Biology definitions
1/70
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
biosphere
The regions of the earth that encompasses all living organisms: plants, animals and bacteria.
Topography
the study of the physical features of an area, including its landforms, elevation, and the arrangement of biological and geological components.
Biomes
an area of the planet that can be classified according to the plants and animals that live in it.
Ecosystem
a geographic area where living and nonliving things interact
Ecology
the study of how living things interact with each other and their environment.
Biotic
living or once living components of a community
Abiotic
the physical and chemical non-living components of an environment.
Community
a group or association of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area at the same time.
Environment
the place where organisms live or occupy
Habitat
the natural home or environment of a plant, animal, or other organism.
Population
a group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area and can reproduce with each other.
Predators
organisms that hunt and kill other organisms for food.
Parasites
an organism that lives on or in a host organism and gets its food from or at the expense of its host.
Terrestrial environments
land-based ecosystem, or community of organisms
Climate
the atmospheric weather of an area, measured and averaged over a long period of time
Biodiversity
the variety of life on Earth, including the different plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as their genes and ecosystems.
Humus
dark, organic material that forms in soil when plant and animal matter decays
Limiting factor
anything that constrains a population's size and slows or stops it from growing.
Substrate
a supporting surface on which an organism such as a plant grows
Aquatic environments
the habitat for water-dependent living species including animals, plants, and microbes.
Photonic zone
the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis.
Dominant species
a species that is the most abundant or has the highest biomass in an ecosystem
binomial nomenclature
a two-part name system that identifies an organisms genus and species
Carl Linnaeus
zoologist that developed the binomial naming system for organisms
Classification keys
tools used by scientists to identify organisms that belong to species that have already been discovered.
dichotomous key
a tool used to identify organisms and objects based on their observable characteristics
competitive exclusion principle
the theory that no two species can occupy the same ecological niche for an extended period of time
Heterotroph (consumers)
An organism that cannot synthesise its own organic compounds from simple inorganic materials; it depends on other organisms for nutrients and energy requirements
Autotroph (producers)
organisms that are able to make their own food from raw materials and energy
Keystone species
a species of relatively low abundance that has a disproportionately large influence over lower trophic levels, determining the coexistence of these species in an area.
trophic level
the position an organism occupies in a food web
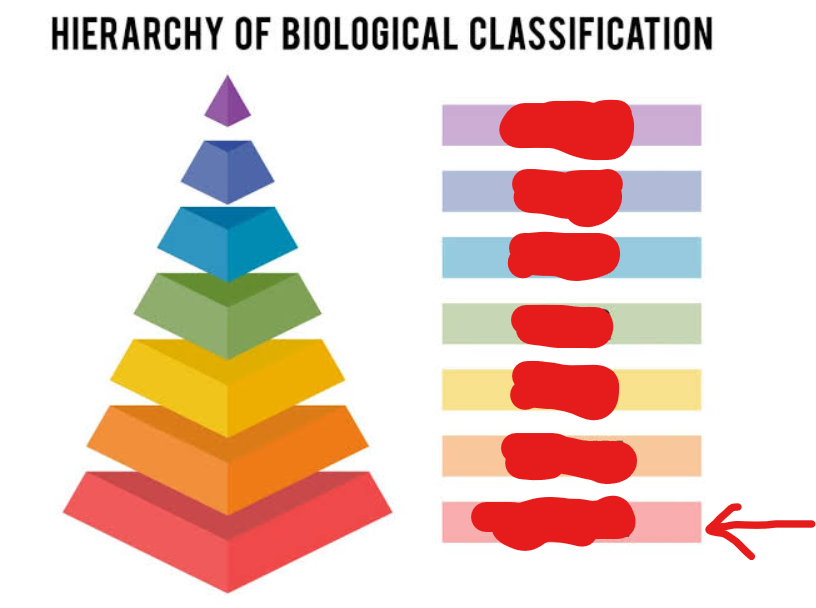
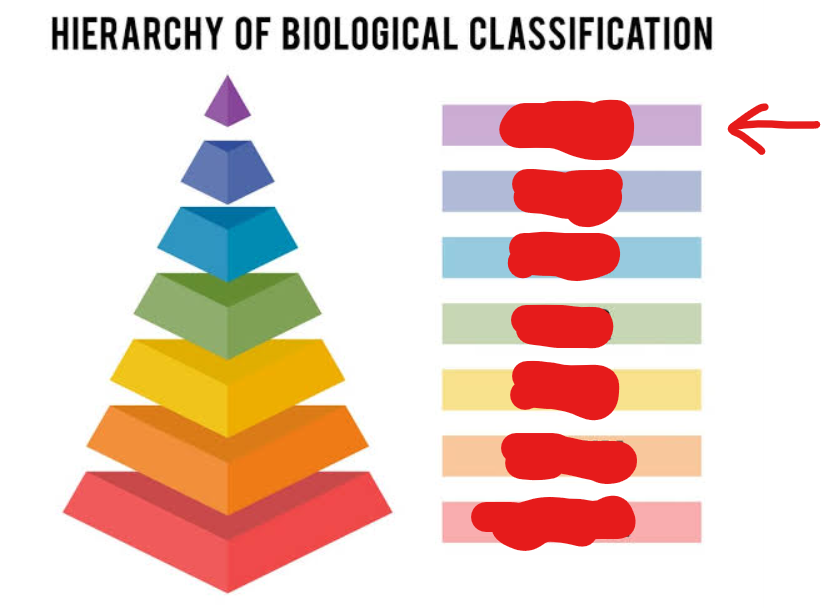
kingdom
1st tier (general → specific)
phylum
2nd tier (general → specific)
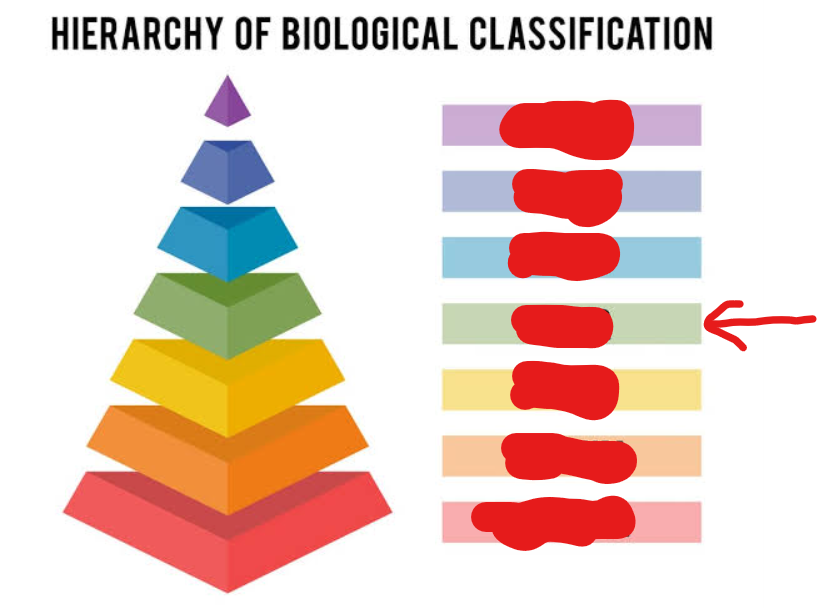
class
3rd tier (general → specific)
order
4th tier (general → specific)
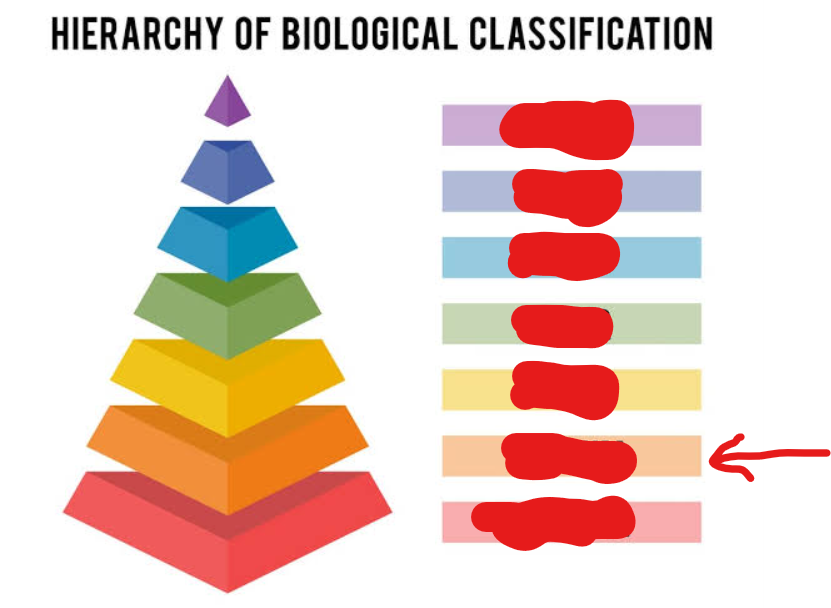
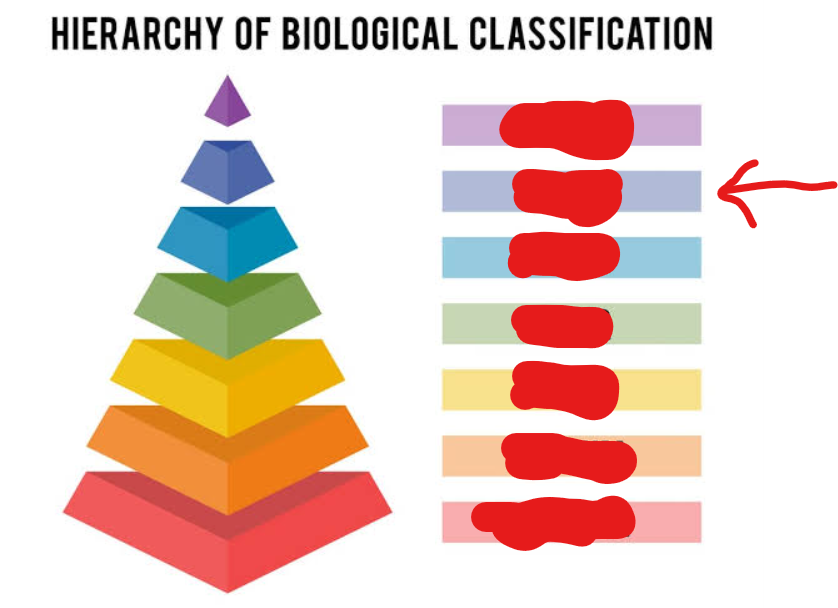
family
5th tier (general → specific)
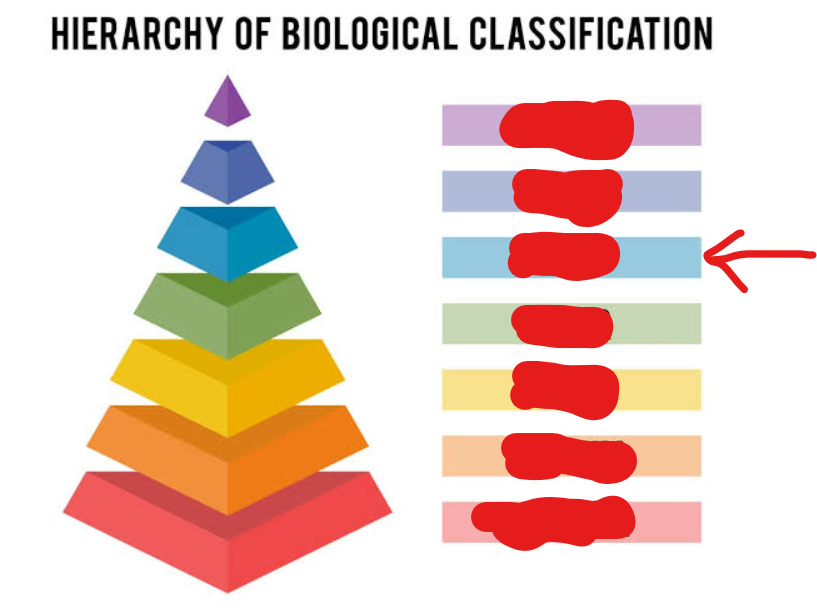
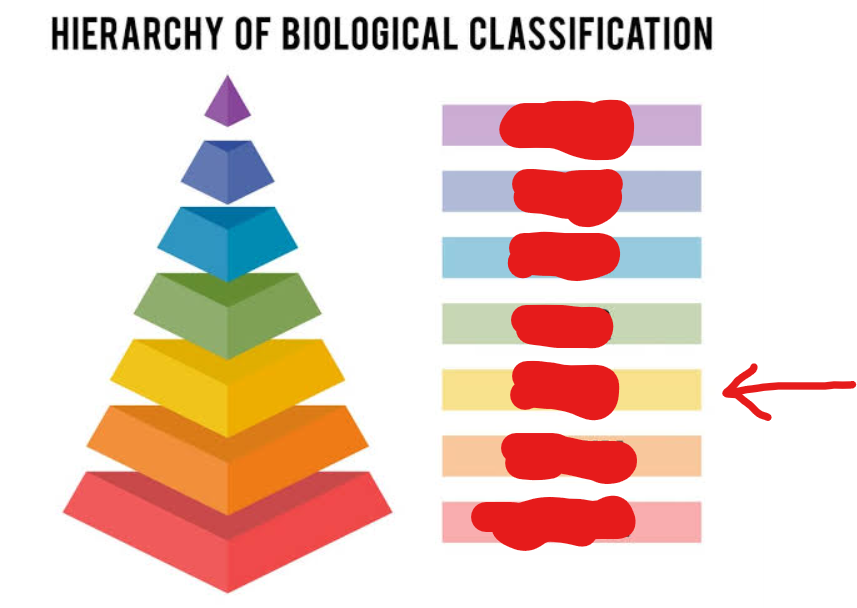
genus
6th tier (general → specific)
species
7th tier (general → specific)
food web
all of the food chains in a single ecosystem
food chain
a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another
carnivore
an organism that eats mostly meat, or the flesh of animals
omnivore
an organism that eats plants and animals
herbivore
an organism that eats plants
decomposer
an organism that breaks down dead or decaying organisms and waste
niche
the match of a species to a specific environmental condition
species diversity
the number of species and abundance of each species that live in a particular location.
fundamental niche
the full range of environmental conditions (abiotic and biotic) an organism could potentially occupy and survive in, without the influence of other species.
edge effect
the change in population or community structure that happens at the boundary of two or more habitats.
phylogenetic trees
a diagram that depicts the lines of evolutionary descent of different species, organisms, or genes from a common ancestor.
salinity
the concentration of dissolved salts in water, particularly in aquatic ecosystems.
pyramid of biomass
a graphical representation that illustrates the total mass of living organisms at each trophic level in a food chain or food web.
invasive species
organisms that cause ecological, economic, or environmental harm in a new environment where they are not native.
how are invasive species introduced to an environment
human activity
biomagnification
the process by which a contaminant accumulates in the tissues of organisms at higher trophic levels in a food chain, becoming increasingly concentrated as it moves up the chain.
eutrophication
the excessive enrichment of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus in a water body, leading to an overgrowth of algae and other aquatic plants, which can deplete oxygen levels and disrupt the entire ecosystem.
secondary succession
an area that was previously occupied by living things is disturbed, then re-colonized following the disturbance.
primary succession
newly exposed or newly formed rock is colonized by living things for the first time.
commensalism
where one species benefits while the other is unaffected in a relationship
mutualism
both species benefit in a relationship
parasitism
one species benefits while one is harmed in a relationship
competition
neither species benefits in a relationship
predation
one species benefits while the other dies in a relationship
neutralism
both species are unaffected in a relationship
symbiosis
describes a close interaction or relationship between two different species. It is a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms
prokaryotic
cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane, but they have no internal membrane-bound organelles within their cytoplasm.
eukaryotic cell
cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms.
unicellular
consisting of a singular cell
multicellular
consisting of multiple cells
realized niche
the actual portion of the fundamental niche that an organism occupies due to biotic and abiotic factors, especially competition and other species interactions.