomes ?.
It is how fermentation occurs
adada
Fermentation
a biochemical process by which NADH is oxidized to NAD+ without the need for oxygen
Lactate fermentation, Ethanol fermentation
Two fermentation processes
Lactate fermentation
enzymatic anaerobic reduction of pyruvate to lactate
sole purpose of this process is the conversion of NADH to NAD+
working muscles often produce lactate
Ethanol fermentation
enzymatic anaerobic conversion of pyruvate to ethanol and carbon dioxide
The first step in conversion of pyruvate to ethanol is a decarboxylation reaction to produce acetaldehyde
Decarboxylation
The first step in conversion of pyruvate to ethanol is a ? reaction to produce acetaldehyde
Cori Cycle
Lactate, formed from glucose under anaerobic conditions in muscle cells (glycolysis), is transferred to the liver, where it is reconverted to glucose (gluconeogenesis), which is then transferred back to the muscle cells.
Glycogenesis and Glycogenolysis
Involved in the regulation of blood glucose concentration
Glycogenesis
is the pathway that converts glucose into glycogen.

Hydrolyzed
When theres need for additional blood glucose, glycogen is ? and released into the bloodstream
Glycogenolysis
is the pathway that hydrolyzes glycogen to glucose
Gluconeogenesis
Metabolic pathway by which glucose is synthesized from non-carbohydrate sources:
—The process is not exact opposite of glycolysis
helps maintain normal blood-glucose levels in times of inadequate dietary carbohydrate intake
12-18 hours
Glycogen stores in muscle and liver tissue are depleted with in ? hours from fasting or in even less time from heavy work or strenuous physical actiivity
90%
About ?% of gluconeogenesis takes place in the liver
Non-carbohydrate starting materials for gluconeogenesis:
Pyruvate
Lactate (from muscles and from RBC)
Glycerol (from triacylglycerol hydrolysis)
Certain amino acids (from dietary protein hydrolysis or from muscle protein during starvation)
Citric Acid Cycle
A series of biochemical reactions in which the acetyl portion of acetyl CoA is oxidized to carbon dioxide and ATP and the reduced coenzymes FADH2 and NADH are produced
Mitochondria
The Citric Acid Cycle takes place in the ?
Tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) or Krebs Cycle
The Citric Acid Cycle is also known as:
Hans Krebs
Krebs cycle is named after ? who elucidated this pathway
Two important types of reactions of The Citric Acid Cycle
Reduction of NAD+ and FAD to produce NADH and FADH2
Decarboxylation of citric acid to produce carbon dioxide
Steps of Citric Acid Cycle
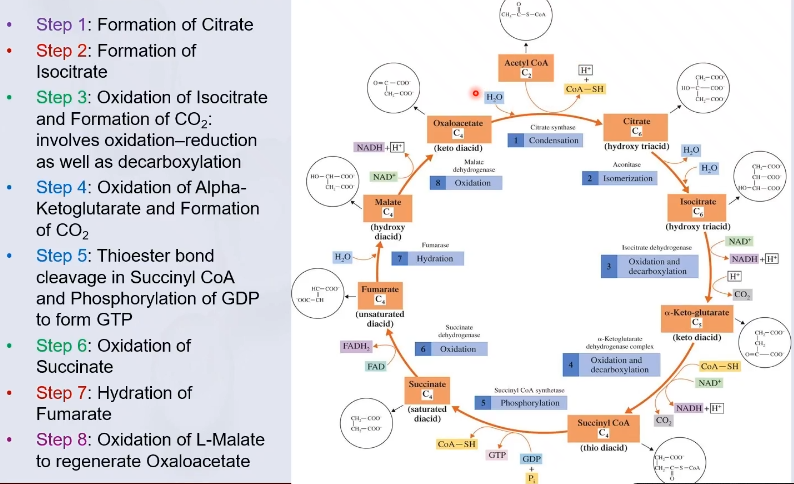
Mitochondrial matrix
The reactions of the citric acid cycle takes place in the ?, except the dehydrogenase reaction that involves FAD.
acetyl CoA
The “fuel” for the citric acid cycle
obtained from the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats and proteins
Oxidation and reduction
Four of the citric acid cycle reactions involve ?
Riboflavin, Nicotinamide, Pantothenic acid and Thiamin
Four B vitamins are necessary for the proper functioning of the cycle:
Regulation of The Citric Acid Cycle
The rate at which the citric acid cycle operates is controlled by ATP and NADH levels
High
In the regulation of the Citric Acid Cycle, When ATP supply is ?, ATP inhibits citrate synthase (Step 1 of Citric Acid Cycle)
Low
In the regulation of the Citric Acid Cycle, When ATP supply is ?, ADP activates citrate synthase
Isocitrate dehydrogenase
In the regulation of the Citric Acid Cycle, Similarly ADP and NADH control ?
Electron transport chain (ETC)
facilitates the passage of electrons trapped in FADH2 and NADH during citric cycle
is a series of biochemical reactions in which intermediate carriers (protein and non-protein) aid the transfer of electrons and hydrogen ions from NADH and FADH2
Molecular oxygen
The ultimate receiver of electrons
Respiration
The electron transport (respiratory chain) gets its name from the fact that electrons are transported to oxygen absorbed via ?
Inner mitochondrial membrane
In ETC, The enzymes and electron carriers needed for the ETC are located along ?
Complex I, Complex II, Complex III, Complex IV
In ETC, The four protein complexes tightly bound to membrane:
Coenzyme Q and cytochrome c.
In ETC, Two mobile electrons carriers are:
Complex 1: NADH-Coenzyme Q Reductase
Facilitates transfer of electrons from NADH to coenzyme Q
Complex II: Succinate-Coenzyme Q Reductase
Succinate is converted to fumarate by this complex
In the process it generates FADH₂
CoQ is the final recipient of the electrons from FADH₂
Complex III: Coenzyme Q – Cytochrome c Reductase
Several iron-sulfur proteins and cytochromes are electron carriers in this complex
Cytochrome is a heme iron protein in which reversible oxidation of an iron atom occurs
Complex IV: Cytochrome c Oxidase
The electrons flow from cyt c to cyt a to cyt a₃
In the final stage of electron transfer, the electrons from cyt a₃, and hydrogen ion (H⁺) combine with oxygen (O₂) to form water
Oxidative phosphorylation
Process by which ATP is synthesized from ADP and Pᵢ using the energy released in the electron transport chain by coupled reactions
Coupled Reactions
Pairs of biochemical reactions that occur concurrently, where energy released by one reaction is used in the other reaction
Example: Oxidative phosphorylation and the oxidation reactions of the electron transport chain are coupled systems
Proton pumps
Complexes I,III and IV of ETC chain also serve as "“?” to transfer protons from the matrix side of the inner membrane to the intermembrane space
two electrons
For every ? electrons passed through ETC:
4 protons cross the inner mitochondrial membrane through complex I
4 through complex III; and
2 more through complex IV
basis for ATP synthesis
The high (H+) in the intermembrane space becomes the basis for ?
potential energy
In Oxidative Phosphorylation, The resulting concentration difference (high in the intermembrane space compared to the matrix) constitutes an electrochemical (proton) gradient which is always associated with potential ?.