ANAPHY: U7.2 Nervous System (Peripheral Nervous System)
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
31 Pairs
How many pairs of spinal nerves originate from the spinal cord?
Through roots
How is the spinal nerve connected to the spinal cord?
Posterior/Dorsal/Sensory Root & Anterior/Ventral/Motor Root
2 Types of Roots that Connect the Spinal Nerve to the Spinal Cord
Posterior/Dorsal/Sensory Root
Type of root that contains sensory nerve fibers which conducts the nerve impulses from periphery to the spinal cord
Anterior/Ventral/Motor Root
Type of root that contains motor nerve fibers conducting the nerve impulses from spinal cord to the periphery
Cervical nerves: 8 pairs
Thoracic nerves: 12 pairs
Lumbar nerves: 5 pairs
Sacral nerves: 5 pairs
Coccygeal nerve: 1 pair
Division of the 31 pairs of spinal nerves
L1-L2, the conus medullaris
What region does the spinal cord end in?
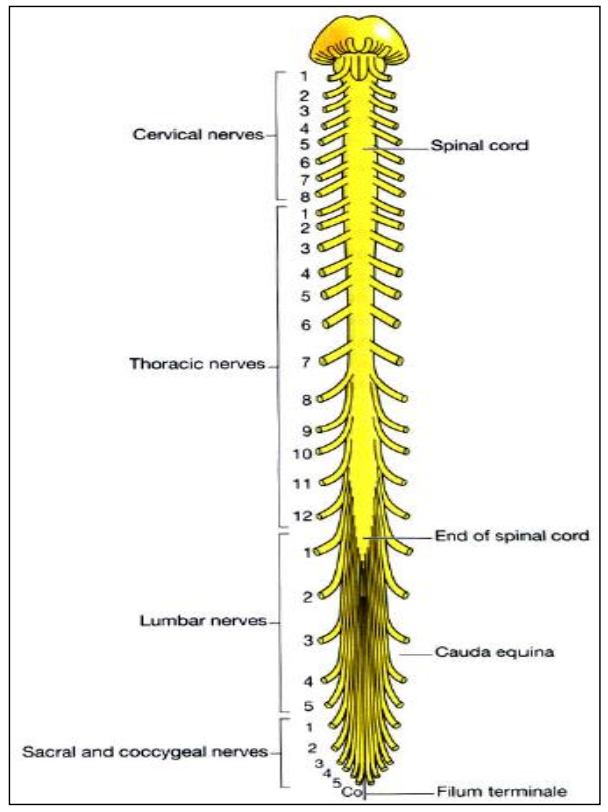
Cauda equina
What is the horse tail-like region after the region the spinal cord ends in?
Filum terminale
Part of the spinal cord that extends from the conus medullaris to the periosteum of the coccyx
grey matter; white matter
The Spinal Cord has ____ ____ in the center and ___ ___ surrounding it.
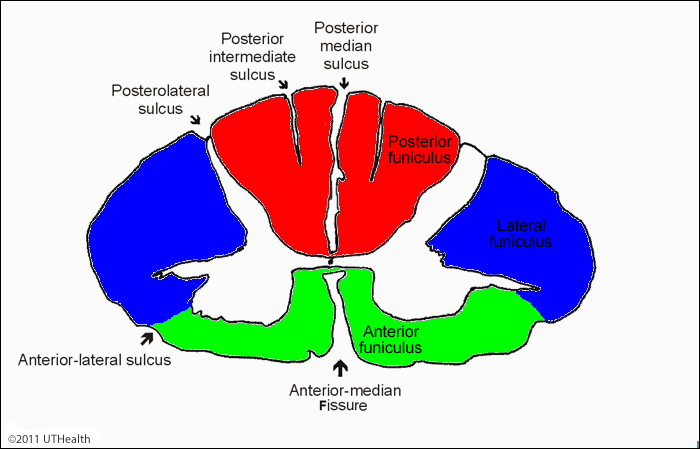
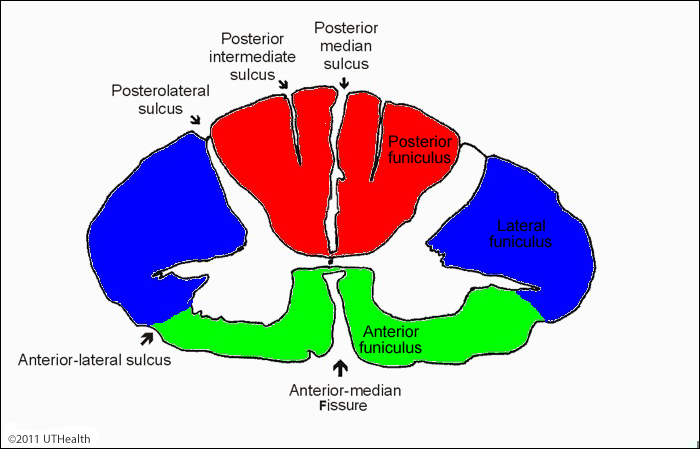
Grooves; right; left
___ penetrate the white matter of the spinal cord dividing it into ___ and ___ sides
Anterior Median Fissure
Internal anatomy of the spinal cord; deep groove on the anterior side
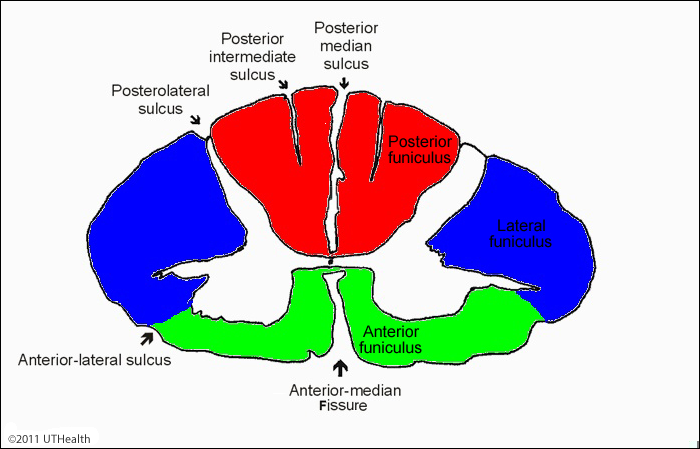
Posterior Median Sulcus
Internal anatomy of the spinal cord; shallower groove on posterior side
letter “H”; butterfly
Internal anatomy of the spinal cord; The grey matter of spinal cord is shaped like ___ ___ or ___ & is surrounded by white matter.
Central Canal
Internal anatomy of the spinal cord; The space that is the center of grey matter
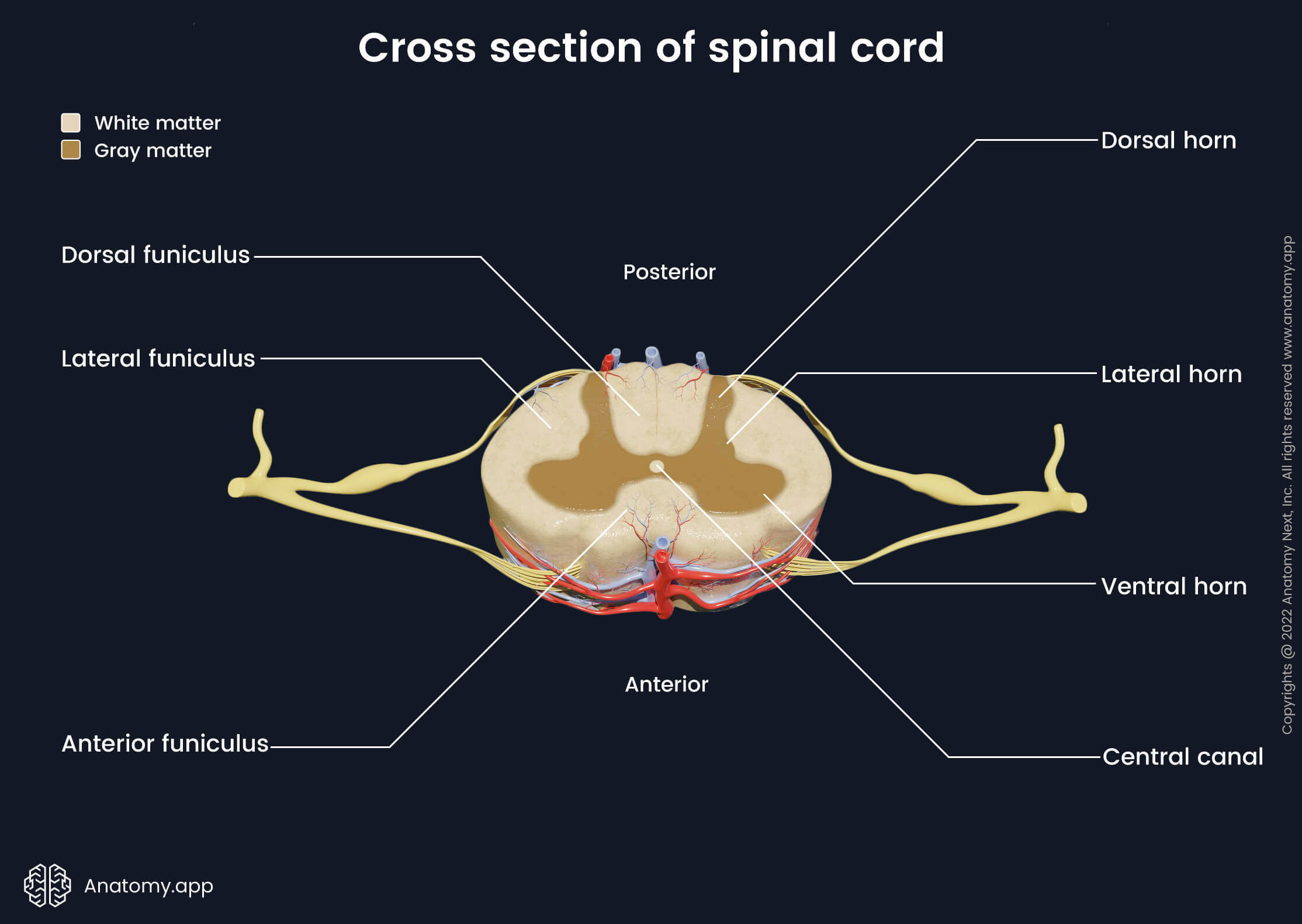
Dendrites, Cell Bodies of Neurons, Unmyelinated Neurons & Neuroglia
Internal anatomy of the spinal cord; What is grey matter in the spinal cord consisted of?
Bundles of Myelinated Axons of Neurons
Internal anatomy of the spinal cord; What is white matter in the spinal cord consisted of?
Horns
Internal anatomy of the spinal cord; The grey matter on each side of the spinal cord is divided into regions called as ___
Anterior/Ventral Horns & Posterior/Dorsal Horns
Internal anatomy of the spinal cord; 2 Types of Horns
columns
Internal anatomy of the spinal cord; The anterior & posterior grey horns divide the white matter on each side into parts called as ____
Anterior/Ventral White Columns, Posterior/Dorsal White Columns, Lateral White Columns
3 Types of Columns in the Spinal Cord
nerves; ganglia
The PNS consists of the ___ and ___ outside the central nervous system
Nerve
Bundle of neuron fibers bundled by connective tissue
Mixed nerves, Afferent (sensory) nerves, efferent (motor) nerves
3 Ways to Classify Nerves in the Peripheral Nervous System
Mixed nerves
Type of nerve in the PNS that includes both sensory and motor fibers
Afferent/Sensory Nerves
Type of nerve in the PNS that carry impulses toward the CNS
Efferent/Motor Nerves
Type of nerve in the PNS that carry impulses away the CNS
12 pairs
How many pairs of cranial nerves originating from the nuclei are present in the brain?
True
True or False: The cranial nerves are sensory, motor or mixed.
False
True or False: The cranial nerves are sensory or motor, not mixed.
Oh, Oh, Oh, To Touch And Feel Very Good Velvet Ah Heaven
Mnemonic to Remember 12 Pairs of Cranial Nerves
Olfactory (I), Optic (II), Oculomotor (III), Trochlear (IV), Trigeminal (V), Abducent (VI), Facial (VII), Vestibulocochlear (auditory (VIII), Glossopharyngeal (IX), Vagus (X), Accessory (XI), Hypoglossal (XII)
12 Pairs of Cranial Nerves
128
Numbers of the 3 Sensory Cranial Nerves
Olfactory (I), Optic (II), Vestibulocochlear (auditory) (VIII)
The 3 Sensory Cranial Nerves
579 10
Numbers of 4 Mixed Cranial Nerves
Trigeminal (V), Facial (VII), Glossopharyngeal (IX), Vagus (X)
The 4 Mixed Cranial Nerves
3 4 6 11 12
Numbers of the 5 Motor Cranial Nerves
Oculomotor (III), Trochlear (IV), Abducent (VI), Accessory (XI), Hypoglossal (XII)
The 5 Motor Cranial Nerves
Olfactory Nerves
Sensory type of nerve that originates in the olfactory lobe (i.e. root of nose) & terminates in the temporal lobe of cerebrum; associated with sense of smell
Smell
What sense are olfactory nerves related to?
Optic Nerve
Sensory type of nerve that originates in the retina of eyes & terminates in the occipital lobe of cerebrum; related with sense of vision.
Vision
What sense are optic nerves related to?
Oculomotor Nerve
Mixed type of nerve that originate in the mid-brain; consists of a motor portion that innervates skeletal muscles that moves the eyeball & innervates smooth muscles that constrict pupil and a sensory portion related to eyeball movement & regulating the size of pupil.
Efferent/Motor Portion & Afferent/Sensory Portion
2 Portions of Oculomotor Nerves
Efferent/Motor Portion
Portion of Oculomotor Nerve that innervates (supplies nerves to) skeletal muscles that moves the eyeball & innervates smooth muscles that constrict pupil
Afferent/Sensory Portion
Portion of Oculomotor Nerve that is related to movement eyeball & regulating the size of pupil
Trochlear
Mixed type of nerve that originates in midbrain; smallest of the 12 cranial nerves; motor portion is related to movement of eyeball & sensory portion carries information from eye to midbrain
Trochlear Nerve
What is the smallest cranial nerve?
eyeball movement
The motor portion of the trochlear nerve is related to ___ ___.
information; eye; midbrain
The sensory portion of the trochlear nerve is related to carrying ___ from the ___ to ___.
Trigeminal Nerve
Mixed type of nerve that is the largest among all the cranial nerves and has motor portion functioning for mastication and a sensory portion functioning in conveying impulses for touch, pain & temperature
Trigeminal Nerve
What is the largest cranial nerve?
Opthalmic, Maxillary, and Mandibular Nerves
What are the 3 branches of the sensory portion of the trigeminal nerve?
Ophthalmic Nerve
One of the 3 branches of the trigeminal nerve that contains nerves from eyelids, eyeball, lacrimal glands, nasal cavity, nose and forehead.
Maxillary Nerve
One of the 3 branches of the trigeminal nerve that contains nerve from the mucosa of nose, pharynx, teeth, upper lip & lower eyelid.
Mandibular Nerve
One of the 3 branches of the trigeminal nerve that contains nerve from tongue, teeth, skin, mandible & cheek
mastication; touch, pain, temperature
The motor function of the trigeminal nerve is ___, while the sensory function is to convey impulses for ___, ___, and ___.
Abducens
Mixed type of nerve that has a motor nerve functioning in movement of the eyeball and sensory nerve functioning in proprioception
eyeball; proprioception
The motor function of the abducens nerve is to innervate the skeletal muscles that move the ____, while the sensory function is related to ____, which is the movement of the eyeball and muscles sense.
Facial Nerve
Mixed type of nerve that has motor nerve functioning in facial expression and sensory nerve functioning in taste & proprioception
Face, nose, palate, lacrimal & salivary gland
The motor nerve of the facial nerve innervates skeletal muscle of ___, ___, ___, ___, & ___ ____.
taste buds; taste; proprioception
The sensory nerve of the facial nerve transmits information from ___ ___ in the tongue and mouth, making its function ___ and ___.
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
Sensory type of nerve that consists of two nerves, one that is associated with posture and balance and the other responsible for hearing
Vestibular & Cochlear Nerve
2 Nerves that make up the Vestibulocochlear Nerve
Vestibular Nerve
One of the nerves that make up the Vestibulocochlear Nerve that arises from the semicircular canals of the inner ear & conveys impulses to the cerebellum; associated with maintenance of posture & balance.
Posture & Balance
What is the Vestibular Nerve (one of the Vestibulocochlear Nerves) associated with?
Cochlear Nerve
One of the nerves that make up the Vestibulocochlear Nerve that originates in the spiral organ of the inner ear & conveys impulses to the hearing area of cerebrum; responsible for hearing
Hearing
What is the Cochlear Nerve (one of the Vestibulocochlear Nerves) associated with?
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
Mixed type of nerve that has motor nerves that originate from medulla oblongata & innervate the tongue & pharynx, functioning in the movement of the pharynx during swallowing and speech & sensory nerves originate from salivary glands & terminates in medulla oblongata, functioning in taste, touch, pain & temperature sensations, monitoring of blood pressure
Movement of pharynx during swallowing & speech
Function of the motor nerve of the glossopharyngeal nerve
Taste, touch, pain & temperature sensations, monitoring of blood pressure
Function of the sensory nerve of the glossopharyngeal nerve
Vagus Nerve
Mixed type of nerve that has:
Motor Fibers that originate in the medulla & innervates the smooth muscles of pharynx, larynx, trachea, heart, esophagus, stomach, intestine, pancreas, gall bladder, bile duct, spleen, kidney, ureter, blood vessels in thoracic & abdominal cavities
Motor Fibers Function: Swallowing, coughing & voice production
Sensory Fibers that convey impulses from same organs to brain.
Sensory Fibers Function: Taste, touch, pain, temperature regulation & monitoring of blood pressure
Accessory Nerve
Motor type of nerve that originates from medulla oblongata & innervates the muscles of pharynx & skeletal muscle of neck; motor function is for swallowing & movement of head & shoulders
Hypoglossal Nerve
Motor type of nerve that originates in the medulla & innervates the muscle of tongue; motor function is for movement of tongue during speech & swallowing
Somatic and Autonomic Nervous System
2 Parts of the Peripheral Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System
Part of the Peripheral Nervous System that consists of sensory neuron & motor neuron
Sensory Neurons
One of the types of neurons in the Somatic Nervous System that conveys message from periphery to the CNS, include sensations of pain, temperature, taste, smell, hearing & vision, etc
Motor Neurons
One of the types of neurons in the Somatic Nervous System that conveys message from brain to periphery
Autonomic Nervous System
Part of the Peripheral Nervous System that cause movement in smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
Autonomic Sensory/Afferent & Autonomic Motor/Efferent Neurons
2 Types of Neurons in the Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic Sensory/Afferent Neurons
One of the Types of Neurons in the Autonomic Nervous System associated with sensory receptors located in blood vessels, visceral organs and muscles
Autonomic Motor/Efferent Neurons
One of the Types of Neurons in the Autonomic Nervous System that regulates visceral activities by either increase or decrease ongoing activities in the effector tissues (cardiac muscle, smooth muscles or glands)
Sympathetic/Thoracolumbar Outflow Division & Parasympathetic/Craniosacral Outflow Division
The Autonomic Nervous System can be further subdivided. What are those 2 divisions?
True
True of False: The Sympathetic/Thoracolumbar Outflow Division & Parasympathetic/Craniosacral Outflow Division of the ANS work in an opposite manner
2 Motor Neurons, Autonomic Ganglia, Effector Organs
3 structures that each division of the ANS has?
Pre-Ganglionic Neurons & Post-Ganglionic Neurons
Two motor neurons of each division of the ANS
Preganglionic Neuron
One of the motor neurons of each division of the ANS that lies before the ganglion
Preganglionic fiber
Myelinated axon of the preganglionic neuron
Postganglionic Neuron
One of the motor neurons of each division of the ANS that lies after the ganglion and terminates in the effector organ
Postganglionic Fibers
Myelinated axon of the postganglionic neuron
Sympathetic Division
The division of the ANS that functions in fight-or-flight, responding to unusual stimulus, takes over to increase activities, and is the “E” division
Exercise, Excitement, Emergency, Embarrassment
The Sympathetic Division is the “E” division. What are the 4 E’s?
Parasympathetic Division
The division of the ANS that functions in housekeeping activities, conserves energy, maintains daily necessary body functions, and is the “D” division
Digestion, defecation, diuresis
The Parasympathetic Division is the “D” division. What are the 3 D’s?
Thoracolumbar Division
What is another name for the Sympathetic Division of the ANS?
shorter; longer
In the Sympathetic Division of the ANS, the preganglionic nerve fibers are ___, while the postganglionic nerve fibers are ___.
Acetylcholine
In the Sympathetic Division of the ANS, the preganglionic neurotransmitter is ____.
Adrenergic; epinephrine; norepinephrine
In the Sympathetic Division of the ANS, the postganglionic nerve fibers are ____, having ___ and/or ___ as their neurotransmitter.
Craniosacral Division
What is another name for the Parasympathetic Division of the ANS?
dispersed
In the Parasympathetic Division of the ANS, the parasympathetic ganglia are ____