Muscle Histology and Physiology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What characterizes the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal
§ Striations
§ Multinucleated
§ Voluntary
§ Attached to bone, skin, or fascia
¡
Smooth (Visceral)
§ Spindle shaped
§ Involuntary
§ Hair follicles in skin, walls of hollow organs
¡
Cardiac (Heart)
§ Striations and Intercalated Disks
§ Involuntary
§ Cells are branched
§ Autorhythmic (pacemaker
What are the five properties of muscle tissue?
Excitability- response to chemicals and action potential
conductivity- electrical signals over membrane and anatomical structures help this function
contractivity- shorten and generate force and different mechanisms for striated versus smooth muscles
extensibility- allows to stretch w/ no damage includes the proteins and CT. Anatomical structure allows smooth muscle to expand hollow organs
elasticity- allows to return back to normal after being stretched
What is meant by the statement “muscles are excitable cells? Explain the statement, “Muscles only contract.”
Muscles are excitable cells because they respond to chemicals released from nerve cells. Muscles only contract because they only shorten and generate force
know the terminology for the muscular system discussed in lecture (myofiber, myofibril, origin, insertion, etc.)
Enthesis (plural entheses): the connection
between the moveable muscle/tendon and
the immoveable bone
¡ Origin: least moveable point of muscle
attachment
¡ Insertion: most moveable point of muscle
attachment
¡ Action: movement resulting when a muscle
contracts

which types are voluntary/involuntary and striated/nonstriated
Smooth muscle are nonstriated and involuntary
Cardiac muscle is striated and involuntary
Skeletal muscle sometimes voluntary other involuntary they are striated
What is epimysium? Perimysium? Endomysium? What structures are contained in each of these CTs?
Epimysium- separates the 10-100 muscle fibers aka fascicles
perimysium-surrounds the fascicles and includes the blood vessels and nerves
endomysium-separates cells aka myofibers
In each CT attaches to the periosteum of the bone and the aponeurosis that extends as a broad flat layer.
Make sure you know the terms muscle, fascicle, myofiber, myofibril, sarcomere, myofilaments and what structure they represent
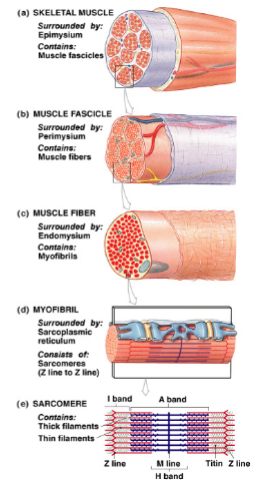
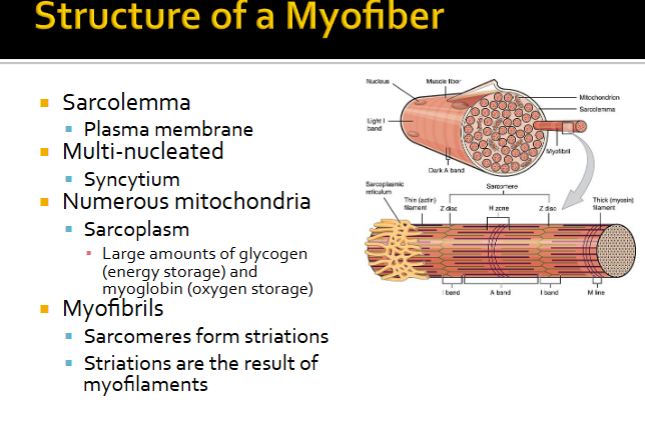
What is the structure of a myofiber? A myofibril? A sarcomere?
What is the sliding filament model of muscle contraction?
The myofiber shortens (contracts) from the insertion
toward the origin
§ Myofibrils within the myofiber shorten because the
sarcomeres get smaller in length
§ Sarcomeres shorten by actin sliding over myosin toward
the M line
§ That happens because myosin forms cross-bridges with
actin and (bonding!) uses an asynchronous power stroke to
move the actin
§ H bands and I bands become smaller but A band remains
the same length
As thin filaments slide over the thick
filaments toward the Z disc, H and I bands
shorten and finally disappear
(summary) This process allows for muscle contraction as the actin filaments slide past the myosin filaments, resulting in a decrease in the overall length of the muscle fiber.
know the structure and functions of skeletal muscle, the neuromuscular junction, and a sarcomere. Make sure you can identify
the proteins in the sarcomere
what are the structures at the neuromuscular junction? What is the neurotransmitter used? What ion is important in muscle
contraction and where is it stored
What is the function of troponin? Tropomyosin? Actin? Myosin? ATP?
Know all the steps of excitation-contraction coupling and cross-bridge formation in skeletal muscle. What is the power stroke and
how is it controlled
Why is ATP required for skeletal muscle contraction and relaxation?
What are the factors effecting whole muscle contraction? What is a motor unit? What type of motor units are required for fine
control? For powerful contractions
What is recruitment?
17. What are the components of a muscle twitch? What is treppe? Summation? Incomplete tetanus? Complete tetanus?
18. Why does a muscle fatigue?
19. What is quantal summation? Frequency summation?
20. What are the factors that influence the force that a muscle can exert? What is the force-velocity relationship? The length-tension
relationship?
21. Compare/contrast fast twitch and slow twitch muscles. What characterizes the three types of muscle fibers and how are they used
in muscle contraction?
22. What are the elastic components in a whole muscle and how do they influence muscle contraction?
23. How do muscles get the ATP required for contraction? Make sure you understand the slide on Muscle Metabolism.
24. What factors limit exercise? Which type of ATP production is the best for long-term exercise? What type of exercise should you
do to reduce body mass?
25. What is an isotonic contraction? An isometric contraction? What is meant by a concentric contraction? An eccentric contaction?
26. How does the fascicle arrangement of a whole muscle influence the type of contractions
26. How does the fascicle arrangement of a whole muscle influence the type of contractions