LECTURE 4-CANCER AND CANCER STEM CELLS
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Key concepts from lecture 3 on stem cells
different types of pluripotency
definition of stem cell (what makes a stem cell?)
definition of stem cell niche
adult stem cells
intestinal epithelial stem cell niche
neural stem cell niches
epithelial stem cell niche
hematopoetic stem cell niche (bone marrow)
WNT signaling (yes)
concept of nuclear reprogramming
gurdon’s experiment
key factors used by Yamanaka for induced pluripotency
Yamanaka’s experiment
Overview: Cancer and Cancer Stem cells
1) fundamentals of oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes
2) metastasis requires invasiveness and migration
3) some tumors contain cancer stem cells (CSCs) also called tumor-initiating cells (TICs)
4) Novel aspects of tumorigenesis and metastasis
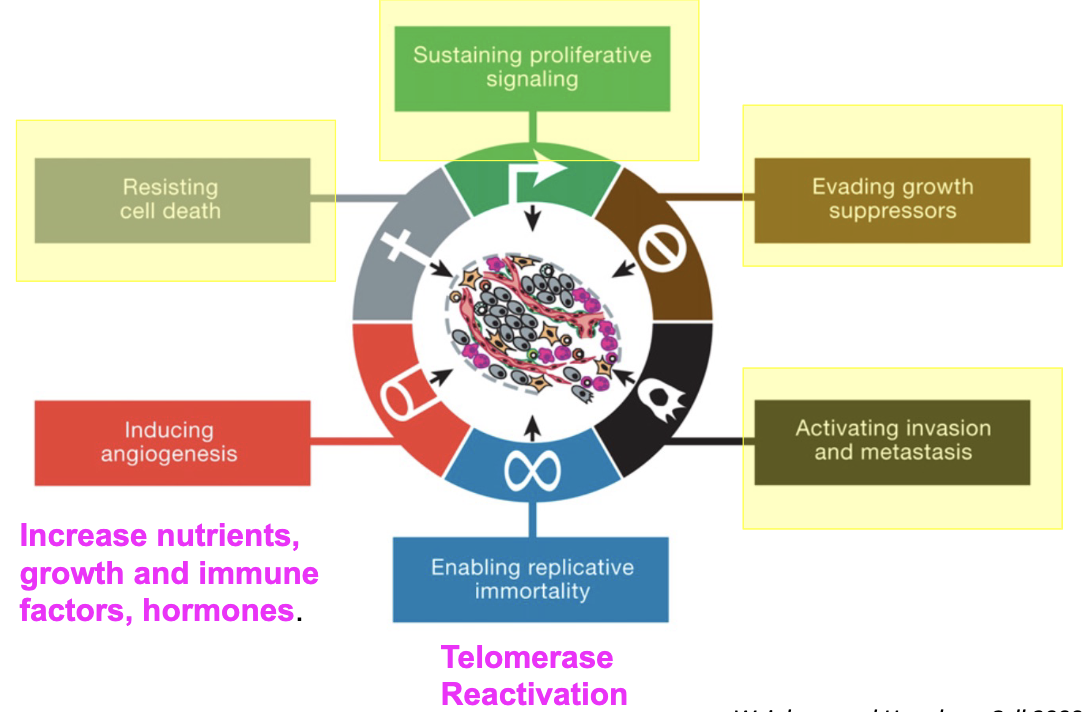
Original Hallmarks of Cancer
telomerase: as the cell divides the telomeres shorten, this enzyme adds protective caps at the ends of chromosomes by adding repetitive DNA sequences
What causes cancer-factors associated with cancer risk?
1) genetic mutations
2) epigenetic dysregulation
3) environmental exposures
4) lifestyle factors
5) viruses
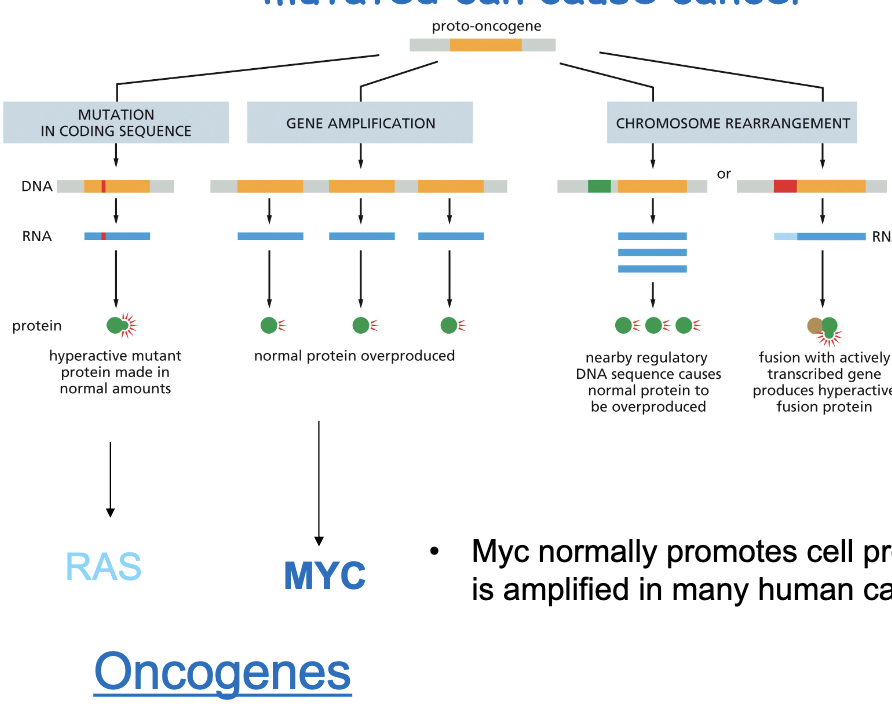
Proto-oncogenes (before alteration, afterwards it is oncogene) normally regulate…
cell growth and proliferation and when mutated can cause cancer
Oncogene examples: MYC and RAS
MYC=normal protein greatly overproduced
RAS=hyperactive protein made in normal amounts
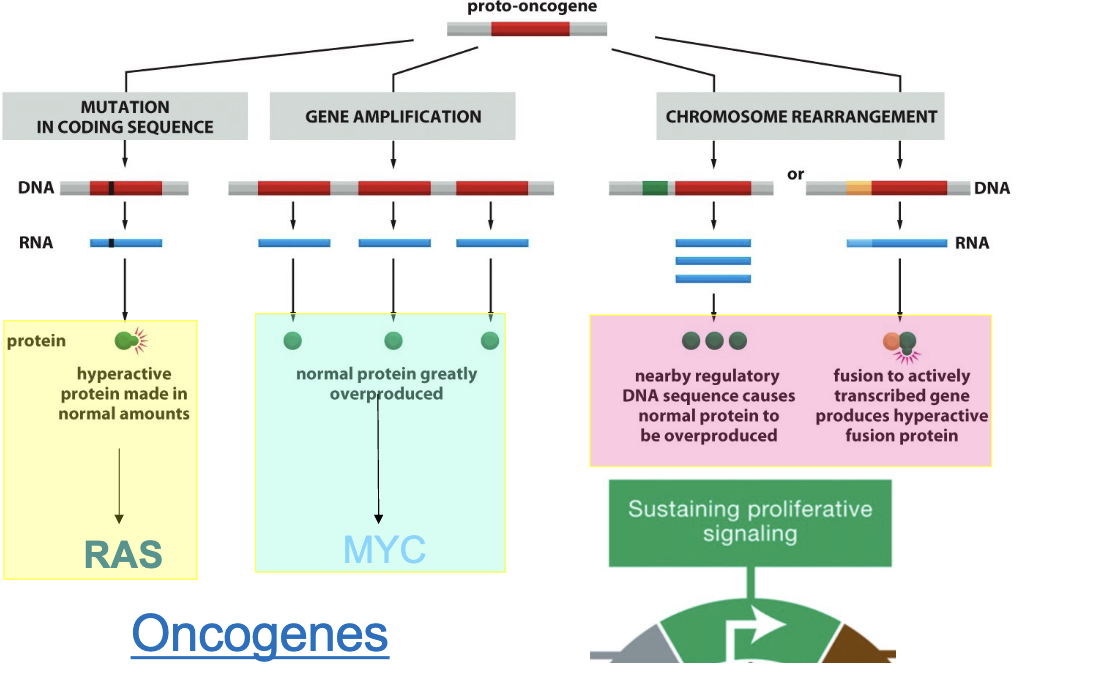
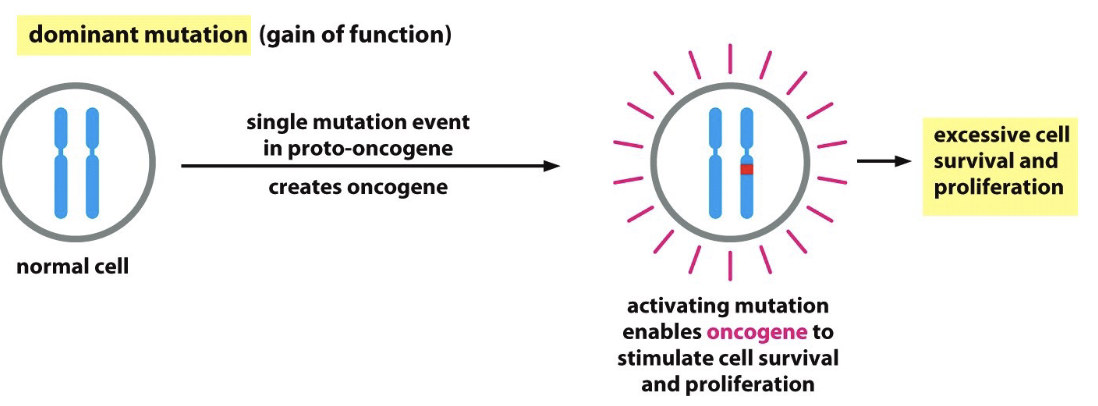
Oncogenes require only…
a single mutation to change function!
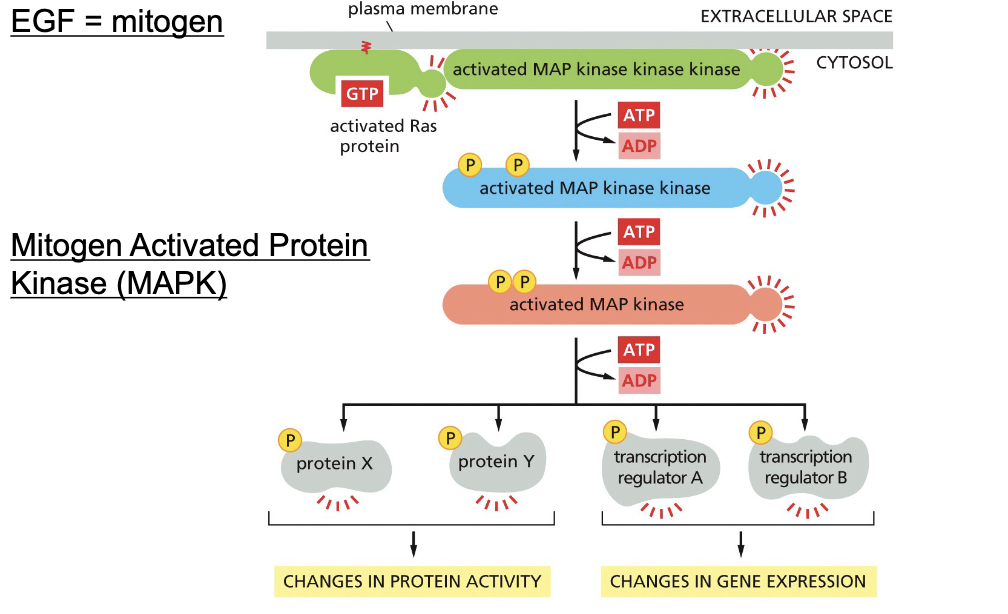
Activated Ras is mutated in…
30% of human cancer
EGF=mitogen
Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK)
single point mutation at G12V in one copy of Ras gives cell selective advantage to proliferate uncontrollably
Proto-oncogenes are genes that when…
mutated can cause cancer
Myc normally promotes cell proliferation but is amplified in many human cancers
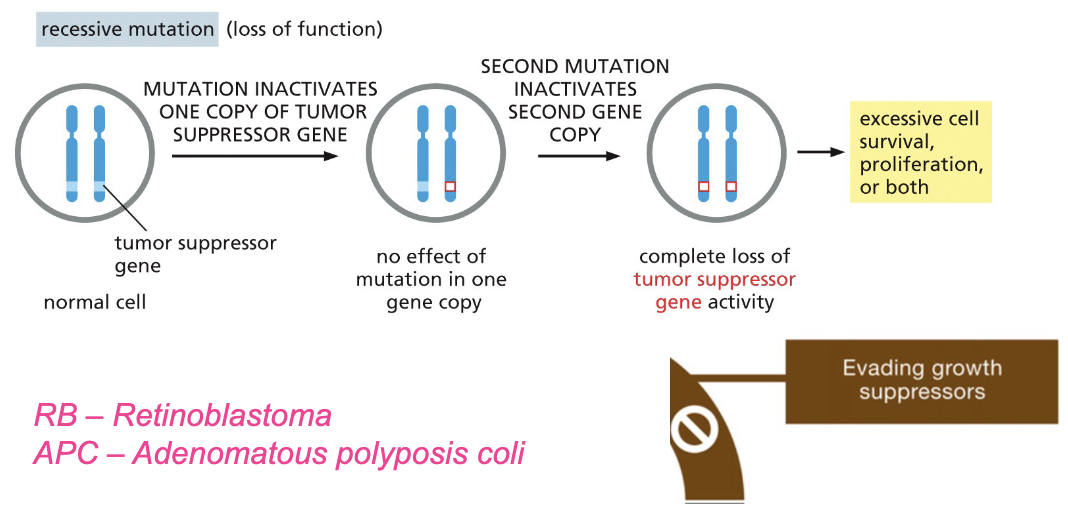
Tumor suppressor genes normally…
negatively regulate cell division
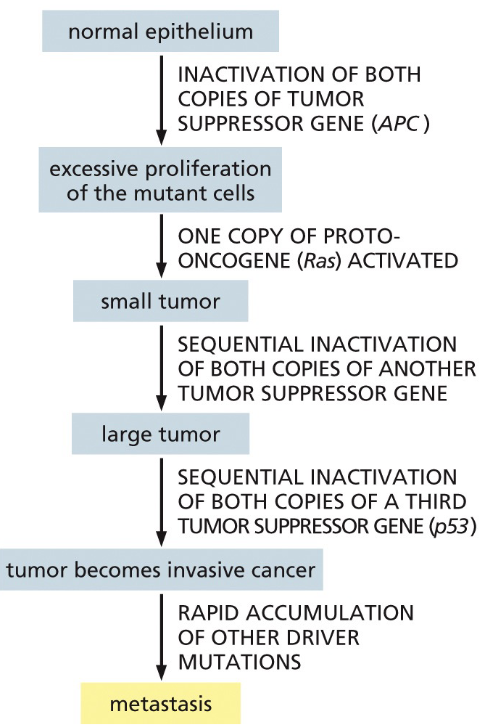
Two hit hypothesis: both copies of a tumor suppressor gene must be inactivated for the efficient tumor growth
tumor suppressor genes—> p53, Rb (retinoblastoma), APC (adenomatous polyposis coli)
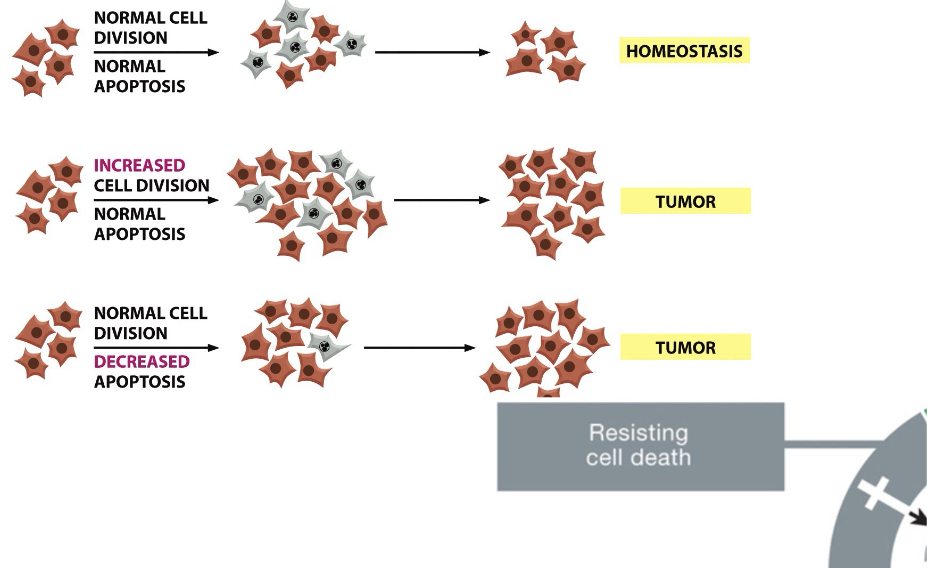
Normal balance between cell division and apoptosis is absent in…
cancer!
or both increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis
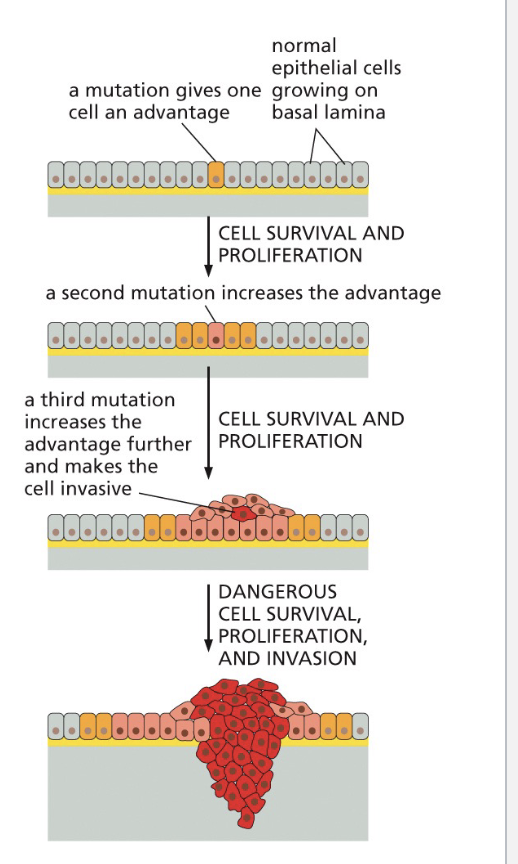
A malignant tumor contains cells with…
multiple mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes
APC=adenomatous polyposis coli
—>familiar colon adenocarcinoma
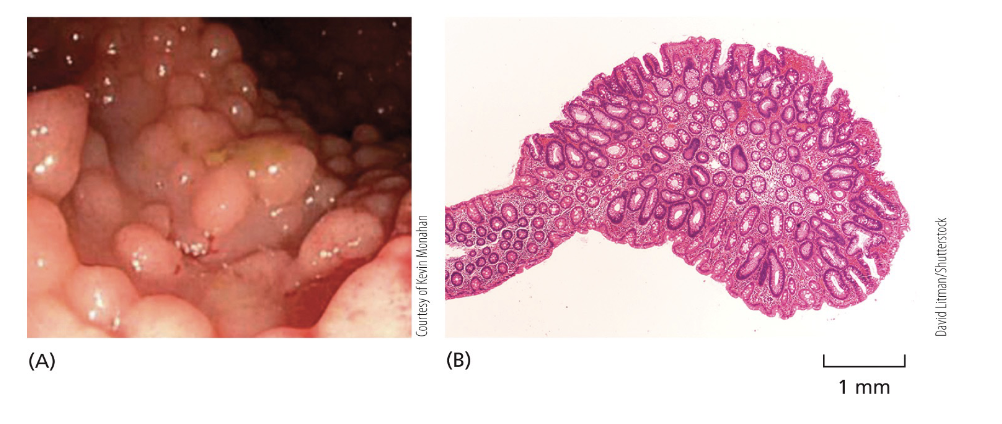
A malignant tumor contains cells with multiple mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes
tumor progression model in colorectal cancer (vogelstein 1990s)
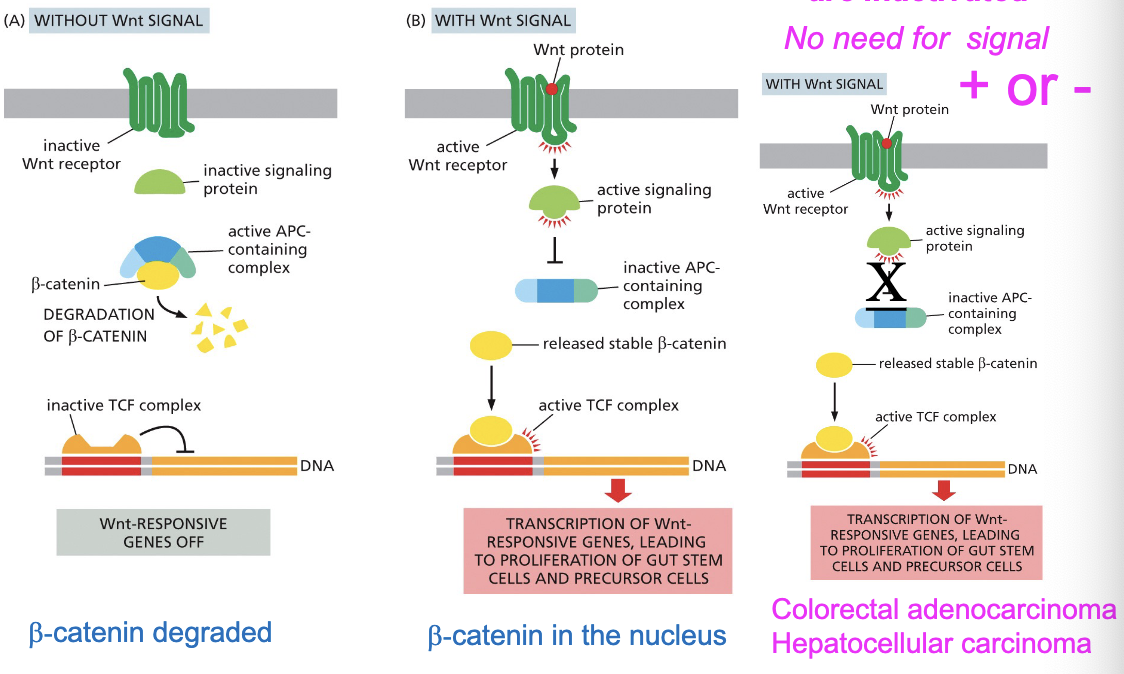
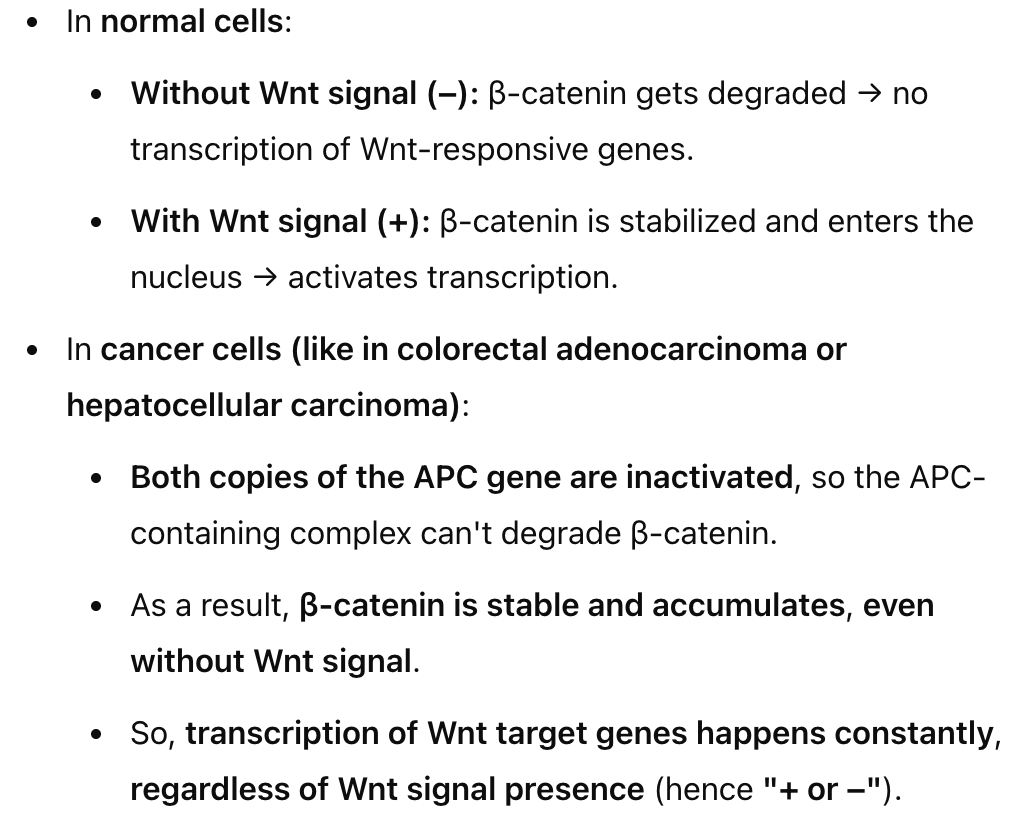
The canonical Wnt signaling pathway is disrupted…
in human cancers
both copies of APC are inactivated-no need for signal + or -
Cancer is not just increased cell survival and proliferation: it also involves…
invasion and metastasis
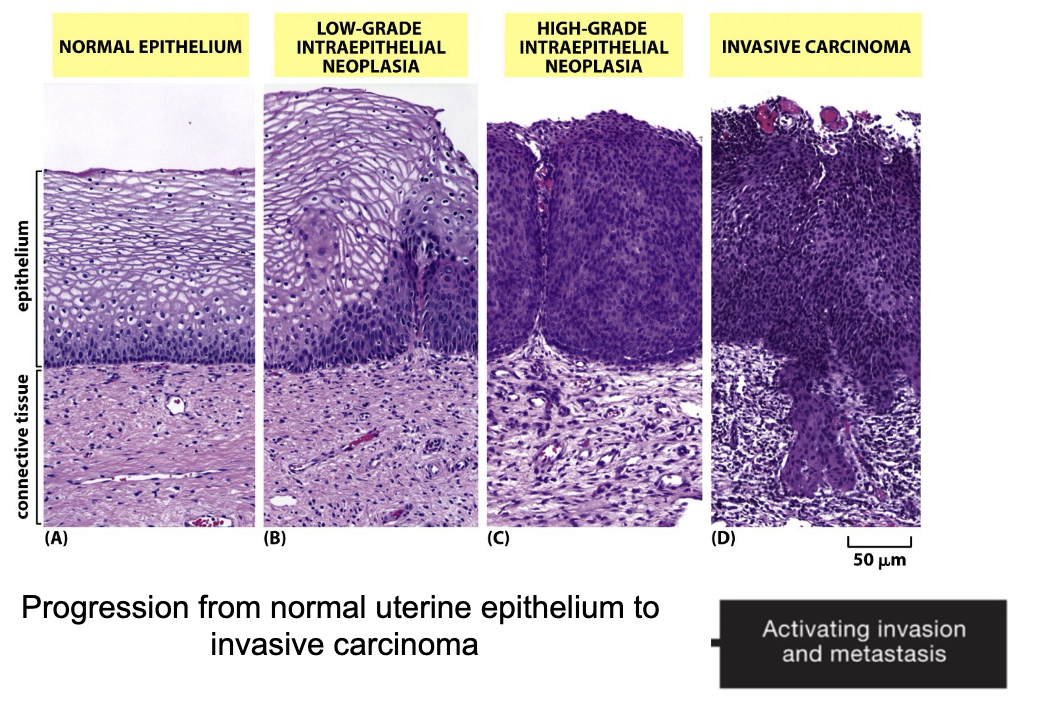
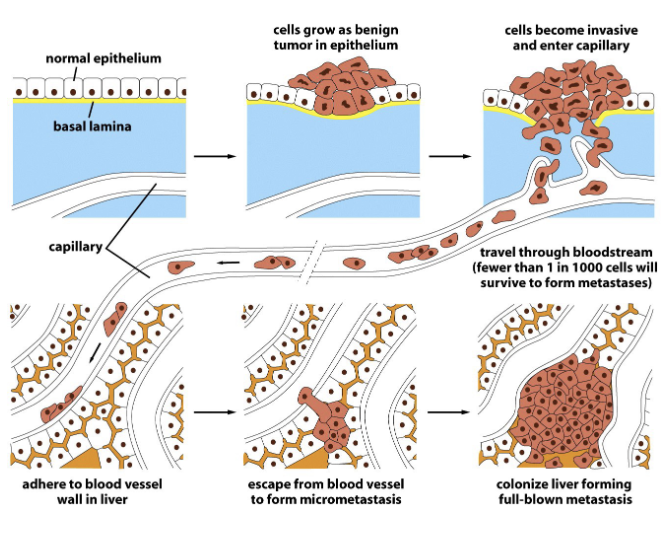
Cancer is not just increased cell survival and proliferation: also involves invasion and metastasis
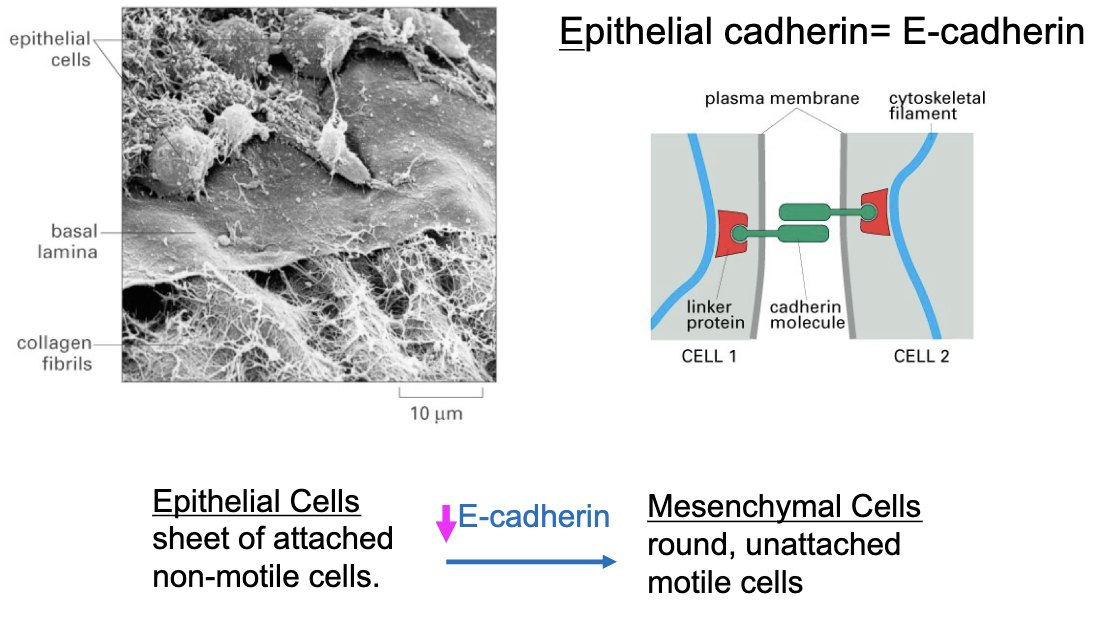
Extracellular Matrix and Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) in animals
Epithelial cadherin=E-cadherin
Metastasis requires…
epithelial cells to invade neighboring tissue, enter blood supply and colonize distant organs
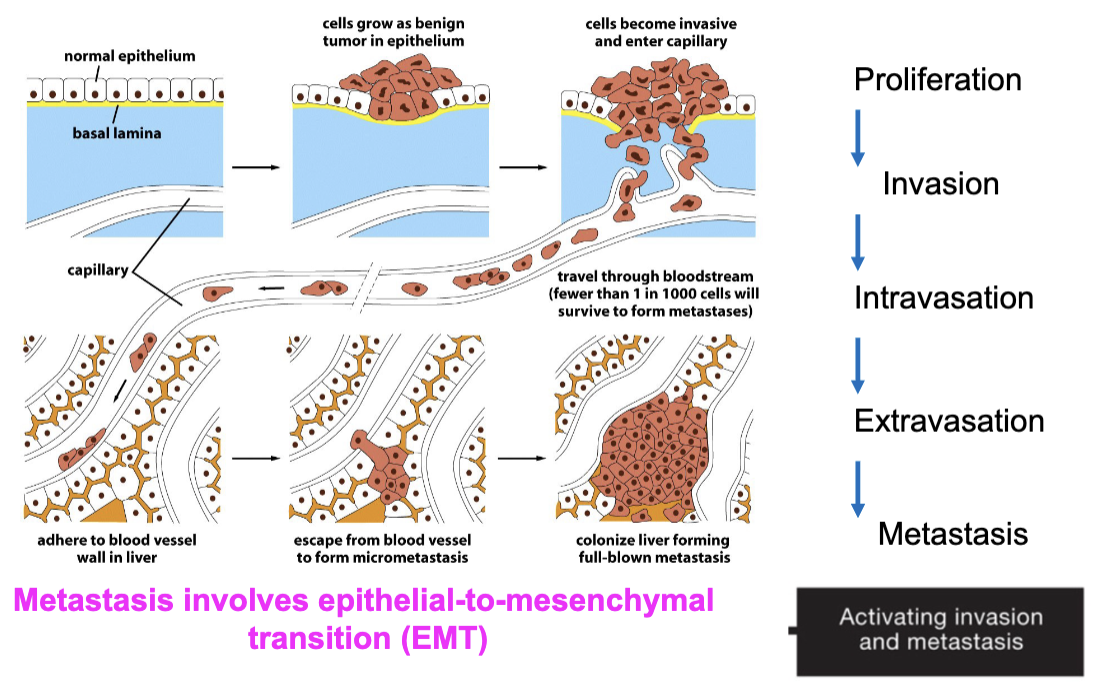
What determines where the metastasized cancer ends up?
Location: breast cancer cells usually go to the lymph nodes because of proximity
Organ environment-bone provides a good environment for prostate cancer cells
Priming: signals send from the primary tumor could start to create a favorable microenvironment for cancer cells to colonize an organ/tissue
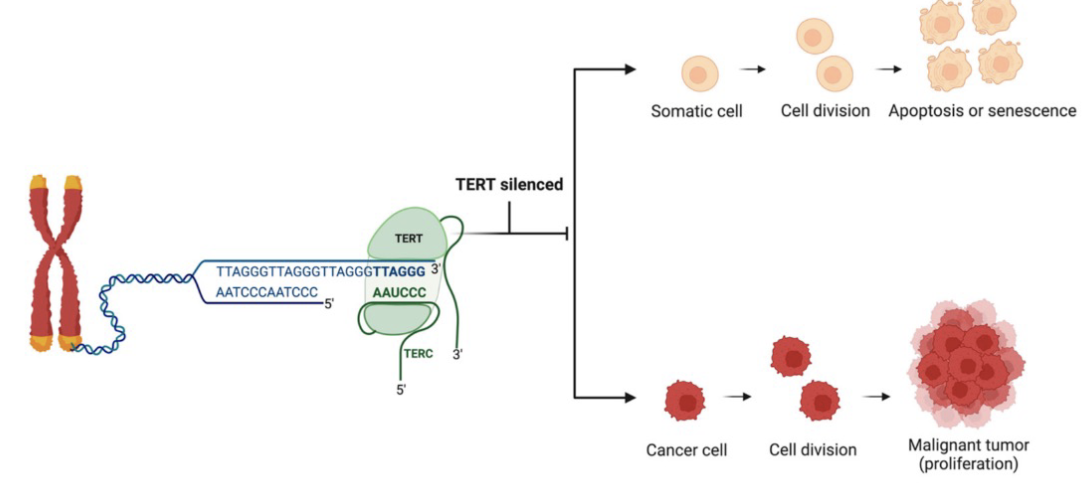
Telomerase Reactivation and cancer cell immortality
Telomerase: TERT(will become suppressed) subunit acts as a reverse transcriptase, TERC subunit provides template for telomere extension
Healthy somatic cells: Telomeres shorten with each cell division and TERT is suppressed to prevent unchecked cell division leading to cell death senescence
Cancer cells: Telomerase reactivates allows for continuous cell division that accumulates mutations by unchecked DNA damage repair of chromosomal abnormalities
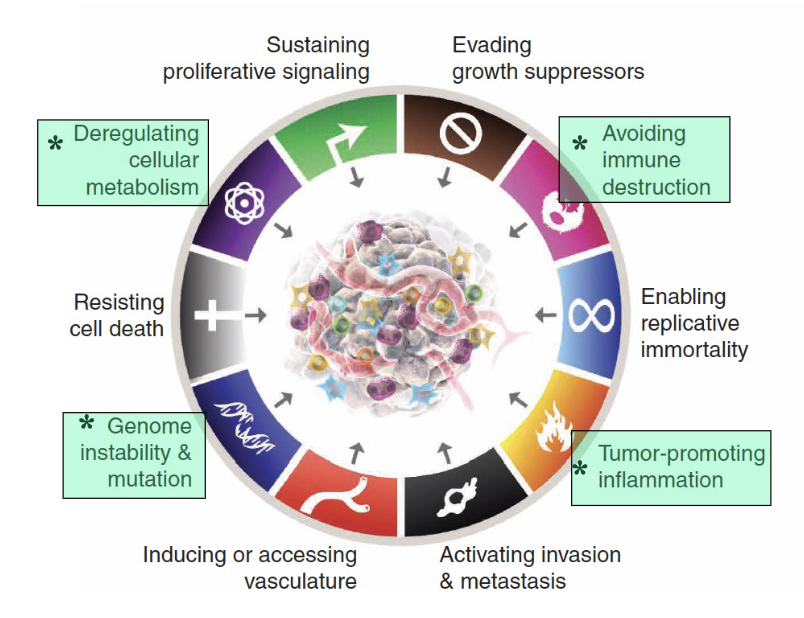
What are the newer hallmarks of cancer cells?
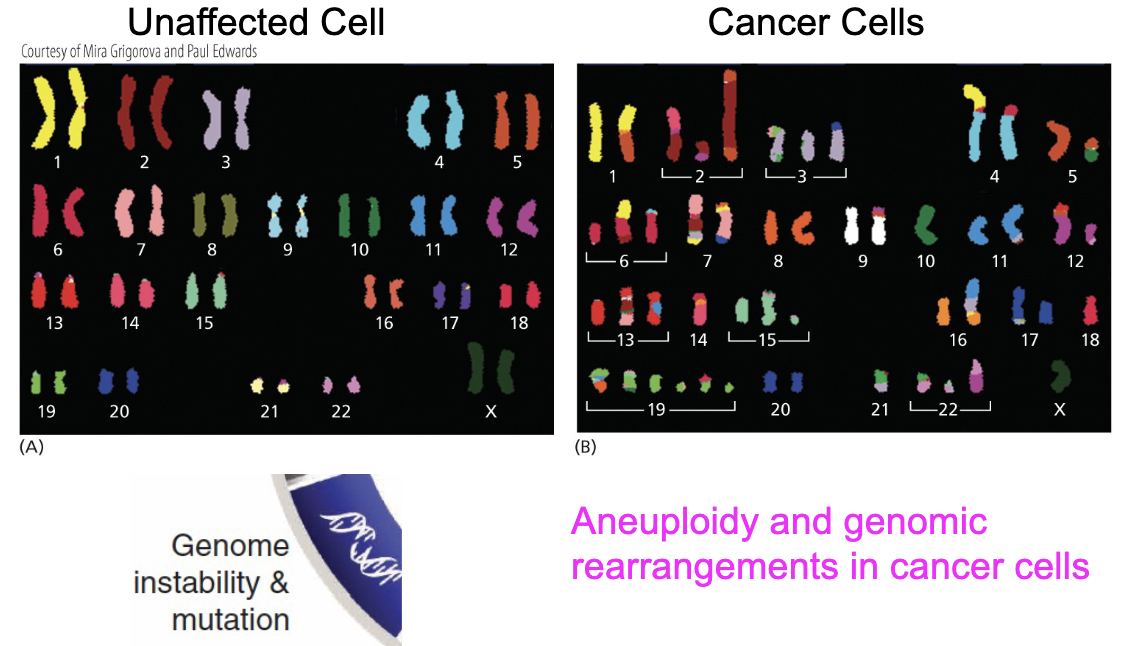
Genomic instability…
aneuploidy and translocations are hallmarks of cancer cells
Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Stem Cell (CSC) hypothesis?
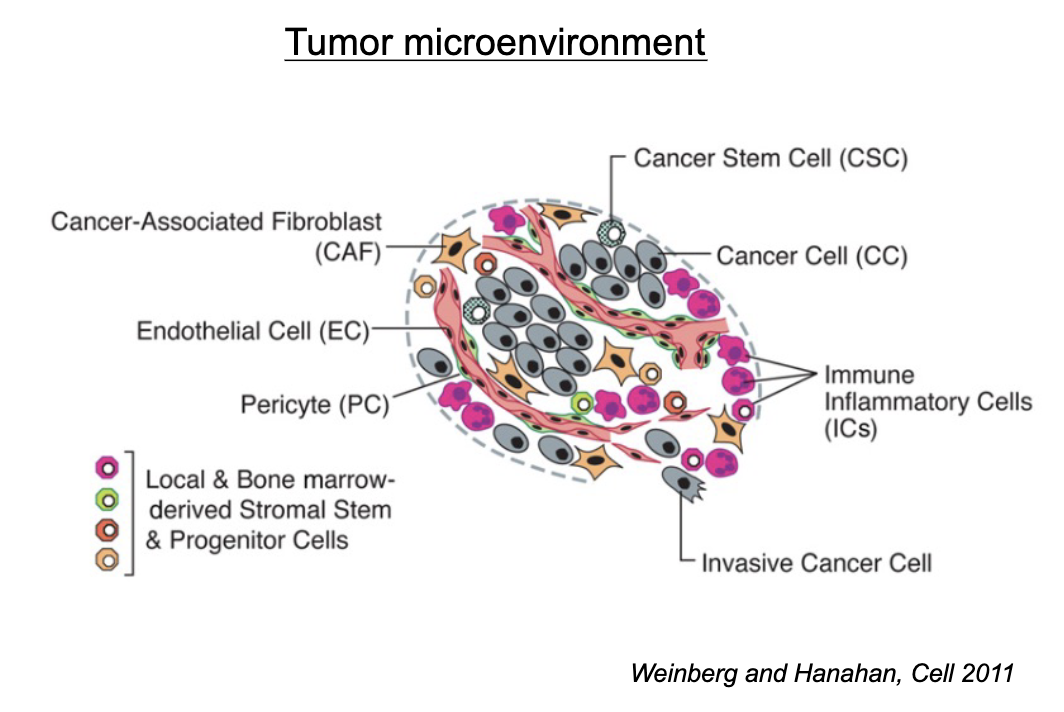
tumor microenvironment
GBM stem cells are …
resistant to therapies
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM)
highly aggressive brain tumor
median survival ~15 months
US incidence 2-3/100,000 individuals
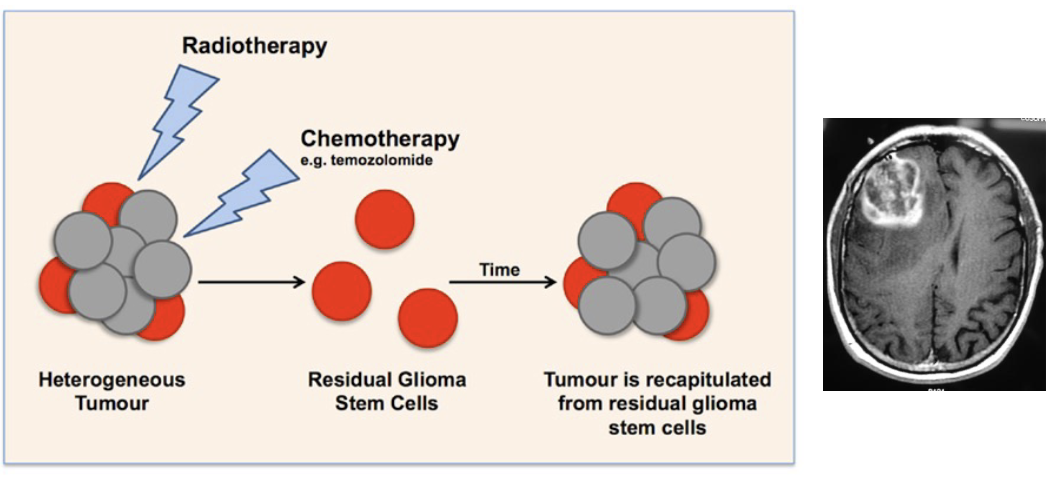
How can cancer stem cells be eliminated?
current cancer therapies use anti-proliferative drugs or radiation
cancer stem cells:
may not be dividing (quiescent)—>can kill neurons so need a precise delivery approach as neurons are also non-dividing
can have increased levels of drug efflux pumps
maintain high capacity to repair DNA
may be highly resistant to stress
How can cancer stem cells be eliminated?
potential therapeutic strategies to target cancer stem cells:
develop drugs to target non-dividing cells
awaken quiescent cancer stem cells, then eliminate them
induce differentiation of cancer stem cells
Hallmarks of cancer cells: circa 2022
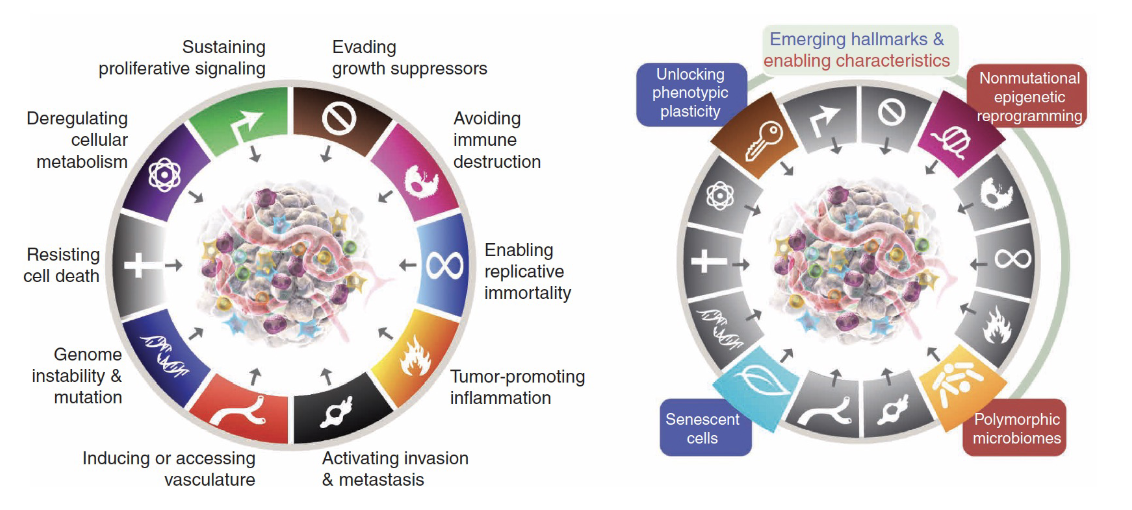
Latest hallmarks of cancer cells: unlocking phenotypic plasticity
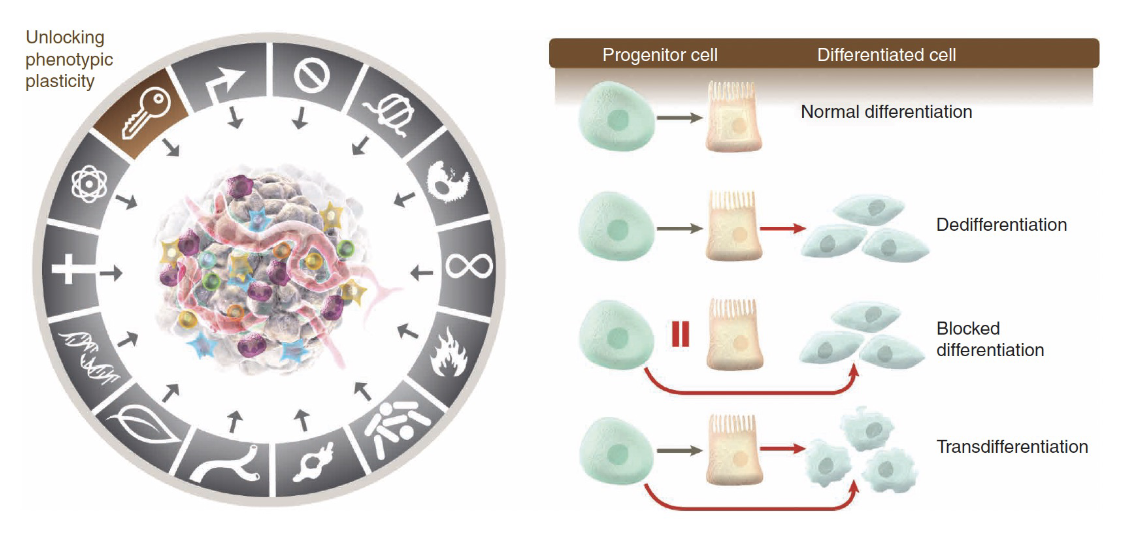
Latest hallmarks of cancer cells; non-mutational epigenetic reprogramming
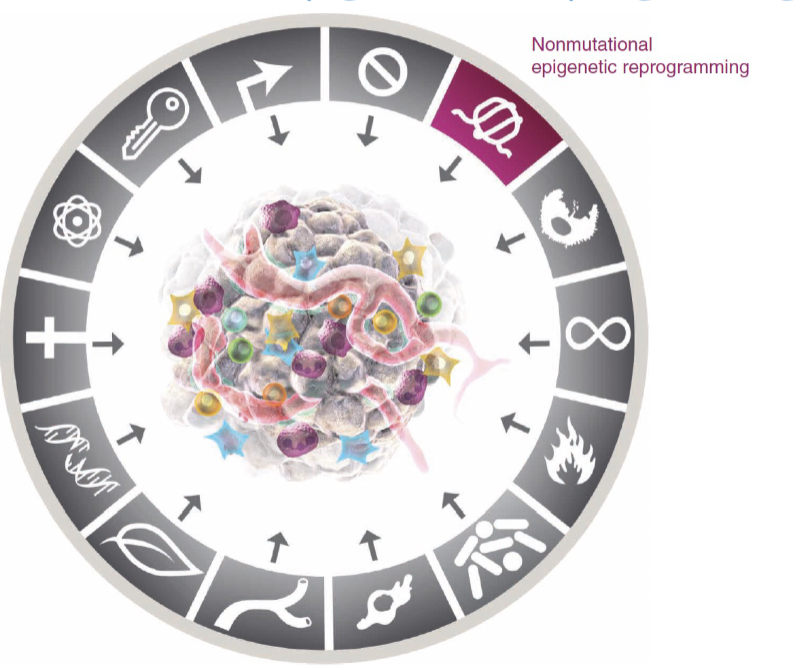
Latest hallmarks of cancer cells: non-mutational epigenetic reprogramming
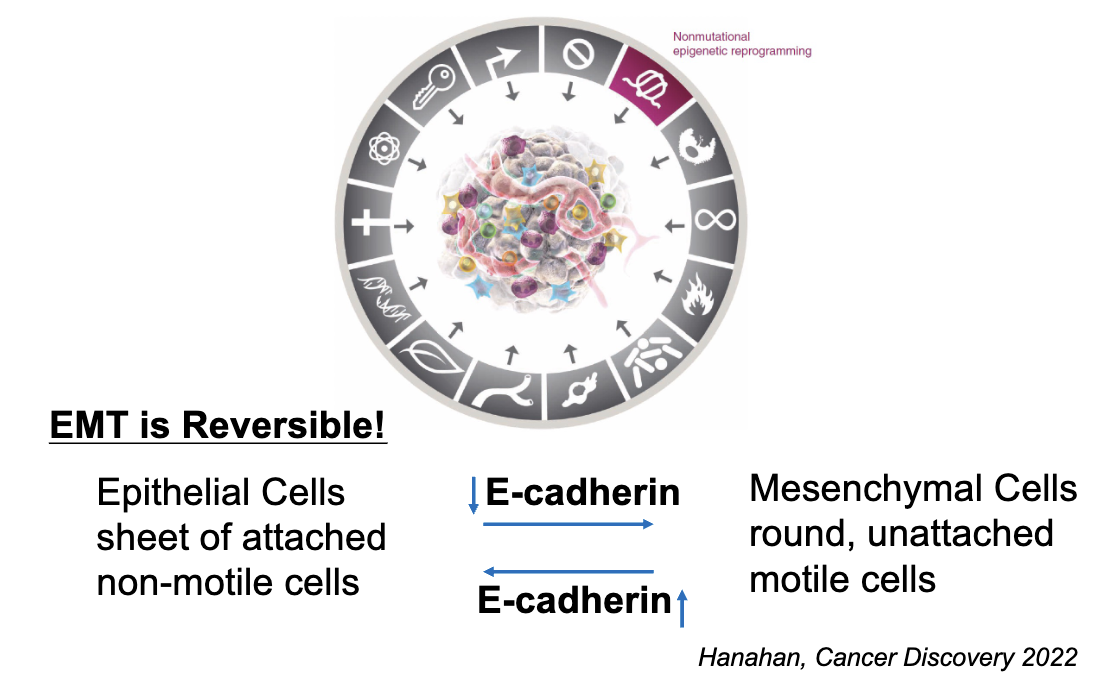
E-cadherin can go back in forth from the epithelial and mesenchymal cells—> inhibits cancer progression as it is a transmembrane glycoprotein
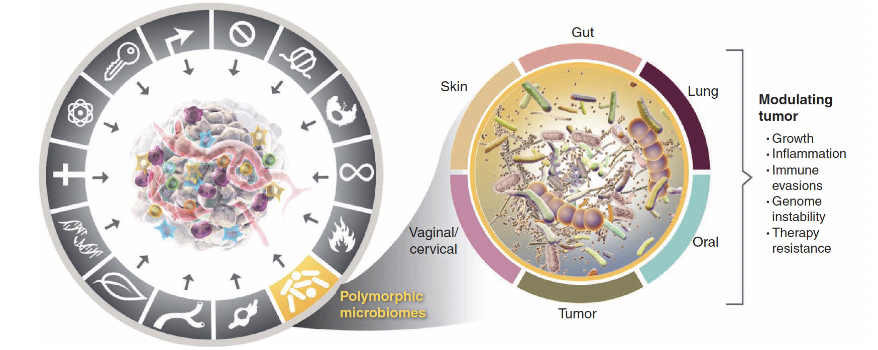
Latest hallmarks of cancer cells: Polymorphic microbiomes #1
colon cancer: cancer protective and tumor promoting microbiomes
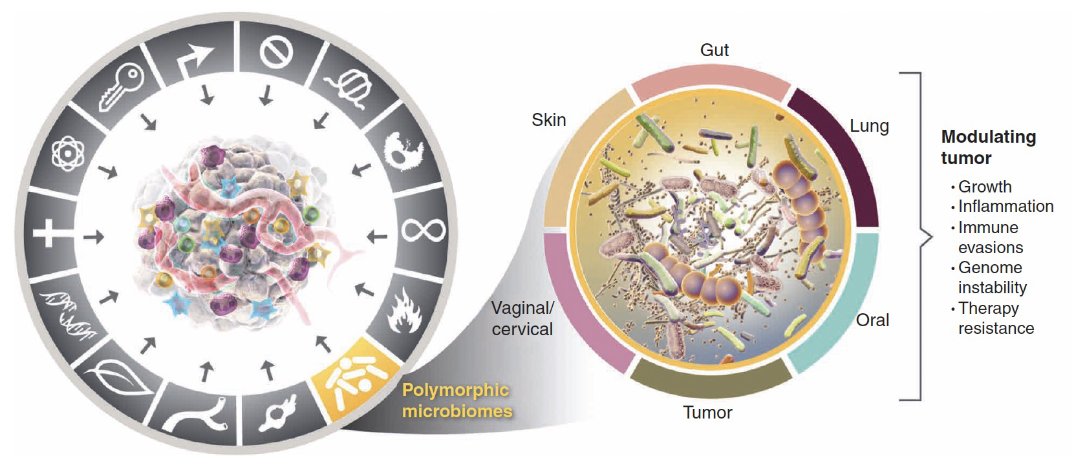
Latest hallmarks of cancer cells: Polymorphic microbiomes #2
microbes could promote DNA damage or chronic inflammation
unrepaired DNA damage could lead to mutations
inflammation could alter tumor microenvironment promoting tumor growth or metastasis
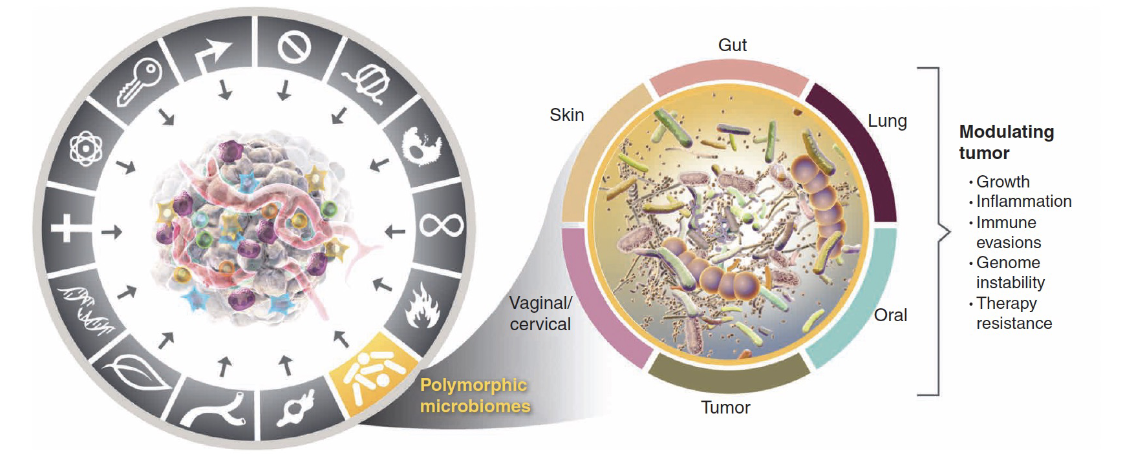
Latest hallmarks of cancer cells: Polymorphic microbiomes #3
Fecal microbiata transplant overcomes resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in melanoma patients
instance where microbes can be beneficial
Current therapeutic approaches to cancer
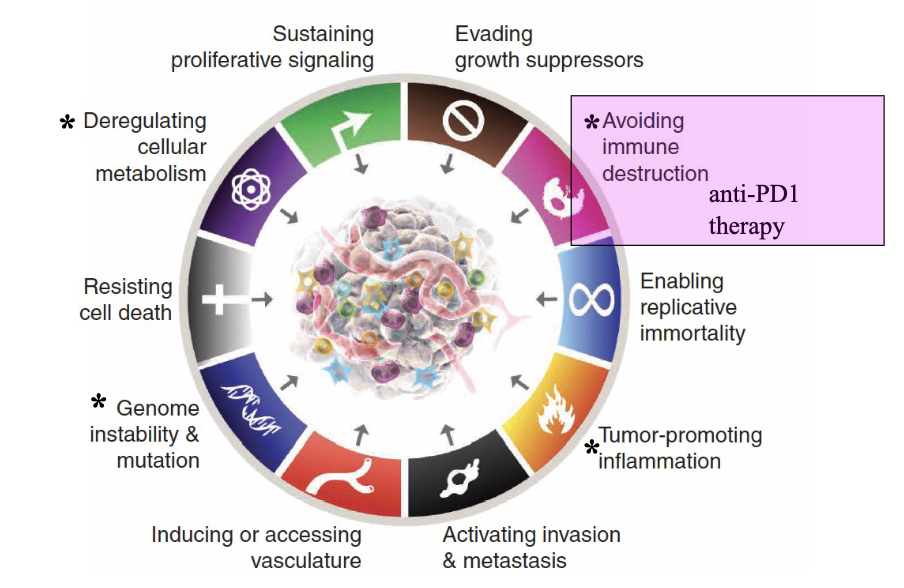
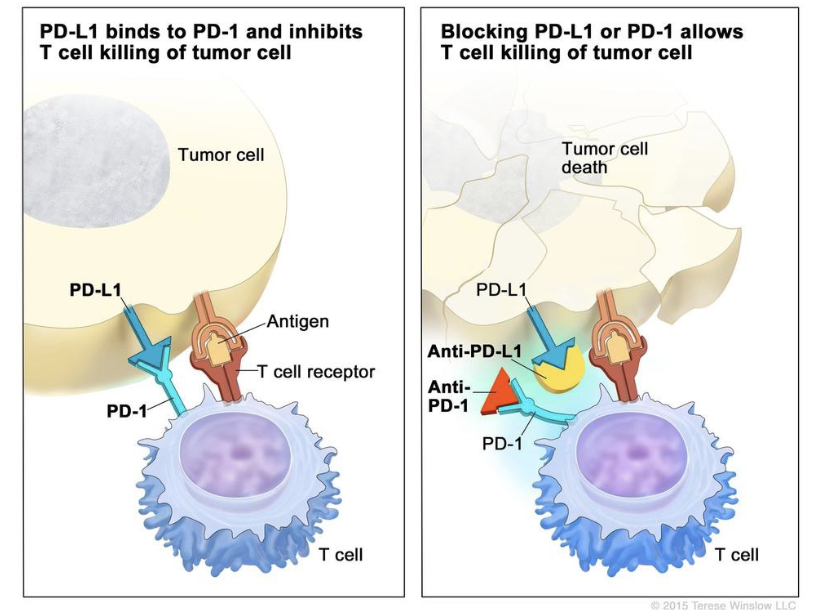
Anti-PD1 Therapy
PD-1 programmed cell death protein 1-found on T cells
PD-1 acts as an inhibitory checkpoint preventing T cells from attacking other cells