GENE MAPPING
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Linkage
genes (alleles) on the same chromosome are likely to be inherited together
Linkage group
set of linked genes
ex: genes located on chromosome 4 are in linkage group IV
ex: genes located on the X chromosome are X-linked
Genetic map
shows the order of linked genes and distances between genes on a chromosome
constructed based the rate of recombination (recombination frequency) between genes of interests observed during test crosses
Distance
the distance between genes determines the likelihood of recombination
the further apart two genes are, the more likely that there will be genetic recombination between them
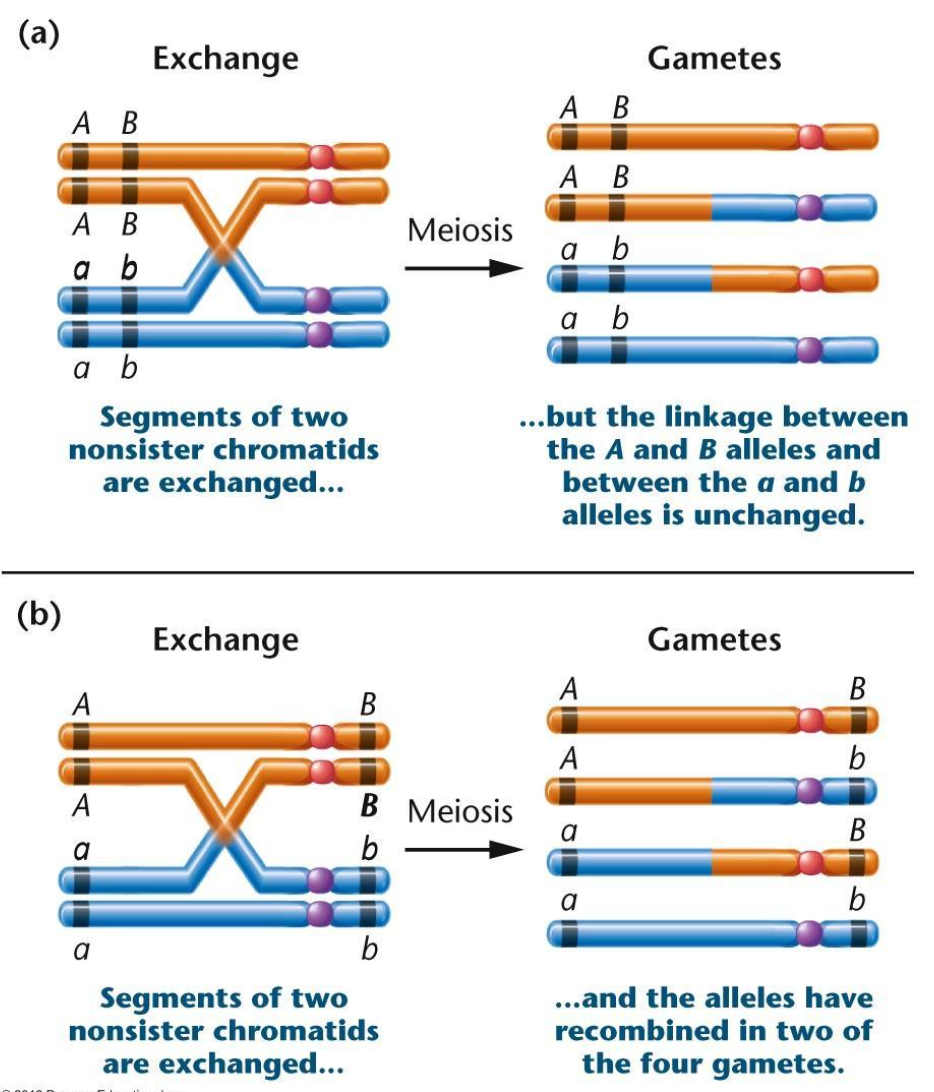
Crossing over
happens every single cycle of meiosis
Genetic marker
DNA sequence, such as SNP or repeat
Physical marker
phenotype associated with a gene locus
Test cross
cross F1 heterozygous with a homozygous recessive testes
if we are interested in two genes, we do a two-point test cross
Recombinant progeny
progeny with a different combination of markers as the parent
genes have undergone recombination
result from crossover gametes
Parental progeny
progeny with the same combination of markers as the parent
result from noncrossover gametes
Two-point test cross
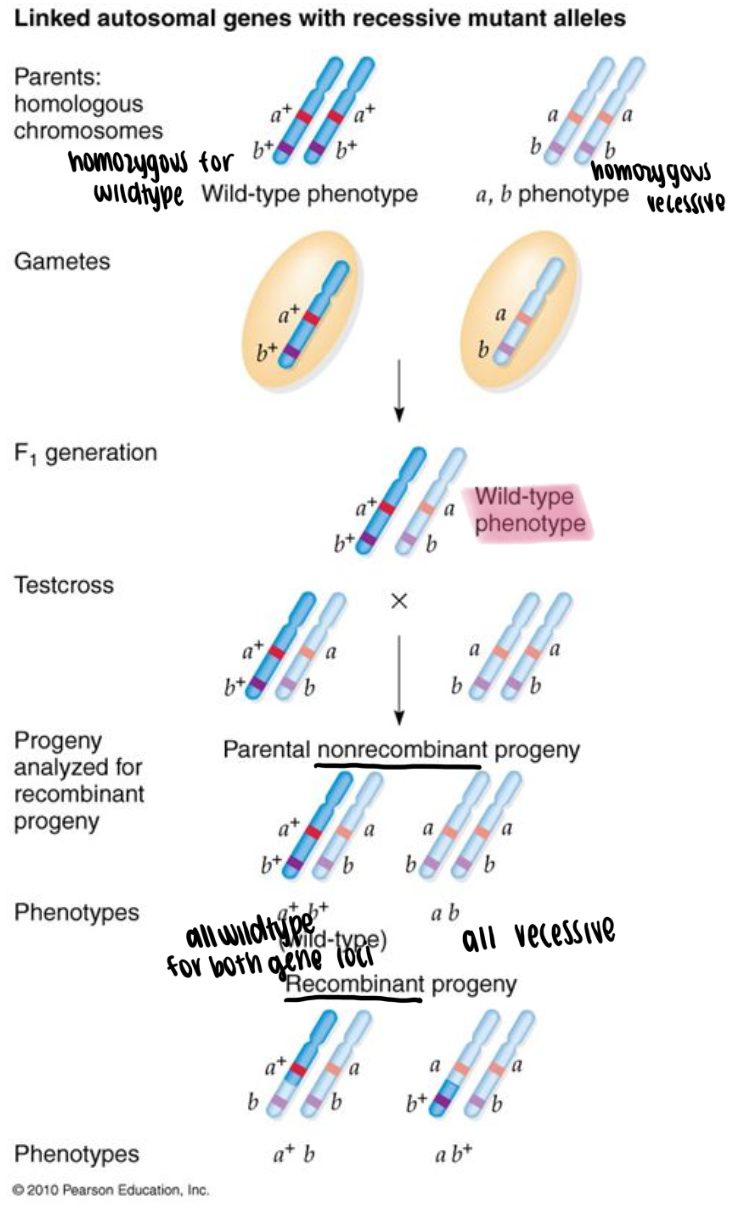
Two extreme scenarios
genes are very far apart on same chromosome or are on different chromosomes (assort independently)
50% recombination between genes
genes are very close on same chromosome
no recombination between genes
Map units
mu (unit)
= % recombination
Map distance formula

Double-crossover (DCO)
occurs when two chiasmata form and there is a double exchange between two nonsister chromatids
DCO is less likely to happen than single crossover
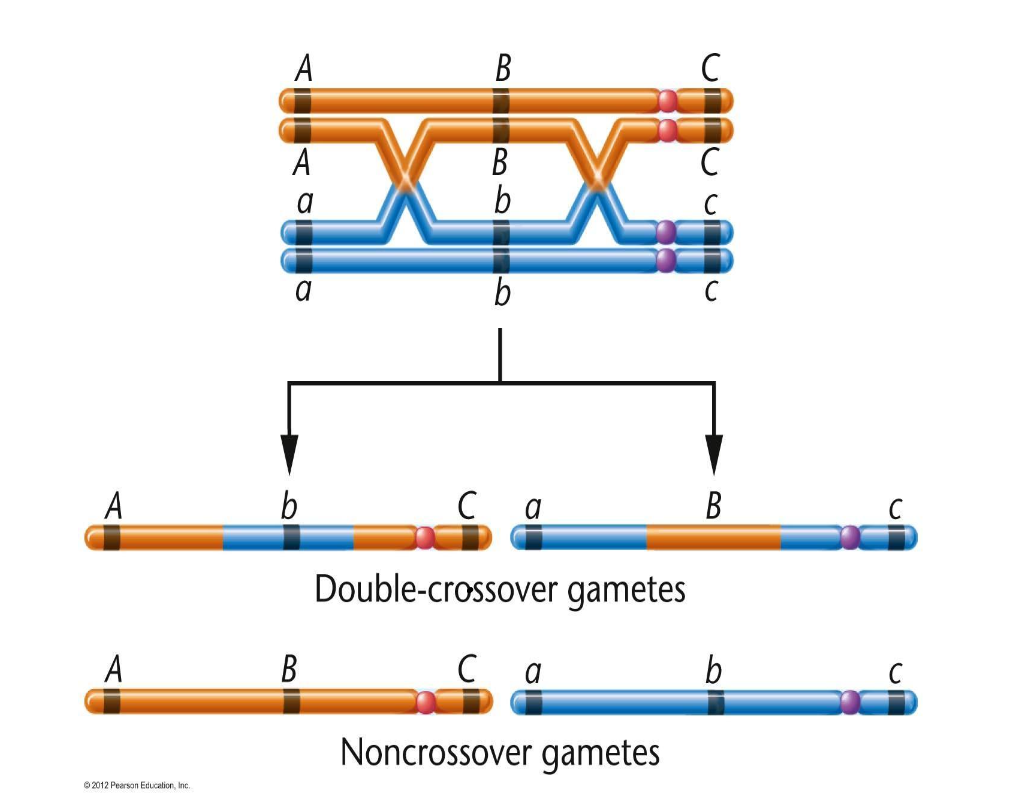
From a three-point test cross…
progeny in the highest abundance = parental
progeny w/ intermediate abundance = single crossover recombinants
progeny in the lowest abundance = double crossover recombinants
Four major steps
determine the order of the genes
reorganize the data table to reflect the gene order
calculate map units for the first two genes
calculate map units for the second two genes