PHYSICS LOCK IN 5555
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
spring-fluid lab - how to find density?
find displacement of object (x) in spring in both water and in air
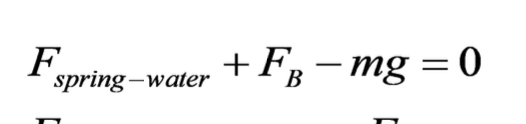
what factors might explain why less pennies may float in a penny-buoyancy experiment?
water too cold → density is higher → buoyancy caulcauted would be less than actual buoyancy
how to find the net force at the bottom of a tank?
atmospheric pressure + pressure of liquid (ugh)
how to find the speed of something coming out
volume/time = area(velocity)
find velocity, plug into bournollis equation
how to solve when something is submerged in water?
set both weights equal
how to find power it takes to empty a pool
change in energy = mgh = pvgh
describe a procedure that you could easily implement to keep the initial velocity of the water constant (water is flowing out of a tank)
pump water being into the tank at the same rate water is leaving the tank.
explain the FBD of a block submerged into 2 liquids (water at bottom and oil at the top)
downward force from oil, downward force of weight, upward for of water
how to solve problems where there is half oil and half water
Weight of cube = Buoyant force from oil + Buoyant force from water
do weight in terms of pvg
make the volume only the part that is submerged in the oil for oil and water for water
formula for buoyant force
DENSITY of FLUID multiplied by VOLUME of OBJECT multiplied by g
what is the buoyant force equal to also
The buoyant force on an object submerged in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
it’s also equal to pvg where p is the water density and V is the objects volume
formula for percent submerged
% submerged = density of object / density of liquid
minimum mass to sink
set buoyant force equal to weight
lift force formula
0.5 x V² x density of air x surface area of the lifting surface
how to find force on pulley by axle (attwood machine)
force of axle - tension A - tension B - MG = 0
what force causes change in angular velocity with respect to center of mass in a rolling sphere?
friction force. the normal and gravitational forces pass through the center of mass, the friction force is the only force that can create a torque about the center of mass.
a rolling sphere is now replaced with a cylinder of the same mass and radius. will the cylinder have an greater than, less than, or equal to the acceleration of the sphere?
less than. the cylinder has a moment of inertia, I, greater than that of the sphere. Since I is inversely proportional to α, the cylinder will have a smaller α. The object is not slipping so α = a/R, thus the cylinder will have a lower acceleration.
is angular momentum conserved when a bullet hits a wheel
Yes. Angular momentum is conserved in the system since there is no net external torque.
The forces between the dart and the wheel are internal action-reaction forces and do not exert an external torque.
is linear momentum conserved when a bullet hits a wheel?
No. Linear momentum is not conserved when there is a net external force.
velocity at the top to complete the loop
sqrt (gR)
what part here did the collision occur? did they stick together?
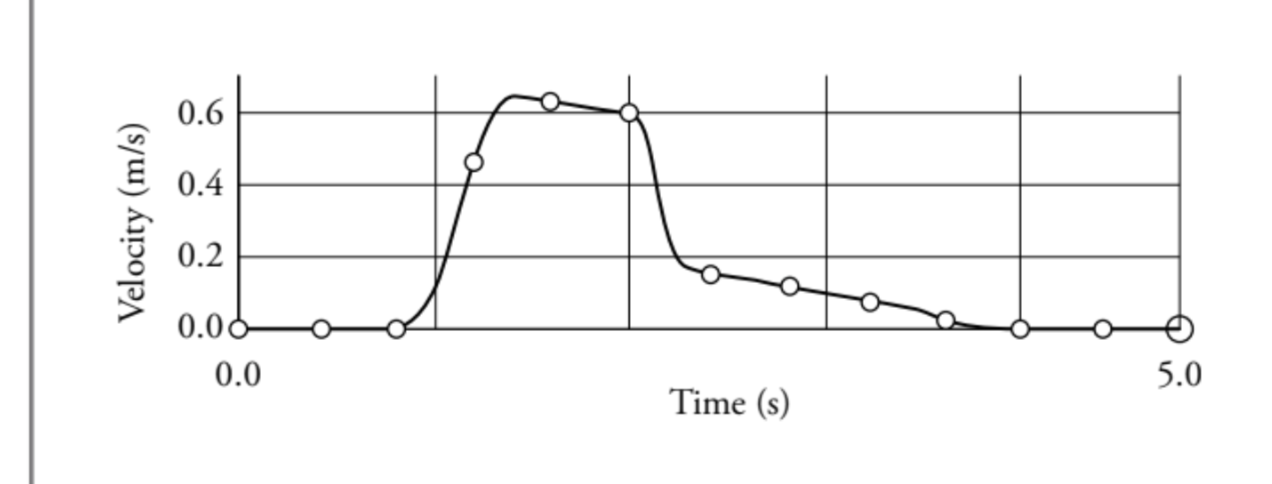
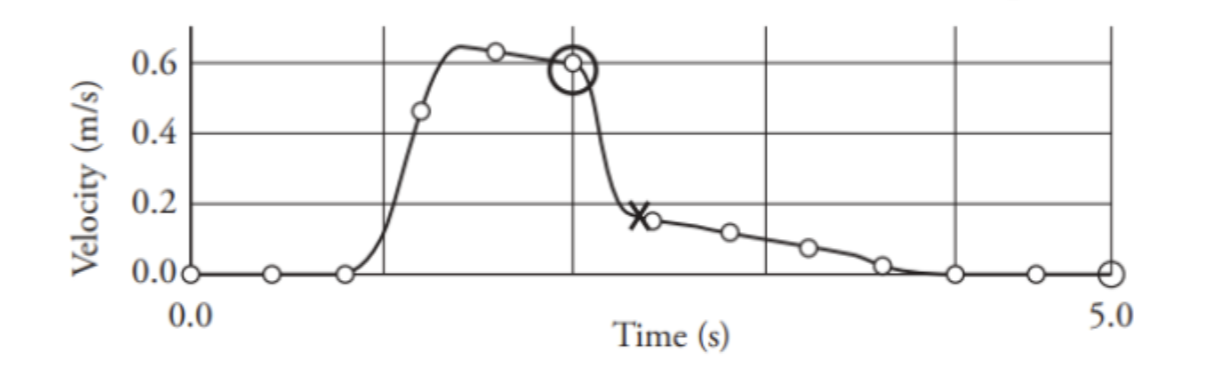
no! they did not stick together. if they did, the final speed would be half of 0.6 (initial speed of first car), however, here it’s only 0.2
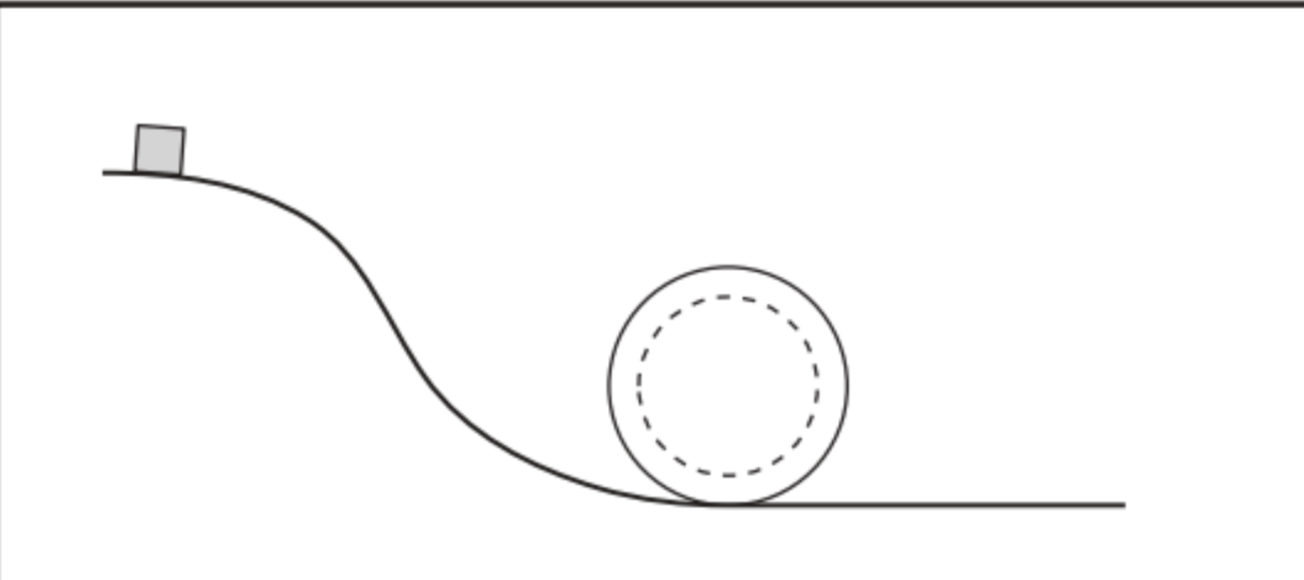
why does the block complete the loop but a sphere won’t?
if the ball rolls, the potential energy will be converted to translational AND rotational kinetic energy
relationship between temperature and pressure
linear upwards slope relationship
Two uniform solid balls, one of radius R and mass M, the other of radius 2R and mass 8M, roll down a high incline. They start together from rest at the top of the incline. Which one will reach the bottom of the incline first?
both reach at the same time
Two masses m1 and 4m1 are on an incline. Both surfaces have the same coefficient of kinetic friction. Both objects start from rest, at the same height. Which mass has the largest speed at the bottom?
SAME SPEED
Two blocks of ice, one five times as heavy as the other, are at rest on a frozen lake. A person then pushes each block the same distance d. Ignore friction and assume that an equal force F is exerted on each block. Which of the following statements is true about the kinetic energy of the heavier block after the push?
EQUAL KINETIC ENERGY
how to find efficiency of something
W(useful)/W(in)
Useful energy output: How much work goes into increasing potential energy (height gained).
Total energy input: The work done by the applied force over the distance.
The gravitational potential energy at a distance r from Earth's center is
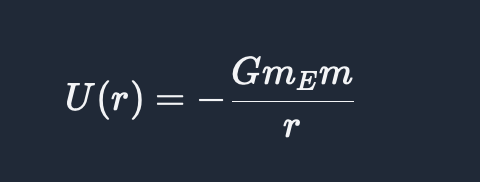
energy conservation with friction
